

原来你是这样的JAVA--[07]聊聊Integer和BigDecimal - 敬YES
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/janes/p/18031284
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

今天来聊聊Java中跟数值处理相关的两个类型Integer和BigDecimal。 说起这两个类型,我们肯定都不陌生,但是其中有些容易踩到的坑需要注意避让。
Integer
整型我们应该每天都会用到,但是每种语言还是有自己的特性。从敬姐刚从.NET转过来的时候踩过的一个坑说起:话说在.NET世界中,数值的基本类型和包装类型是会自动转换的,所以数值比较很自然地就会使用 a==b,但是到java这却行不通了,顿时一脸懵。
数值比较及自动装箱
@Test
public void Interger(){
Integer x = 127;
Integer y = 127;
Integer m = 99999;
Integer n = 99999;
System.out.println("x == y: " + (x==y));
System.out.println("m == n: " + (m==n));
System.out.println("x.equals(y): " + x.equals(y));
System.out.println("m.equals(n): " + m.equals(n));
//执行结果
// x == y: true
// m == n: false
// x.equals(y): true
// m.equals(n): true
}
仔细观察可以发现,==比较,较小的两个相同的Integer返回true,较大的两个相同的Integer返回false,这是为何呢?
一起看一下Integer类的源码,发现其中的IntegerCache类。这是Java为了节省空间、提升性能采取的优化机制,常量池的大小为一个字节(-128~127)。
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer[] cache;
static Integer[] archivedCache;
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
h = Math.max(parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue), 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(h, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
// Load IntegerCache.archivedCache from archive, if possible
CDS.initializeFromArchive(IntegerCache.class);
int size = (high - low) + 1;
// Use the archived cache if it exists and is large enough
if (archivedCache == null || size > archivedCache.length) {
Integer[] c = new Integer[size];
int j = low;
for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
c[i] = new Integer(j++);
}
archivedCache = c;
}
cache = archivedCache;
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
而对于valueOf(int i)方法,直接使用了常量池IntegerCache
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
所以当遇到 Integer x = 127; 时,会进行自动装箱,调用的是:
Integer x = Integer.valueOf(127);
为了节省内存,Integer.valueOf()对于较小的数,始终返回相同的实例,因此,比较“恰好”为true。但我们绝不能因为Java标准库的Integer内部有缓存优化就用比较,必须用equals()方法比较两个Integer。
因为Integer.valueOf()可能始终返回同一个Integer实例,因此,在我们自己创建Integer的时候,以下两种方法:
方法1:Integer n = new Integer(100);
方法2:Integer n = Integer.valueOf(100);
方法2更好,因为方法1总是创建新的Integer实例,方法2把内部优化留给Integer的实现者去做,即使在当前版本没有优化,也有可能在下一个版本进行优化。
我们把能创建“新”对象的静态方法称为静态工厂方法。Integer.valueOf()就是静态工厂方法,它尽可能地返回缓存的实例以节省内存。简而言之:创建新对象时,优先选用静态工厂方法而不是new操作符。
上个看个有点特别的例子:
@Test
public void instance() {
//每次创建一个新实例
Integer a1 = new Integer(100);
Integer a2 = new Integer(100);
Assert.assertFalse(a1 == a2);
//add
Integer a3 = new Integer(200);
//注意这里喽!!
Assert.assertTrue(a1 + a2 == 200);
Assert.assertTrue(a1 + a2 == a3);
}
因为+这个操作符不适用于 Integer 对象,首先 a1 和 a2 进行自动拆箱操作,进行数值相加,即a3 == 40。
BigDecimal
BigDecimal适合商业计算场景,用来对超过16位有效位的数进行精确的运算。
Double转换为BigDecimal
我们在使用BigDecimal时,为了防止精度丢失,推荐使用它的 BigDecimal(String) 构造方法来创建对象。
@Test
public void double2decimal() {
Double d = 0.1d;
System.out.println(new BigDecimal(d));//0.1000000000000000055511151231257827021181583404541015625
System.out.println(new BigDecimal(d.toString()));//0.1
System.out.println(BigDecimal.valueOf(d));//0.1
}
保留几位小数
通过 setScale方法设置保留几位小数以及保留规则。
@Test
public void decimalTest() {
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("1.2345");
System.out.println(a.toString());
//BigDecimal保留几位小数
BigDecimal b = a.setScale(3, RoundingMode.HALF_DOWN);
System.out.println(b.toString());
}
BigDecimal 值比较
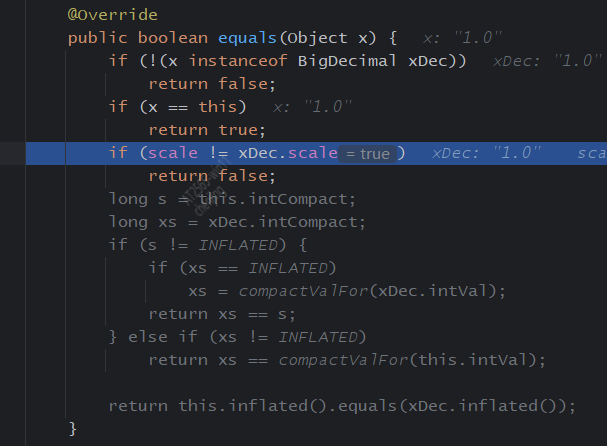
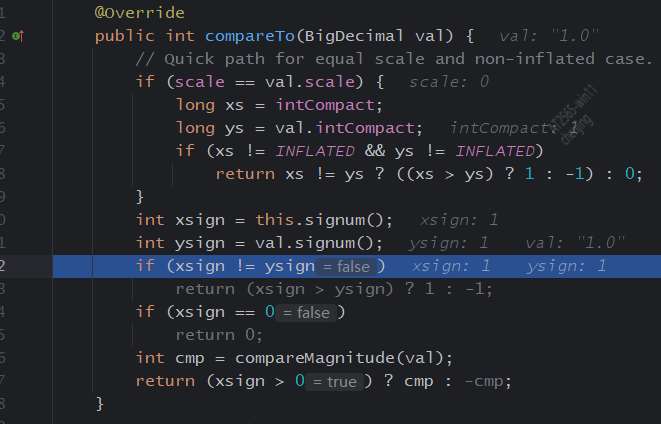
BigDecimal的等值比较应该使用compareTo()方法,而不是equals()方法。
/**
* BigDecimal等值比较
* equals:既比较数值,又比较精度;
* compareTo:仅比较数值
*/
@Test
public void compare() {
BigDecimal a = BigDecimal.valueOf(1);
BigDecimal b = BigDecimal.valueOf(1.00);
Assert.assertFalse(a.equals(b));
Assert.assertEquals(0, a.compareTo(b));
}
调试一下BigDecimal的equals和compareTo方法,发现equals()方法会比较精度,但是compare()方法不会。
BigDecimal 除法
BigDecimal.divide(),除法运算注意要设置精度,否则在除不尽的情况下会抛异常。
@Test
public void divide(){
BigDecimal a=BigDecimal.valueOf(1);
BigDecimal b=BigDecimal.valueOf(3);
//直接抛异常
// System.out.println(a.divide(b));
//正常返回 0.3333
System.out.println(a.divide(b,4,RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN));
}
文示例代码参考:jing-yes-java (https://github.com/cathychen00/jing-yes-java/tree/master/jing-yes-j2se/src/test/java/com/jingyes/j2se/tests)
本人公众号[ 敬YES ]同步更新,欢迎大家关注~

Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK