

最简最快了解RPC核心流程
source link: https://www.51cto.com/article/781953.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

最简最快了解RPC核心流程
本文主要以最简易最快速的方式介绍RPC调用核心流程,文中以Dubbo为例。同时,会写一个简易的RPC调用代码,方便理解和记忆核心组件和核心流程。

一、核心思想
RPC调用过程中,最粗矿的核心组件3个:Registry、Provider、Consumer。最粗矿的流程4个:注册、订阅、通知、调用。最简单的流程图就1个:
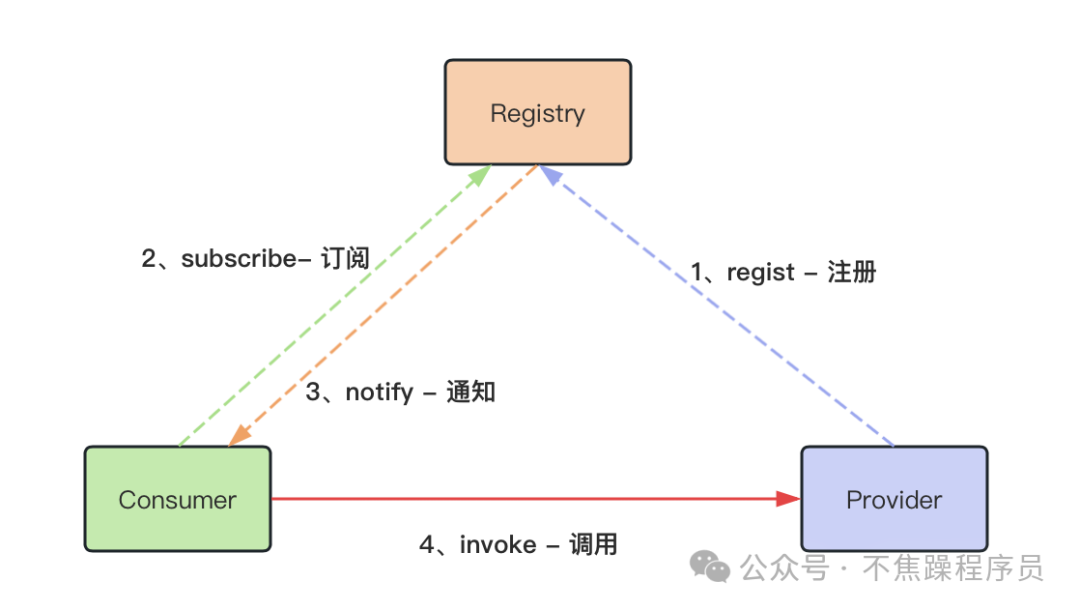
本文会继续细粒度地拆解以上流程,拆解之前,请牢记这段话:
RPC调用,不管中间流程多么复杂,不管代码多么复杂,所有的努力也只为做2件事情:
- 在Consumer端,将ReferenceConfig配置的类转换成Proxy代理。
- 在Provider端,将ServiceConfig配置的类转换成Proxy代理。
二、核心组件
为了能在Consumer端和Provider端生成各自的Proxy代理,并且发起调用和响应,需要如下核心组件:
(1) Registry:注册中心,主要是为了实现 Provider接口注册、Consumer订阅接口、接口变更通知、接口查找等功能。
(2) Proxy:服务代理,核心中的核心,一切的努力都是为了生成合适的Proxy服务代理。
- Consumer的Proxy:Consumer端根据ReferenceConfig生成Proxy,此Proxy主要用于找到合适的Provider接口,然后发起网络调用。
- Provider的Proxy:Provider端根据ServiceConfig生成Proxy,此Proxy主要作用是通过类似反射的方法调用本地代码,再将结果返回给Consumer。
(3) Protocol:服务协议,它相当于一个中间层,用于与注册中心打交道 和 封装 RPC 调用。它在初始化时会创建Client模块 与 服务端建立连接,也会生成用于远程调用的Invoker。
(4) Cluster:服务集群,主要用于路由、负载均衡、服务容错等。
(5) Invoker:服务调用者。
- Consumer的服务调用者主要是利用Client模块发起远程调用,然后等待Provider返回结果。
- Provider的服务调用者主要是根据接收到的消息利用反射生成本地代理,然后执行方法,再将结果返回到Consumer。
(6) Client:客户端模块,默认是Netty实现,主要用于客户端和服务端通讯(主要是服务调用),比如将请求的接口、参数、请求ID等封装起来发给Server端。
(7) Server:服务端模拟,默认是Netty实现。主要是用于客户端和服务端通讯。
三、核心流程
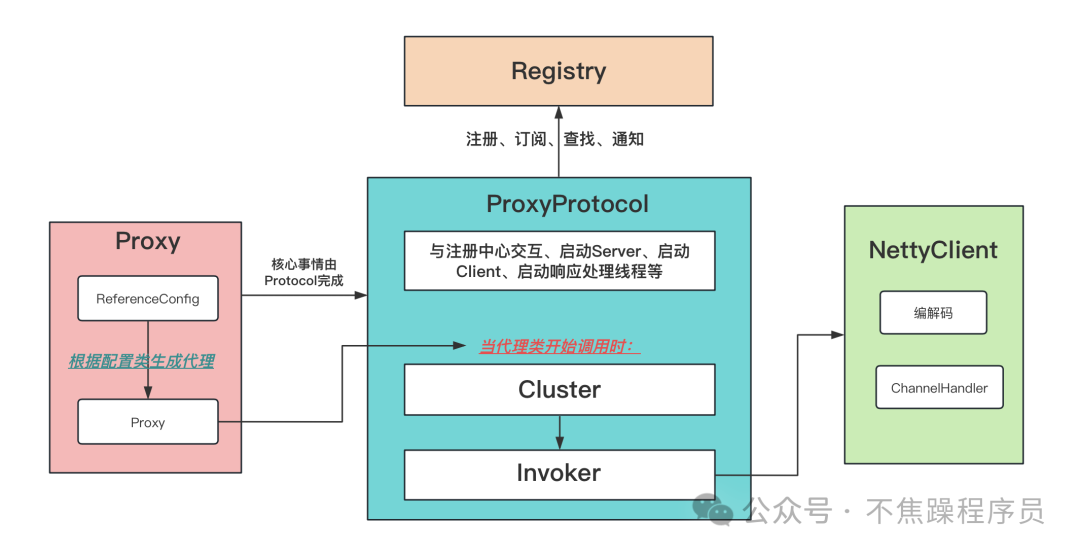
1.Consumer流程
(1) 流程
Consumer的流程实际上就是一个从ReferenceConfig 生成Proxy代理的过程。核心事情由Protocol完成。
- 根据ReferenceConfig生成代理
- 注册到注册中心、订阅注册中心事件
- 建立NettyClient,并且与NettyServer建立连接
- 生成客户端的ClientInvoker
- 选择负载均衡和集群容错
- ClientInvoker发起网络调用和等待结果
(2) 流程图:
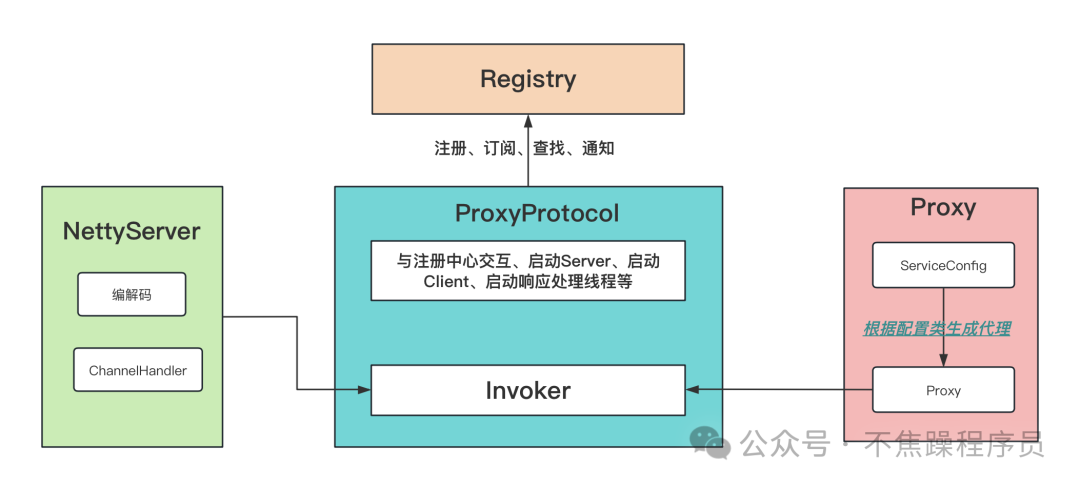
2.Provider流程
(1) 流程
Provider的流程实际上就是个从ServiceConfig生成Proxy代理的过程。核心事情由PorxyProtocol完成。
- 根据ServiceConfig生成本地代理
- 注册到注册中心
- 启动NettyServer等待客户端连接
- 生成服务端Invoker
- Invoker监听调用请求
- 接收到请求后新建任务丢入到线程池去执行
- 执行时会生成本地代理执行(比如通过反射去调用具体的方法),再将返回结果写出去
(2) 流程图:
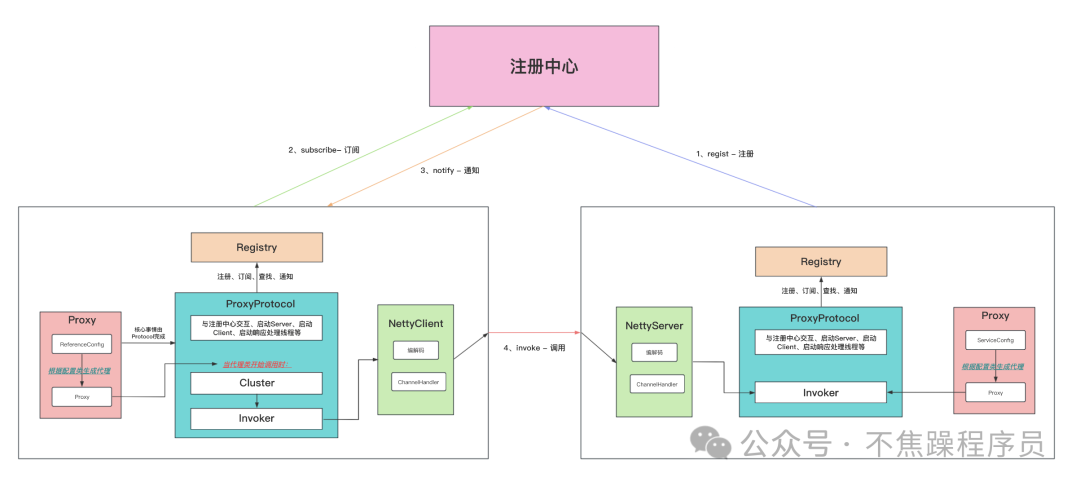
3.整体流程图
四、简易代码实现
1.核心代码介绍
(1) 客户端Proxy:
/**
* 获取代理Service
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getService(Class clazz) throws Exception {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{clazz}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if ("equals".equals(methodName) || "hashCode".equals(methodName)) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("不能访问" + methodName + "方法");
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName)) {
return clazz.getName() + "#" + methodName;
}
List<RegistryInfo> registryInfoList = interfaceMethodsRegistryInfoMap.get(clazz);
if (registryInfoList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("无法找到对应的服务提供者");
}
LoadBalancer loadBalancer = new RandomLoadBalancer();
RegistryInfo registryInfo = loadBalancer.choose(registryInfoList);
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = registryChannelMap.get(registryInfo);
String identity = InvokeUtils.buildInterfaceMethodIdentify(clazz, method);
String requestId;
synchronized (ProxyProtocol.this) {
requestIdWorker.increment();
requestId = String.valueOf(requestIdWorker.longValue());
}
ClientInvoker clientInvoker = new DefaultClientInvoker(method.getReturnType(), ctx, requestId, identity);
inProcessInvokerMap.put(identity + "#" + requestId, clientInvoker);
return clientInvoker.invoke(args);
}
});
}(2) 服务端Proxy
private class RpcInvokerTask implements Runnable {
private RpcRequest rpcRequest;
public RpcInvokerTask(RpcRequest rpcRequest) {
this.rpcRequest = rpcRequest;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = rpcRequest.getCtx();
String interfaceIdentity = rpcRequest.getInterfaceIdentity();
String requestId = rpcRequest.getRequestId();
Map<String, Object> parameterMap = rpcRequest.getParameterMap();
//interfaceIdentity组成:接口类+方法+参数类型
Map<String, String> interfaceIdentityMap = string2Map(interfaceIdentity);
//拿出是哪个类
String interfaceName = interfaceIdentityMap.get("interface");
Class interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName);
Object o = interfaceInstanceMap.get(interfaceClass);
//拿出是哪个方法
Method method = interfaceMethodMap.get(interfaceIdentity);
//反射执行
Object result = null;
String parameterStr = interfaceIdentityMap.get("parameter");
if (parameterStr != null && parameterStr.length() > 0) {
String[] parameterTypeClasses = parameterStr.split(",");//接口方法参数参数可能有多个,用,号隔开
Object[] parameterInstance = new Object[parameterTypeClasses.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypeClasses.length; i++) {
parameterInstance[i] = parameterMap.get(parameterTypeClasses[i]);
}
result = method.invoke(o, parameterInstance);
} else {
result = method.invoke(o);
}
//将结果封装成rcpResponse
RpcResponse rpcResponse = RpcResponse.create(JSONObject.toJSONString(result), interfaceIdentity, requestId);
//ctx返回执行结果
String resultStr = JSONObject.toJSONString(rpcResponse) + DELIMITER_STR;
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(resultStr.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(byteBuf);
System.out.println("响应给客户端:" + resultStr);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}(3) Protocol
public ProxyProtocol(String registryUrl, List<ServiceConfig> serviceConfigList, List<ReferenceConfig> referenceConfigList, int port) throws Exception {
this.serviceConfigList = serviceConfigList == null ? new ArrayList<>() : serviceConfigList;
this.registryUrl = registryUrl;
this.port = port;
this.referenceConfigList = referenceConfigList == null ? new ArrayList<>() : referenceConfigList;
//1、初始化注册中心
initRegistry(this.registryUrl);
//2、将服务注册到注册中心
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
String hostName = addr.getHostName();
String hostAddr = addr.getHostAddress();
registryInfo = new RegistryInfo(hostName, hostAddr, this.port);
doRegistry(registryInfo);
//3、初始化nettyServer,启动nettyServer
if (!this.serviceConfigList.isEmpty()) {
nettyServer = new NettyServer(this.serviceConfigList, this.interfaceMethodMap);
nettyServer.init(this.port);
}
//如果是客户端引用启动,则初始化处理线程
if (!this.referenceConfigList.isEmpty()) {
initProcessor();
}
}(4) 客户端Invoker
@Override
public T invoke(Object[] args) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("interfaces", identity);
JSONObject param = new JSONObject();
if (args != null) {
for (Object obj : args) {
param.put(obj.getClass().getName(), obj);
}
}
jsonObject.put("parameter", param);
jsonObject.put("requestId", requestId);
String msg = jsonObject.toJSONString() + Constants.DELIMITER_STR;
System.out.println("发送给服务端JSON为:" + msg);
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(msg.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(byteBuf);
wait4Result();
return result;
}
private void wait4Result() {
synchronized (this) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void setResult(String result) {
synchronized (this) {
this.result = (T) JSONObject.parseObject(result, returnType);
notifyAll();
}
}(5) 服务端Invoker
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String message = (String) msg;
System.out.println("提供者收到消息:" + message);
//解析消费者发来的消息
RpcRequest rpcRequest = RpcRequest.parse(message, ctx);
//接受到消息,启动线程池处理消费者发过来的请求
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new RpcInvokerTask(rpcRequest));
}
/**
* 处理消费者发过来的请求
*/
private class RpcInvokerTask implements Runnable {
private RpcRequest rpcRequest;
public RpcInvokerTask(RpcRequest rpcRequest) {
this.rpcRequest = rpcRequest;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = rpcRequest.getCtx();
String interfaceIdentity = rpcRequest.getInterfaceIdentity();
String requestId = rpcRequest.getRequestId();
Map<String, Object> parameterMap = rpcRequest.getParameterMap();
//interfaceIdentity组成:接口类+方法+参数类型
Map<String, String> interfaceIdentityMap = string2Map(interfaceIdentity);
//拿出是哪个类
String interfaceName = interfaceIdentityMap.get("interface");
Class interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName);
Object o = interfaceInstanceMap.get(interfaceClass);
//拿出是哪个方法
Method method = interfaceMethodMap.get(interfaceIdentity);
//反射执行
Object result = null;
String parameterStr = interfaceIdentityMap.get("parameter");
if (parameterStr != null && parameterStr.length() > 0) {
String[] parameterTypeClasses = parameterStr.split(",");//接口方法参数参数可能有多个,用,号隔开
Object[] parameterInstance = new Object[parameterTypeClasses.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypeClasses.length; i++) {
parameterInstance[i] = parameterMap.get(parameterTypeClasses[i]);
}
result = method.invoke(o, parameterInstance);
} else {
result = method.invoke(o);
}
//将结果封装成rcpResponse
RpcResponse rpcResponse = RpcResponse.create(JSONObject.toJSONString(result), interfaceIdentity, requestId);
//ctx返回执行结果
String resultStr = JSONObject.toJSONString(rpcResponse) + DELIMITER_STR;
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(resultStr.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(byteBuf);
System.out.println("响应给客户端:" + resultStr);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}(6) Client
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024 * 1024, Constants.DELIMITER));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler());
System.out.println("initChannel - " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.connect(ip, port).sync();
// cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
System.out.println("客户端启动成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
group.shutdownGracefully();
}(7) Server
public NettyServer(List<ServiceConfig> serviceConfigList, Map<String, Method> interfaceMethodMap) {
this.serviceConfigList = serviceConfigList;
this.interfaceMethodMap = interfaceMethodMap;
}
public int init(int port) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
channel.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024 * 1024, DELIMITER));
channel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
channel.pipeline().addLast(new RpcInvokeHandler(serviceConfigList, interfaceMethodMap));
}
});
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("启动NettyServer,端口为:" + port);
return port;
}2.项目地址
https://github.com/yclxiao/rpc-demo.git
本文主要以Dubbo为例介绍了RPC调用核心流程,同时,写了个简易的RPC调用代码。
记住以上的流程图即可搞明白整个调用流程。然后再记住最核心的2句话:
所有的努力都是为了能在Consumer端和Provider端生成功能丰富的Proxy。核心事情由Protocol完成。
核心的5个部件:Registry、Proxy、Protocol、Invoker、Client、Server。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK