

【KNN】理论与实现
source link: https://www.guofei.site/2017/10/24/knn.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

【KNN】理论与实现
2017年10月24日Author: Guofei
文章归类: 2-1-有监督学习 ,文章编号: 225
版权声明:本文作者是郭飞。转载随意,但需要标明原文链接,并通知本人
原文链接:https://www.guofei.site/2017/10/24/knn.html
KNN既可以做回归,也可以做拟合,这里只讲回归
1">模型1
直观地说,给定训练集,对于1个新实例,在训练集中找到最近的k个实例,看这k个实例属于哪一类,判断这个新实例也属于这一类。
KNN模型有3个基本要素:距离,K值,投票规则。
1. 距离
参见范数、测度和距离
根据数据特征,可以是曼哈顿距离、欧氏距离、闵可夫斯基距离。
2. K值
- K太小时,容易过拟合。
- K太大,误差也会很大。
3. 投票规则
多数表决规则(majority voting rule)
误分类概率为P(Y≠f(X))=1−P(Y=f(X))P(Y≠f(X))=1−P(Y=f(X))
经验风险为1/k∑i∈N(k,x)I(yi≠cj)=1−1/k∑i∈N(k,x)I(yi=ci)1/k∑i∈N(k,x)I(yi≠cj)=1−1/k∑i∈N(k,x)I(yi=ci)
在某些假设下,∑i∈N(k,x)I(yi=ci)∑i∈N(k,x)I(yi=ci)最大就是多数表决规则,它等价于经验风险最小。
算法
1. 线性扫描
linear scan
要计算每个新的instance与train set中每个instance的距离。
计算量非常大(O(Ninstance)O(Ninstance))
2">2. kd树2
为了减少计算量,引入二叉树算法。
首先生成kd树,然后用kd树找到最近的点。
3">2.1 生成kd树3
输入:train set 输出:kd树
递归:对于深度为j的节点,选择xlxl作为切分的坐标轴 (l=jmodk+1l=jmodk+1)
以xlxl的median作为切分点,生成深度为j+1的2个子节点。
左子节点小,右子节点大。
递归,直到所有的点全部切分完毕。
2.2 搜索kd树
输入:kd树,目标点x
输出:x的最近邻
step1:找到包含x的叶节点。(从根节点递归向下搜索)
step2:nearest=此叶节点,nearest_length=x和nearest的距离
step3:向父节点回退
step4: 当前节点进行2个操作:
- 如果当前节点与x的距离,比nearest_length小,那么nearest=此叶节点,nearest_length=x和nearest的距离
- 如果以x为圆心,nearest_length为圆心的圆,与兄弟节点矩形相交,那么搜索兄弟节点
step5:转到step3,直到退回到根节点。nearest就是要找的x的最近邻点。
算法评价:
- 如果点是随机分布的,复杂度为O(logN)O(logN)
- 维度越大,复杂度越高,当维度接近实例数时,效率接近线性搜索。
sklearn实现
from sklearn import neighbors, datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=15, weights='uniform')
clf.fit(X, y)
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm=’auto’, leaf_size=30, metric=’minkowski’,metric_params=None, n_jobs=1, n_neighbors=15, p=2,weights=’uniform’)
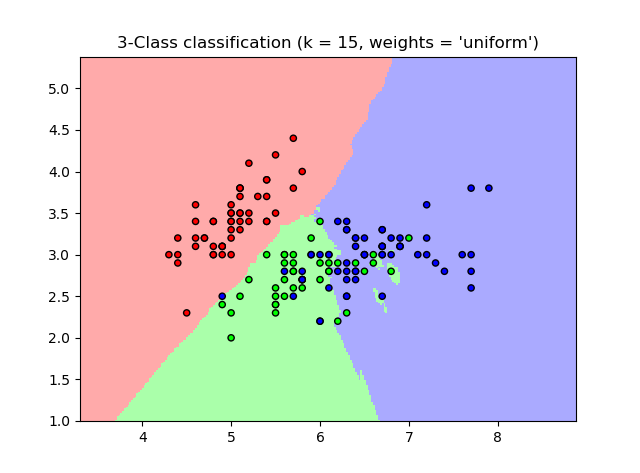
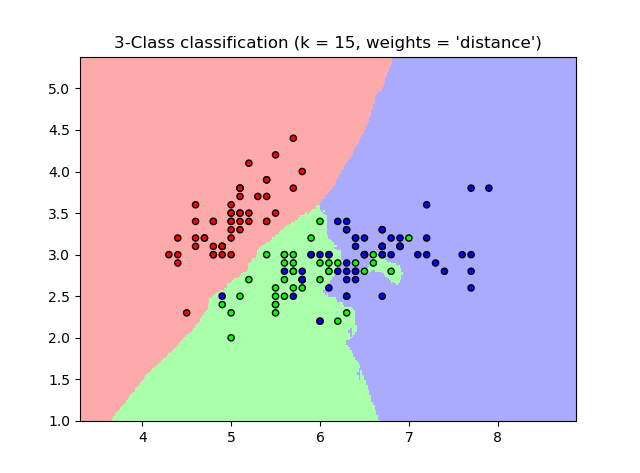
一个完整的例子
这个例子来自CDA课程4
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn import neighbors, datasets
n_neighbors = 15
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
# Create color maps
cmap_light = ListedColormap(['#FFAAAA', '#AAFFAA', '#AAAAFF'])
cmap_bold = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#00FF00', '#0000FF'])
for weights in ['uniform', 'distance']:
# we create an instance of Neighbours Classifier and fit the data.
clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors, weights=weights)
clf.fit(X, y)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure()
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap_light)
# Plot also the training points
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=cmap_bold,
edgecolor='k', s=20)
plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
plt.title("3-Class classification (k = %i, weights = '%s')"
% (n_neighbors, weights))
plt.show()
这个图可以用于很多分类模型(二维)
参考资料
您的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK