

Yufan's Blog - DS 自平衡二叉搜索树
source link: https://alphafan.github.io/posts/avl_tree.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

AVL 树是一个自平衡二叉搜索树(BST),作为一个二叉搜索树的变种,AVL 除了满足左节点的值永远小于根节点的值,右节点的值永远大于根节点的值的基本二叉搜索树的特征外,它还要求左右子树的高度差不能超过一。
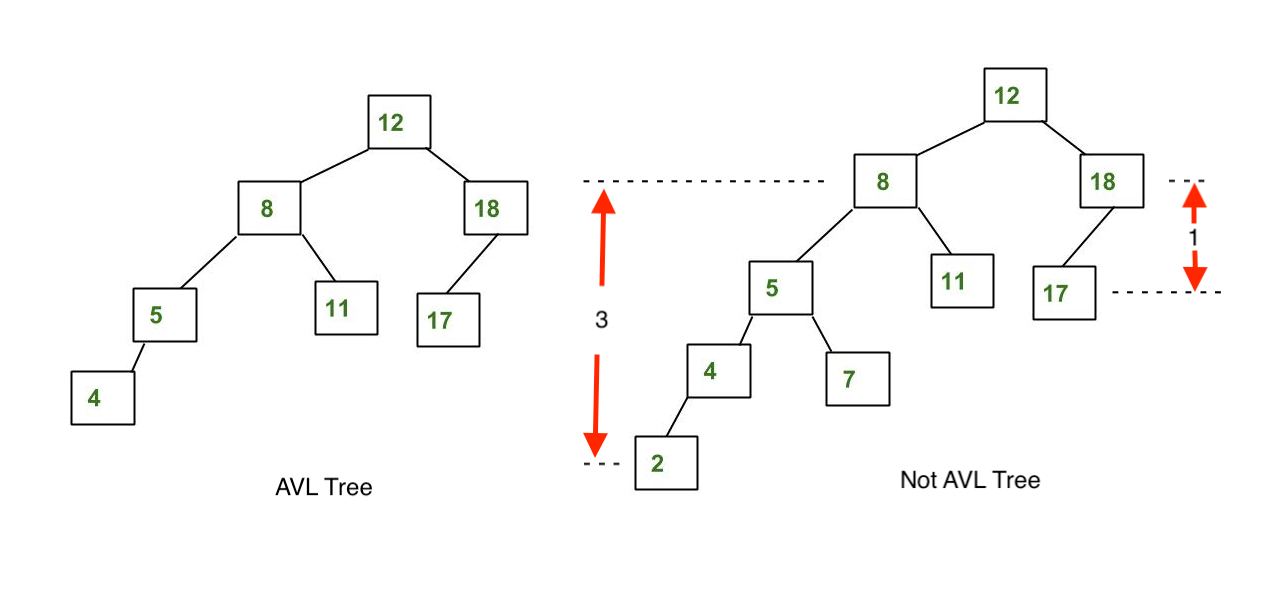
举个栗子,上图中的左边的树是一个 AVL Tree,而右边的的则不是,因为可以看到左边的子树的高度和右边的子树的高度差已经超过了一。
Why AVL?
大多数 BST 操作(例如搜索,最大值,最小值,插入,删除等)都需要 O ( h ) 时间,其中 h 是 BST 的高度。这些操作的代价可能变成 O ( n ) 对于偏斜的二叉树。 如果在每次插入和删除之后确保树的高度保持 O ( logn ),那么我们可以保证所有这些操作的 O ( logn ) 的上限。 AVL 树的高度始终为 O ( logn ),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。
Insertion
为了确保给定的树在每次插入后都保持 AVL,我们必须增加标准的 BST 插入操作来执行一些重新平衡。 以下是可以在不违反 BST 属性的情况下重新平衡 BST 的两个基本操作:1. 向左旋转;2. 向右旋转。下图中展示了插入节点时旋转的过程,其中节点右上方的数字,代表的是平衡因子,即是左右两边子树的高度差。
首先来分解一下这两个最基本的动作,向左旋转和向右旋转。左右旋转,是保持树是平衡状态的关键步骤。
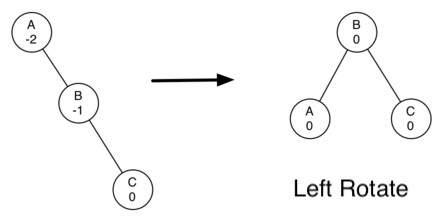
上图一个左旋转的例子。执行左旋转的时候,我们需要做到以下几点:
- 1. 使右节点(B)成为子树的根。
- 2. 移动旧的根节点(A)到新根的左节点。
- 3. 如果新根(B)原来有左节点,那么让原来B的左节点成为新根左节点(A)的右节点。
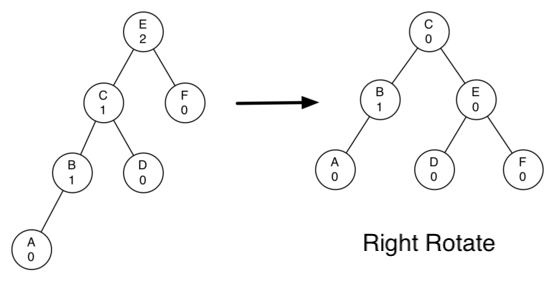
在右旋转的时候,我们需要做到:
- 1. 使左节点 ( C ) 成为子树的根。
- 2. 移动旧根 ( E ) 到新根的右节点。
- 3. 如果新根 ( C ) 原来有右节点 ( D ),那么让 D 成为新根右节点(E)的左节点。
Steps to Follow for Insertion
对于新插入的节点为 w ,插入的步骤如下:
- 1. 为 w 执行标准BST插入。
- 2. 从 w 开始,往上走,找到第一个不平衡节点。 设 z 是第一个不平衡节点,y 是从 w 到 z 的路径上出现的 z 的孩子,x 是从 w 到 z 的路径上出现的 z 的孙子。
-
3. 通过在以 z 为根的子树上执行适当的旋转来重新平衡树。 可以有4种可能的情况需要处理,因为x,y 和 z 可以按4种方式排列。 以下是可能的4种安排:
- a : y 是 z 的左边孩子,x 是 y 的左边孩子(Left Left Case)
- b : y 是 z 的左边孩子,x 是 y 的右边孩子(Left Right Case)
- c : y 是 z 的右边孩子,x 是 y 的右边孩子(Right Right Case)
- d : y 是 z 的右边孩子,x 是 y 的左边孩子(Right Left Case)
a) Left Left Case
z y
/ \ / \
y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z
/ \ - - - - - - - - -> / \ / \
x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4
/ \
T1 T2
b) Left Right Case
z z x
/ \ / \ / \
y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z
/ \ - - - - - - - - -> / \ - - - - - - - -> / \ / \
T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4
/ \ / \
T2 T3 T1 T2
c) Right Right Case
z y
/ \ / \
T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x
/ \ - - - - - - - -> / \ / \
T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4
/ \
T3 T4
d) Right Left Case
z z x
/ \ / \ / \
T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y
/ \ - - - - - - - - -> / \ - - - - - - - -> / \ / \
x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4
/ \ / \
T2 T3 T3 T4
Algorithm Implementation
以下是 AVL 树插入节点的算法。使用递归 BST 的插入方法来插入新节点。在递归 BST 插入的过程中,插入之后,我们可以获得以自下而上的方式一个一个指向祖先节点的指针。所以我们不需要父指针来进行额外的存储。递归代码本身遍历并访问新插入的节点的所有祖先。
- 1)执行正常的 BST 插入。
- 2)当前节点必须是新插入节点的祖先之一。更新当前节点的高度。
- 3)获取当前节点的平衡因子(左子树高度 - 右子树高度)。
- 4)如果平衡因子大于1,则当前节点不平衡,并且我们处于 Left Left 或 Left Right 情况。为了检查是否遗留左大小,将新插入的值与左子树根中的值进行比较。
- 5)如果平衡因子小于-1,那么当前节点不平衡,我们处于 Right Right 或 Right Left 情况。要检查它是否正确的情况下,将新插入的值与右子树根中的值进行比较。
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree
# Generic tree node class
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.height = 1
# AVL tree class which supports the
# Insert operation
class AVLTree(object):
# Recursive function to insert key in
# subtree rooted with node and returns
# new root of subtree.
def insert(self, root, key):
# Step 1 - Perform normal BST
if not root:
return TreeNode(key)
elif key < root.val:
root.left = self.insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = self.insert(root.right, key)
# Step 2 - Update the height of the
# ancestor node
root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left),
self.getHeight(root.right))
# Step 3 - Get the balance factor
balance = self.getBalance(root)
# Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced,
# then try out the 4 cases
# Case 1 - Left Left
if balance > 1 and key < root.left.val:
return self.rightRotate(root)
# Case 2 - Right Right
if balance < -1 and key > root.right.val:
return self.leftRotate(root)
# Case 3 - Left Right
if balance > 1 and key > root.left.val:
root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left)
return self.rightRotate(root)
# Case 4 - Right Left
if balance < -1 and key < root.right.val:
root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right)
return self.leftRotate(root)
return root
def leftRotate(self, z):
y = z.right
T2 = y.left
# Perform rotation
y.left = z
z.right = T2
# Update heights
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
# Return the new root
return y
def rightRotate(self, z):
y = z.left
T3 = y.right
# Perform rotation
y.right = z
z.left = T3
# Update heights
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
# Return the new root
return y
def getHeight(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return root.height
def getBalance(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right)
def preOrder(self, root):
if not root:
return
print("{0} ".format(root.val), end="")
self.preOrder(root.left)
self.preOrder(root.right)
# Driver program to test above function
myTree = AVLTree()
root = None
root = myTree.insert(root, 10)
root = myTree.insert(root, 20)
root = myTree.insert(root, 30)
root = myTree.insert(root, 40)
root = myTree.insert(root, 50)
root = myTree.insert(root, 25)
"""
The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50
"""
# Preorder Traversal
print("Preorder traversal of the",
"constructed AVL tree is")
myTree.preOrder(root)
print()Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK