

TDD vs. BDD: Choosing The Suitable Framework
source link: https://dzone.com/articles/tdd-vs-bdd-choosing-the-suitable-framework
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

TDD vs. BDD: Choosing The Suitable Framework
In this article, we compared two of the most commonly used development techniques, i.e., TDD vs. BDD — to help you pick the right one for you.
Most Software Developers in Test are familiar with Test-Driven Development, or TDD, but Behavior-Driven Development, or BDD, is often misunderstood. The truth is that both of these approaches have advantages and disadvantages to consider.
This blog deep dives into TDD vs. BDD comparison by looking at both these approaches individually. Later, we would compare them to functionalities, supported frameworks, and more.
I could say BDD is merely the evolution of TDD.
What Is Test-Driven Development (TDD)?
Test-Driven Development is a programming practice implemented from a developer’s perspective. In this process, a QA engineer begins designing and writing test cases for every small functionality of an application.
This technique tries to answer a simple question — Is the code valid? The primary purpose of this practice is to modify or write a new code only when the tests fail. Consequently, it results in lesser duplication of test scripts. This technique is mainly popular in agile development ecosystems. In a TDD approach, automated test scripts are written before functional pieces of code.
How To Implement Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Test-driven development gives preference to testing instead of the implementation phase. As all the tests pass, it signals the end of the first iteration. However, if more features have to be implemented, all the phases must be repeated with new feature tests. The figure below summarizes the flow of TDD:
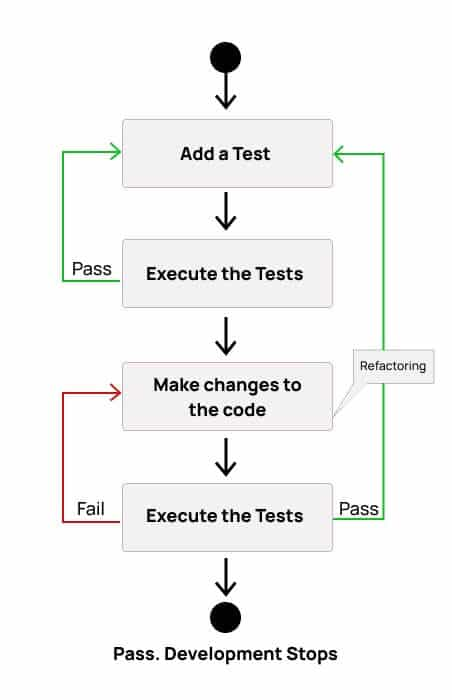
Pros and Cons of Test-Driven Development (TDD)
TDD is a test-first approach, where automated test scripts are typically written before implementing the product’s actual features. However, TDD has its own share of advantages (or pros) and disadvantages(or cons)
Advantages of Test-Driven Development (TDD)
- Reduced cost of development: The development process in TDD is divided into smaller chunks to simplify the detection of issues at the early stages of design and development.
- Focus on design and architecture: Writing tests before the implementation makes the development process more seamless and efficient.
- Improved code coverage: Through TDD, a well-designed system can achieve 100 percent code coverage.
- Code visibility: Tests are written to verify smaller functionalities, making it easy to refactor and maintain the code.
- Detailed documentation: Since tests are written for verifying micro-level functionalities, writing documentation becomes an easy task.
Disadvantages of Test-Driven Development (TDD)
- Bugs leading to faulty code: Tests could contain bugs which in turn results in faulty implementation. This can be averted by using the right BDD framework, performing detailed code reviews, and more.
- Costly architectural mistakes: If the generated test code is not in line with the desired architecture, it could result in huge losses.
- Slowness in development: Creating test cases before code development slows product development. In addition, framing test cases may take a huge amount of time as the actual implementation is not available at that time.
- Requires prior experience: Prior experience with TDD is a must since many teams commit the mistake of not running tests at the Red Stage.
In this section, we have covered what TDD is, including its advantages and disadvantages. In the next section, we will look into BDD.
What Is Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)?
Behavioral-Driven Development (BDD) is derived from the Test-Driven Development (TDD) methodology. In BDD, tests are based on systems behavior. The BDD approach describes different ways to develop a feature based on its behavior. In most cases, the Given-When-Then approach is used for writing test cases. You can learn more about Gherkin by reading the article on Behavior Driven Development By Selenium Testing With Gherkin.
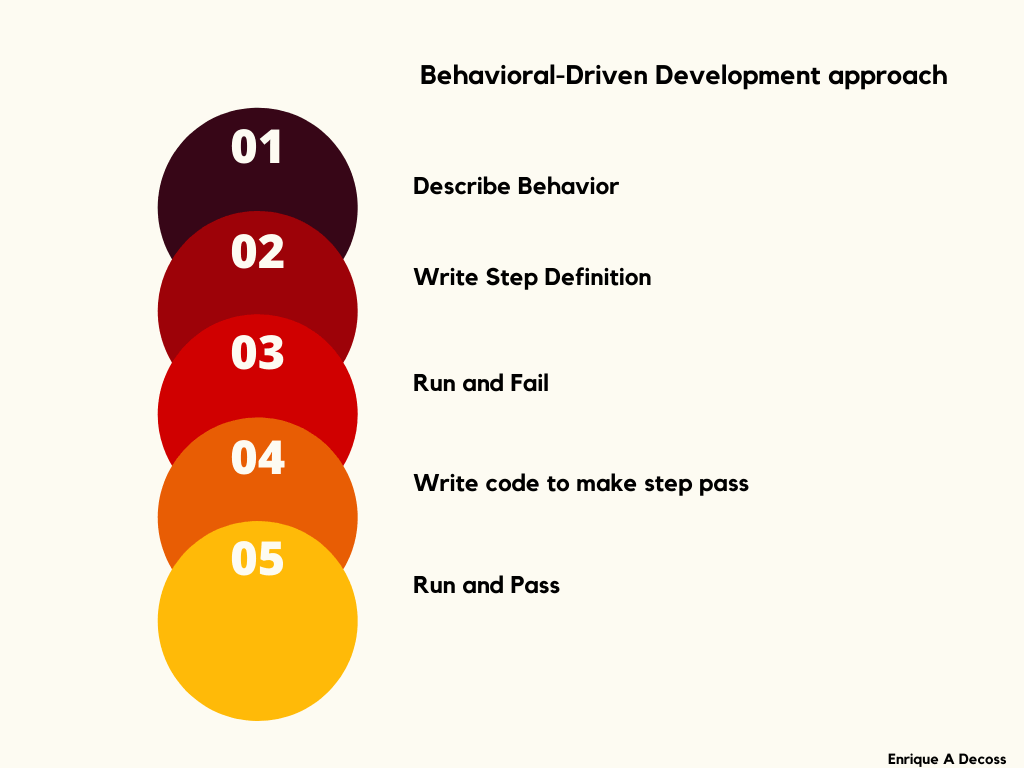
Let’s take an example for better understanding:
Scenario: User Can Sign In
- Given a valid user with username “lambdatest1.”
- When I log in as “lambdatest1.”
- Then I should see the message “Welcome, lambdatest1”
Here is the overall approach to BDD:
Debugging the errors in the latter stages of the development life cycle often proves to be very expensive. In most cases, ambiguity in understanding the requirements is the root cause behind this. Therefore, one must ensure that all the development efforts remain aligned toward fulfilling pre-determined requirements. BDD allows developers to do the above by:
- Allowing the requirements to be defined in a standard approach using simple English.
- Providing several ways to illustrate real-world scenarios for understanding requirements.
- Providing a platform that enables the tech and non-tech teams to collaborate and understand the requirements
How To Implement Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
As we know, BDD is an extension of TDD. BDD plays a crucial role in cutting back on the bugs and errors you would encounter at later stages of product development. Effective test automation strategy, including scenarios, can be developed by involving different teams (e.g., engineering, product management, marketing, etc.).
The BDD approach accords technical and non-technical teams with the collaboration of knowledge and ideas. It’s time for some action.
Cucumber is a tool that supports BDD; anyone can write specifications in plain English using Gherkin. It is as simple as adding a test from the business value point of view, as I like to call business-centric Test Automation. If you are new to Cucumber, you can also check out the step-by-step tutorial on Selenium Cucumber with examples.
Let’s start by adding the Cucumber plugin using npm to our current Cypress Testing project.
1. Please install the plugin.
npm install --save-dev cypress-cucumber-preprocessor2. The following dependency with the latest version will be added to your package.json of the project. At the time of writing this recipe, the version of cypress-cucumber-preprocessor is 4.1.4.
devDependencies": { "cypress-cucumber-preprocessor": "^4.1.4" }3. To make it work, we would need to add it to Cypress plugins as part of Cypress Configuration under cypress/plugins/index.js
const cucumber = required('cypress-cucumber-preprocessor').defaultmodule.exports = (on, config) => {
on('file:preprocessor', cucumber())
}4. Next, we need to add cosmiconfig configuration to the package.json. Cosmiconfig searches and loads the required configuration of the project. In this case, we are defining to locate the step definitions by setting up the below property.
"cypress-cucumber-preprocessor": {
"nonGlobalStepDefinitions": true
}5. Let’s create a new folder under Cypress -> Integration directory as ‘cucumber-test’ and then create a new feature, “Home.feature.”
Feature: Home / Landing Page
Scenario: Navigating to E-commerce Store
Given I open home page
Then I should see Homepage6. For step definition location, let’s create a folder named “home.” Let’s create a step definition file ‘homeSteps.js.”
import { Given } from "cypress-cucumber-preprocessor/steps";
Given('I open home page', () => {
cy.visit('https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/')
})
Then('I should see Homepage', () => {
cy.get('#search').should('be.visible')
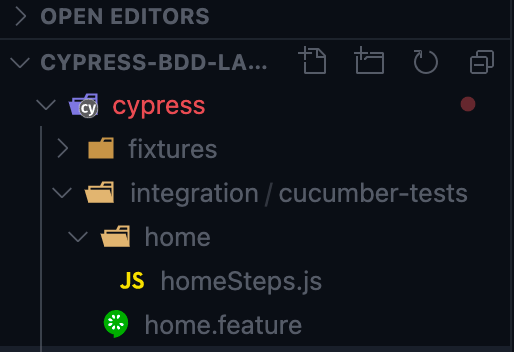
})1. The folder structure should be as the following:
7. Now, let’s run using the following command in the Terminal or command console to execute the test:
npx cypress open8. On Cypress Test runner, select ‘home.feature.’
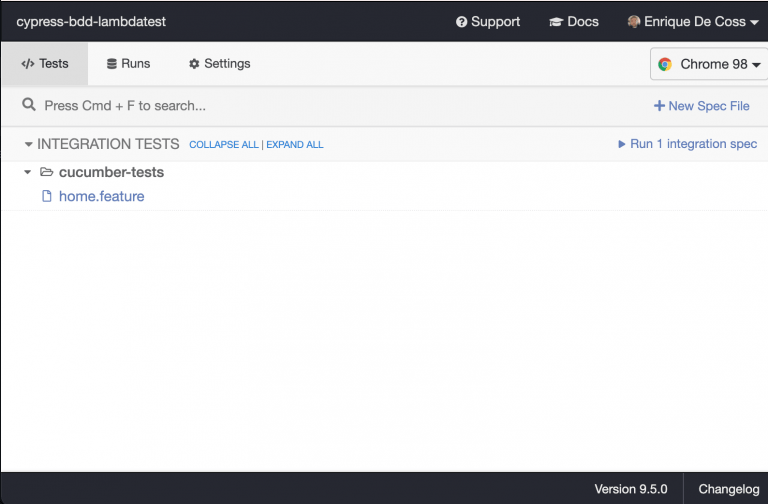
And you should see the results correctly:
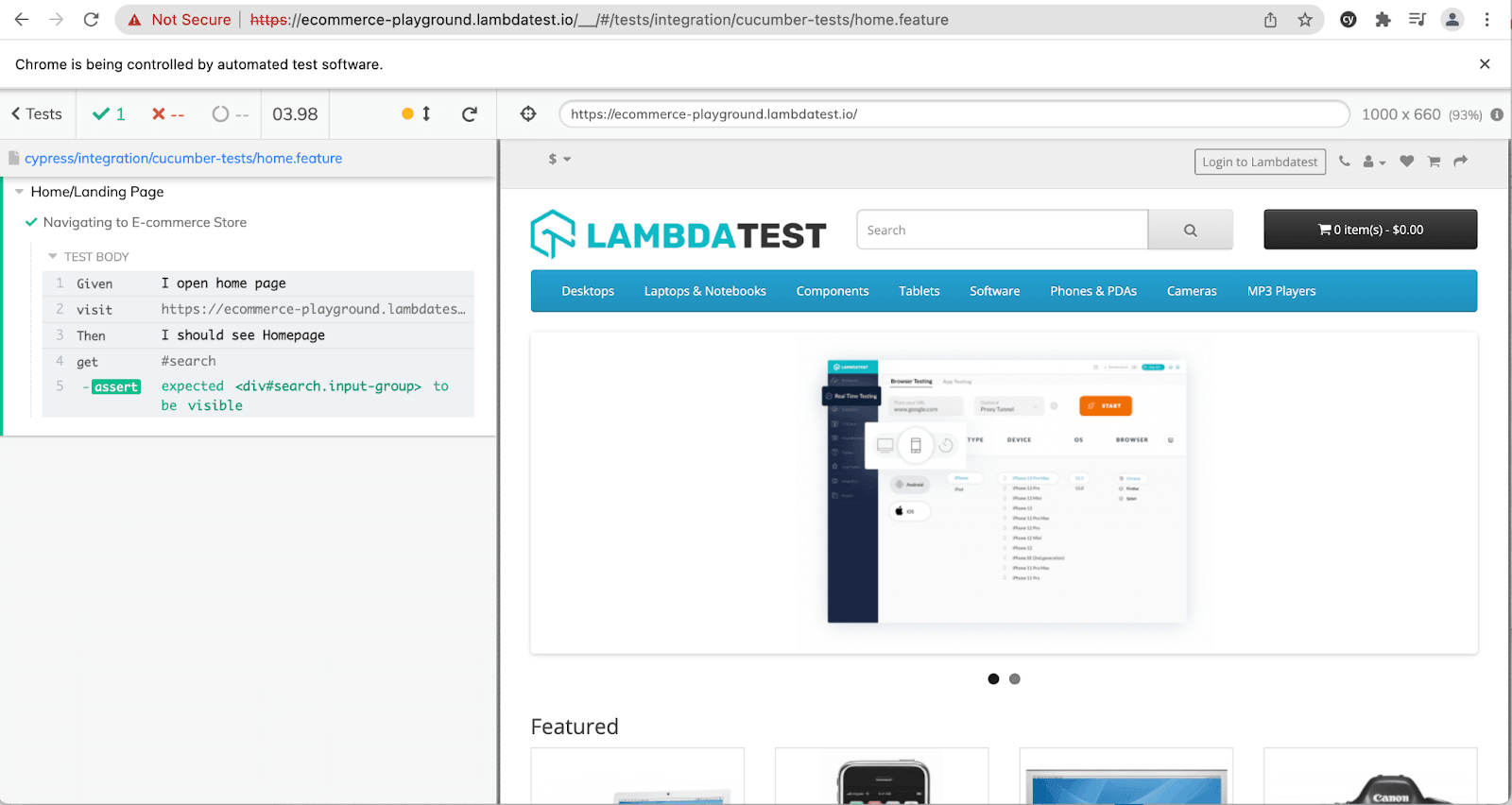
Note: You can download the code from the GitHub Repository.
Gherkin Keywords
Keywords are used to give structure & meaning to the executable specifications. Every specification or a feature file starts one of the keywords as:
- Feature
- Scenario
- Scenario Outline
- Background
Feature: It is the primary key in the Gherkin; it is used to describe the specification name.
Feature: Hello
In order to start a conversation with someone
chat bot needs to start with greetings
so the user gets the interactive feel.Scenario: It is the collection of actions or steps that need to be performed to fulfill a test objective.
Feature: Greetings
In order to start the conversation with someone
chat bot needs to start with greetings
so the user gets the interactive feel.
Scenario: example
Given greeting has been set to "hello"
When name is "Frank"
Then greetings equals "Hello Frank"Scenario Outline: is used when the same scenario needs to be executed with multiple data sets. Scenario Outline is always defined with the Examples keyword. That’s where data sets can be defined to execute the same scenario multiple times. Scenario Outline is used for Data-driven tests.
Feature: Greetings
In order to start the conversation with someone
chat bot needs to start with greetings
so the user gets the interactive feel.
Scenario Outline: example
Given greeting has been set to""
When name is ""
Then greetings equals ""
Examples:
| greeting | name | conversation |
| Hello | Frank | Hello Frank |
| Hi | Maria | Hi Maria |
| Hey | Johnny | Hey Johnny |Implementation example:
let myName, greeting, finalword
Given("greeting has been set to {string}", setGreeting => {
greeting = setGreeting + ' '
})
When("name is {string}", setName => {
myName = setName
finalString = greeting.concat(myName)
})
Then("greetings equals {string}", expectedValue => { expect(finalword).to.equal(expectedValue)
})Background: It is used to define a step or series of steps common to all the tests included in the feature file. The steps defined as part of the background get executed before each scenario. Adding the Background section is helpful to avoid duplication of feature steps.
Feature: Background Example
Background:
Given greeting has been set
Scenario: example1
When name is "Frank"
Then greetings equals "Hello Frank"
Scenario: example2
When name is "Maria"
Then greetings equals "Hello Maria"Pros and Cons of Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
BDD is an approach that involves managers, testers, developers, etc., in the whole process. As a result, BDD offers a huge number of benefits. Let’s look at some of the major ones in this section.
Advantages of Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
- Improved Communication: Creating scenarios requires close coordination between clients, managers, developers, testers, etc. This unifies the team in understanding the product behavior.
- Reduced cost of Quality Control: Automated acceptance tests are used to depict the scenarios, which in turn helps in reducing the costs involved in inspecting the product quality.
- Accurate task estimation: Since the expected behavior is predicted before, there are few chances to change the software application’s architecture.
- Better user experience: The scenarios and tests written before development take the user’s perspective into account. The focus is on the desired behavior rather than on implementing features.
- Excellent documentation: When a certain test fails, the specification is updated, resulting in detailed documentation.
Challenges of Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
- Requires more involvement from all the stakeholders: Putting all the people together becomes difficult for teams. Is it the three amigos sitting down together, talking, collaborating, and leaving with a common language around the system requirements?
- BDD tools struggle with parallelization: Cucumber and SpecFlow do parallelization or support parallel testing in a sub-optimal manner. They parallelize at the feature file level. It implies that if you want to run 50 tests in parallel, you need to have 50 feature files. That’s a lot of feature files.
- Writing incorrect Gherkin syntax: The issue is that most of us do not follow the correct Gherkin syntax as prescribed by the BDD creators. Just remember Given-When-Then steps must appear in order and cannot repeat.
TDD vs. BDD: The Final Showdown
TDD vs. BDD is a quest for some developers. Even experienced developers find it difficult to differentiate between these approaches. Now that we have touched upon the working and implementation of TDD and BDD let’s deep dive into the major differences in this epic TDD vs. BDD clash:
| Criteria | Test-Driven Development (TDD) |
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) |
| Language | Test cases designed in TDD are Technical. These are similar to the test cases that are normally written during the testing phase. | The test scenarios designed in BDD are written in simple English language. |
| Implementation Level | There is a low-level implementation in TDD. | The scenarios are easy to understand and implement, making BDD a high-level implementation with regard to test case development. |
| Key Stages | Test case development is the major phase in TDD. | Discussion and creation of scenarios are the major stages in BDD. |
| Stages involved in Development | TDD involves three main stages, Test creation, implementation, and code refactoring are the major stages in TDD. | BDD involves a number of stages like feature discussion, scenario creation, testing, implementation, and code refactoring. |
| Participants | Only technical teams like development teams take part in TDD processes. | BDD involves many teams, right from client to business analysts, testers, developers, etc. |
| Primary Focus | Development of required functionality based on test cases is the primary focus in TDD. | BDD focuses on the correspondence between implemented features and expected behavior. |
| Documentation | TDD requires documentation for the creation of accurate test cases. | Thrust is laid on documentation created during the scenario creation process. |
| Tools | The tools (or frameworks) used in TDD involve JUnit, TestNG, NUnit, etc. These are used to run test cases. | Gherkin is used for writing scenarios in BDD. Cucumber, SpecFlow, etc., are some of the widely used test automation frameworks. |
| Applicable Domain | The main focus in TDD is to get appropriate functionality through implementation. | BDD has the defined domain as “Behavior.” This focuses on the product’s behavior at the end of implementing the product functionality. |
| Bug Tracking | Bug tracking is easier in TDD, as the tests indicate whether they have passed or failed. | Bug tracking in BDD requires integration between multiple tools across the organization. |
So, these were the key differences as far as TDD vs. BDD is concerned. So, make sure to look at these differences when you have to decide between TDD and BDD.
Can TDD and BDD Work Together?
So far, we have seen what is different as far as TDD vs. BDD is concerned. The best part is that these processes are not mutually exclusive. While it’s not unusual for Agile teams to use one without the other, making these two work together can ensure a higher degree of efficiency in testing use cases, thereby bringing confidence in the performance.
TDD, when used alongside BDD, gives importance to web testing from the developer’s perspective, with greater emphasis laid on the application’s behavior. To implement the specifics, developers can create separate testing units to get robust components. This is beneficial since the same component can be used in different places across the software development process.
You can use cloud tools like LambdaTest to leverage the capabilities of both TDD and BDD frameworks and perform live testing. LambdaTest is a cross-browser testing platform that enables you to run your test scripts on an online device farm of 3000+ real browsers and real operating systems.
LambdaTest integration with tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, etc., makes discussions between the teams efficient and easy. TDD or BDD, the choice is governed by the individual needs of an application or the enterprise.

The combination of TDD and BDD frameworks can add more value to the software development process. This is where automation testing tools like LambdaTest can be beneficial since they can be integrated with major TDD and BDD frameworks.
TDD vs. BDD: Which Approach Is Best for Your Project?
BDD and TDD have differences and similarities. Although, at the same time, it’s not unusual for Agile teams to use one without the other, making the two work together can guarantee a higher degree of efficiency in testing application use cases, thus obtaining greater confidence in their performance.
TDD vs. BDD, an Agile team, alongside TDD, can use the BDD approach to put in place a higher level of testing that takes care of technical nuances from the Agile team’s point of view and assesses the application’s behavior.
To implement the specifics, we can create separate testing units to maintain the robustness of different components. It can be beneficial, considering that the same component can be used in other places across an application.
The testing process is based on specifying test scenarios in simple language. Then, Automation Engineers add TDD parts for testing certain specific components. Whether to choose BDD over TDD or use a combination of the two methods is a choice ruled by the needs of an application or organization.
Experimenting with BDD if you’re already doing TDD testing can add value to the Agile process. Using the two together is more accessible, and you don’t need to change or rework the existing approach. All it takes is updating the testing framework to adjust the other.
Selenium 101 certification from LambdaTest is a great way to validate your expertise in Selenium automation testing. There are plenty of good reasons to get Selenium certified. You can use it to prove that you’re on top of things, or you can use it as a way to help yourself learn.
Final Thoughts
In this TDD vs. BDD article, you can always view the big picture and decide which approach is best for your software requirements. However, whether you choose to implement test-driven or behavior-driven development, you will require strong QA and testing skills and tools.
Understanding TDD vs. BDD approaches work can help Agile teams and other stakeholders improve the development process by zeroing in on the best test strategy for their needs. Then, depending on the nature of the project and the desired result, you can choose between a mix of the two techniques to enhance test coverage efficiency.
Thus, till then, Happy Testing!
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK