

Groovy加载类导致OOM分析
source link: https://wakzz.cn/2021/11/21/java/Groovy%E5%8A%A0%E8%BD%BD%E7%B1%BB%E5%AF%BC%E8%87%B4OOM%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Groovy加载类导致OOM分析
项目中需要使用动态规则引擎,因此对热门的Groovy进行了调研。但早先就对Groovy会有OOM的问题有所耳闻,因此调研的时候特地关注了高频率使用Groovy加载类的场景,结果果然与预期一直稳定复现OOM故障。
GroovyClassLoader loader = new GroovyClassLoader();
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
String source = "" +
"public class CustomApplication {\n" +
" public void print() {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"" + i + "\");\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
Class<?> clazz = loader.parseClass(source);
Object target = clazz.newInstance();
Method method = clazz.getMethod("print");
method.invoke(target);
}
执行以上代码,并通过JVM自带的jconsole工具监控类加载数量和元数据区的内存,如下图所示。监控显示,JVM的类数量从三千一路飙升到一万三,元数据内存使用也是一路飙涨,直到OOM后应用报错。
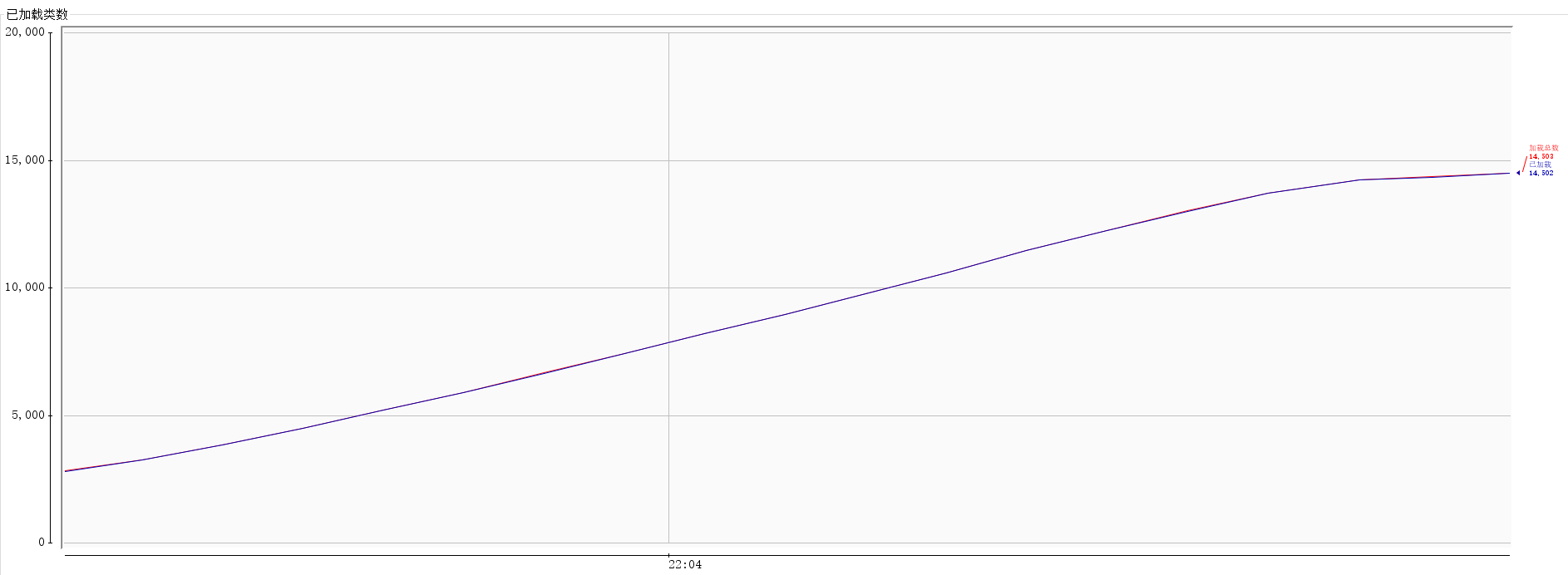
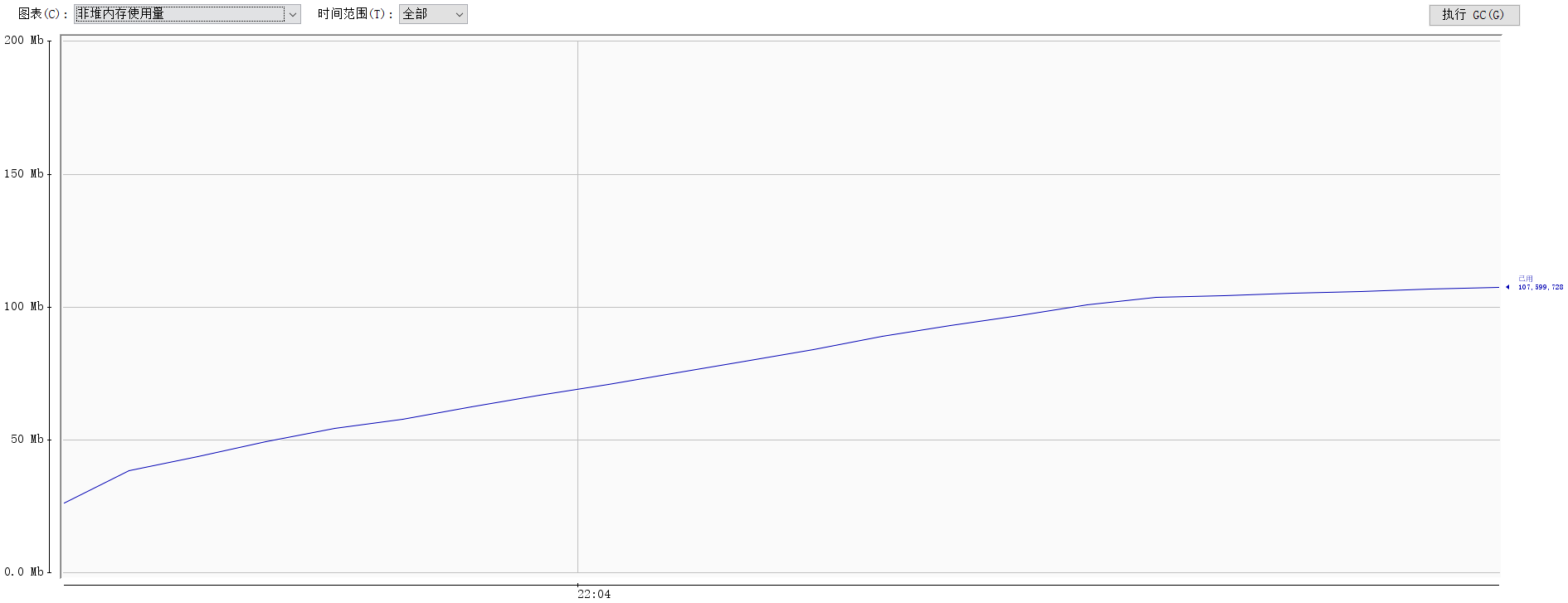
分析OOM
通过以上两张图,显而易见,应用OOM的原因是Groovy加载的类即使只使用一次,但却并没有被释放,最终导致元数据内存空间不足而OOM。因此接下来的思路是需要分析类如何才能被回收释放,以及如何才能让Groovy加载的类回收释放掉。
首先分析一个类的回收的前置条件,一个类如果需要被垃圾回收,则需要同时满足下面3个条件:
- 该类所有的实例都已经被回收
- 加载该类的ClassLoader已经被回收
- 该类对应的java.lang.Class对象没有在任何地方被引用,无法在任何地方通过反射访问该类的方法
对照复现场景中的测试代码,显然条件1和条件3是满足的,所有的类对象和类实例都没有被外部持有。至于条件2则需要了解Groovy的类加载机制才能解答。
Groovy类加载机制
Groovy加载类的核心逻辑在groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader#doParseClass,其实现细节是通过GroovyClassLoader对象执行parseClass方法尝试加载类时,实际是每次类加载都会新建一个新的GroovyClassLoader.InnerLoader类加载器来真正执行类加载,加载完成后则不再引用该GroovyClassLoader.InnerLoader类加载器对象。
// 创建GroovyClassLoader.InnerLoader类加载器
ClassCollector collector = createCollector(unit, su);
unit.setClassgenCallback(collector);
int goalPhase = Phases.CLASS_GENERATION;
if (config != null && config.getTargetDirectory() != null) goalPhase = Phases.OUTPUT;
// 最终调用groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader.ClassCollector#createClass方法
unit.compile(goalPhase);
protected ClassCollector createCollector(CompilationUnit unit, SourceUnit su) {
InnerLoader loader = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<InnerLoader>() {
public InnerLoader run() {
return new InnerLoader(GroovyClassLoader.this);
}
});
return new ClassCollector(loader, unit, su);
}
public static class ClassCollector extends CompilationUnit.ClassgenCallback {
private Class generatedClass;
private final GroovyClassLoader cl;
private final SourceUnit su;
private final CompilationUnit unit;
private final Collection<Class> loadedClasses;
protected ClassCollector(InnerLoader cl, CompilationUnit unit, SourceUnit su) {
this.cl = cl;
this.unit = unit;
this.loadedClasses = new ArrayList<Class>();
this.su = su;
}
public GroovyClassLoader getDefiningClassLoader() {
return cl;
}
protected Class createClass(byte[] code, ClassNode classNode) {
BytecodeProcessor bytecodePostprocessor = unit.getConfiguration().getBytecodePostprocessor();
byte[] fcode = code;
if (bytecodePostprocessor!=null) {
fcode = bytecodePostprocessor.processBytecode(classNode.getName(), fcode);
}
// 实际使用的是GroovyClassLoader.InnerLoader类加载器
GroovyClassLoader cl = getDefiningClassLoader();
Class theClass = cl.defineClass(classNode.getName(), fcode, 0, fcode.length, unit.getAST().getCodeSource());
this.loadedClasses.add(theClass);
if (generatedClass == null) {
ModuleNode mn = classNode.getModule();
SourceUnit msu = null;
if (mn != null) msu = mn.getContext();
ClassNode main = null;
if (mn != null) main = (ClassNode) mn.getClasses().get(0);
if (msu == su && main == classNode) generatedClass = theClass;
}
return theClass;
}
...
}
通过arthas工具监控类加载器如下图,通过GroovyClassLoader对象加载类时,实际上是使用的GroovyClassLoader.InnerLoader对象加载目标类,且每个GroovyClassLoader.InnerLoader类加载器对象只加载一个类。
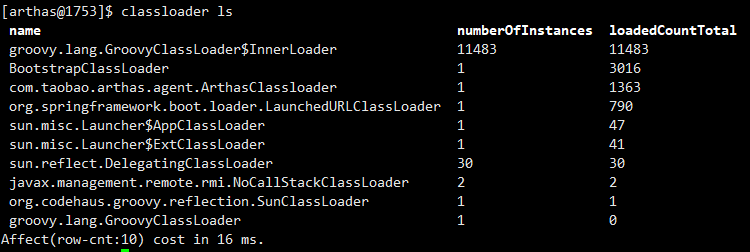
我们再回忆一下一个类的回收的3个前置条件:
- 该类所有的实例都已经被回收
- 加载该类的ClassLoader已经被回收
- 该类对应的java.lang.Class对象没有在任何地方被引用,无法在任何地方通过反射访问该类的方法
测试代码中条件1和条件3满足,根据Groovy的类加载机制,明显类加载器加载完成目标类后就不再引用,因此条件2也满足,但实际上类并没有按预期被垃圾回收。显然在测试代码之外,有代码引用到了类对象或者类实例亦或者类加载器,导致最终类木有被垃圾回收。
这里就需要借助其他工具来分析对象引用,为了方便分析,使用OOM的内存快照,来分析导致内存溢出的对象,可直接定位到被偷偷引用的漏网之鱼。
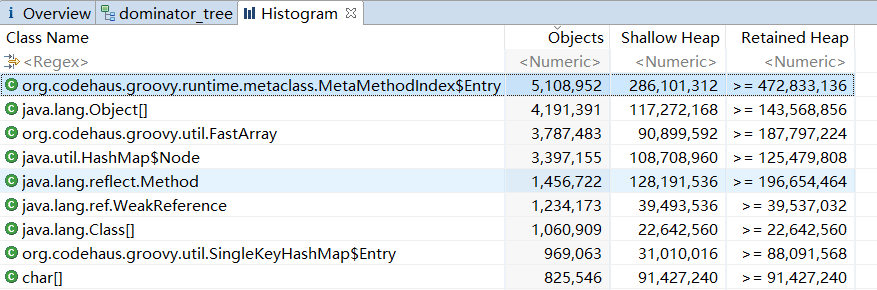
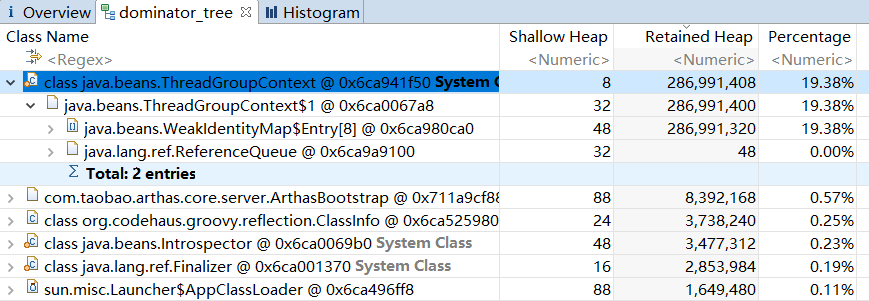
如上图,最终定位出java.beans.ThreadGroupContext下引用了类对象,因此上述的类回收的3个条件未满足而导致类不会被垃圾回收。
那么问题来了,类对象为什么会被java.beans.ThreadGroupContext引用?经过层层debug后发现,当对Groovy加载的类执行反射时,会将该类的结构缓存到java.beans.ThreadGroupContext中,且不会主动清除缓存。核心代码如下:
groovy.lang.MetaClassImpl
// 对Groovy加载的类执行反射时,会执行该方法
private void addProperties() {
BeanInfo info;
final Class stopClass;
// introspect
try {
if (isBeanDerivative(theClass)) {
info = (BeanInfo) AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
public Object run() throws IntrospectionException {
// 创建类结构缓存
return Introspector.getBeanInfo(theClass, Introspector.IGNORE_ALL_BEANINFO);
}
});
} else {
info = (BeanInfo) AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
public Object run() throws IntrospectionException {
// 创建类结构缓存
return Introspector.getBeanInfo(theClass);
}
});
}
} catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw new GroovyRuntimeException("exception during bean introspection", pae.getException());
}
...
}
java.beans.Introspector
public static BeanInfo getBeanInfo(Class<?> beanClass)
throws IntrospectionException
{
if (!ReflectUtil.isPackageAccessible(beanClass)) {
return (new Introspector(beanClass, null, USE_ALL_BEANINFO)).getBeanInfo();
}
// 注意:ThreadGroupContext和线程group绑定
ThreadGroupContext context = ThreadGroupContext.getContext();
BeanInfo beanInfo;
synchronized (declaredMethodCache) {
beanInfo = context.getBeanInfo(beanClass);
}
if (beanInfo == null) {
beanInfo = new Introspector(beanClass, null, USE_ALL_BEANINFO).getBeanInfo();
synchronized (declaredMethodCache) {
context.putBeanInfo(beanClass, beanInfo);
}
}
return beanInfo;
}
综上,虽然Groovy通过GroovyClassLoader.InnerLoader来加载类,实现类加载器在类加载完成后就会被垃圾回收,但由于Groovy加载的类在反射时会被java.beans.ThreadGroupContext缓存,且该缓存不会被主动清除,因此最终类没有按预期被垃圾回收。
所以只要定期清除java.beans.ThreadGroupContext中的缓存,就能释放所有类引用,让Groovy加载的类被垃圾回收。测试代码如下:
GroovyClassLoader loader = new GroovyClassLoader();
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
String source = "" +
"public class CustomApplication {\n" +
" public void print() {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"" + i + "\");\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
Class<?> clazz = loader.parseClass(source);
Object target = clazz.newInstance();
Method method = clazz.getMethod("print");
method.invoke(target);
// 模拟定期清除ThreadGroupContext中的缓存
if (i % 100 == 0) {
// 需要与反射线程同ThreadGroup
Introspector.flushCaches();
}
}
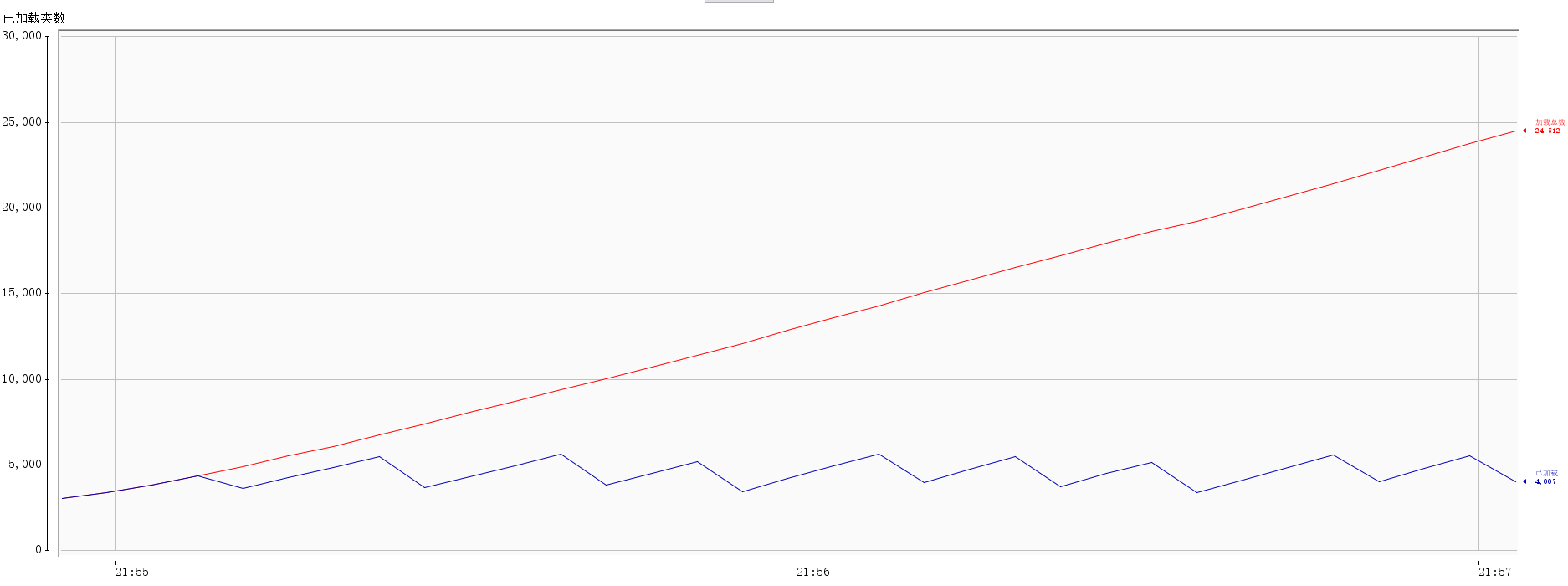
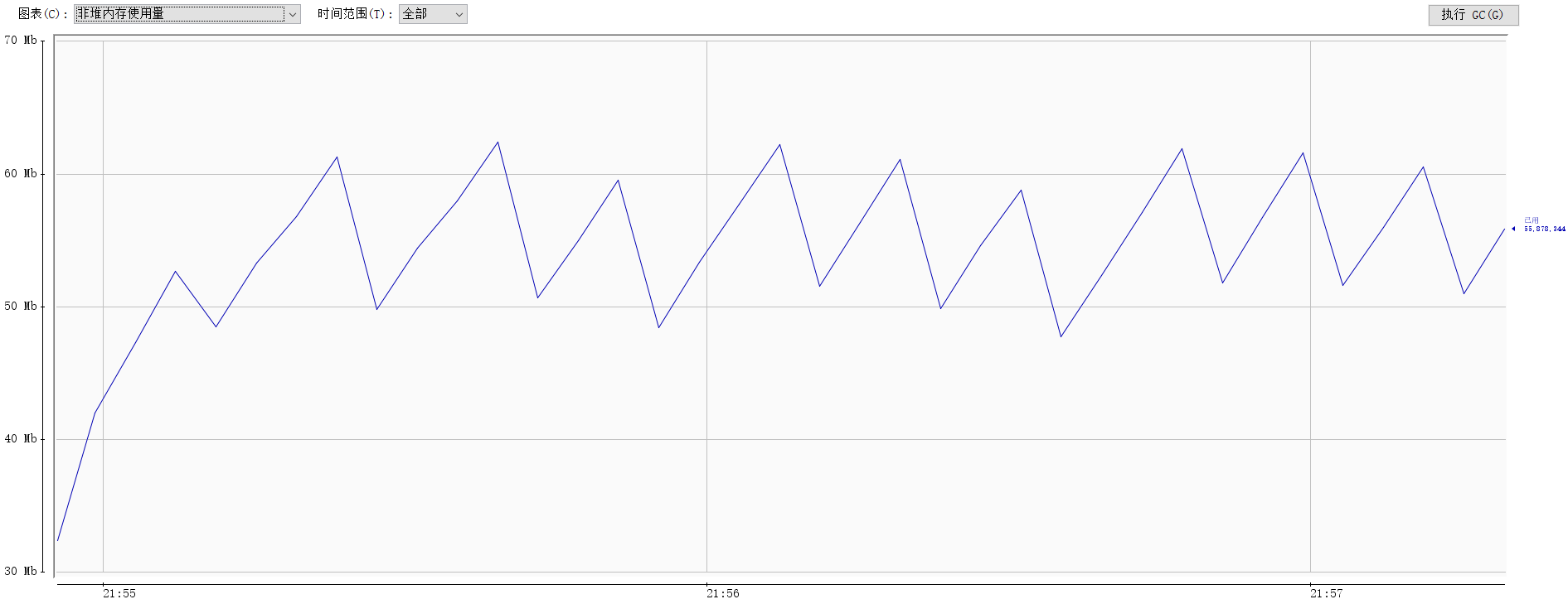
如下图,图1为类加载数量图,其中红线为累计加载类数量,蓝色为当前加载类数量,而图二为元数据内存使用情况。可见在定期清除ThreadGroupContext中的缓存后,实现了对Groovy加载类的垃圾回收,不再出现OOM的问题。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK