
6

LeetCode: 142. Linked List Cycle II
source link: https://mozillazg.com/2020/10/leetcode-142-linked-list-cycle-ii.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
解法¶
遍历链表,记录访问过的节点,找出环开始的节点¶
遍历链表,把访问过的节点都记下来,如果发现有节点指向了一个已访问过的节点,说明链表存在环,并且当前节点就是环开始的节点
这个方法的 Python 代码类似下面这样:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
if head is None:
return None
seen = {}
while head is not None:
if head in seen:
return head
seen[head] = True
head = head.next
return None
快慢双指针方法,判断是否有环,然后再找出环开始的节点¶
快慢双指针判断是否有环的方法的思路是:
- 定义快和慢两个指针,从 head 开始遍历链表,慢指针一次移动一个节点,快指针一次移动两个节点
- 如果快指针到达了链表尾部,说明没有环(因为如果有环的话,会死循环没有尾部)
- 如果快指针和慢指针移动到了同一个节点上,说明有环(因为如果没环的话,快指针永远在慢指针前面,有环时,因为快指针比慢指针移动的速度要快,在移动到有环的地方的时候会跑到慢指针后面去(多次移动后会出现),最终出现快慢两个指针相遇移动到同一个节点的情况(多次移动后出现))
对于有环的链表,通过下面的方法找出环开始的节点:
- 将慢指针移动到 head 位置重新开始遍历链表,快指针继续往前移动,当快慢指针相遇时,当前节点即为环开始的节点
为啥通过这个新的快慢指针的移动可以找到环开始的节点,看一下移动轨迹:
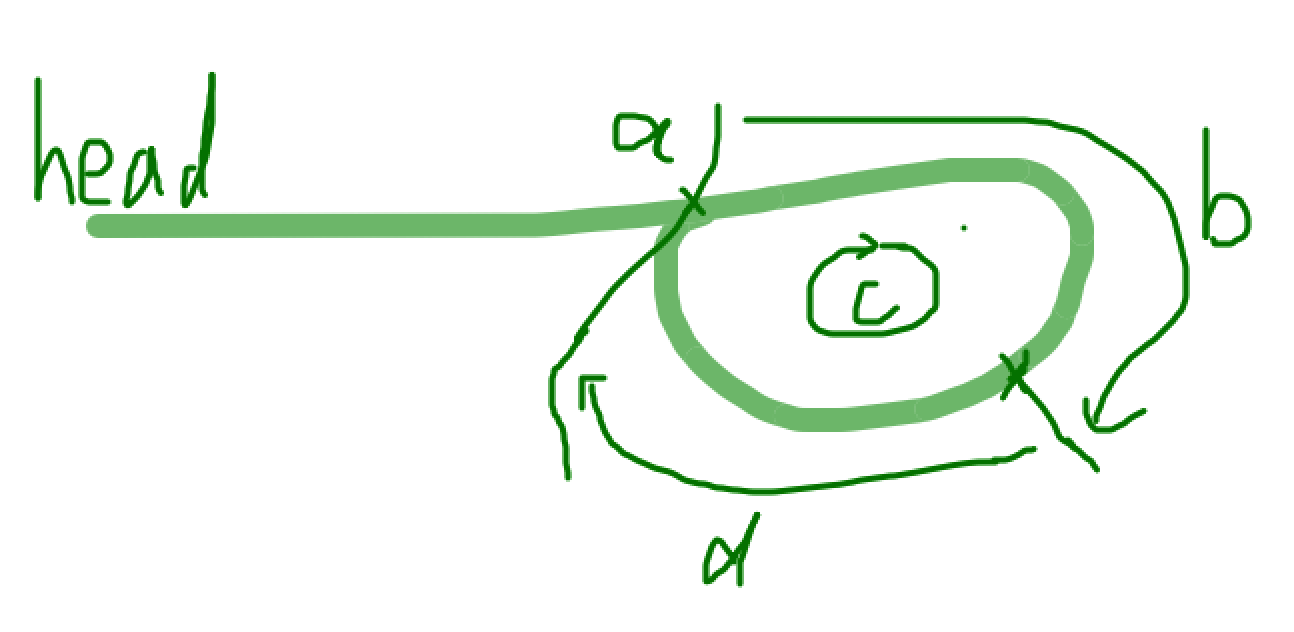
假设环开始位置为 a , 第一次快慢指针相遇时,相遇位置距离环开始位置 b 步, 绕环一圈需要移动 c 步, 从 b 往前移动到环开始位置需要 d 步,快指针绕环移动了 x 圈,慢指针绕环移动了 y 圈。
# 快指针移动的步数是慢指针的 2 倍 a + b + x * c = 2 * (a + b + y * c) a + b + x * c = 2a + 2b + 2y *c x * c - 2y * c = a + b (x - 2y) * c = a + b a + b = (x - 2y) * c a = (x - 2y) * c - b # b = c - d a = (x - 2y) * c - (c - d) a = (x - 2y - 1) * c + d # 可以得出,从 head 到 a 的步数等于绕环 n 圈然后再走 d 步的步数 # # 可以从相遇位置绕环 n 圈再走 d 步,此时刚好到达环起始位置 # 同时从 head 走 a 步也会到达环起始位置
这个方法的 Python 代码类似下面这样:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
if head is None:
return None
slow, fast = head, head
has_cycle = False
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if fast is slow:
has_cycle = True
break
if not has_cycle:
return None
slow = head
while slow is not fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return slow
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK