

一个公式看懂:为什么 Dubbo 线程池会打满
source link: https://developer.51cto.com/article/701019.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

本文转载自微信公众号「JAVA前线」,作者IT徐胖子。转载本文请联系JAVA前线公众号。
0 文章概述
大家可能都遇到过DUBBO线程池打满这个问题,刚开始遇到这个问题可能会比较慌,常见方案可能就是重启服务,但也不知道重启是否可以解决。我认为重启不仅不能解决问题,甚至有可能加剧问题,这是为什么呢?本文我们就一起分析DUBBO线程池打满这个问题。
1 基础知识
1.1 DUBBO线程模型
1.1.1 基本概念
DUBBO底层网络通信采用Netty框架,我们编写一个Netty服务端进行观察:
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8);
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(7777).sync();
System.out.println("服务端准备就绪");
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
BossGroup线程组只有一个线程处理客户端连接请求,连接完成后将完成三次握手的SocketChannel连接分发给WorkerGroup处理读写请求,这两个线程组被称为「IO线程」。
我们再引出「业务线程」这个概念。服务生产者接收到请求后,如果处理逻辑可以快速处理完成,那么可以直接放在IO线程处理,从而减少线程池调度与上下文切换。但是如果处理逻辑非常耗时,或者会发起新IO请求例如查询数据库,那么必须派发到业务线程池处理。
DUBBO提供了多种线程模型,选择线程模型需要在配置文件指定dispatcher属性:
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" dispatcher="all" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" dispatcher="direct" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" dispatcher="message" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" dispatcher="execution" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" dispatcher="connection" />
不同线程模型在选择是使用IO线程还是业务线程,DUBBO官网文档说明:
all
所有消息都派发到业务线程池,包括请求,响应,连接事件,断开事件,心跳
direct
所有消息都不派发到业务线程池,全部在IO线程直接执行
message
只有请求响应消息派发到业务线程池,其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息直接在IO线程执行
execution
只有请求消息派发到业务线程池,响应和其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息直接在IO线程执行
connection
在IO线程上将连接断开事件放入队列,有序逐个执行,其它消息派发到业务线程池
all所有消息都派发到业务线程池,包括请求,响应,连接事件,断开事件,心跳direct所有消息都不派发到业务线程池,全部在IO线程直接执行message只有请求响应消息派发到业务线程池,其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息直接在IO线程执行execution只有请求消息派发到业务线程池,响应和其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息直接在IO线程执行connection在IO线程上将连接断开事件放入队列,有序逐个执行,其它消息派发到业务线程池
1.1.2 确定时机
生产者和消费者在初始化时确定线程模型:
// 生产者
public class NettyServer extends AbstractServer implements Server {
public NettyServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
super(url, ChannelHandlers.wrap(handler, ExecutorUtil.setThreadName(url, SERVER_THREAD_POOL_NAME)));
}
}
// 消费者
public class NettyClient extends AbstractClient {
public NettyClient(final URL url, final ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
super(url, wrapChannelHandler(url, handler));
}
}
生产者和消费者默认线程模型都会使用AllDispatcher,ChannelHandlers.wrap方法可以获取Dispatch自适应扩展点。如果我们在配置文件中指定dispatcher,扩展点加载器会从URL获取属性值加载对应线程模型。本文以生产者为例进行分析:
public class NettyServer extends AbstractServer implements Server {
public NettyServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
// ChannelHandlers.wrap确定线程策略
super(url, ChannelHandlers.wrap(handler, ExecutorUtil.setThreadName(url, SERVER_THREAD_POOL_NAME)));
}
}
public class ChannelHandlers {
protected ChannelHandler wrapInternal(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
return new MultiMessageHandler(new HeartbeatHandler(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Dispatcher.class).getAdaptiveExtension().dispatch(handler, url)));
}
}
@SPI(AllDispatcher.NAME)
public interface Dispatcher {
@Adaptive({Constants.DISPATCHER_KEY, "channel.handler"})
ChannelHandler dispatch(ChannelHandler handler, URL url);
}
1.1.3 源码分析
我们分析其中两个线程模型源码,其它线程模型请阅读DUBBO源码。AllDispatcher模型所有消息都派发到业务线程池,包括请求,响应,连接事件,断开事件,心跳:
public class AllDispatcher implements Dispatcher {
// 线程模型名称
public static final String NAME = "all";
// 具体实现策略
@Override
public ChannelHandler dispatch(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
return new AllChannelHandler(handler, url);
}
}
public class AllChannelHandler extends WrappedChannelHandler {
@Override
public void connected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException {
// 连接完成事件交给业务线程池
ExecutorService cexecutor = getExecutorService();
try {
cexecutor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.CONNECTED));
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ExecutionException("connect event", channel, getClass() + " error when process connected event", t);
}
}
@Override
public void disconnected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException {
// 断开连接事件交给业务线程池
ExecutorService cexecutor = getExecutorService();
try {
cexecutor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.DISCONNECTED));
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ExecutionException("disconnect event", channel, getClass() + " error when process disconnected event", t);
}
}
@Override
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
// 请求响应事件交给业务线程池
ExecutorService cexecutor = getExecutorService();
try {
cexecutor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.RECEIVED, message));
} catch (Throwable t) {
if(message instanceof Request && t instanceof RejectedExecutionException) {
Request request = (Request)message;
if(request.isTwoWay()) {
String msg = "Server side(" + url.getIp() + "," + url.getPort() + ") threadpool is exhausted ,detail msg:" + t.getMessage();
Response response = new Response(request.getId(), request.getVersion());
response.setStatus(Response.SERVER_THREADPOOL_EXHAUSTED_ERROR);
response.setErrorMessage(msg);
channel.send(response);
return;
}
}
throw new ExecutionException(message, channel, getClass() + " error when process received event", t);
}
}
@Override
public void caught(Channel channel, Throwable exception) throws RemotingException {
// 异常事件交给业务线程池
ExecutorService cexecutor = getExecutorService();
try {
cexecutor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.CAUGHT, exception));
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ExecutionException("caught event", channel, getClass() + " error when process caught event", t);
}
}
}
DirectDispatcher策略所有消息都不派发到业务线程池,全部在IO线程直接执行:
public class DirectDispatcher implements Dispatcher {
// 线程模型名称
public static final String NAME = "direct";
// 具体实现策略
@Override
public ChannelHandler dispatch(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
// 直接返回handler表示所有事件都交给IO线程处理
return handler;
}
}
1.2 DUBBO线程池策略
1.2.1 基本概念
上个章节分析了线程模型,我们知道不同的线程模型会选择使用还是IO线程还是业务线程。如果使用业务线程池,那么使用什么线程池策略是本章节需要回答的问题。DUBBO官网线程派发模型图展示了线程模型和线程池策略的关系:
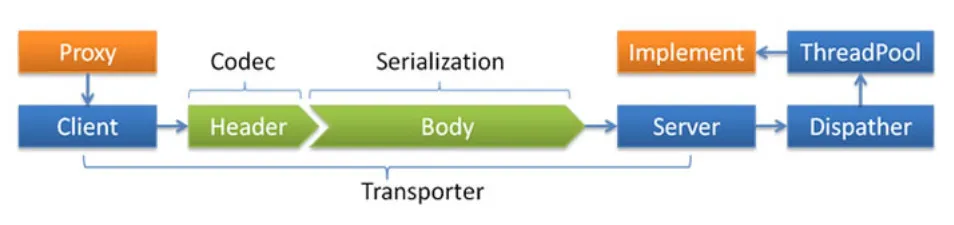
DUBBO提供了多种线程池策略,选择线程池策略需要在配置文件指定threadpool属性:
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" threadpool="fixed" threads="100" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" threadpool="cached" threads="100" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" threadpool="limited" threads="100" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" threadpool="eager" threads="100" />
不同线程池策略会创建不同特性的线程池:
fixed
包含固定个数线程
cached
线程空闲一分钟会被回收,当新请求到来时会创建新线程
limited
线程个数随着任务增加而增加,但不会超过最大阈值。空闲线程不会被回收
eager
当所有核心线程数都处于忙碌状态时,优先创建新线程执行任务,而不是立即放入队列
fixed包含固定个数线程cached线程空闲一分钟会被回收,当新请求到来时会创建新线程limited线程个数随着任务增加而增加,但不会超过最大阈值。空闲线程不会被回收eager当所有核心线程数都处于忙碌状态时,优先创建新线程执行任务,而不是立即放入队列
1.2.2 确定时机
本文我们以AllDispatcher为例分析线程池策略在什么时候确定:
public class AllDispatcher implements Dispatcher {
public static final String NAME = "all";
@Override
public ChannelHandler dispatch(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
return new AllChannelHandler(handler, url);
}
}
public class AllChannelHandler extends WrappedChannelHandler {
public AllChannelHandler(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
super(handler, url);
}
}
在WrappedChannelHandler构造函数中如果配置指定了threadpool属性,扩展点加载器会从URL获取属性值加载对应线程池策略,默认策略为fixed:
public class WrappedChannelHandler implements ChannelHandlerDelegate {
public WrappedChannelHandler(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
this.handler = handler;
this.url = url;
// 获取线程池自适应扩展点
executor = (ExecutorService) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ThreadPool.class).getAdaptiveExtension().getExecutor(url);
String componentKey = Constants.EXECUTOR_SERVICE_COMPONENT_KEY;
if (Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE.equalsIgnoreCase(url.getParameter(Constants.SIDE_KEY))) {
componentKey = Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE;
}
DataStore dataStore = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(DataStore.class).getDefaultExtension();
dataStore.put(componentKey, Integer.toString(url.getPort()), executor);
}
}
@SPI("fixed")
public interface ThreadPool {
@Adaptive({Constants.THREADPOOL_KEY})
Executor getExecutor(URL url);
}
1.2.3 源码分析
(1) FixedThreadPool
public class FixedThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
// 线程名称
String name = url.getParameter(Constants.THREAD_NAME_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
// 线程个数默认200
int threads = url.getParameter(Constants.THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_THREADS);
// 队列容量默认0
int queues = url.getParameter(Constants.QUEUES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_QUEUES);
// 队列容量等于0使用阻塞队列SynchronousQueue
// 队列容量小于0使用无界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue
// 队列容量大于0使用有界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(threads, threads, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()
: (queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(queues)),
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true), new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
}
}
(2) CachedThreadPool
public class CachedThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
// 获取线程名称
String name = url.getParameter(Constants.THREAD_NAME_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
// 核心线程数默认0
int cores = url.getParameter(Constants.CORE_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CORE_THREADS);
// 最大线程数默认Int最大值
int threads = url.getParameter(Constants.THREADS_KEY, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 队列容量默认0
int queues = url.getParameter(Constants.QUEUES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_QUEUES);
// 线程空闲多少时间被回收默认1分钟
int alive = url.getParameter(Constants.ALIVE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_ALIVE);
// 队列容量等于0使用阻塞队列SynchronousQueue
// 队列容量小于0使用无界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue
// 队列容量大于0使用有界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(cores, threads, alive, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()
: (queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(queues)),
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true), new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
}
}
(3) LimitedThreadPool
public class LimitedThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
// 获取线程名称
String name = url.getParameter(Constants.THREAD_NAME_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
// 核心线程数默认0
int cores = url.getParameter(Constants.CORE_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CORE_THREADS);
// 最大线程数默认200
int threads = url.getParameter(Constants.THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_THREADS);
// 队列容量默认0
int queues = url.getParameter(Constants.QUEUES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_QUEUES);
// 队列容量等于0使用阻塞队列SynchronousQueue
// 队列容量小于0使用无界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue
// 队列容量大于0使用有界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue
// keepalive时间设置Long.MAX_VALUE表示不回收空闲线程
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(cores, threads, Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()
: (queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(queues)),
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true), new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
}
}
(4) EagerThreadPool
我们知道ThreadPoolExecutor是普通线程执行器。当线程池核心线程达到阈值时新任务放入队列,当队列已满开启新线程处理,当前线程数达到最大线程数时执行拒绝策略。
但是EagerThreadPool自定义线程执行策略,当线程池核心线程达到阈值时,新任务不会放入队列而是开启新线程进行处理(要求当前线程数没有超过最大线程数)。当前线程数达到最大线程数时任务放入队列。
public class EagerThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
// 线程名
String name = url.getParameter(Constants.THREAD_NAME_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
// 核心线程数默认0
int cores = url.getParameter(Constants.CORE_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CORE_THREADS);
// 最大线程数默认Int最大值
int threads = url.getParameter(Constants.THREADS_KEY, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 队列容量默认0
int queues = url.getParameter(Constants.QUEUES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_QUEUES);
// 线程空闲多少时间被回收默认1分钟
int alive = url.getParameter(Constants.ALIVE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_ALIVE);
// 初始化自定义线程池和队列重写相关方法
TaskQueue<Runnable> taskQueue = new TaskQueue<Runnable>(queues <= 0 ? 1 : queues);
EagerThreadPoolExecutor executor = new EagerThreadPoolExecutor(cores,
threads,
alive,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
taskQueue,
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true),
new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
taskQueue.setExecutor(executor);
return executor;
}
}
1.3 一个公式
现在我们知道DUBBO会选择线程池策略进行业务处理,那么应该如何估算可能产生的线程数呢?我们首先分析一个问题:一个公司有7200名员工,每天上班打卡时间是早上8点到8点30分,每次打卡时间系统执行时长为5秒。请问RT、QPS、并发量分别是多少?
RT表示响应时间,问题已经告诉了我们答案:
QPS表示每秒查询量,假设签到行为平均分布:
QPS = 7200 / (30 * 60) = 4
并发量表示系统同时处理的请求数量:
并发量 = QPS x RT = 4 x 5 = 20
根据上述实例引出如下公式:
并发量 = QPS x RT
如果系统为每一个请求分配一个处理线程,那么并发量可以近似等于线程数。基于上述公式不难看出并发量受QPS和RT影响,这两个指标任意一个上升就会导致并发量上升。
但是这只是理想情况,因为并发量受限于系统能力而不可能持续上升,例如DUBBO线程池就对线程数做了限制,超出最大线程数限制则会执行拒绝策略,而拒绝策略会提示线程池已满,这就是DUBBO线程池打满问题的根源。下面我们分析RT上升和QPS上升这两个原因。
2 RT上升
2.1 生产者发生慢服务
2.1.1 原因分析
(1) 生产者配置
<beans>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="9999" />
<dubbo:service interface="com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloService" ref="helloService" />
</beans>
(2) 生产者业务
package com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider;
public interface HelloService {
public String sayHello(String name) throws Exception;
}
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
public String sayHello(String name) throws Exception {
String result = "hello[" + name + "]";
// 模拟慢服务
Thread.sleep(10000L);
System.out.println("生产者执行结果" + result);
return result;
}
}
(3) 消费者配置
<beans>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" />
<dubbo:reference id="helloService" interface="com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloService" />
</beans>
(4) 消费者业务
public class Consumer {
@Test
public void testThread() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] { "classpath*:METAINF/spring/dubbo-consumer.xml" });
context.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
HelloService helloService = (HelloService) context.getBean("helloService");
String result;
try {
result = helloService.sayHello("微信公众号「JAVA前线」");
System.out.println("客户端收到结果" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
依次运行生产者和消费者代码,会发现日志中出现报错信息。生产者日志会打印线程池已满:
Caused by: java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Thread pool is EXHAUSTED! Thread Name: DubboServerHandler-x.x.x.x:9999, Pool Size: 200 (active: 200, core: 200, max: 200, largest: 200), Task: 201 (completed: 1), Executor status:(isShutdown:false, isTerminated:false, isTerminating:false), in dubbo://x.x.x.x:9999!
at org.apache.dubbo.common.threadpool.support.AbortPolicyWithReport.rejectedExecution(AbortPolicyWithReport.java:67)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:830)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1379)
at org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.all.AllChannelHandler.caught(AllChannelHandler.java:88)
消费者日志不仅会打印线程池已满,还会打印服务提供者信息和调用方法,我们可以根据日志找到哪一个方法有问题:
Failed to invoke the method sayHello in the service com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloService.
Tried 3 times of the providers [x.x.x.x:9999] (1/1) from the registry 127.0.0.1:2181 on the consumer x.x.x.x
using the dubbo version 2.7.0-SNAPSHOT. Last error is: Failed to invoke remote method: sayHello,
provider: dubbo://x.x.x.x:9999/com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloService?anyhost=true&application=xpz-consumer1&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&group=&interface=com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloService&logger=log4j&methods=sayHello&pid=33432®ister.ip=x.x.x.x&release=2.7.0-SNAPSHOT&remote.application=xpz-provider&remote.timestamp=1618632597509&side=consumer&timeout=100000000×tamp=1618632617392,
cause: Server side(x.x.x.x,9999) threadpool is exhausted ,detail msg:Thread pool is EXHAUSTED! Thread Name: DubboServerHandler-x.x.x.x:9999, Pool Size: 200 (active: 200, core: 200, max: 200, largest: 200), Task: 401 (completed: 201), Executor status:(isShutdown:false, isTerminated:false, isTerminating:false), in dubbo://x.x.x.x:9999!
2.1.2 解决方案
(1) 找出慢服务
DUBBO线程池打满时会执行拒绝策略:
public class AbortPolicyWithReport extends ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy {
protected static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbortPolicyWithReport.class);
private final String threadName;
private final URL url;
private static volatile long lastPrintTime = 0;
private static Semaphore guard = new Semaphore(1);
public AbortPolicyWithReport(String threadName, URL url) {
this.threadName = threadName;
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
String msg = String.format("Thread pool is EXHAUSTED!" +
" Thread Name: %s, Pool Size: %d (active: %d, core: %d, max: %d, largest: %d), Task: %d (completed: %d)," +
" Executor status:(isShutdown:%s, isTerminated:%s, isTerminating:%s), in %s://%s:%d!",
threadName, e.getPoolSize(), e.getActiveCount(), e.getCorePoolSize(), e.getMaximumPoolSize(), e.getLargestPoolSize(),
e.getTaskCount(), e.getCompletedTaskCount(), e.isShutdown(), e.isTerminated(), e.isTerminating(),
url.getProtocol(), url.getIp(), url.getPort());
logger.warn(msg);
// 打印线程快照
dumpJStack();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(msg);
}
private void dumpJStack() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 每10分钟输出线程快照
if (now - lastPrintTime < 10 * 60 * 1000) {
return;
}
if (!guard.tryAcquire()) {
return;
}
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
pool.execute(() -> {
String dumpPath = url.getParameter(Constants.DUMP_DIRECTORY, System.getProperty("user.home"));
System.out.println("AbortPolicyWithReport dumpJStack directory=" + dumpPath);
SimpleDateFormat sdf;
String os = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase();
// linux文件位置/home/xxx/Dubbo_JStack.log.2021-01-01_20:50:15
// windows文件位置/user/xxx/Dubbo_JStack.log.2020-01-01_20-50-15
if (os.contains("win")) {
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd_HH-mm-ss");
} else {
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd_HH:mm:ss");
}
String dateStr = sdf.format(new Date());
try (FileOutputStream jStackStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(dumpPath, "Dubbo_JStack.log" + "." + dateStr))) {
JVMUtil.jstack(jStackStream);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("dump jStack error", t);
} finally {
guard.release();
}
lastPrintTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
});
pool.shutdown();
}
}
拒绝策略会输出线程快照文件,在分析线程快照文件时BLOCKED和TIMED_WAITING线程状态需要我们重点关注。如果发现大量线程阻塞或者等待状态则可以定位到具体代码行:
DubboServerHandler-x.x.x.x:9999-thread-200 Id=230 TIMED_WAITING
at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native Method)
at com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloServiceImpl.sayHello(HelloServiceImpl.java:13)
at org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode.Wrapper1.invokeMethod(Wrapper1.java)
at org.apache.dubbo.rpc.proxy.javassist.JavassistProxyFactory$1.doInvoke(JavassistProxyFactory.java:56)
at org.apache.dubbo.rpc.proxy.AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke(AbstractProxyInvoker.java:85)
at org.apache.dubbo.config.invoker.DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker.invoke(DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker.java:56)
at org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.InvokerWrapper.invoke(InvokerWrapper.java:56)
(2) 优化慢服务
现在已经找到了慢服务,此时我们就可以优化慢服务了。优化慢服务就需要具体问题具体分析了,这不是本文的重点在此不进行展开。
2.2 生产者预热不充分
2.2.1 原因分析
还有一种RT上升的情况是我们不能忽视的,这种情况就是提供者重启后预热不充分即被调用。因为当生产者刚启动时需要预热,需要和其它资源例如数据库、缓存等建立连接,建立连接是需要时间的。如果此时大量消费者请求到未预热的生产者,链路时间增加了连接时间,RT时间必然会增加,从而也会导致DUBBO线程池打满问题。
2.2.2 解决方案
(1) 等待生产者充分预热
因为生产者预热不充分导致线程池打满问题,最容易发生在系统发布时。例如发布了一台机器后发现线上出现线程池打满问题,千万不要着急重启机器,而是给机器一段时间预热,等连接建立后问题大概率消失。同时我们在发布时也要分多批次发布,不要一次发布太多机器导致服务因为预热问题造成大面积影响。
(2) DUBBO升级版本大于等于2.7.4
DUBBO消费者在调用选择生产者时本身就会执行预热逻辑,为什么还会出现预热不充分问题?这是因为2.5.5之前版本以及2.7.2版本预热机制是有问题的,简而言之就是获取启动时间不正确,2.7.4版本彻底解决了这个问题,所以我们要避免使用问题版本。下面我们阅读2.7.0版本预热机制源码,看看预热机制如何生效:
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "random";
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// invokers数量
int length = invokers.size();
// 权重是否相同
boolean sameWeight = true;
// invokers权重数组
int[] weights = new int[length];
// 第一个invoker权重
int firstWeight = getWeight(invokers.get(0), invocation);
weights[0] = firstWeight;
// 权重值之和
int totalWeight = firstWeight;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
// 计算权重值
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
weights[i] = weight;
totalWeight += weight;
// 任意一个invoker权重值不等于第一个invoker权重值则sameWeight设置为FALSE
if (sameWeight && weight != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
// 权重值不等则根据总权重值计算
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
// 不断减去权重值当小于0时直接返回
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= weights[i];
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 所有服务权重值一致则随机返回
return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
}
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalance implements LoadBalance {
static int calculateWarmupWeight(int uptime, int warmup, int weight) {
// uptime/(warmup*weight)
// 如果当前服务提供者没过预热期,用户设置的权重将通过uptime/warmup减小
// 如果服务提供者设置权重很大但是还没过预热时间,重新计算权重会很小
int ww = (int) ((float) uptime / ((float) warmup / (float) weight));
return ww < 1 ? 1 : (ww > weight ? weight : ww);
}
protected int getWeight(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 获取invoker设置权重值默认权重=100
int weight = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.WEIGHT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_WEIGHT);
// 如果权重大于0
if (weight > 0) {
// 服务提供者发布服务时间戳
long timestamp = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.REMOTE_TIMESTAMP_KEY, 0L);
if (timestamp > 0L) {
// 服务已经发布多少时间
int uptime = (int) (System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp);
// 预热时间默认10分钟
int warmup = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.WARMUP_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_WARMUP);
// 生产者发布时间大于0但是小于预热时间
if (uptime > 0 && uptime < warmup) {
// 重新计算权重值
weight = calculateWarmupWeight(uptime, warmup, weight);
}
}
}
// 服务发布时间大于预热时间直接返回设置权重值
return weight >= 0 ? weight : 0;
}
}
3 QPS上升
上面章节大篇幅讨论了由于RT上升造成的线程池打满问题,现在我们讨论另一个参数QPS。当上游流量激增会导致创建大量线程池,也会造成线程池打满问题。这时如果发现QPS超出了系统承受能力,我们不得不采用降级方案保护系统,请参看我之前文章《从反脆弱角度谈技术系统的高可用性》
4 文章总结
本文首先介绍了DUBBO线程模型和线程池策略,然后我们引出了公式,发现并发量受RT和QPS两个参数影响,这两个参数任意一个上升都可以造成线程池打满问题。生产者出现慢服务或者预热不充分都有可能造成RT上升,而上游流量激增会造成QPS上升,同时本文也给出了解决方案。DUBBO线程池打满是一个必须重视的问题,希望本文对大家有所帮助。


 分享到微信
分享到微信  分享到微博
分享到微博Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK