C++ Program For Printing Nth Node From The End Of A Linked List
source link: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cpp-program-for-printing-nth-node-from-the-end-of-a-linked-list/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

C++ Program For Printing Nth Node From The End Of A Linked List
- Last Updated : 08 Dec, 2021
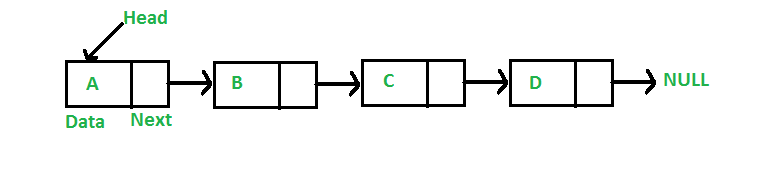
Given a Linked List and a number n, write a function that returns the value at the n’th node from the end of the Linked List.
For example, if the input is below list and n = 3, then output is “B”
Method 1 (Use length of linked list):
- Calculate the length of Linked List. Let the length be len.
- Print the (len – n + 1)th node from the beginning of the Linked List.
Double pointer concept : First pointer is used to store the address of the variable and second pointer used to store the address of the first pointer. If we wish to change the value of a variable by a function, we pass pointer to it. And if we wish to change value of a pointer (i. e., it should start pointing to something else), we pass pointer to a pointer.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
- C++14
// C++ program to find n'th node from // end#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// Link list node struct Node {int data;struct Node* next;};/* Function to get the nth node from the last of a linked list*/void printNthFromLast(struct Node* head, int n){int len = 0, i;struct Node* temp = head;// count the number of nodes in // Linked Listwhile (temp != NULL) {temp = temp->next;len++;}// check if value of n is not// more than length of the // linked listif (len < n)return;temp = head;// get the (len-n+1)th node from // the beginningfor (i = 1; i < len - n + 1; i++)temp = temp->next;cout << temp->data;return;}void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data){// Allocate nodestruct Node* new_node = new Node();// Put in the data new_node->data = new_data;// Link the old list off the // new node new_node->next = (*head_ref);// Move the head to point to // the new node (*head_ref) = new_node;}// Driver Codeint main(){// Start with the empty list struct Node* head = NULL;// Create linked 35->15->4->20push(&head, 20);push(&head, 4);push(&head, 15);push(&head, 35);printNthFromLast(head, 4);return 0;} |
Output:
35
void printNthFromLast(struct Node* head, int n){int i = 0;if (head == NULL)return;printNthFromLast(head->next, n);if (++i == n)cout<<head->data;} |
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the length of linked list.
Method 2 (Use two pointers)
Maintain two pointers – reference pointer and main pointer. Initialize both reference and main pointers to head. First, move the reference pointer to n nodes from head. Now move both pointers one by one until the reference pointer reaches the end. Now the main pointer will point to nth node from the end. Return the main pointer.
Below image is a dry run of the above approach:

Below is the implementation of the above approach:
// Simple C++ program to // find n'th node from end#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;/* Link list node */struct Node{int data;struct Node* next;};/* Function to get the nth node from the last of a linked list*/void printNthFromLast(struct Node *head, int n){struct Node *main_ptr = head;struct Node *ref_ptr = head;int count = 0;if(head != NULL){while( count < n ){if(ref_ptr == NULL){printf("%d is greater than the no. of ""nodes in list", n);return;}ref_ptr = ref_ptr->next;count++;} /* End of while*/if(ref_ptr == NULL){head = head->next;if(head != NULL)printf("Node no. %d from last is %d ", n, main_ptr->data);}else{while(ref_ptr != NULL){main_ptr = main_ptr->next;ref_ptr = ref_ptr->next;}printf("Node no. %d from last is %d ", n, main_ptr->data);}}}// Function to pushvoid push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data){/* allocate node */struct Node* new_node = new Node(); /* put in the data */new_node->data = new_data;/* link the old list off the new node */new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* move the head to point to the new node */(*head_ref) = new_node;}/* Driver program to test above function*/int main(){/* Start with the empty list */struct Node* head = NULL;push(&head, 20);push(&head, 4);push(&head, 15);push(&head, 35);printNthFromLast(head, 4);} |
Node no. 4 from last is 35
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the length of linked list.
Please refer complete article on Program for n’th node from the end of a Linked List for more details!
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK