

Apache Kafka Use cases
source link: https://www.cloudkarafka.com/blog/apache-kafka-usecases.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Website activity tracking
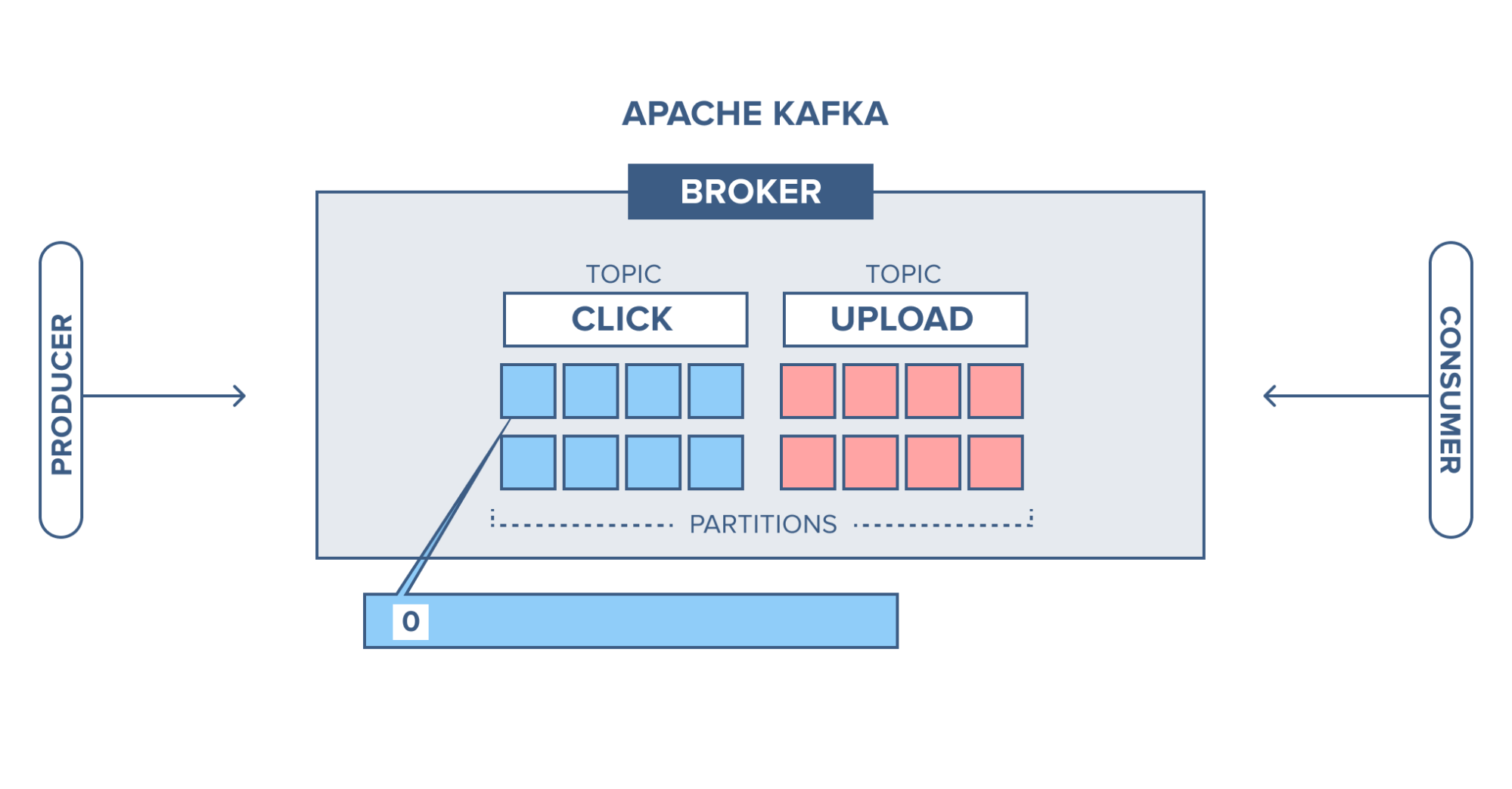
This use case follows a scenario with a simple website where users can click around, sign in, write blog articles, upload images, and publish articles.
When an event happens in the blog (e.g when someone logs in, when someone presses a button or when someone uploads an image to the article), a tracking event and information about the event is placed into a record, and the record is placed on a specified Kafka topic. One topic is named "click" and one is named "upload".
Partitioning setup is based on the user's id. A user with id 0, maps to partition 0, and the user with id 1 to partition 1, etc. The "click" topic will be split up into three partitions (three users) on two different machines.
- A user with user-id 0 clicks on a button on the website.
- The web application publishes a record to partition 0 in the topic "click".
- The record is appended to its commit log and the message offset is incremented.
- The consumer can pull messages from the click-topic and show monitoring
usage in real-time, or it can replay previously consumed messages by setting
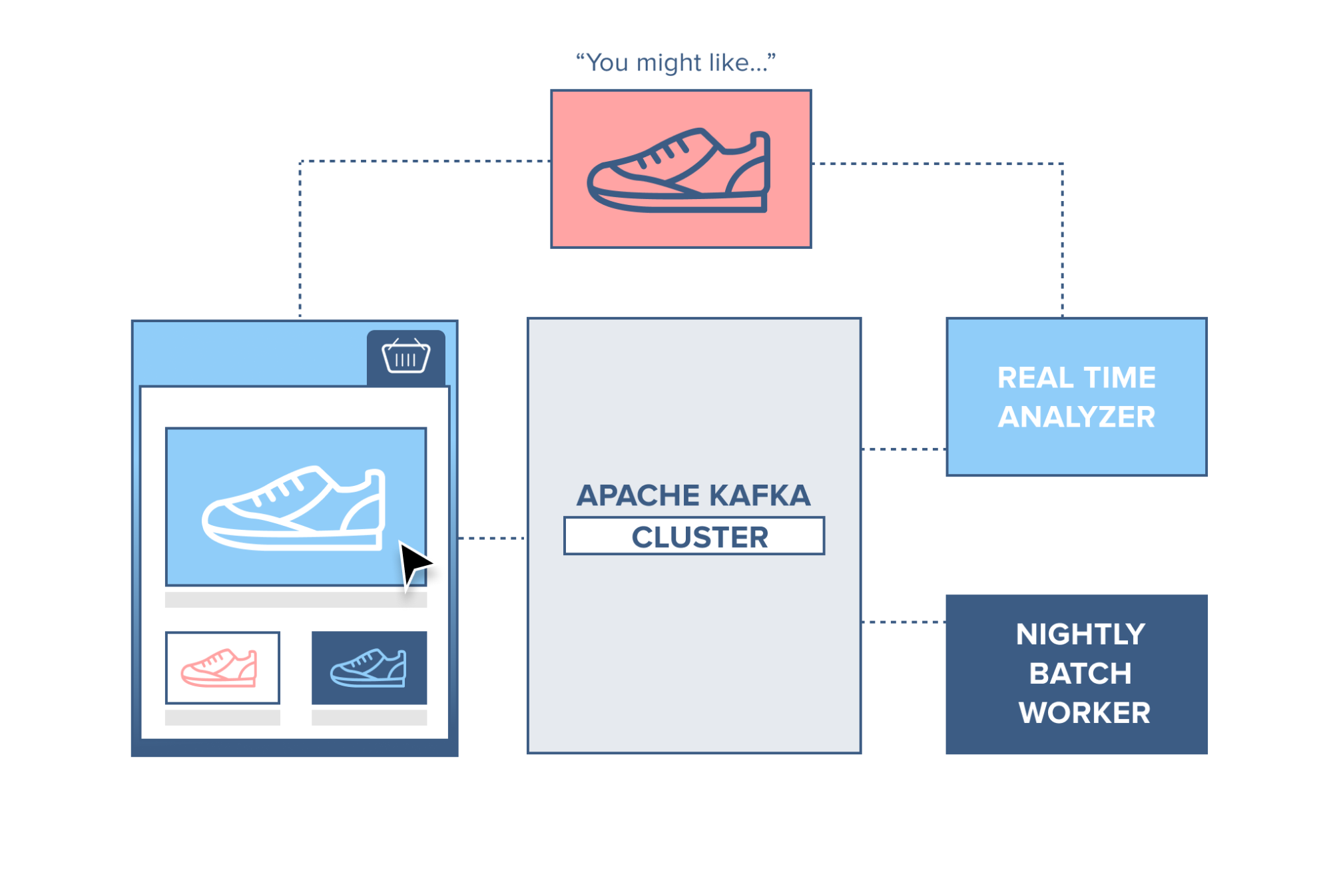
Web Shop
A webshop with a ‘similar products’ feature included on the site. To make this work, each action performed by a consumer is recorded and sent to Kafka. A separate application comes along and consumes these messages, filtering out the products the consumer has shown an interest in and gathering information on similar products. This ‘similar product’ information is then sent back to the webshop for it to display to the consumer in real-time.
Alternatively, since all data is persistent in Kafka, a batch job can run overnight on the ‘similar product’ information gathered by the system, generating an email for the customer with suggestions of products.
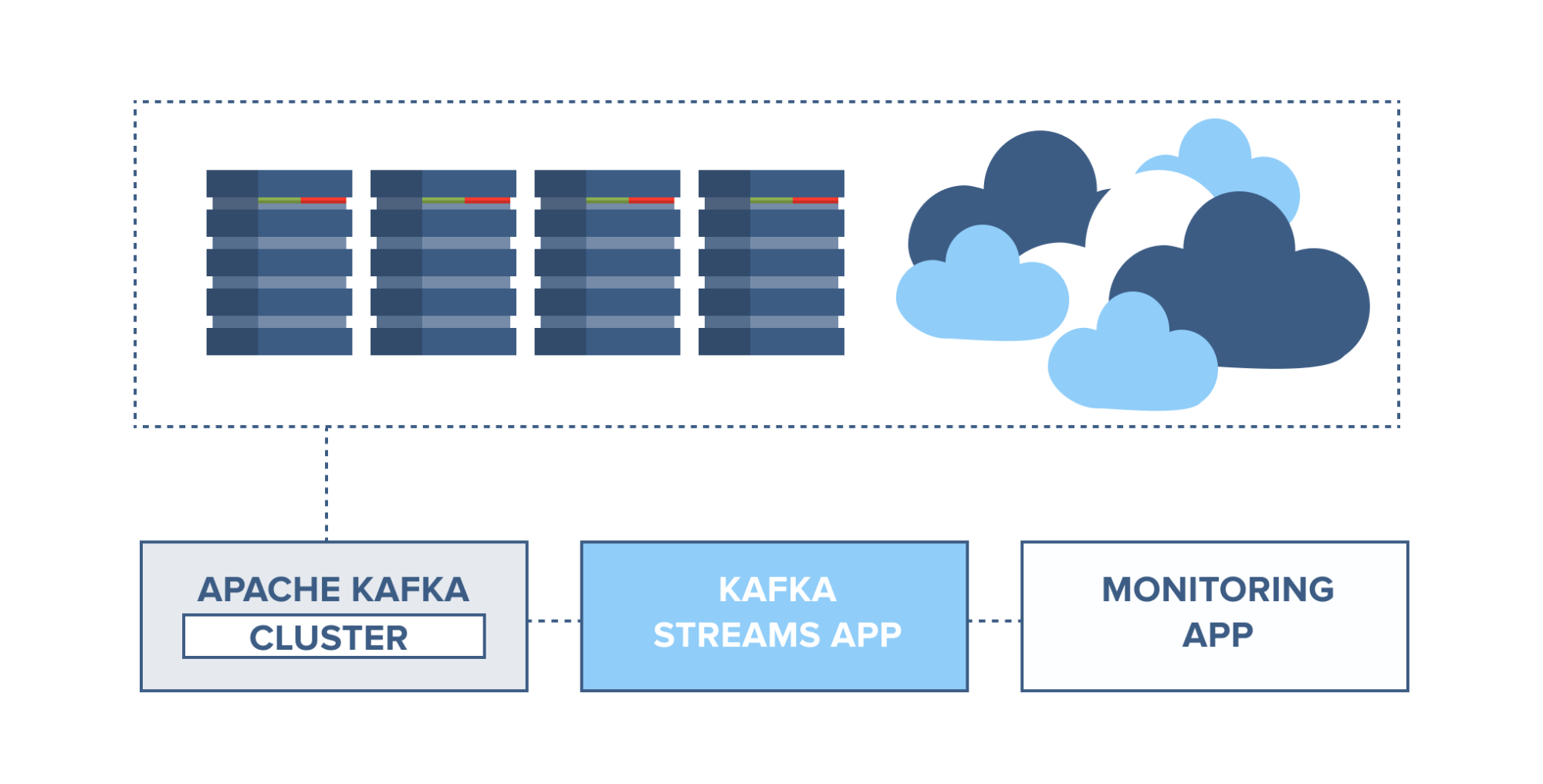
Application health monitoring
Servers can be monitored and set to trigger alarms in case of rapid changes
in usage or system faults. Information from server agents can be combined with
the server syslog and sent to a Kafka cluster. Through Kafka Streams, these
topics can be joined and set to trigger alarms based on usage thresholds,
containing full information for easier troubleshooting of system problems
before they become catastrophic.
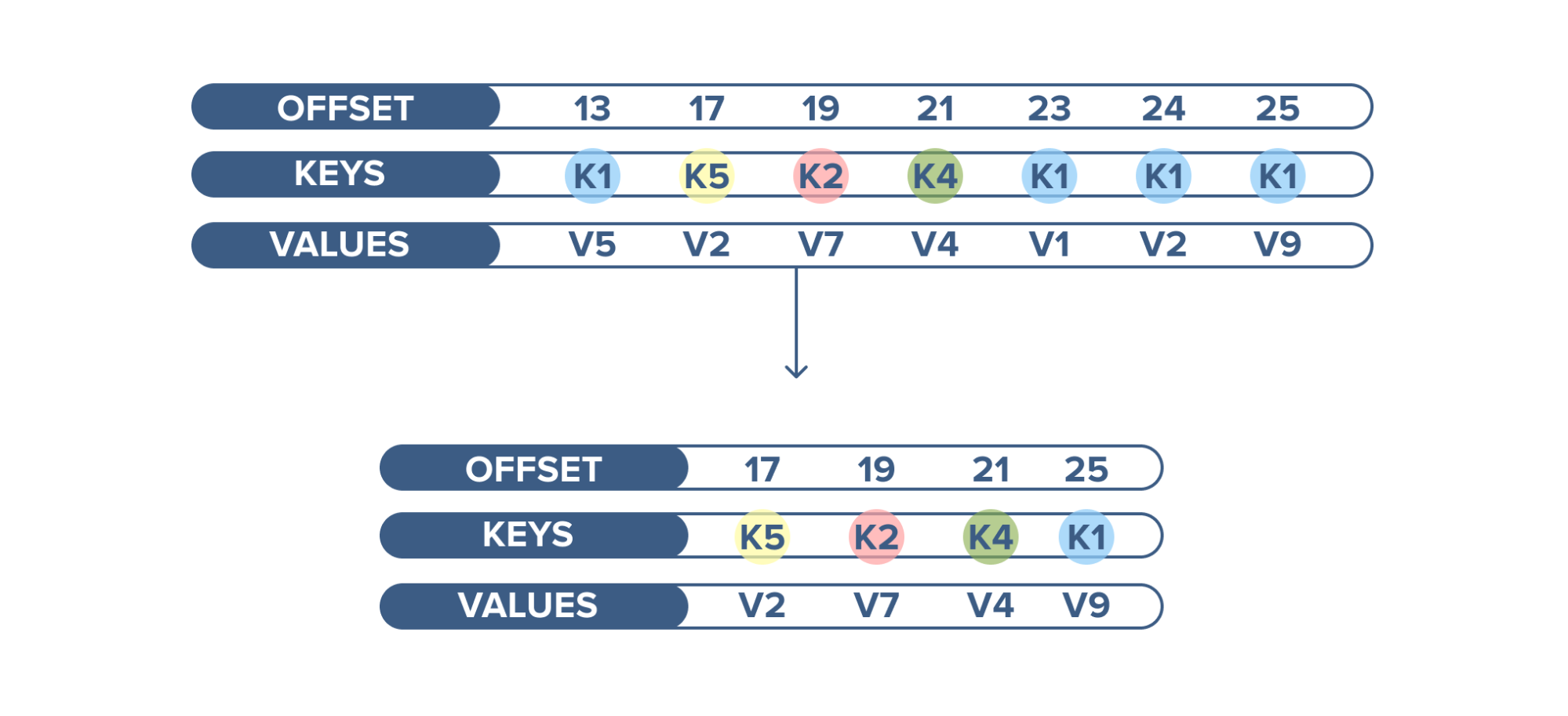
Kafka as a Database
Apache Kafka has another interesting feature not found in RabbitMQ - log compaction. Log compaction ensures that Kafka always retains the last known value for each record key. Kafka simply keeps the latest version of a record and deletes the older versions with the same key.
An example of log compaction use is when displaying the latest status of a cluster
among thousands of clusters running. The current status of the cluster is written
into Kafka and the topic is configured to compact the records. When this topic is
consumed, it displays the latest status first and then a continuous stream of new statuses.
Message queue
Choosing Kafka can be beneficial where large amounts of data need to be processed at a rapid speed. Communication with Kafka as a broker decouples processes and creates a highly scalable system.
Instead of building one large application, decoupling involves taking different parts of an application and only communicating between them asynchronously with messages. That way different parts of the application can evolve independently, be written in different languages, and/or maintained by separated developer teams. In comparison to many messaging systems, Kafka has better throughput. It has built-in partitioning, replication, and fault-tolerance that makes it a good solution for large-scale message processing applications.
We hope that you like this blogpost.
Get in touch with us at [email protected].
Enjoy this article? Don't forget to share it with others. 😉
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK