

【调试】pstore原理和使用方法总结 - 嵌入式与Linux那些事
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/dongxb/p/18011157
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

什么是pstore
pstore最初是用于系统发生oops或panic时,自动保存内核log buffer中的日志。不过在当前内核版本中,其已经支持了更多的功能,如保存console日志、ftrace消息和用户空间日志。同时,它还支持将这些消息保存在不同的存储设备中,如内存、块设备或mtd设备。 为了提高灵活性和可扩展性,pstore将以上功能分别抽象为前端和后端,其中像dmesg、console等为pstore提供数据的模块称为前端,而内存设备、块设备等用于存储数据的模块称为后端,pstore core则分别为它们提供相关的注册接口。
通过模块化的设计,实现了前端和后端的解耦,因此若某些模块需要利用pstore保存信息,就可以方便地向pstore添加新的前端。而若需要将pstore数据保存到新的存储设备上,也可以通过向其添加后端设备的方式完成。
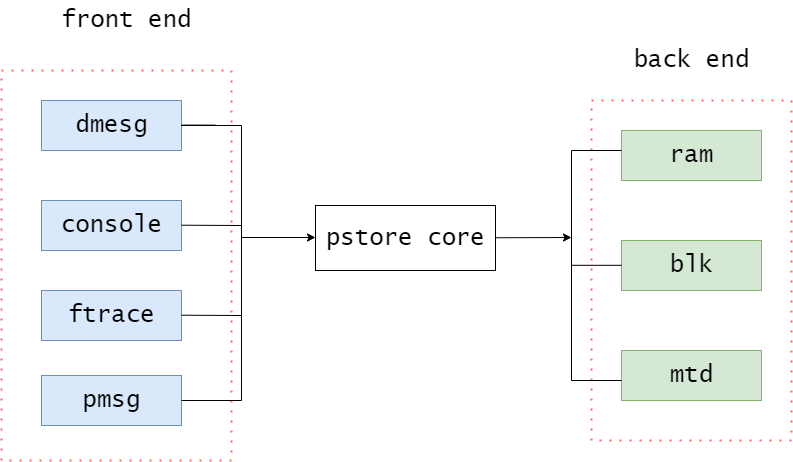
除此之外,pstore还设计了一套pstore文件系统,用于查询和操作上一次重启时已经保存的pstore数据。当该文件系统被挂载时,保存在backend中的数据将被读取到pstore fs中,并以文件的形式显示。
pstore工作原理
pstore 源文件主要有以下几个:fs/pstore/ram_core.c
fs/pstore/
├── ftrace.c # ftrace 前端的实现
├── inode.c # pstore 文件系统的注册与操作
├── internal.h
├── Kconfig
├── Makefile
├── platform.c # pstore 前后端功能的核心
├── pmsg.c # pmsg 前端的实现
├── ram.c # pstore/ram 后端的实现,dram空间分配与管理
├── ram_core.c # pstore/ram 后端的实现,dram的读写操作
pstore文件系统位置在:
# ls /sys/fs/pstore
console-ramoops-0 dmesg-ramoops-0
控制台日志位于 pstore 目录下的console-ramoops文件中,因为采用console机制,该文件中的日志信息也受printk level控制,并不一定是全的。
oops/panic日志位于 pstore 目录下的dmesg-ramoops-x文件中,根据缓冲区大小可以有多个文件,x从0开始。
函数调用序列日志位于 pstore 目录下的ftrace-ramoops文件中。
相关代码在inode.c pstore_mkfile里:
/*
* Make a regular file in the root directory of our file system.
* Load it up with "size" bytes of data from "buf".
* Set the mtime & ctime to the date that this record was originally stored.
*/
int pstore_mkfile(enum pstore_type_id type, char *psname, u64 id, int count,
char *data, bool compressed, size_t size,
struct timespec time, struct pstore_info *psi)
{
........................
rc = -ENOMEM;
inode = pstore_get_inode(pstore_sb);
..............................
switch (type) {
case PSTORE_TYPE_DMESG:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "dmesg-%s-%lld%s",
psname, id, compressed ? ".enc.z" : "");
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_CONSOLE:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "console-%s-%lld", psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_FTRACE:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "ftrace-%s-%lld", psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_MCE:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "mce-%s-%lld", psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_PPC_RTAS:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "rtas-%s-%lld", psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_PPC_OF:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "powerpc-ofw-%s-%lld",
psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_PPC_COMMON:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "powerpc-common-%s-%lld",
psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_PMSG:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "pmsg-%s-%lld", psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_PPC_OPAL:
sprintf(name, "powerpc-opal-%s-%lld", psname, id);
break;
case PSTORE_TYPE_UNKNOWN:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "unknown-%s-%lld", psname, id);
break;
default:
scnprintf(name, sizeof(name), "type%d-%s-%lld",
type, psname, id);
break;
}
....................
dentry = d_alloc_name(root, name);
.......................
d_add(dentry, inode);
................
}
pstore_mkfile根据不同的type,使用snprintf函数生成文件名name。生成的文件名格式为<type>-<psname>-<id>,其中type是enum pstore_type_id类型的一个值,psname是给定的psname参数,id是给定的id参数。
接着使用d_alloc_name函数为根目录创建一个目录项dentry,最后使用d_add函数将目录项dentry与索引节点inode关联起来,将其添加到文件系统中。
pstore_register
ramoops负责把message write到某个ram区域上,platform负责从ram读取存到/sys/fs/pstore,ok,先来看机制代码platform.c。
backend需要用pstore_register来注册:
/*
* platform specific persistent storage driver registers with
* us here. If pstore is already mounted, call the platform
* read function right away to populate the file system. If not
* then the pstore mount code will call us later to fill out
* the file system.
*/
int pstore_register(struct pstore_info *psi)
{
struct module *owner = psi->owner;
if (backend && strcmp(backend, psi->name))
return -EPERM;
spin_lock(&pstore_lock);
if (psinfo) {
spin_unlock(&pstore_lock);
return -EBUSY;
}
if (!psi->write)
psi->write = pstore_write_compat;
if (!psi->write_buf_user)
psi->write_buf_user = pstore_write_buf_user_compat;
psinfo = psi;
mutex_init(&psinfo->read_mutex);
spin_unlock(&pstore_lock);
...
/*
* Update the module parameter backend, so it is visible
* through /sys/module/pstore/parameters/backend
*/
backend = psi->name;
module_put(owner);
backend判断确保一次只能有一个并记录了全局psinfo。
看下结构体pstore_info:
struct pstore_info {
struct module *owner;
char *name;
spinlock_t buf_lock; /* serialize access to 'buf' */
char *buf;
size_t bufsize;
struct mutex read_mutex; /* serialize open/read/close */
int flags;
int (*open)(struct pstore_info *psi);
int (*close)(struct pstore_info *psi);
ssize_t (*read)(u64 *id, enum pstore_type_id *type,
int *count, struct timespec *time, char **buf,
bool *compressed, ssize_t *ecc_notice_size,
struct pstore_info *psi);
int (*write)(enum pstore_type_id type,
enum kmsg_dump_reason reason, u64 *id,
unsigned int part, int count, bool compressed,
size_t size, struct pstore_info *psi);
int (*write_buf)(enum pstore_type_id type,
enum kmsg_dump_reason reason, u64 *id,
unsigned int part, const char *buf, bool compressed,
size_t size, struct pstore_info *psi);
int (*write_buf_user)(enum pstore_type_id type,
enum kmsg_dump_reason reason, u64 *id,
unsigned int part, const char __user *buf,
bool compressed, size_t size, struct pstore_info *psi);
int (*erase)(enum pstore_type_id type, u64 id,
int count, struct timespec time,
struct pstore_info *psi);
void *data;
};
name就是backend的name了。
*write和*write_buf_user如果backend没有给出会有个默认compat func,最终都走的*write_buf。
if (!psi->write)
psi->write = pstore_write_compat;
if (!psi->write_buf_user)
psi->write_buf_user = pstore_write_buf_user_compat;
static int pstore_write_compat(enum pstore_type_id type,
enum kmsg_dump_reason reason,
u64 *id, unsigned int part, int count,
bool compressed, size_t size,
struct pstore_info *psi)
{
return psi->write_buf(type, reason, id, part, psinfo->buf, compressed,
size, psi);
}
static int pstore_write_buf_user_compat(enum pstore_type_id type,
enum kmsg_dump_reason reason,
u64 *id, unsigned int part,
const char __user *buf,
bool compressed, size_t size,
struct pstore_info *psi)
{
...
ret = psi->write_buf(type, reason, id, part, psinfo->buf,
...
}
继续pstore注册:
if (pstore_is_mounted())
pstore_get_records(0);
如果pstore已经mounted,那就创建并填充文件by pstore_get_records:
/*
* Read all the records from the persistent store. Create
* files in our filesystem. Don't warn about -EEXIST errors
* when we are re-scanning the backing store looking to add new
* error records.
*/
void pstore_get_records(int quiet)
{
struct pstore_info *psi = psinfo; //tj: global psinfo
...
mutex_lock(&psi->read_mutex);
if (psi->open && psi->open(psi))
goto out;
while ((size = psi->read(&id, &type, &count, &time, &buf, &compressed,
&ecc_notice_size, psi)) > 0) {
if (compressed && (type == PSTORE_TYPE_DMESG)) {
if (big_oops_buf)
unzipped_len = pstore_decompress(buf,
big_oops_buf, size,
big_oops_buf_sz);
if (unzipped_len > 0) {
if (ecc_notice_size)
memcpy(big_oops_buf + unzipped_len,
buf + size, ecc_notice_size);
kfree(buf);
buf = big_oops_buf;
size = unzipped_len;
compressed = false;
} else {
pr_err("decompression failed;returned %d\n",
unzipped_len);
compressed = true;
}
}
rc = pstore_mkfile(type, psi->name, id, count, buf,
compressed, size + ecc_notice_size,
time, psi);
if (unzipped_len < 0) {
/* Free buffer other than big oops */
kfree(buf);
buf = NULL;
} else
unzipped_len = -1;
if (rc && (rc != -EEXIST || !quiet))
failed++;
}
if (psi->close)
psi->close(psi);
out:
mutex_unlock(&psi->read_mutex);
if needed,call pstore_decompress解压然后创建pstore文件by vfs接口pstore_mkfile。
pstore注册接下来是按类别分别注册:
if (psi->flags & PSTORE_FLAGS_DMESG)
pstore_register_kmsg();
if (psi->flags & PSTORE_FLAGS_CONSOLE)
pstore_register_console();
if (psi->flags & PSTORE_FLAGS_FTRACE)
pstore_register_ftrace();
if (psi->flags & PSTORE_FLAGS_PMSG)
pstore_register_pmsg();
psi->flags仍是由backend决定,只看pstore_register_kmsg和pstore_register_console。
pstore panic log注册
static struct kmsg_dumper pstore_dumper = {
.dump = pstore_dump,
};
/*
* Register with kmsg_dump to save last part of console log on panic.
*/
static void pstore_register_kmsg(void)
{
kmsg_dump_register(&pstore_dumper);
}
pstore_dump最终会call backend的write,直接用全局psinfo。
/*
* callback from kmsg_dump. (s2,l2) has the most recently
* written bytes, older bytes are in (s1,l1). Save as much
* as we can from the end of the buffer.
*/
static void pstore_dump(struct kmsg_dumper *dumper,
enum kmsg_dump_reason reason)
{
...
ret = psinfo->write(PSTORE_TYPE_DMESG, reason, &id, part,
oopscount, compressed, total_len, psinfo);
kmsg_dump_register是内核一种增加log dumper方法,called when kernel oopses or panic。
/**
* kmsg_dump_register - register a kernel log dumper.
* @dumper: pointer to the kmsg_dumper structure
*
* Adds a kernel log dumper to the system. The dump callback in the
* structure will be called when the kernel oopses or panics and must be
* set. Returns zero on success and %-EINVAL or %-EBUSY otherwise.
*/
int kmsg_dump_register(struct kmsg_dumper *dumper)
{
unsigned long flags;
int err = -EBUSY;
/* The dump callback needs to be set */
if (!dumper->dump)
return -EINVAL;
spin_lock_irqsave(&dump_list_lock, flags);
/* Don't allow registering multiple times */
if (!dumper->registered) {
dumper->registered = 1;
list_add_tail_rcu(&dumper->list, &dump_list);
err = 0;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dump_list_lock, flags);
return err;
}
/**
* kmsg_dump - dump kernel log to kernel message dumpers.
* @reason: the reason (oops, panic etc) for dumping
*
* Call each of the registered dumper's dump() callback, which can
* retrieve the kmsg records with kmsg_dump_get_line() or
* kmsg_dump_get_buffer().
*/
void kmsg_dump(enum kmsg_dump_reason reason)
{
struct kmsg_dumper *dumper;
unsigned long flags;
if ((reason > KMSG_DUMP_OOPS) && !always_kmsg_dump)
return;
rcu_read_lock();
list_for_each_entry_rcu(dumper, &dump_list, list) {
if (dumper->max_reason && reason > dumper->max_reason)
continue;
/* initialize iterator with data about the stored records */
dumper->active = true;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&logbuf_lock, flags);
dumper->cur_seq = clear_seq;
dumper->cur_idx = clear_idx;
dumper->next_seq = log_next_seq;
dumper->next_idx = log_next_idx;
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&logbuf_lock, flags);
/* invoke dumper which will iterate over records */
dumper->dump(dumper, reason);
/* reset iterator */
dumper->active = false;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
}
pstore console 注册
static struct console pstore_console = {
.name = "pstore",
.write = pstore_console_write,
.flags = CON_PRINTBUFFER | CON_ENABLED | CON_ANYTIME,
.index = -1,
};
static void pstore_register_console(void)
{
register_console(&pstore_console);
}
->write最终也会call backend write:
#ifdef CONFIG_PSTORE_CONSOLE
static void pstore_console_write(struct console *con, const char *s, unsigned c)
{
const char *e = s + c;
while (s < e) {
unsigned long flags;
u64 id;
if (c > psinfo->bufsize)
c = psinfo->bufsize;
if (oops_in_progress) {
if (!spin_trylock_irqsave(&psinfo->buf_lock, flags))
break;
} else {
spin_lock_irqsave(&psinfo->buf_lock, flags);
}
memcpy(psinfo->buf, s, c);
psinfo->write(PSTORE_TYPE_CONSOLE, 0, &id, 0, 0, 0, c, psinfo); // tj: here
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&psinfo->buf_lock, flags);
s += c;
c = e - s;
}
}
ramoops
下面来看下RAM backend: ramoops,先看probe:
static int ramoops_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
struct ramoops_platform_data *pdata = dev->platform_data;
...
if (!pdata->mem_size || (!pdata->record_size && !pdata->console_size &&
!pdata->ftrace_size && !pdata->pmsg_size)) {
pr_err("The memory size and the record/console size must be "
"non-zero\n");
goto fail_out;
}
...
cxt->size = pdata->mem_size;
cxt->phys_addr = pdata->mem_address;
cxt->memtype = pdata->mem_type;
cxt->record_size = pdata->record_size;
cxt->console_size = pdata->console_size;
cxt->ftrace_size = pdata->ftrace_size;
cxt->pmsg_size = pdata->pmsg_size;
cxt->dump_oops = pdata->dump_oops;
cxt->ecc_info = pdata->ecc_info;
pdata应该来源ramoops_register_dummy:
static void ramoops_register_dummy(void)
{
...
pr_info("using module parameters\n");
dummy_data = kzalloc(sizeof(*dummy_data), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dummy_data) {
pr_info("could not allocate pdata\n");
return;
}
dummy_data->mem_size = mem_size;
dummy_data->mem_address = mem_address;
dummy_data->mem_type = mem_type;
dummy_data->record_size = record_size;
dummy_data->console_size = ramoops_console_size;
dummy_data->ftrace_size = ramoops_ftrace_size;
dummy_data->pmsg_size = ramoops_pmsg_size;
dummy_data->dump_oops = dump_oops;
/*
* For backwards compatibility ramoops.ecc=1 means 16 bytes ECC
* (using 1 byte for ECC isn't much of use anyway).
*/
dummy_data->ecc_info.ecc_size = ramoops_ecc == 1 ? 16 : ramoops_ecc;
dummy = platform_device_register_data(NULL, "ramoops", -1,
dummy_data, sizeof(struct ramoops_platform_data));
有几个可配参数:
/*
* Ramoops platform data
* @mem_size memory size for ramoops
* @mem_address physical memory address to contain ramoops
*/
struct ramoops_platform_data {
unsigned long mem_size;
phys_addr_t mem_address;
unsigned int mem_type;
unsigned long record_size;
unsigned long console_size;
unsigned long ftrace_size;
unsigned long pmsg_size;
int dump_oops;
struct persistent_ram_ecc_info ecc_info;
};
mem_size:用于Ramoops的内存大小,表示分配给Ramoops的物理内存的大小。mem_address:用于Ramoops的物理内存地址,指定用于存储Ramoops的物理内存的起始地址。mem_type:内存类型,用于进一步描述内存的属性和特征。record_size:每个记录的大小console_size:控制台记录的大小ftrace_size:Ftrace记录的大小pmsg_size:pmsg消息记录的大小dump_oops:是否转储oops信息的标志,表示是否将oops信息转储到Ramoops中。ecc_info:RAM的ECC(纠错码)信息,用于提供关于ECC配置和处理的详细信息。
有个结构表示了ramoops的context:
struct ramoops_context {
struct persistent_ram_zone **przs;
struct persistent_ram_zone *cprz;
struct persistent_ram_zone *fprz;
struct persistent_ram_zone *mprz;
phys_addr_t phys_addr;
unsigned long size;
unsigned int memtype;
size_t record_size;
size_t console_size;
size_t ftrace_size;
size_t pmsg_size;
int dump_oops;
struct persistent_ram_ecc_info ecc_info;
unsigned int max_dump_cnt;
unsigned int dump_write_cnt;
/* _read_cnt need clear on ramoops_pstore_open */
unsigned int dump_read_cnt;
unsigned int console_read_cnt;
unsigned int ftrace_read_cnt;
unsigned int pmsg_read_cnt;
struct pstore_info pstore;
};
在ramoops_probe时也是把ramoops_platform_data的成员赋给了context对应的。要了解具体含义,继续probe:
paddr = cxt->phys_addr;
dump_mem_sz = cxt->size - cxt->console_size - cxt->ftrace_size
- cxt->pmsg_size;
err = ramoops_init_przs(dev, cxt, &paddr, dump_mem_sz);
if (err)
goto fail_out;
err = ramoops_init_prz(dev, cxt, &cxt->cprz, &paddr,
cxt->console_size, 0);
if (err)
goto fail_init_cprz;
err = ramoops_init_prz(dev, cxt, &cxt->fprz, &paddr, cxt->ftrace_size,
LINUX_VERSION_CODE);
if (err)
goto fail_init_fprz;
err = ramoops_init_prz(dev, cxt, &cxt->mprz, &paddr, cxt->pmsg_size, 0);
if (err)
goto fail_init_mprz;
cxt->pstore.data = cxt;
可见,是逐个init每个persistant ram zone,size一共有4段:
dump_mem_sz + cxt->console_size + cxt->ftrace_size + cxt->pmsg_size = cxt->size
mem_size就是总大小了,mem_address是ramoops的物理地址,record_size再看下oops/panic ram:
static int ramoops_init_przs(struct device *dev, struct ramoops_context *cxt,
phys_addr_t *paddr, size_t dump_mem_sz)
{
int err = -ENOMEM;
int i;
if (!cxt->record_size)
return 0;
if (*paddr + dump_mem_sz - cxt->phys_addr > cxt->size) {
dev_err(dev, "no room for dumps\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
cxt->max_dump_cnt = dump_mem_sz / cxt->record_size;
if (!cxt->max_dump_cnt)
return -ENOMEM;
ok dump_mem_size大小的区域分成max_dump_cnt个,每个记录大小是record_size。
接着会call persistent_ram_new来分配内存给这个ram zone。
for (i = 0; i < cxt->max_dump_cnt; i++) {
cxt->przs[i] = persistent_ram_new(*paddr, cxt->record_size, 0,
&cxt->ecc_info,
cxt->memtype, 0);
console/ftrace/pmsg ram zone同上分配。
最后处理flags并注册pstore:
cxt->pstore.flags = PSTORE_FLAGS_DMESG; //tj: 默认dump oops/panic
if (cxt->console_size)
cxt->pstore.flags |= PSTORE_FLAGS_CONSOLE;
if (cxt->ftrace_size)
cxt->pstore.flags |= PSTORE_FLAGS_FTRACE;
if (cxt->pmsg_size)
cxt->pstore.flags |= PSTORE_FLAGS_PMSG;
err = pstore_register(&cxt->pstore);
if (err) {
pr_err("registering with pstore failed\n");
goto fail_buf;
}
来看下ramoops pstore的定义的callback,他们通过全局psinfo而来:
static struct ramoops_context oops_cxt = {
.pstore = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "ramoops",
.open = ramoops_pstore_open,
.read = ramoops_pstore_read, // psi->read
.write_buf = ramoops_pstore_write_buf, //for non pmsg
.write_buf_user = ramoops_pstore_write_buf_user, //for pmsg
.erase = ramoops_pstore_erase,
},
};
pstore使用方法
ramoops
CONFIG_PSTORE=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_CONSOLE=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_PMSG=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_RAM=y
CONFIG_PANIC_TIMEOUT=-1
由于log数据存放于DDR,不能掉电,只能依靠自动重启机制来查看,故而要配置:CONFIG_PANIC_TIMEOUT,让系统在 panic 后能自动重启。
ramoops_mem: ramoops_mem {
reg = <0x0 0x110000 0x0 0xf0000>;
reg-names = "ramoops_mem";
};
ramoops {
compatible = "ramoops";
record-size = <0x0 0x20000>;
console-size = <0x0 0x80000>;
ftrace-size = <0x0 0x00000>;
pmsg-size = <0x0 0x50000>;
memory-region = <&ramoops_mem>;
};
mtdoops
内核配置
CONFIG_PSTORE=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_CONSOLE=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_PMSG=y
CONFIG_MTD_OOPS=y
CONFIG_MAGIC_SYSRQ=y
分区配置
cmdline方式:
bootargs = "console=ttyS1,115200 loglevel=8 rootwait root=/dev/mtdblock5 rootfstype=squashfs mtdoops.mtddev=pstore";
blkparts = "mtdparts=spi0.0:64k(spl)ro,256k(uboot)ro,64k(dtb)ro,128k(pstore),3m(kernel)ro,4m(rootfs)ro,-(data)";
part of方式:
bootargs = "console=ttyS1,115200 loglevel=8 rootwait root=/dev/mtdblock5 rootfstype=squashfs mtdoops.mtddev=pstore";
partition@60000 {
label = "pstore";
reg = <0x60000 0x20000>;
};
blkoops
配置内核
CONFIG_PSTORE=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_CONSOLE=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_PMSG=y
CONFIG_PSTORE_BLK=y
CONFIG_MTD_PSTORE=y
CONFIG_MAGIC_SYSRQ=y
配置分区
cmdline方式:
bootargs = "console=ttyS1,115200 loglevel=8 rootwait root=/dev/mtdblock5 rootfstype=squashfs pstore_blk.blkdev=pstore";
blkparts = "mtdparts=spi0.0:64k(spl)ro,256k(uboot)ro,64k(dtb)ro,128k(pstore),3m(kernel)ro,4m(rootfs)ro,-(data)";
part of方式:
bootargs = "console=ttyS1,115200 loglevel=8 rootwait root=/dev/mtdblock5 rootfstype=squashfs pstore_blk.blkdev=pstore";
partition@60000 {
label = "pstore";
reg = <0x60000 0x20000>;
};
pstore fs
挂载pstore文件系统
mount -t pstore pstore /sys/fs/pstore
挂载后,通过mount能看到类似这样的信息:
# mount
pstore on /sys/fs/pstore type pstore (rw,relatime)
如果需要验证,可以这样主动触发内核崩溃:
# echo c > /proc/sysrq-trigger
不同配置方式日志名称不同
ramoops
# mount -t pstore pstore /sys/fs/pstore/
# cd /sys/fs/pstore/
# ls
console-ramoops-0 dmesg-ramoops-0 dmesg-ramoops-1
mtdoops
# cat /dev/mtd3 > 1.txt
# cat 1.txt
blkoops
cd /sys/fs/pstore/
ls
dmesg-pstore_blk-0 dmesg-pstore_blk-1
pstore setup 流程:
ramoops_init
ramoops_register_dummy
ramoops_probe
ramoops_register
查看 pstore 数据保存流程:
register a pstore_dumper
// when panic happens, kmsg_dump is called
call dumper->dump
pstore_dump
查看 pstore 数据读取流程:
ramoops_probe
persistent_ram_post_init
pstore_register
pstore_get_records
ramoops_pstore_read
pstore_decompress (only for dmesg)
pstore_mkfile (save to files)
https://heapdump.cn/article/1961461
https://blog.csdn.net/u013836909/article/details/129894795
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK