

怎样优雅地增删查改(一):从0开始搭建Volo.Abp项目 - 林晓lx
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/jevonsflash/p/17535877.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

怎样优雅地增删查改(一):从0开始搭建Volo.Abp项目
软件系统中数据库或者持久层的基本操作功能可以用Curd描述,Curd即 增加(Create)、更新(Update)、读取查询(Retrieve)和删除(Delete), 这4个单词的首字母。
在常见的业务系统中,对数据的大部分操作都是Curd,在实践的过程中对数据的筛选、排序、分页、关联查询等功能抽象和封装。
本系列博文将从0开始,逐步搭建一个基于Volo.Abp + Vue 的前后端分离的,具有Curd通用查询功能的项目。
-
怎样优雅地增删查改(二):扩展身份管理模块
本项目是基于一个简单的用户健康数据管理系统,我们将对业务常用的查询功能进行扩展,抽象这些业务并封装成接口,称之为通用查询接口(GeneralCurdInterfaces),本项目关注的是基础设施层,但大部分实现还是围绕业务,对于普适性有待研究,所以我还是决定以Sample为名。
Abp模块是可以供主模块重用的独立功能单元,每个模块可以包含应用服务、领域层、数据访问层、Web API等,模块可以被其他模块引用,也可以被主模块引用。
本项目模块化的目的除了可重用,更多是为微服务架构做准备。微服务架构不在本博文的讨论范围,为了简化,还是使用单体应用架构。
由框架实现的
Volo.Abp 为我们实现了CrudAppService,(在旧版本的AbpBoilerplate中称Crud为Curd,在我看来两者没有什么区别,本项目还是以Curd命名)
CrudAppService为我们提供了基本的增删改查,以及分页、排序的实现
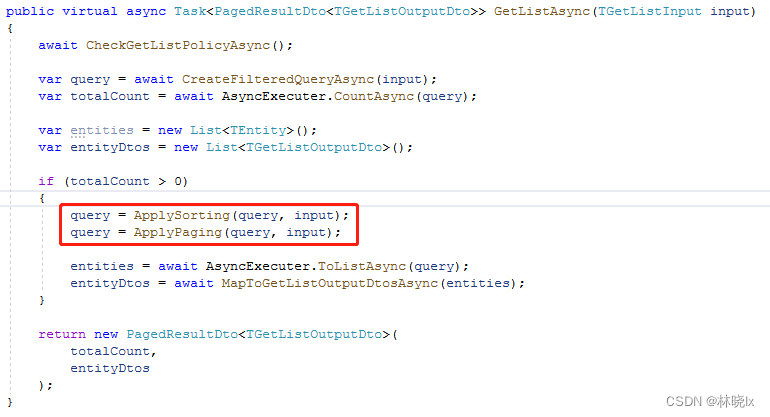
需要实现的
-
按任意字段关键字查询
-
按任意字段排序
-
按组织架构查询
-
按用户查询
-
按用户关系查询
-
按创建日期查询(起始日期,结束日期)
本项目虽然是用Volo.Abp实现,但对于旧版本的AbpBoilerplate仍然可以方便的移植,可以看我之前的博文:[Volo.Abp升级笔记]使用旧版Api规则替换RESTful Api以兼容老程序,如何以最大限度保持接口的兼容性。
创建空白文件夹,在文件夹内打开命令行
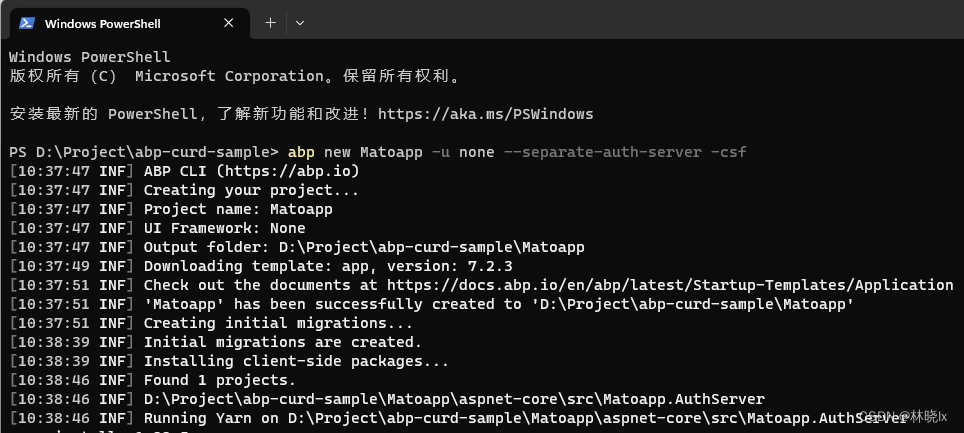
使用AbpCli创建一个无UI的项目 拆分Auth Server,执行以下命令
abp new Matoapp -u none --separate-auth-server -csf
等待项目创建成功
创建业务模块
作为命名空间前缀,Matoapp是一个虚构的企业名称。
在解决方案目录中创建新目录src/modules,在该目录下创建员工健康管理模块Health,公共业务模块Common,以及扩展了Volo.Abp.Indentity的Identity模块
在modules目录下打开命令行,分别执行以下命令
abp new Matoapp.Health -t module --no-ui
abp new Matoapp.Common -t module --no-ui
abp new Matoapp.Identity -t module --no-ui
等待模块创建完成
打开解决方案,将业务模块中的各个项目添加到解决方案中,我们只需要添加各模块的Application,Application.Contracts,Domain,Domain.Shared,EntityFrameworkCore,HttpApi以及HttpApi.Client。
添加完成后的解决方案结构看上去像这样:
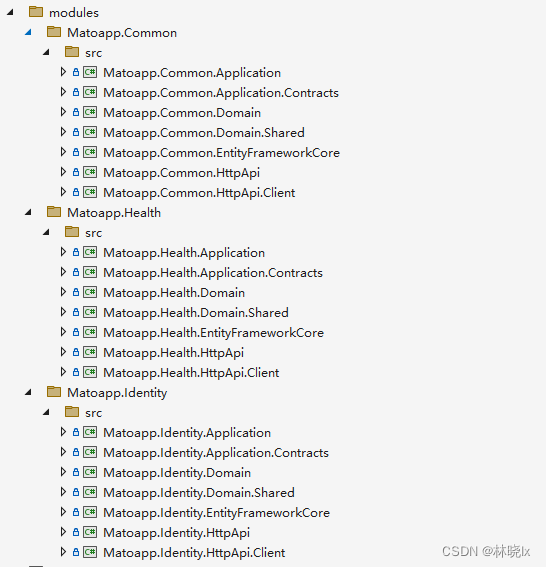
配置引用和依赖
将Volo.Abp.Identity.Application添加到Application项目的引用中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.Application
将Volo.Abp.Identity.Application.Contracts添加到Application.Contracts项目的引用中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.Application.Contracts
将Volo.Abp.Identity.Domain,Volo.Abp.PermissionManagement.Domain添加到Domain项目的引用中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.Domain
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.PermissionManagement.Domain
将Volo.Abp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore添加到EntityFrameworkCore项目的引用中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore
Application层
Application层添加对各模块的引用,
ApplicationModule中添加对各模块的依赖
[DependsOn(
...
typeof(CommonApplicationModule),
typeof(HealthApplicationModule),
typeof(IdentityApplicationModule)
)]
public class MatoappApplicationModule : AbpModule
{
}
AuthServer添加Identity数据访问层引用,并配置依赖关系
[DependsOn(
...
typeof(IdentityDomainModule),
typeof(IdentityEntityFrameworkCoreModule)
)]
public class MatoappAuthServerModule : AbpModule
{
}
HttpApi层添加对各模块的引用,
HttpApiModule中添加对各模块的依赖
[DependsOn(
...
typeof(CommonHttpApiModule),
typeof(HealthHttpApiModule),
typeof(IdentityHttpApiModule)
)]
public class MatoappHttpApiModule : AbpModule
{
}
配置DbContext
用CodeFirst方式创建一些业务表,比如员工表,客户表,报警表等,这些表都是在Health模块中创建的,
Tag相关的表放入Common模块中,Relation表放入Identity模块中。
这些业务表按照业务模块的划分,放入各自的DbContext中。
public interface IIdentityDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
{
DbSet<Relation.Relation> Relation { get; set; }
}
public interface IHealthDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
{
DbSet<Client.Client> Client { get; set; }
DbSet<Employee.Employee> Employee { get; set; }
DbSet<Alarm.Alarm> Alarm { get; set; }
DbSet<SimpleValueRecord> SimpleValueRecord { get; set; }
}
public interface ICommonDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
{
DbSet<DataEnum.DataEnum> DataEnum { get; set; }
DbSet<DataEnumCategory.DataEnumCategory> DataEnumCategory { get; set; }
DbSet<Tag.Tag> Tag { get; set; }
}
各业务模块的DbContextModelCreatingExtensions中添加对各表的字段,约束,索引等的配置。以便在DbContext的OnModelCreating中调用
builder.ConfigureCommon();
builder.ConfigureHealth();
builder.ConfigureMatoIdentity();
EntityFrameworkCore层中改写MatoappDbContext如下:
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(Matoapp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore.IIdentityDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(IHealthDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(ICommonDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(ITenantManagementDbContext))]
[ConnectionStringName("Default")]
public class MatoappDbContext :
AbpDbContext<MatoappDbContext>,
Matoapp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore.IIdentityDbContext,
IHealthDbContext,
ICommonDbContext,
ITenantManagementDbContext
{
#region Entities from the modules
public DbSet<Relation> Relation { get; set; }
// Tenant Management
public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; }
public DbSet<TenantConnectionString> TenantConnectionStrings { get; set; }
public DbSet<Client> Client { get; set; }
public DbSet<Employee> Employee { get; set; }
public DbSet<Alarm> Alarm { get; set; }
public DbSet<SimpleValueRecord> SimpleValueRecord { get; set; }
public DbSet<DataEnum> DataEnum { get; set; }
public DbSet<DataEnumCategory> DataEnumCategory { get; set; }
public DbSet<Tag> Tag { get; set; }
#endregion
public MatoappDbContext(DbContextOptions<MatoappDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
/* Include modules to your migration db context */
builder.ConfigurePermissionManagement();
builder.ConfigureSettingManagement();
builder.ConfigureBackgroundJobs();
builder.ConfigureAuditLogging();
builder.ConfigureIdentity();
builder.ConfigureOpenIddict();
builder.ConfigureFeatureManagement();
builder.ConfigureTenantManagement();
builder.ConfigureCommon();
builder.ConfigureHealth();
builder.ConfigureMatoIdentity();
/* Configure your own tables/entities inside here */
//builder.Entity<YourEntity>(b =>
//{
// b.ToTable(MatoappConsts.DbTablePrefix + "YourEntities", MatoappConsts.DbSchema);
// b.ConfigureByConvention(); //auto configure for the base class props
// //...
//});
}
}
在AuthServer创建AuthServerDbContextFactory,AuthServerDbContext。
AuthServerDbContext.cs代码如下
public class AuthServerDbContext : AbpDbContext<AuthServerDbContext>
{
public AuthServerDbContext(DbContextOptions<AuthServerDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.ConfigureIdentity();
modelBuilder.ConfigureIdentityServer();
modelBuilder.ConfigureAuditLogging();
modelBuilder.ConfigurePermissionManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureSettingManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureTenantManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureFeatureManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureMatoIdentity();
}
}
创建实体和Dto
在各业务模块中创建实体类,以及对应的Dto类
此处以Health模块为例,创建以下实体类
- Employee 员工
- Client 客户
- Alarm 报警
- SimpleValueRecord 简单值记录
配置AutoMapper
根据实际业务需求,配置AutoMapper,将实体类映射到DTO类。此处以Health模块为例。
public HealthApplicationAutoMapperProfile()
{
CreateMap<Client.Client, ClientDto>().Ignore(c => c.EntityVersion);
CreateMap<Employee.Employee, EmployeeDto>().Ignore(c => c.EntityVersion);
CreateMap<ClientDto, Client.Client>();
CreateMap<EmployeeDto, Employee.Employee>();
CreateMap<Alarm.Alarm, AlarmDto>();
CreateMap<Alarm.Alarm, AlarmBriefDto>();
CreateMap<AlarmDto, Alarm.Alarm>().Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp);
CreateMap<CreateAlarmInput, Alarm.Alarm>().IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.User)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp)
.Ignore(c => c.Id);
CreateMap<UpdateAlarmInput, Alarm.Alarm>().IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.User)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp);
CreateMap<SimpleValueRecord, SimpleValueRecordBriefDto>();
CreateMap<SimpleValueRecord, SimpleValueRecordDto>();
CreateMap<SimpleValueRecordDto, SimpleValueRecord>().Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.Alarm)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp);
CreateMap<CreateClientInput, Client.Client>()
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
CreateMap<CreateClientWithUserInput, Client.Client>()
.IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnabled)
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnd)
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp)
.Ignore(c => c.EmailConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.PhoneNumberConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.Id)
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
CreateMap<CreateEmployeeInput, Employee.Employee>()
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
CreateMap<CreateEmployeeWithUserInput, Employee.Employee>()
.IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnabled)
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnd)
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp)
.Ignore(c => c.EmailConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.PhoneNumberConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.Id)
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
}
至此,我们有了基础的数据库,实体类,Dto类。下一步我们将创建通用Curd应用服务,以及通用查询接口。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK