

DGIM算法及其Python实现
source link: http://nathanlvzs.github.io/DGIM-Algorithm-and-Python-Implementation.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

前两个月学习DGIM算法的时候,实现了一下。最近整理代码时发现还有些问题,于是重新写一份,顺带将相关内容整理成blog。
在许多数据挖掘场景中,在分析挖掘的时候我们通常都已掌握了所需的全部数据集。数据流(Data Stream)跟数据集(Dataset)所不同的是,数据流是非静态的,它的分布随时间而变化,它可以是无限长度的,有些场景下数据流入速度十分快。一般来说,对于数据流的处理有如下两种方式
-
对数据流进行采样
-
通过滑动窗口进行处理
假如我们要计算比特流最近的N位中有多少为1的位,N(滑动窗口的大小)非常大,我们无法存储这最近的N位数据,在这种情况下我们是无法得知准确的答案的。但是,对于一个差不多的答案,我们是可以接受的。DGIM算法可以给我们一个近似的答案,对于一个数据流只需使用O(log N)的空间,结果误差不超过50%。
DGIM算法
DGIM算法的主要思想是用bucket来记录数据流中的1的个数,它保存一个范围内1的个数(记作size以方便说明)以及该范围的结束位的时间戳,它记录的1的个数必须是2的指数大小。
对于任意某一个size,系统运行时的某一时刻都只会存在要么1个要么2个该size的bucket,如果有3个size的bucket,则将其中时间戳最早的两个bucket合并为大小为两倍size的bucket。这里可以联系2048小游戏的规则来理解一下。
所有的bucket的时间戳都不会重叠。bucket按照size排序,所以时间戳早的bucket的size大小是不小于时间戳比较晚的bucket的size。
当一个新的比特位进来之后,那些超出滑动窗口大小的bucket需要删除掉。
下图是一个例子,其中将数据流表示成几个bucket(2个size为1的,1个size为2的,2个size为4的和1个size为8的)。
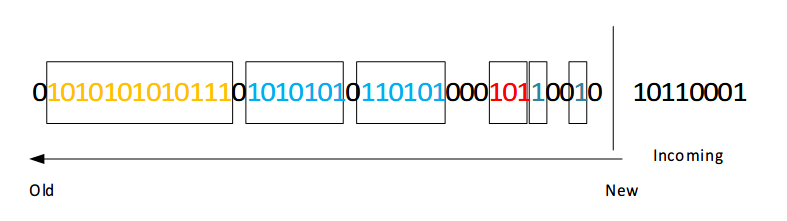
当进来一个位1之后,bucket表示更新如下图所示。
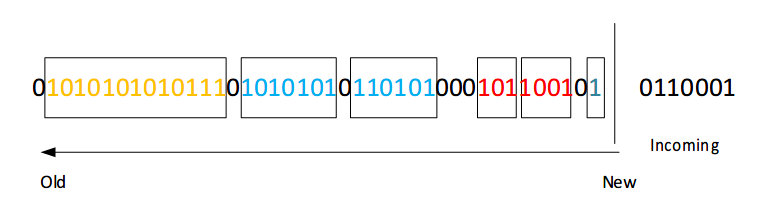
当一个比特位进来的时候,更新时间戳。通常可以将(索引编号 mod N)来作为时间戳,这里mod表示取余,N为滑动窗口的大小。然后把那些时间戳已经超出滑动窗口的bucket丢弃掉。
如果当前位为0,无需动作。
如果当前位为1,则
-
创建一个size为1的bucket,设置其时间戳。
-
如果已有三个size为1的bucket,则将其中最早的两个bucket合并为一个size为2的bucket,将这两个bucket中出现比较晚的的时间戳作为新bucket的时间戳。
-
如果已有三个size为2的bucket,则将其中最早的两个bucket合并为一个size为4的bucket,如此更新下去。
将滑动窗口中所有的bucket的size加起来,然后减去最早的那个bucket的一半size。
换一种说法,就是除了最早的那个bucket,将其他所有的bucket的size加起来,然后再加上0.5 × 最早那个bucket的size。
因为我们不清楚最早的那个bucket中有多少个1是还留在滑动窗口中,在没有其他信息的情况下只能假设其中0和1均匀分布了。
-
方法比较简单
-
空间复杂度低
-
误差率有限制,不大于50%
误差率的证明
假设最早的那个bucket(记作b_e)的size为 2s2s。
因为在查询结果时我们加上了b_e的一半size,当b_e只有结束位位于滑动窗口中时,此时会造成最大的误差,大小为2s−12s−1。对于每个size,滑动窗口中都至少存在一个bucket,所以滑动窗口中1的真正个数不小于 1+2+...+2s−1=2s−11+2+...+2s−1=2s−1。所以误差率最多为 2s−1/(2s−1)2s−1/(2s−1), 约等于50%。
Python实现
主要用了一个字典,key为bucket的size,value为对应size的bucket列表。
这里并没有定义bucket对象,直接用bucket的时间戳表示一个bucket了。
import math
filename = "test.txt"
container = {}
windowsize = 1000
timestamp = 0
updateinterval = 1000# no larger than the windowsize
updateindex = 0
keysnum = int(math.log(windowsize, 2)) + 1
keylist = list()
# initialize the container
for i in range(keysnum):
key = int(math.pow(2, i))
keylist.append(key)
container[key] = list()
def UpdateContainer(inputdict, klist, numkeys):
for key in klist:
if len(inputdict[key]) > 2:
inputdict[key].pop(0)
tstamp = inputdict[key].pop(0)
if key != klist[-1]:
inputdict[key * 2].append(tstamp)
else:
break
def OutputResult(inputdict, klist, wsize):
cnt = 0
firststamp = 0
for key in klist:
if len(inputdict[key]) > 0:
firststamp = inputdict[key][0]
for tstamp in inputdict[key]:
print "size of bucket: %d, timestamp: %d" % (key, tstamp)
for key in klist:
for tstamp in inputdict[key]:
if tstamp != firststamp:
cnt += key
else:
cnt += 0.5 * key
print "Estimated number of ones in the last %d bits: %d" % (wsize, cnt)
with open(filename, 'r') as sfile:
while True:
char = sfile.read(1)
if not char:# no more input
OutputResult(container, keylist, windowsize)
break
timestamp = (timestamp + 1) % windowsize
for k in container.iterkeys():
for itemstamp in container[k]:
if itemstamp == timestamp:# remove record which is out of the window
container[k].remove(itemstamp)
if char == "1":# add it to the container
container[1].append(timestamp)
UpdateContainer(container, keylist, keysnum)
updateindex = (updateindex + 1) % updateinterval
if updateindex == 0:
OutputResult(container, keylist, windowsize)
print "\n"Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK