

LeetCode: 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
source link: https://mozillazg.com/2020/11/leetcode-145-binary-tree-postorder-traversal.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
题目¶
原题地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:
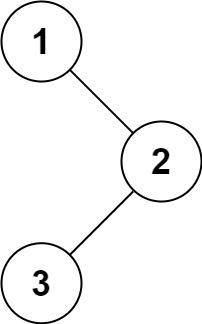
Input: root = [1,null,2,3] Output: [3,2,1]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Example 4:
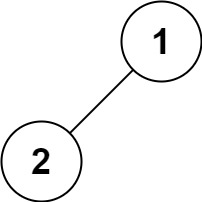
Input: root = [1,2] Output: [2,1]
Example 5:
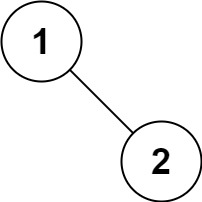
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: [2,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up:
Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
解法¶
递归法实现后序遍历¶
这个方法的 Python 代码类似下面这样:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def postorderTraversal(self, root):
nodes = []
self._postorder(nodes, root)
return nodes
def _postorder(self, nodes, root):
if root is None:
return
self._postorder(nodes, root.left)
self._postorder(nodes, root.right)
nodes.append(root.val)
stack 法实现后序遍历¶
这个方法的 Python 代码类似下面这样:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def postorderTraversal(self, root):
if root is None:
return []
nodes = []
stack1 = []
stack2 = []
stack1.append(root)
while stack1:
curr = stack1.pop()
stack2.append(curr)
if curr.left is not None:
stack1.append(curr.left)
if curr.right is not None:
stack1.append(curr.right)
while stack2:
node = stack2.pop()
nodes.append(node.val)
return nodes
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK