

spring循环依赖过程解析
source link: https://wakzz.cn/2019/11/03/springboot/spring%E5%BE%AA%E7%8E%AF%E4%BE%9D%E8%B5%96%E8%BF%87%E7%A8%8B%E8%A7%A3%E6%9E%90/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

spring解决循环依赖
spring在创建和依赖注入单例对象时,通过三级缓存的设计,可以解决大多数的循环依赖问题,但是基于三级缓存的解决方案,对于部分场景还是无法解决循环依赖的问题,会由spring抛出异常。
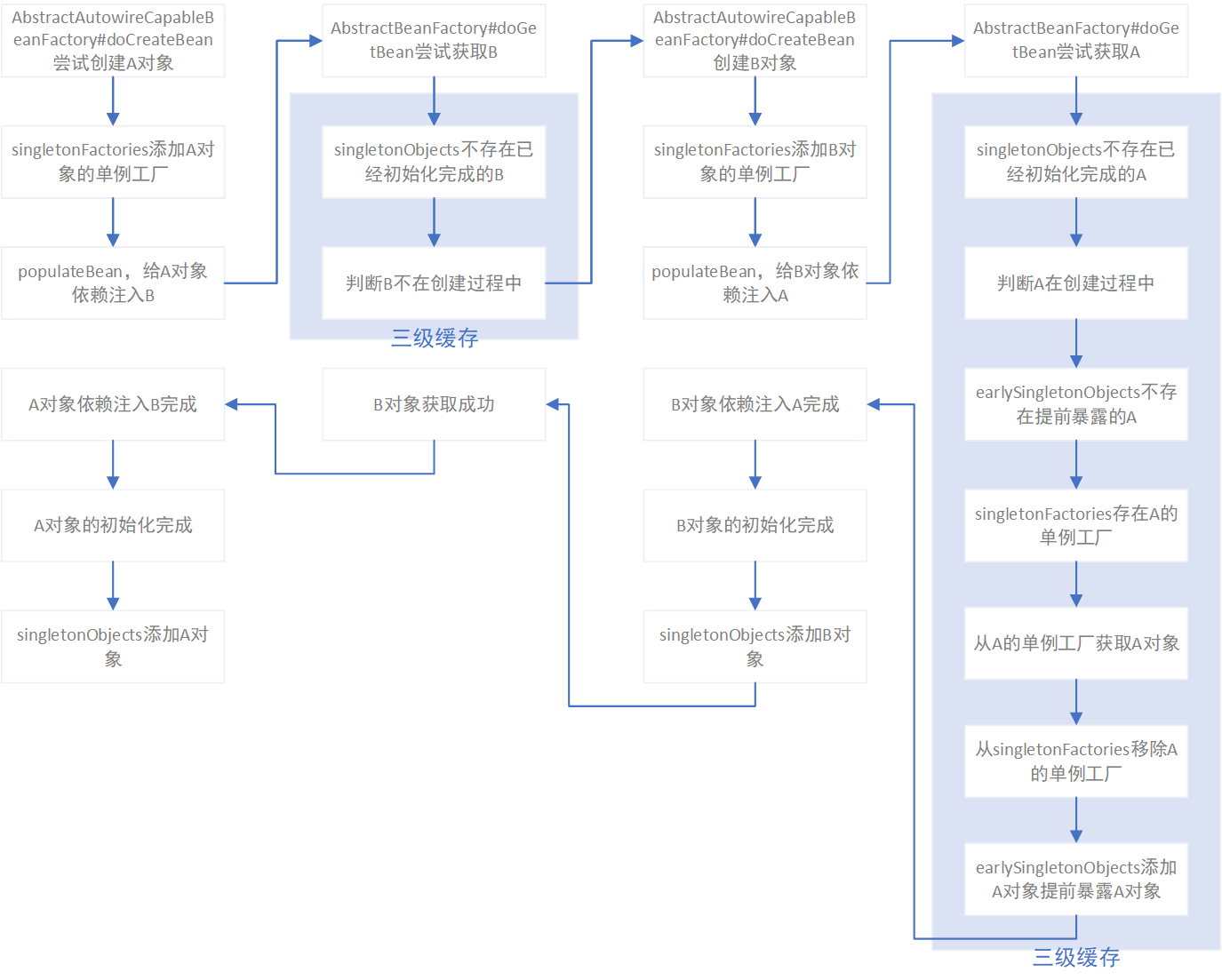
spring的三级缓存由singletonObjects、earlySingletonObjects、singletonFactories组成:
- singletonObjects:保存初始化完成的单例bean实例;
- earlySingletonObjects:保存提前曝光的单例bean实例;
- singletonFactories:保存单例bean的工厂函数对象;
对于通常的A依赖B、B依赖A的简单循环依赖的场景,spring的单例对象创建和依赖注入的流程如下图:
@Service
public class A {
@Autowired
private B b;
public A() {
}
}
@Service
public class B {
@Autowired
private A a;
public B() {
}
}
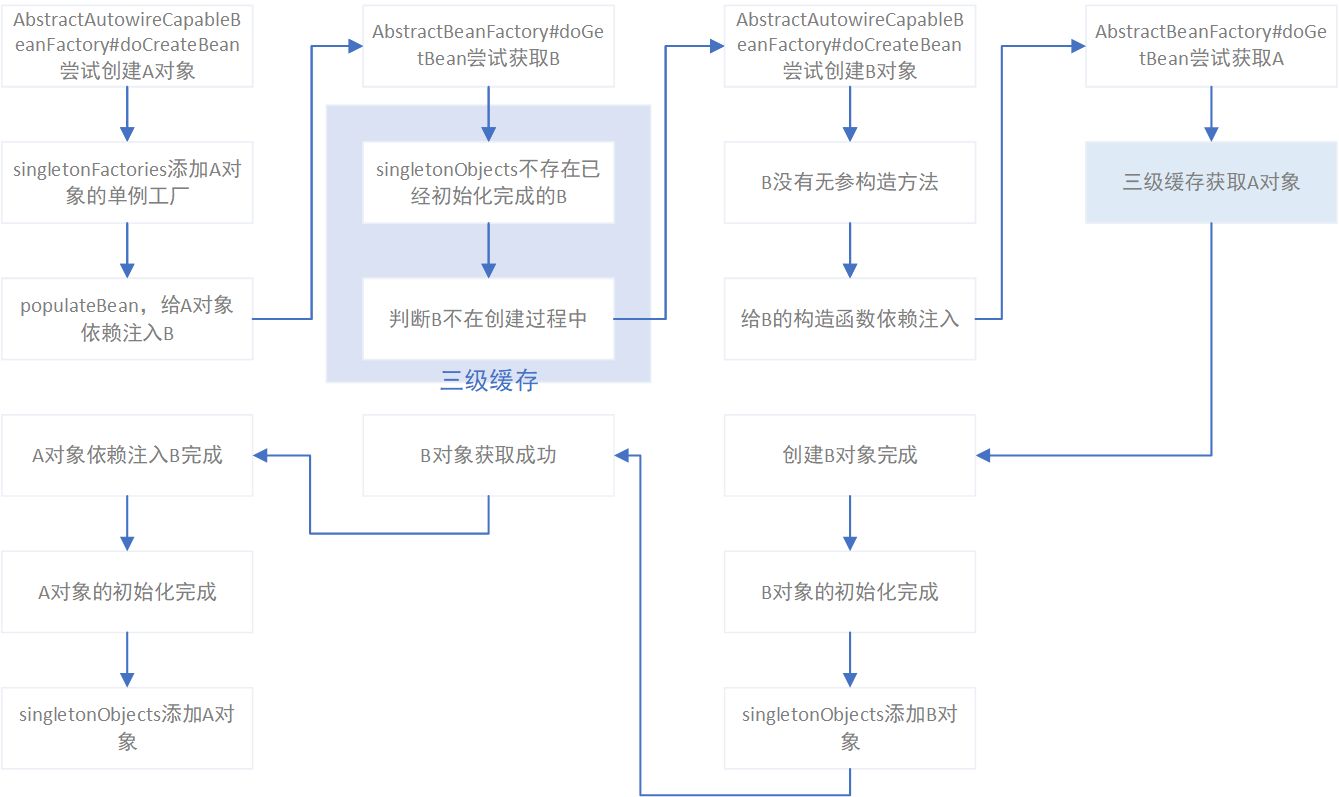
构造方法注入导致循环依赖
对于相互依赖的Bean,如果全部都是构造方法依赖注入,spring必然无法解决这种循环依赖。但是如果如下场景,A通过@Autowired依赖B,而B通过构造方法依赖A,spring可以成功解决循环依赖。
@Service
public class A {
@Autowired
private B b;
public A() {
}
}
@Service
public class B {
private A a;
public B(A a) {
this.a = a;
}
}
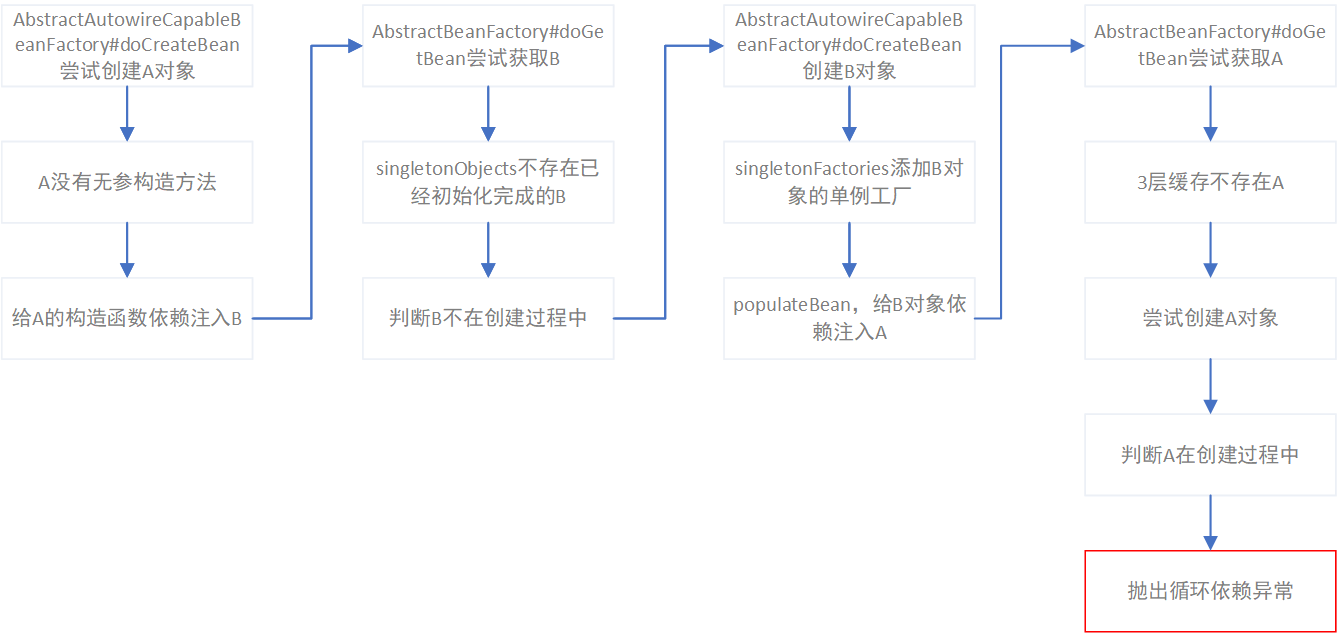
循环依赖异常
但是对于这种部分Bean通过构造方法依赖注入的场景,spring的三级缓存并不是百试百灵。把上面成功依赖注入的A和B相互换位,A通过构造方法依赖B,而B通过@Autowired依赖A,则会出现spring无法解决循环依赖而抛出循环依赖的异常。
并没有修改依赖复杂度,仅仅是A与B相互换了依赖位置,spring就抛出了循环依赖异常,其中的流程如下图:
@Service
public class A {
private B b;
public A(B b) {
this.b = b;
}
}
@Service
public class B {
@Autowired
private A a;
public B() {
}
}
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************
Description:
The dependencies of some of the beans in the application context form a cycle:
┌─────┐
| a defined in file [D:\Program\workspace\other\springboot\target\classes\com\wakzz\autowire\A.class]
↑ ↓
| b (field private com.wakzz.autowire.A com.wakzz.autowire.B.a)
└─────┘
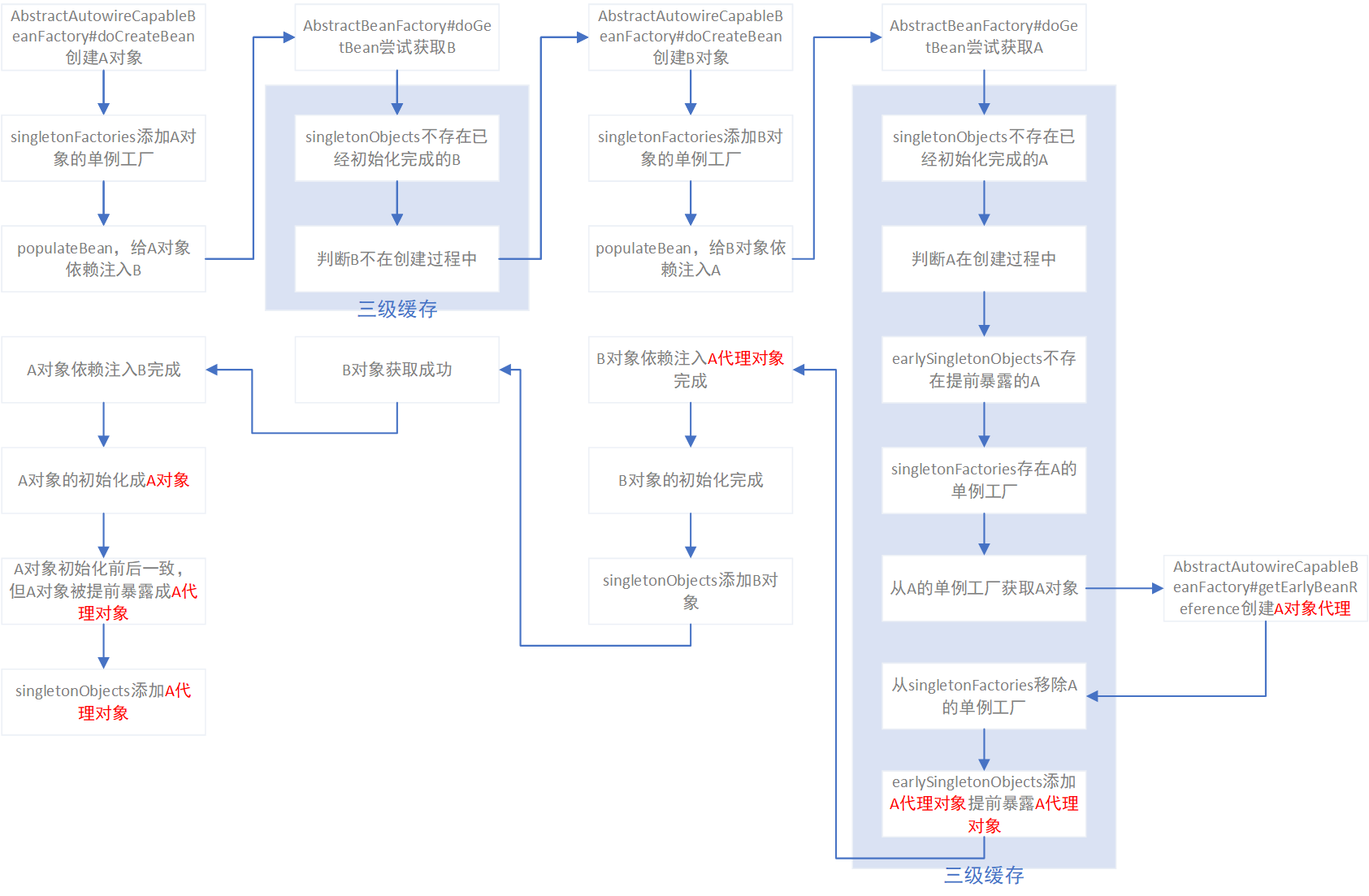
代理导致循环依赖
@Transactional代理成功
spring经常会对创建的单例对象进行代理,对于代理对象的依赖注入与非代理对象依赖注入有稍微的区别。例如通过@Transactional注解代理A后的依赖注入流程如下图:
@Transactional
@Service
public class A {
@Autowired
private B b;
public A() {
}
}
@Service
public class B {
@Autowired
private A a;
public B() {
}
}
@Async代理循环依赖异常
然而并不是每个代理对象的依赖注入流程都是一样的,典型的例子就是@Async注解,@Async经常会造成循环依赖的问题。将上面成功代理依赖注入的案例中的@Transactional注解换成@Async注解,应用启动后spring就会抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常,该流程如下图:
@Async
@Service
public class A {
@Autowired
private B b;
public A() {
}
}
@Service
public class B {
@Autowired
private A a;
public B() {
}
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'a': Bean with name 'a' has been injected into other beans [b] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using 'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:602) ~[spring-beans-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:495) ~[spring-beans-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.lambda$doGetBean$0(AbstractBeanFactory.java:317) ~[spring-beans-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:222) ~[spring-beans-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:315) ~[spring-beans-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:199) ~[spring-beans-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:759) ~[spring-beans-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(AbstractApplicationContext.java:869) ~[spring-context-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:550) ~[spring-context-5.0.8.RELEASE.jar:5.0.8.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:762) ~[spring-boot-2.0.4.RELEASE.jar:2.0.4.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext(SpringApplication.java:398) ~[spring-boot-2.0.4.RELEASE.jar:2.0.4.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:330) ~[spring-boot-2.0.4.RELEASE.jar:2.0.4.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder.run(SpringApplicationBuilder.java:137) [spring-boot-2.0.4.RELEASE.jar:2.0.4.RELEASE]
at com.wakzz.Application.main(Application.java:20) [classes/:na]
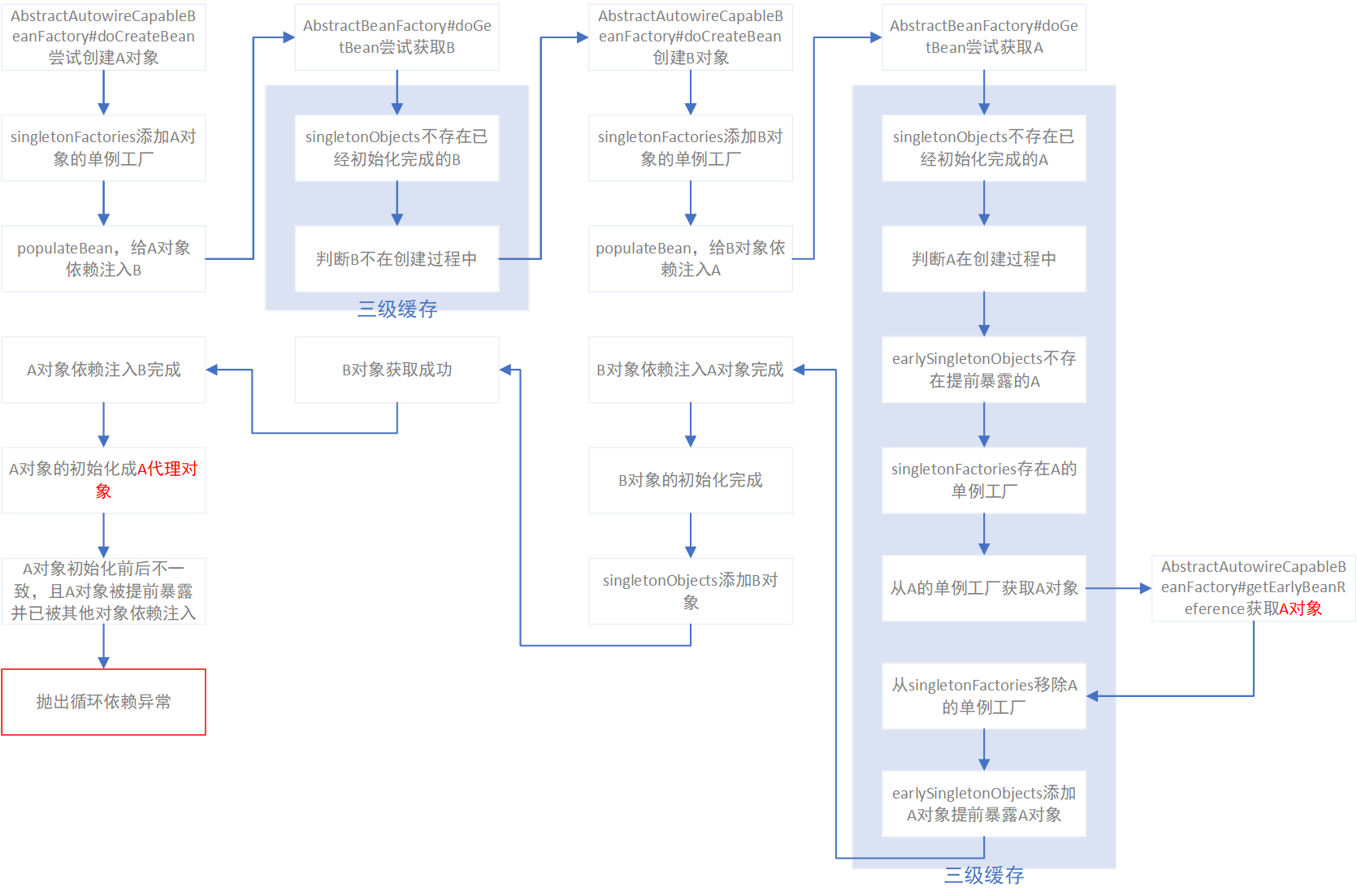
有图可见,@Async和@Transactional在对象创建和依赖注入的流程中的区别,仅仅是Bean对象被代理成代理对象的时机。@Transactional的代理是当从单例工程获取对象时,由单例工厂完成单例对象的代理;而@Async的代理则是在Bean对象依赖注入完成之后,再初始化并代理成代理对象。
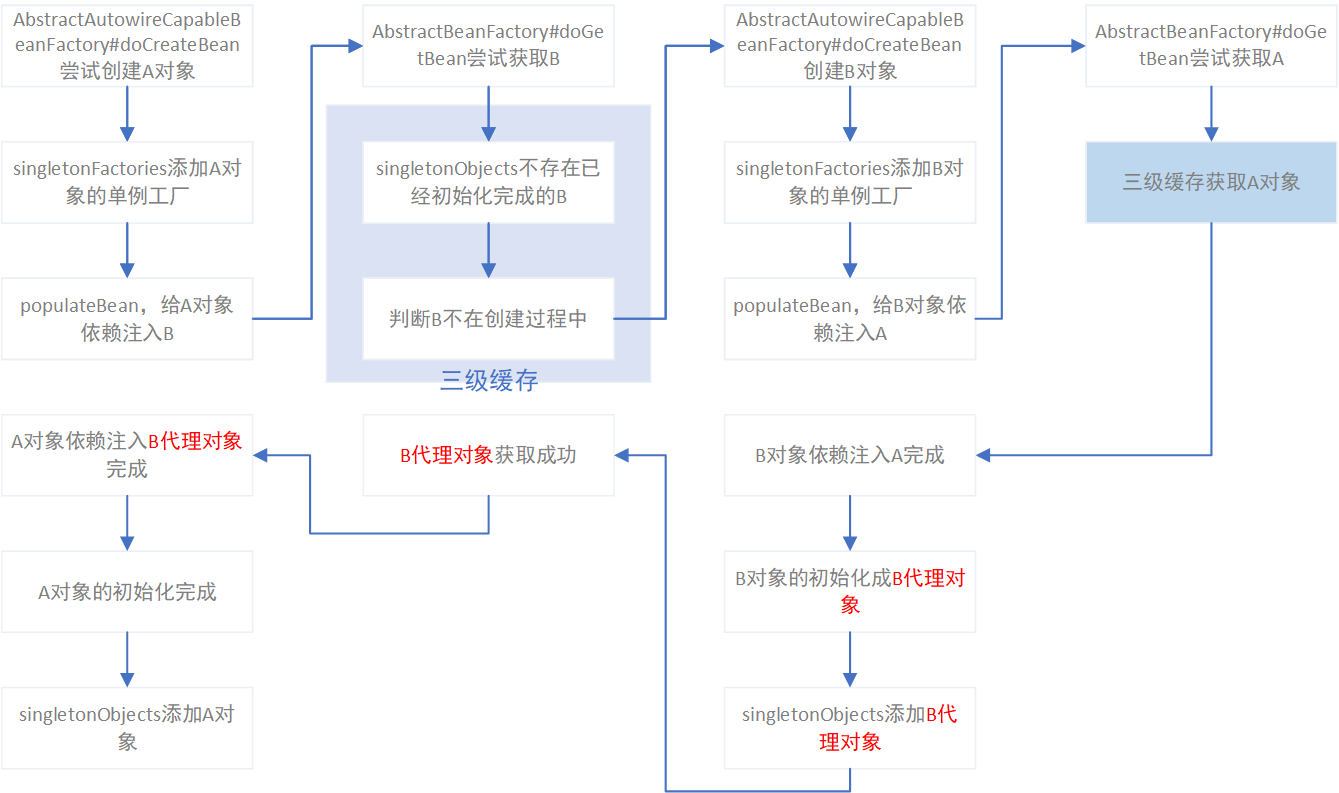
@Async代理成功
跟部分对象构造方法注入的场景一样,不需要修改依赖复杂度,仅仅是修改了A与B的依赖关系,让被代理的对象后一步创建,就可以解决该依赖关系成功启动应用。spring的流程如下图:
@Service
public class A {
@Autowired
private B b;
public A() {
}
}
@Async
@Service
public class B {
@Autowired
private A a;
public B() {
}
}
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK