

Linux 服务器功耗与性能管理(四):监控、配置、调优(2024)
source link: http://arthurchiao.art/blog/linux-cpu-4-zh/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Linux 服务器功耗与性能管理(四):监控、配置、调优(2024)
Published at 2024-02-15 | Last Update 2024-02-15
整理一些 Linux 服务器性能相关的 CPU 硬件基础及内核子系统知识。
水平有限,文中不免有错误或过时之处,请酌情参考。
1 sysfs 相关目录
1.1 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu{N}/ 目录
系统中的每个 CPU,都对应一个 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/cpuidle/ 目录,
其中 N 是 CPU ID,
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
├── cache
│ ├── index0
│ ├── ...
│ ├── index3
│ └── uevent
├── cpufreq -> ../cpufreq/policy0
├── cpuidle
│ ├── state0
│ │ ├── above
│ │ ├── below
│ │ ├── default_status
│ │ ├── desc
│ │ ├── disable
│ │ ├── latency
│ │ ├── name
│ │ ├── power
│ │ ├── rejected
│ │ ├── residency
│ │ ├── time
│ │ └── usage
│ └── state1
│ ├── above
│ ├── below
│ ├── default_status
│ ├── desc
│ ├── disable
│ ├── latency
│ ├── name
│ ├── power
│ ├── rejected
│ ├── residency
│ ├── time
│ └── usage
├── crash_notes
├── crash_notes_size
├── driver -> ../../../../bus/cpu/drivers/processor
├── firmware_node -> ../../../LNXSYSTM:00/LNXCPU:00
├── hotplug
│ ├── fail
│ ├── state
│ └── target
├── node0 -> ../../node/node0
├── power
│ ├── async
│ ├── autosuspend_delay_ms
│ ├── control
│ ├── pm_qos_resume_latency_us
│ ├── runtime_active_kids
│ ├── runtime_active_time
│ ├── runtime_enabled
│ ├── runtime_status
│ ├── runtime_suspended_time
│ └── runtime_usage
├── subsystem -> ../../../../bus/cpu
├── topology
│ ├── cluster_cpus
│ ├── cluster_cpus_list
│ ├── cluster_id
│ ├── core_cpus
│ ├── core_cpus_list
│ ├── core_id
│ ├── core_siblings
│ ├── core_siblings_list
│ ├── die_cpus
│ ├── die_cpus_list
│ ├── die_id
│ ├── package_cpus
│ ├── package_cpus_list
│ ├── physical_package_id
│ ├── thread_siblings
│ └── thread_siblings_list
└── uevent
里面包括了很多硬件相关的子系统信息,跟我们本次主题相关的几个:
- cpufreq
- cpuidle
- power:PM QoS 相关信息,可以在这里面查到
- topology:第一篇介绍的 PKG-CORE-CPU 拓扑,信息可以在这里面查到
下面分别看下这几个子目录。
1.1.1 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/cpufreq/ (p-state)
处理器执行任务时的运行频率、超频等等相关的参数,管理的是 p-state:
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/
├── affected_cpus
├── cpuinfo_max_freq
├── cpuinfo_min_freq
├── cpuinfo_transition_latency
├── related_cpus
├── scaling_available_governors
├── scaling_cur_freq
├── scaling_driver
├── scaling_governor
├── scaling_max_freq
├── scaling_min_freq
└── scaling_setspeed
1.1.2 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/cpuidle/ (c-states)
每个 struct cpuidle_state 对象都有一个对应的 struct cpuidle_state_usage
对象(上一篇中有更新这个 usage 的相关代码),其中包含了这个 idle state 的统计信息,
也是就是我们下面看到的这些:
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/
├── state0
│ ├── above
│ ├── below
│ ├── default_status
│ ├── desc
│ ├── disable
│ ├── latency
│ ├── name
│ ├── power
│ ├── rejected
│ ├── residency
│ ├── time
│ └── usage
├── state1
│ ├── above
│ ├── below
│ ├── default_status
│ ├── desc
│ ├── disable
│ ├── latency
│ ├── name
│ ├── power
│ ├── rejected
│ ├── residency
│ ├── s2idle
│ │ ├── time
│ │ └── usage
│ ├── time
│ └── usage
│...
state0、state1 等目录对应 idle state 对象,也跟这个 CPU 的 c-state 对应,数字越大,c-state 越深。
文件说明,
desc/name:都是这个 idle state 的描述。name 比较简洁,desc 更长。除了这俩,其他字段都是整型。above:idle duration < target_residency的次数。也就是请求到了这个状态,但是 idle duration 太短,最终放弃进入这个状态。below:idle duration虽然大于target_residency,但是大的比较多,最终找到了一个更深的 idle state 的次数。disable:唯一的可写字段:1表示禁用,governor 就不会在这个 CPU 上选这状态了。注意这个是 per-cpu 配置,此外还有一个全局配置。default_status:default status of this state, “enabled” or “disabled”.latency:这个 idle state 的exit latency,单位us。power:这个字段通常是0,表示不支持。因为功耗的统计很复杂,这个字段的定义也不是很明确。建议不要参考这个值。residency:这个 idle state 的target residency,单位us。time:内核统计的该 CPU 花在这个状态的总时间,单位 ms。这个是内核统计的,可能不够准,因此如有处理器硬件统计的类似指标,建议参考后者。usage:成功进入这个 idle state 的次数。rejected:被拒绝的要求进入这个 idle state 的 request 的数量。
1.1.3 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/power/
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
├── power
│ ├── async
│ ├── autosuspend_delay_ms
│ ├── control
│ ├── pm_qos_resume_latency_us
│ ├── runtime_active_kids
│ ├── runtime_active_time
│ ├── runtime_enabled
│ ├── runtime_status
│ ├── runtime_suspended_time
│ └── runtime_usage
1.1.4 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu<N>/topology/
$ tree /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/
├── topology
│ ├── cluster_cpus
│ ├── cluster_cpus_list
│ ├── cluster_id
│ ├── core_cpus
│ ├── core_cpus_list
│ ├── core_id
│ ├── core_siblings
│ ├── core_siblings_list
│ ├── die_cpus
│ ├── die_cpus_list
│ ├── die_id
│ ├── package_cpus
│ ├── package_cpus_list
│ ├── physical_package_id
│ ├── thread_siblings
│ └── thread_siblings_list
└── uevent
1.2 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/:governor/driver
这个目录是全局的,可以获取可用的 governor/driver 信息,也可以在运行时更改 governor。
$ ls /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/
available_governors current_driver current_governor current_governor_ro
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/available_governors
menu
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_driver
acpi_idle
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_governor
menu
2 内核启动项
除了 sysfs,还可以通过内核命令行参数做一些配置,可以加在 /etc/grub2.cfg 等位置。
2.1 idle loop 配置
5.15 内核启动参数文档:
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.15/Documentation/admin-guide/kernel-parameters.txt
idle= [X86]
Format: idle=poll, idle=halt, idle=nomwait
1. idle=poll forces a polling idle loop that can slightly improve the performance of waking up a
idle CPU, but will use a lot of power and make the system run hot. Not recommended.
2. idle=halt: Halt is forced to be used for CPU idle. In such case C2/C3 won't be used again.
3. idle=nomwait: Disable mwait for CPU C-states
2.1.1 idle=poll
CPU 空闲时,将执行一个“轻量级”的指令序列(”lightweight” sequence of instructions in a tight loop) 来防止 CPU 进入任何节能模式。
这种配置除了功耗问题,还超线程场景下可能有副作用,性能反而降低,后面单独讨论。
2.1.2 idle=halt
强制 cpuidle 子系统使用 HLT 指令
(一般会 suspend 程序的执行并使硬件进入最浅的 idle state)来实现节能。
这种配置下,最大 c-state 深度是 C1。
2.1.3 idle=nomwait
禁用通过 MWAIT 指令来要求硬件进入 idle state。
内核文档 CPU Idle Time Management
说,在 Intel 机器上,这会禁用 intel_idle,用 acpi_idle(idle states / p-states 从 ACPI 获取)。
2.2 厂商相关的 p-state 参数
2.2.1 intel_pstate
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.15/Documentation/admin-guide/kernel-parameters.txt#L1988
intel_pstate= [X86]
disable
Do not enable intel_pstate as the default
scaling driver for the supported processors
passive
Use intel_pstate as a scaling driver, but configure it
to work with generic cpufreq governors (instead of
enabling its internal governor). This mode cannot be
used along with the hardware-managed P-states (HWP)
feature.
force
Enable intel_pstate on systems that prohibit it by default
in favor of acpi-cpufreq. Forcing the intel_pstate driver
instead of acpi-cpufreq may disable platform features, such
as thermal controls and power capping, that rely on ACPI
P-States information being indicated to OSPM and therefore
should be used with caution. This option does not work with
processors that aren't supported by the intel_pstate driver
or on platforms that use pcc-cpufreq instead of acpi-cpufreq.
no_hwp
Do not enable hardware P state control (HWP)
if available.
hwp_only
Only load intel_pstate on systems which support
hardware P state control (HWP) if available.
support_acpi_ppc
Enforce ACPI _PPC performance limits. If the Fixed ACPI
Description Table, specifies preferred power management
profile as "Enterprise Server" or "Performance Server",
then this feature is turned on by default.
per_cpu_perf_limits
Allow per-logical-CPU P-State performance control limits using
cpufreq sysfs interface
2.2.2 AMD_pstat
AMD_idle.max_cstate=1 AMD_pstat=disable 等等,上面的内核文档还没收录,或者在别的地方。
2.3 *.max_cstate
intel_idle.max_cstate=<n>AMD_idle.max_cstate=<n>processor.max_cstate=<n>
这里面的 n 就是我们在 sysfs 目录中看到
/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/state{n}。
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.15/Documentation/admin-guide/kernel-parameters.txt
intel_idle.max_cstate= [KNL,HW,ACPI,X86]
0 disables intel_idle and fall back on acpi_idle.
1 to 9 specify maximum depth of C-state.
processor.max_cstate= [HW,ACPI]
Limit processor to maximum C-state
max_cstate=9 overrides any DMI blacklist limit.
AMD 的没收录到这个文档中。
2.4 cpuidle.off
cpuidle.off=1 完全禁用 CPU 空闲时间管理。
加上这个配置后,
- 空闲 CPU 上的 idle loop 仍然会运行,但不会再进入 cpuidle 子系统;
- idle loop 通过
CPU architecture support code使硬件进入 idle state。
不建议在生产使用。
2.5 cpuidle.governor
指定要使用的 CPUIdle 管理器。例如 cpuidle.governor=menu 强制使用 menu 管理器。
2.6 nohz
可设置 on/off,是否启用每秒 HZ 次的定时器中断。
3.1 频率
可以从 /proc/cpuinfo 获取,
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | awk '/cpu MHz/ { printf("cpu=%d freq=%s\n", i++, $NF)}'
cpu=0 freq=3393.622
cpu=1 freq=3393.622
cpu=2 freq=3393.622
cpu=3 freq=3393.622
某些开源组件可能已经采集了,如果没有的话自己采一下,然后送到 prometheus。
这里拿一台 base freq 2.8GHz、max freq 3.7GHz,配置了 idle=poll 测试机,
下面是各 CPU 的频率,
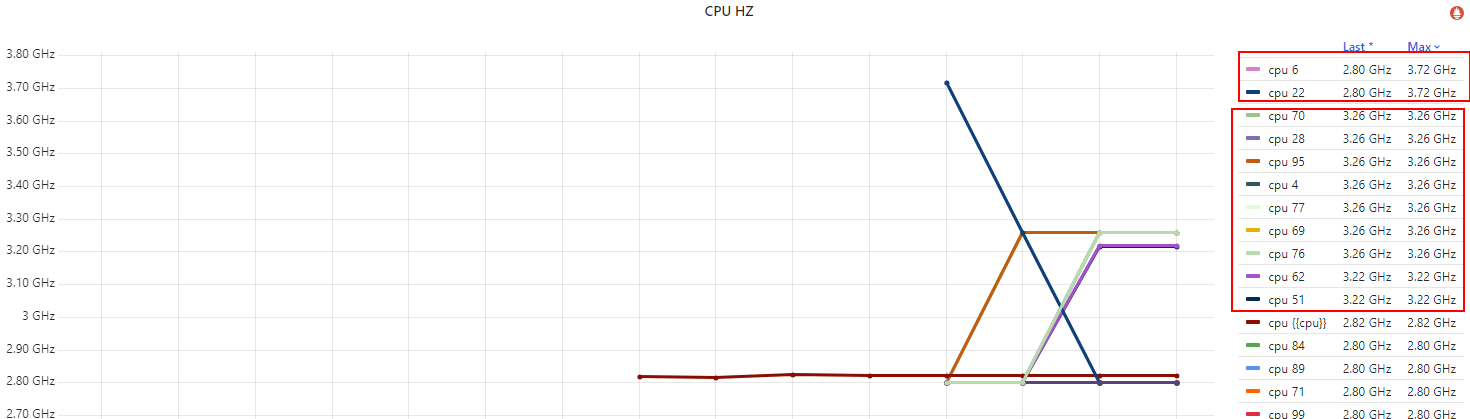
Fig. Per-CPU running frequency
几点说明,
idle=poll禁用了节能模式(c1/c2/c3..),没有负载也会空转(执行轻量级指令),避免频率掉下去;- 不是所有 CPU 都能同时达到 3.7GHz 的
max/turbo freq,原因我们在第二篇解释过了; - 实际上,只有很少的 CPU 能同时达到 max freq。
3.2 功耗、电流
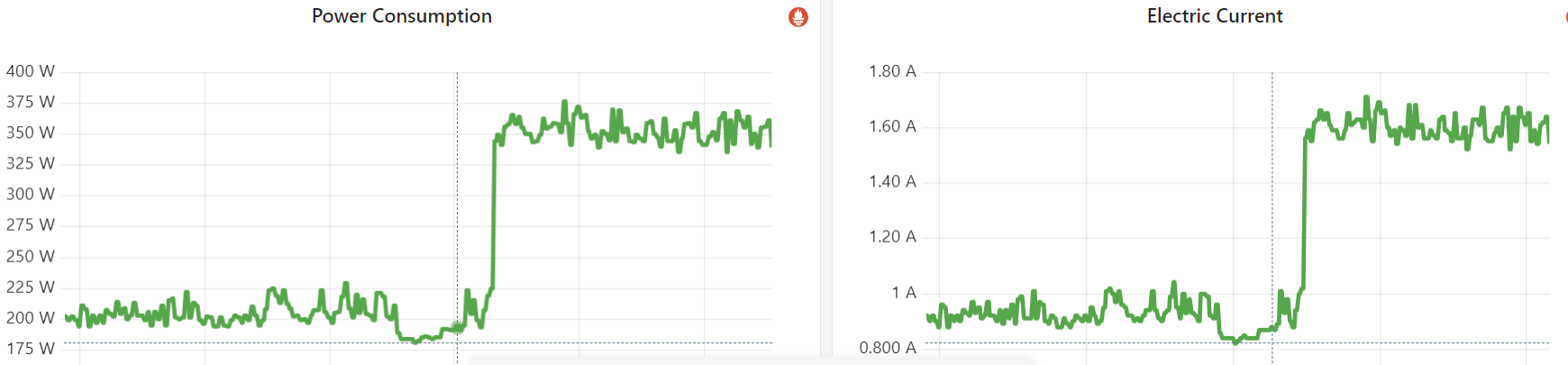
Fig. Power consumption and electic current of an empty node (no workload before and after)
after setting idle=poll for test
3.3 温度等
服务器厂商一般能提供。
3.4 sysfs 详细信息
4 调优工具
除了通过 sysfs 和内核启动项,还可以通过一些更上层的工具配置功耗和性能模式。
4.1 tuned/tuned-adm
$ tuned-adm list
Available profiles:
- balanced - General non-specialized tuned profile
- desktop - Optimize for the desktop use-case
- latency-performance - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption
- network-latency - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption, focused on low latency network performance
- network-throughput - Optimize for streaming network throughput, generally only necessary on older CPUs or 40G+ networks
- powersave - Optimize for low power consumption
- throughput-performance - Broadly applicable tuning that provides excellent performance across a variety of common server workloads
- virtual-guest - Optimize for running inside a virtual guest
- virtual-host - Optimize for running KVM guests
Current active profile: latency-performance
$ tuned-adm active
Current active profile: latency-performance
$ tuned-adm profile_info latency-performance
Profile name:
latency-performance
Profile summary:
Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption
$ tuned-adm profile_mode
Profile selection mode: manual
4.2 turbostat:查看 turbo freq
来自 man page:
turbostat - Report processor frequency and idle statistics
turbostat reports processor topology, frequency, idle power-state statistics, temperature and power on X86 processors.
- –interval
- –num_iterations
$ turbostat --quiet --hide sysfs,IRQ,SMI,CoreTmp,PkgTmp,GFX%rc6,GFXMHz,PkgWatt,CorWatt,GFXWatt
Core CPU Avg_MHz Busy% Bzy_MHz TSC_MHz CPU%c1 CPU%c3 CPU%c6 CPU%c7
- - 488 12.52 3900 3498 12.50 0.00 0.00 74.98
0 0 5 0.13 3900 3498 99.87 0.00 0.00 0.00
0 4 3897 99.99 3900 3498 0.01
1 1 0 0.00 3856 3498 0.01 0.00 0.00 99.98
1 5 0 0.00 3861 3498 0.01
2 2 1 0.02 3889 3498 0.03 0.00 0.00 99.95
2 6 0 0.00 3863 3498 0.05
3 3 0 0.01 3869 3498 0.02 0.00 0.00 99.97
3 7 0 0.00 3878 3498 0.03
- 出于性能考虑,turbostat 以 topology order 运行,这样同属一个 CORE 的两个 hyper-thread 在输出中是相邻的。
Busy%:C0状态所占的时间百分比。
Note that cpu4 in this example is 99.99% busy, while the other CPUs are all under 1% busy. Notice that cpu4’s HT sibling is cpu0, which is under 1% busy, but can get into CPU%c1 only, because its cpu4’s activity on shared hardware keeps it from entering a deeper C-state.
5 调优案例
5.1 c-state 太深导致网络收发包不及时
- Controlling Processor C-State Usage in Linux, A Dell technical white paper describing the use of C-states with Linux operating systems, 2013
- Linux 网络栈接收数据(RX):配置调优
- C-state tuning guide opensuse.org
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK