

【logistics】理论与实现
source link: https://www.guofei.site/2017/05/07/LogisticRegression.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

【logistics】理论与实现
2017年05月07日Author: Guofei
文章归类: 2-1-有监督学习 ,文章编号: 220
版权声明:本文作者是郭飞。转载随意,但需要标明原文链接,并通知本人
原文链接:https://www.guofei.site/2017/05/07/LogisticRegression.html
logistics regression是一种典型的分类模型
logistic regression, logit regression, logit model这三个模型本质和用法非常相似,因此这里不加区分
logistic distribution
定义
CDF满足这个的随机变量叫做logistic distribution
F(x;μ,s)=11+e−(x−μ)/sF(x;μ,s)=11+e−(x−μ)/s
性质
不难推导出PDF:
f(x;μ,s)=e−(x−μ)/ss(1+e−(x−μ)/s)2f(x;μ,s)=e−(x−μ)/ss(1+e−(x−μ)/s)2
logistic regression
模型
P(Y=1∣x)=exp(wx)1+exp(wx)P(Y=1∣x)=exp(wx)1+exp(wx)
P(Y=0∣x)=11+exp(wx)P(Y=0∣x)=11+exp(wx)
算法
求参数的方法,就是经典的 MLE (极大似然估计)方法。
先求似然函数,
l(w;x)=∏i=1N[P(Y=1|x)]yi[P(Y=0|x)]1−yil(w;x)=∏i=1N[P(Y=1|x)]yi[P(Y=0|x)]1−yi
取对数后求argmaxlnl(w)argmaxlnl(w)
这是一个 凸函数 ,(凸函数的知识参见我的另一篇博文最优化方法理论篇)
由于是一个凸函数,可以用导数值为0确定最大值点,还可以用梯度下降法迭代求解最大值点。
推导似然函数:
令L(w;x)=lnl(w;x)L(w;x)=lnl(w;x)L(w;x)=∑i=1N(yiwxi−ln(1+ewxi))L(w;x)=∑i=1N(yiwxi−ln(1+ewxi))
w和x都是向量。下面研究向量的第j个分量
偏导数为:
∂L(w;x)∂wj=∑i=1N(yixij−ewxixij1+ewxi)=∑i=1N(yi−ewxi1+ewxi)xij∂L(w;x)∂wj=∑i=1N(yixij−ewxixij1+ewxi)=∑i=1N(yi−ewxi1+ewxi)xij
- 令导数为0,遗憾的是无法求出解析解。
- 因此用梯度法可以求解
Python实现(自己编程)
梯度法
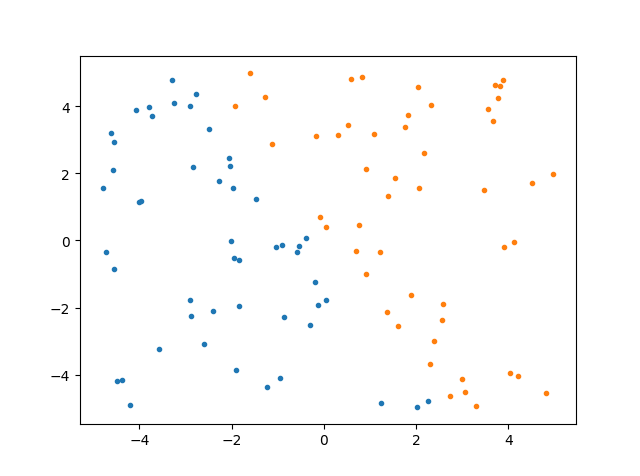
首先生成模拟数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = np.random.uniform(low=-5, high=5, size=(100, 2))
data=pd.DataFrame(data)
mask = (data.iloc[:, 0] + 0.5* data.iloc[:, 1])<0
data['y']=mask*1
data1 = data[data.iloc[:, 2] == 1] #为了画图,两类不同颜色
data2 = data[data.iloc[:, 2] == 0]
plt.plot(data1.iloc[:, 0], data1.iloc[:, 1], '.')
plt.plot(data2.iloc[:, 0], data2.iloc[:, 1], '.')
plt.show()
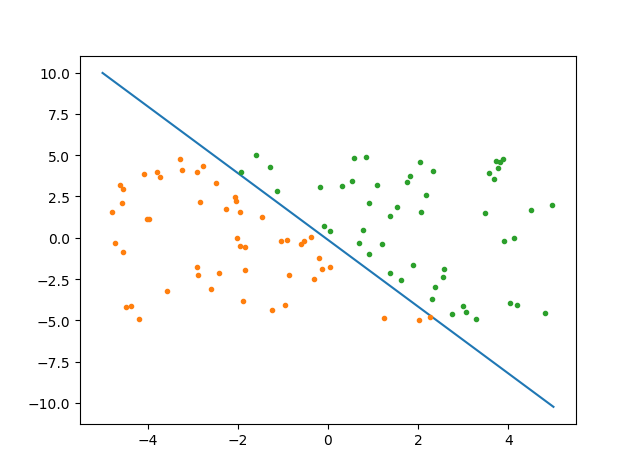
迭代求解:
alpha = 0.001 # 步长
step = 500 # 总共的迭代次数
m, n = data.shape
weights = np.ones((n, 1))
data_x = np.concatenate((np.ones((m, 1)), np.array(data.iloc[:, :2])), axis=1) # 去掉y列,并添加全1的第一列
target = np.array(data.iloc[:, 2])
target.shape = -1, 1
def logistic(wTx):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-wTx))
for i in range(step):
wTx = np.dot(data_x, weights)
output = logistic(wTx)
errors = target - output
weights = weights + alpha * np.dot(data_x.T, errors)
X = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
Y = -(weights[0] + X * weights[1]) / weights[2]
plt.plot(X, Y)
plt.plot(data1.iloc[:, 0], data1.iloc[:, 1], '.')
plt.plot(data2.iloc[:, 0], data2.iloc[:, 1], '.')
plt.show()
随机梯度下降法
随机梯度下降法并没有引入新理论,解决的主要问题是步长alpha的问题。
alpha太大,容易越过极值点,导致震荡不收敛。
alpha太小,收敛速度会降低。
算法的伪代码是这样的:
for 第i次迭代
for 第j次收取
alpha=2/(1+i+j)+0.001
从全部样本中随机抽取样本,梯度下降,步长为alphaPython实现(sklearn)
step1:建立模型1
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
dataset=load_iris()
from sklearn import linear_model
clf=linear_model.LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(dataset.data,dataset.target)
关于参数的选择,一定要看sklearn官网2
step2:模型使用
clf.predict(dataset.data)#判断数据属于哪个类别
clf.predict_proba(dataset.data)#判断属于各个类别的概率
clf.score(dataset.data,dataset.target)#准确率
clf.coef_ #系数
clf.intercept_ #截距
clf.n_iter_ #迭代次数备注
筛选+回归
用到sklearn中的两个模型
RandomizedLogisticRegression用来筛选变量
LogisticRegression用来做逻辑回归
step1:用RandomizedLogisticRegression筛选有效变量
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression as LR
from sklearn.linear_model import RandomizedLogisticRegression as RLR
rlr = RLR() #建立随机逻辑回归模型,用于筛选变量
rlr.fit(x, y) #训练模型
rlr.get_support() #获取特征筛选结果,是一个boll类型的array
rlr.scores_#各个特征的分数,是1darray
print('通过随机逻辑回归模型筛选特征结束。')
print('有效特征为:%s' % ','.join(x.columns[rlr.get_support()]))
step2:用LogisticRegression做逻辑回归
x_new = x[x.columns[rlr.get_support()]] #筛选好特征
lr = LR() #建立逻辑回归模型
lr.fit(x_new, y) #用筛选后的特征数据来训练模型
print('逻辑回归模型训练结束。')
print('模型的平均正确率为:%s' % lr.score(x_new, y)) #给出模型的平均正确率,本例为81.4%参考文献
您的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK