

Linux音频采集和在国产化平台中遇到的坑(二) - haibindev
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/haibindev/p/17090607.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Linux音频采集和在国产化平台中遇到的坑(二)
ALSA采集这条路走不通,只能尝试其他途径,这里通过PulseAudio的接口成功实现了采集麦克风和系统声音的功能。
linux PulseAudio音频采集
首先,PulseAudio跟ALSA不同的不同之处是,ALSA是内核级的,而PulseAudio则是用户层的服务,并且是作为Sound Server的形式,来管理应用程序的各种音频输入和输出,跟ALSA相同,大多数linux发行版都默认安装PulseAudio。我们这里的国产化芯片平台的银河麒麟自然也不例外。PulseAudio的结构图是这个样子的:
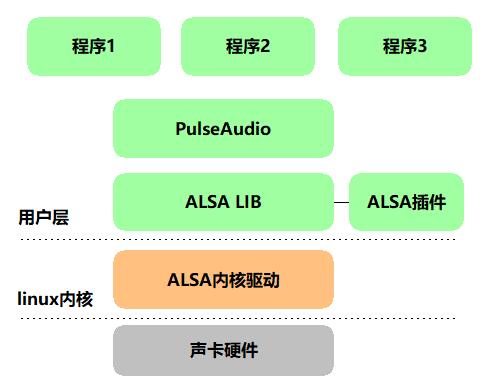
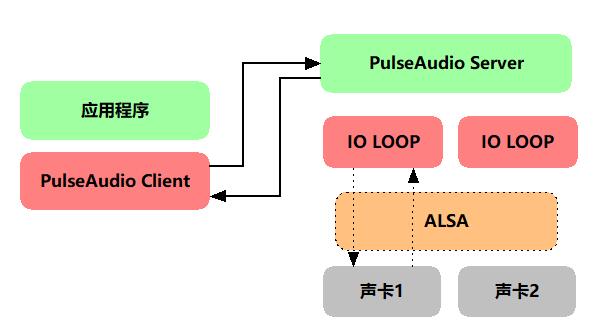
可以看到,PulseAudio作为服务,是位于ALSA上层的,可以让多个应用程序同时调用PulseAudio,由它内部做音频的mixer,这样可以避免由于ALSA的独占性而导致程序在不同的硬件环境下出现无法正常使用的情况。应用程序和PulseAudio之间的调用关系如下:
通常情况下,系统不会预装PulseAudio的开发包,这个时候我们需要安装一下,这样才能在代码中调用接口。
sudo apt-get install libpulse-dev
PulseAudio音频采集,是明显比ALSA复杂的多,每个应用程序,都考虑是作为一个PulseAudio的client端,与系统的PulseAudio服务进行连接,并且都需要维护一个线程来作为数据传递的循环队列。下面罗列一下种族要使用的几个函数:
#include <pulse/pulseaudio.h>
/***
申请一个包含线程的事件循环
*/
pa_threaded_mainloop* pa_threaded_mainloop_new();
/***
开启事件循环
@return: 0表示成功,小于0表示错误码
*/
int pa_threaded_mainloop_start(pa_threaded_mainloop* m);
/***
终止事件循环,在调用此函数前,必须确保事件循环已经解锁
*/
void pa_threaded_mainloop_stop(pa_threaded_mainloop* m);
/***
阻塞并等待事件循环中消息被触发,注意,该函数返回并不一定是因为调用了pa_threaded_mainloop_signal()
需要甄别这一点
*/
void pa_threaded_mainloop_wait(pa_threaded_mainloop* m);
/***
触发消息
*/
void pa_threaded_mainloop_signal(pa_threaded_mainloop* m, int wait_for_accept);
#include <pulse/pulseaudio.h>
/***
创建PulseAudio连接上下文
*/
pa_context* pa_context_new(pa_mainloop_api *mainloop, const char *name);
/***
将context连接到指定的PulseAudio服务,如果server为NULL,则连接到系统默认服务。
@return: 小于0表示错误
*/
int pa_context_connect(pa_context *c, const char *server, pa_context_flags_t flags, const pa_spawn_api *api);
/***
终止事件循环,在调用此函数前,必须确保事件循环已经解锁
*/
void pa_context_disconnect(pa_context* c);
/***
引用计数减1
*/
void pa_context_unref(pa_context* c);
/***
返回当前上下文状态
*/
pa_context_state_t pa_context_get_state(const pa_context* c);
#include <pulse/pulseaudio.h>
/***
在当前PulseAudio连接上,创建一个stream,用于输入或输出音频数据
*/
pa_stream* pa_stream_new(pa_context *c, const char *name, const pa_sample_spec *ss, const pa_channel_map *map);
/***
将context连接到指定的PulseAudio服务,如果server为NULL,则连接到系统默认服务。
@return: 小于0表示错误
*/
int pa_stream_connect_record(pa_context *c, const char *server, pa_context_flags_t flags, const pa_spawn_api *api);
/***
从缓冲区中读取下一个采集的音频片段
*/
int pa_stream_peek(pa_stream *p, const void **data, size_t *nbytes);
/***
放弃当前输入(采集)的音频片段
*/
void pa_stream_drop(pa_stream* s);
/***
关闭输入输出流
*/
void pa_stream_disconnect(pa_stream* s);
/***
引用计数减1
*/
void pa_stream_unref(pa_stream* s);
/***
返回当前stream状态
*/
pa_context_state_t pa_stream_get_state(const pa_stream* s);
下面写个简单的例子演示下如何调用
- 创建事件循环,连接PulseAudio服务器,创建stream并设置参数。为了看起来更加直观,这里我删除了一些错误判断的代码。
bool PulseAudioCapture::Start(Observer* ob)
{
observer_ = ob;
SIMPLE_LOG("try open %s\n", device_name_.c_str());
int ret = 0;
const char* name = "HbsPulse";
const char* stream_name = "HbsPulseStream";
char* device = NULL;
if (false == device_name_.empty())
{
device = (char*)device_name_.c_str();
}
const struct pa_sample_spec *pss = nullptr;
pa_sample_format_t sam_fmt = AV_NE(PA_SAMPLE_S16BE, PA_SAMPLE_S16LE);
const pa_sample_spec ss = { sam_fmt, sample_rate_, channel_count_ };
pa_buffer_attr attr = { (uint32_t)-1 };
pa_channel_map cmap;
const pa_buffer_attr *queried_attr = nullptr;
int stream_flag = 0;
pa_channel_map_init_extend(&cmap, channel_count_, PA_CHANNEL_MAP_WAVEEX);
mainloop_ = pa_threaded_mainloop_new();
context_ = pa_context_new(pa_threaded_mainloop_get_api(mainloop_), name);
pa_context_set_state_callback(context_, context_state_cb, this);
pa_context_connect(context_, pulse_server_, /*0*/PA_CONTEXT_NOFLAGS, NULL);
pa_threaded_mainloop_lock(mainloop_);
pa_threaded_mainloop_start(mainloop_);
for (;;)
{
pa_context_state_t state = pa_context_get_state(context_);
if (state == PA_CONTEXT_READY)
break;
if (!PA_CONTEXT_IS_GOOD(state))
{
int ec = pa_context_errno(context_);
SIMPLE_LOG("pulse context state bad: %d, err: %d\n", state, ec);
goto unlock_and_fail;
}
/* Wait until the context is ready */
pa_threaded_mainloop_wait(mainloop_);
}
SIMPLE_LOG("pulse context ready!\n");
stream_ = pa_stream_new(context_, stream_name, &ss, &cmap);
pa_stream_set_state_callback(stream_, stream_state_cb, this);
pa_stream_set_read_callback(stream_, stream_read_cb, this);
pa_stream_set_write_callback(stream_, stream_write_cb, this);
pa_stream_set_latency_update_callback(stream_, stream_latency_update_cb, this);
ret = pa_stream_connect_record(stream_, device, &attr,
PA_STREAM_ADJUST_LATENCY|PA_STREAM_AUTO_TIMING_UPDATE);
for (;;)
{
pa_stream_state_t state = pa_stream_get_state(stream_);
if (state == PA_STREAM_READY)
break;
if (!PA_STREAM_IS_GOOD(state))
{
int ec = pa_context_errno(context_);
SIMPLE_LOG("pulse stream state bad: %d, err: %d\n", state, ec);
goto unlock_and_fail;
}
/* Wait until the stream is ready */
pa_threaded_mainloop_wait(mainloop_);
}
pa_threaded_mainloop_unlock(mainloop_);
SIMPLE_LOG("pulse audio start ok, fragsize: %d, framesize: %d\n", fragment_size_, pa_frame_size_);
ThreadStart();
return true;
unlock_and_fail:
pa_threaded_mainloop_unlock(mainloop_);
ClosePulse();
return false;
}
- 读取音频数据
bool PulseAudioCapture::ReadData()
{
int ret;
size_t read_length;
const void *read_data = NULL;
pa_usec_t latency;
int negative;
ptrdiff_t pos = 0;
pa_threaded_mainloop_lock(mainloop_);
if (IsPulseDead())
{
SIMPLE_LOG("pulse is dead\n");
goto unlock_and_fail;
}
while (pos < fragment_size_)
{
int r = pa_stream_peek(stream_, &read_data, &read_length);
if (r != 0)
{
SIMPLE_LOG("pa_stream_peek: %d\n", r);
goto unlock_and_fail;
}
if (read_length <= 0)
{
pa_threaded_mainloop_wait(mainloop_);
if (IsPulseDead())
{
SIMPLE_LOG("pulse is dead\n");
goto unlock_and_fail;
}
}
else if (!read_data)
{
/* There's a hole in the stream, skip it. We could generate
* silence, but that wouldn't work for compressed streams. */
r = pa_stream_drop(stream_);
if (r != 0)
{
SIMPLE_LOG("null data, pa_stream_drop: %d\n", r);
goto unlock_and_fail;
}
}
else
{
if (!pos)
{
if (pcm_buf_.empty())
{
pcm_buf_.resize(fragment_size_);
}
//pcm_dts_ = av_gettime();
pa_operation_unref(pa_stream_update_timing_info(stream_, NULL, NULL));
if (pa_stream_get_latency(stream_, &latency, &negative) >= 0)
{
if (negative)
{
pcm_dts_ += latency;
}
else
pcm_dts_ -= latency;
}
else
{
SIMPLE_LOG("pa_stream_get_latency() failed\n");
}
}
if (pcm_buf_.size() - pos < read_length)
{
if (pos)
break;
pa_stream_drop(stream_);
/* Oversized fragment??? */
SIMPLE_LOG("Oversized fragment\n");
goto unlock_and_fail;
}
memcpy(pcm_buf_.data() + pos, read_data, read_length);
pos += read_length;
pa_stream_drop(stream_);
}
}
SIMPLE_LOG("read pos: %d\n", pos);
pa_threaded_mainloop_unlock(mainloop_);
return true;
unlock_and_fail:
pa_threaded_mainloop_unlock(mainloop_);
return false;
}
选择音频设备的时候,音频设备名称,必须是通过PulseAudio相关接口查询出来的,对于音频采集设备,可以调用pa_context_get_source_info_list()函数。经过实验,通过PulseAudio来做音频采集,成功实现了在国产化平台的麒麟系统上采集麦克风和系统声音的功能,避免了之前使用ALSA代码在多声卡环境下所出现的各种麻烦。
另外,需要注意一点的是,这样通过PulseAudio采集出来的数据大小,可能并不是编码所需要的,还需要做一下数据缓冲。

合作请加WX:hbstream或叩叩:229375788。(转载请注明作者和出处)
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK