

Curve Finance 漏洞复现
source link: https://kiprey.github.io/2023/08/curve_finance_vuln/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

智能合约在区块链的世界中较为重要。本文记录了笔者在复现 Python 智能合约编译器 Vyper 中的一个编译漏洞,该漏洞导致智能合约中的重入锁变得无效,进而使得合约易受重入攻击。
二、环境搭建
1. Vyper 构建
下载 Vyper 编译器源代码并通过 pip 安装依赖。
git clone [email protected]:vyperlang/vyper.git
cd vyper
# 依赖来自 setup.py & requirements-docs.txt,不可直接照搬
pip3 install "asttokens>=2.0.5,<3" "pycryptodome>=3.5.1,<4" "semantic-version>=2.10,<3" "importlib-metadata" "wheel" "sphinx==4.5.0" "recommonmark==0.6.0" "sphinx_rtd_theme==0.5.2"
运行 python3 -m vyper --help,能正常输出帮助信息即可:
$ python3 -m vyper --help
usage: __main__.py [-h] [--version] [--show-gas-estimates] [-f FORMAT] [--storage-layout-file STORAGE_LAYOUT [STORAGE_LAYOUT ...]]
[--evm-version {istanbul,berlin,london,paris,shanghai,cancun}] [--no-optimize] [--optimize {gas,codesize,none}] [--debug] [--no-bytecode-metadata]
[--traceback-limit TRACEBACK_LIMIT] [--verbose] [--standard-json] [--hex-ir] [-p ROOT_FOLDER] [-o OUTPUT_PATH]
input_files [input_files ...]
Pythonic Smart Contract Language for the EVM
positional arguments:
input_files Vyper sourcecode to compile
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--version show program's version number and exit
...
最后切换到漏洞引入点:
# https://github.com/vyperlang/vyper/commit/a09cdddd8ba249d1ce68ac31ec4496e50b8a25c7
git checkout a09cdddd
如果想要单步调试跟进,那就需要:
# 在 vyper 项目根目录下
cp ./vyper/__main__.py vyper.py
python3 vyper.py --help
2. 合约下载
合约的代码可以在链上合约地址处找到,例如 https://bscscan.com/address/0x245a45cdf2271d026976811a80c091fe5b49ac40#code
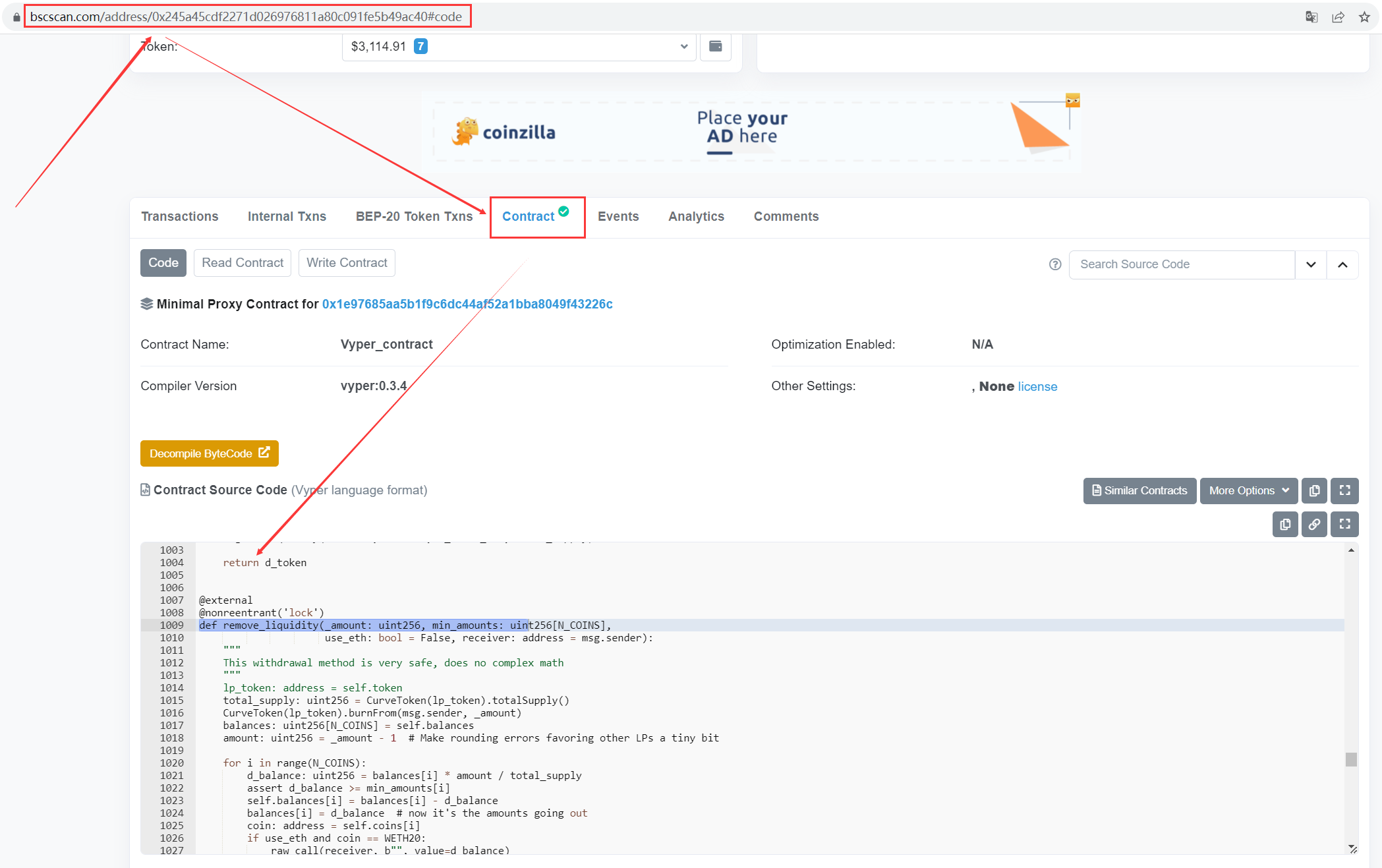
合约是开源的,肯定有不止一种找到合约源代码的方式,上面也只是举例演示一下。
三、漏洞根因
1. 安全的重入锁状态维护逻辑
在讲解漏洞根因之前,我们先来简单了解一下在引入漏洞 commit 之前,关于重入锁的状态维护逻辑。
对于重入锁来说,自然是需要在 Storage 上有一个 slot 用来存放锁的状态。也就是 get_nonreentrant_lock 函数做的事情:
# 引入漏洞 commit 前
def get_nonreentrant_lock(func_type, global_ctx):
nonreentrant_pre = [["pass"]]
nonreentrant_post = [["pass"]]
if func_type.nonreentrant:
nkey = global_ctx.get_nonrentrant_counter(func_type.nonreentrant)
nonreentrant_pre = [["seq", ["assert", ["iszero", ["sload", nkey]]], ["sstore", nkey, 1]]]
nonreentrant_post = [["sstore", nkey, 0]]
return nonreentrant_pre, nonreentrant_post
从代码中可以看到,当某个函数被标记为禁止重入时,vyper 会在需要用到重入锁的合约逻辑时,编译生成以上一系列的 IR。这些 IR 做的事情很简单,获取锁时检查锁是否为 0 && 将锁状态设置为 1;释放锁时重设锁状态为 0。
而存放锁状态的 slot 是通过 global_ctx.get_nonrentrant_counter 函数所得,也就是那个在漏洞 commit 里被标记为 dead code 的函数,该函数会根据传入的 key 来确定要用哪个 slot 来存放锁状态:
def get_nonrentrant_counter(self, key):
"""
Nonrentrant locks use a prefix with a counter to minimise deployment cost of a contract.
We're able to set the initial re-entrant counter using the sum of the sizes
of all the storage slots because all storage slots are allocated while parsing
the module-scope, and re-entrancy locks aren't allocated until later when parsing
individual function scopes. This relies on the deprecated _globals attribute
because the new way of doing things (set_data_positions) doesn't expose the
next unallocated storage location.
"""
if key in self._nonrentrant_keys:
return self._nonrentrant_keys[key]
else:
counter = (
sum(v.size for v in self._globals.values() if not isinstance(v.typ, MappingType))
+ self._nonrentrant_counter
)
self._nonrentrant_keys[key] = counter
self._nonrentrant_counter += 1
return counter
而在函数重入中,这个 key 值是 vyper 脚本中的那个字符串,例如以下代码中的 lock 字符串,它用于区分开不同的重入锁:
@external
@nonreentrant('lock')
def add_liquidity() -> uint256:
return 0
@external
@nonreentrant('lock')
def exchange() -> uint256:
return 0
总结一句话,在引入漏洞 commit 之前,vyper 使用脚本里重入锁的字符串来区分开不同的重入锁,而区分的方式是根据字符串来选择用于存放重入锁状态的 slot 位置。这样一来,倘若不同函数使用了相同名称的重入锁,则这些重入锁将会使用同一个 slot,来抵御重入攻击。
2. 带有漏洞的重入锁状态维护逻辑
引入漏洞前,vyper 用于存放重入锁状态的各个 slot 是直接追加在全局变量分配存储的末尾:
def get_nonrentrant_counter(self, key):
if key in self._nonrentrant_keys:
return self._nonrentrant_keys[key]
else:
# 注意这里的 counter 是怎么计算得出的
counter = (
sum(v.size for v in self._globals.values() if not isinstance(v.typ, MappingType))
+ self._nonrentrant_counter
)
self._nonrentrant_keys[key] = counter
self._nonrentrant_counter += 1
return counter
漏洞 commit 尝试将重入锁的状态变量与其他全局变量的分配合并掉,即在解析 vyper AST 阶段时就一并做掉重入锁的 slot 分配,而非在后续生成 IR 阶段时再去动态生成和指定重入锁的 slot 位置。因此 global_ctx.get_nonrentrant_counter 这个用来动态生成重入锁 slot 位置的函数就不再被调用了,被开发者标记为 dead code。而指定重入锁位置的重任则交付到了 set_storage_slots 函数上,该函数在 AST 解析阶段执行,其先前的作用只是用来指定各个变量存储的 slot 位置。
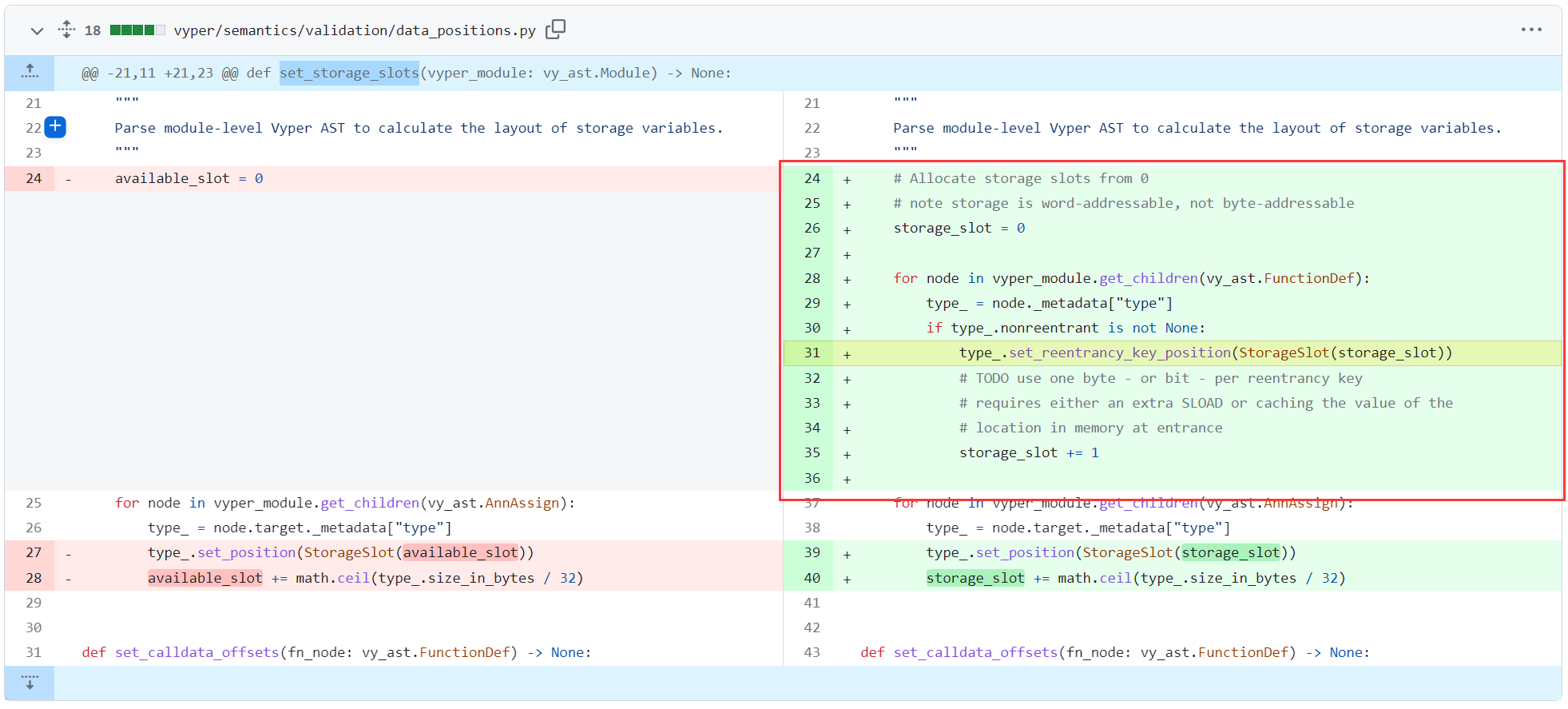
从这里我们可以看到,在漏洞 commit 里 vyper 是怎么指定各个函数的重入锁所在 slot 呢?没错,它每个函数分配一个重入锁 slot,也就是说对于不同函数的同名重入锁而言,这些重入锁相互之间不会阻止重入。
3. 漏洞演示
以下是一个关于该 vyper 重入漏洞的 POC:
@external
@nonreentrant('lock')
def add_liquidity() -> uint256:
return 0
@external
@nonreentrant('lock')
def exchange() -> uint256:
return 0
这个 POC 的逻辑很简单,它声明了两个不同的函数,但这两个函数使用了相同名称的重入锁。我们来输出它的 IR 看看:
输出 IR 命令:python3 vyper.py -f ir <vyper-script-path>
$ python3 vyper.py -f ir vyper_workdir/test.vy
[seq,
[return,
0,
[lll,
[seq,
[if, [lt, calldatasize, 4], [goto, fallback]],
[mstore, 28, [calldataload, 0]],
[with,
_func_sig,
[mload, 0],
[seq,
[assert, [iszero, callvalue]],
# Line 3
[if,
[eq, _func_sig, 3964006281 <add_liquidity()>],
[seq,
[assert, [iszero, [sload, 0]]], # 检查重入锁状态
[sstore, 0 /*slot*/, 1 /*val*/], # 获取重入锁
pass,
# Line 4
[mstore, 0, 0],
[seq_unchecked, [sstore, 0, 0], [return, 0, 32]],
# Line 3
[sstore, 0, 0], # 释放重入锁
stop]],
# Line 8
[if,
[eq, _func_sig, 3539412570 <exchange()>],
[seq,
[assert, [iszero, [sload, 1]]], # 检查重入锁状态
[sstore, 1, 1], # 获取重入锁
pass,
# Line 9
[mstore, 0, 0],
[seq_unchecked, [sstore, 1, 0], [return, 0, 32]],
# Line 8
[sstore, 1, 0], # 释放重入锁
stop]]]],
[seq_unchecked, [label, fallback], /* Default function */ [revert, 0, 0]]],
0]]]
可以看到那两对 sstore 指令使用的 slot 不是同一个,第一个函数使用了 slot0,而第二个函数使用了 slot1。
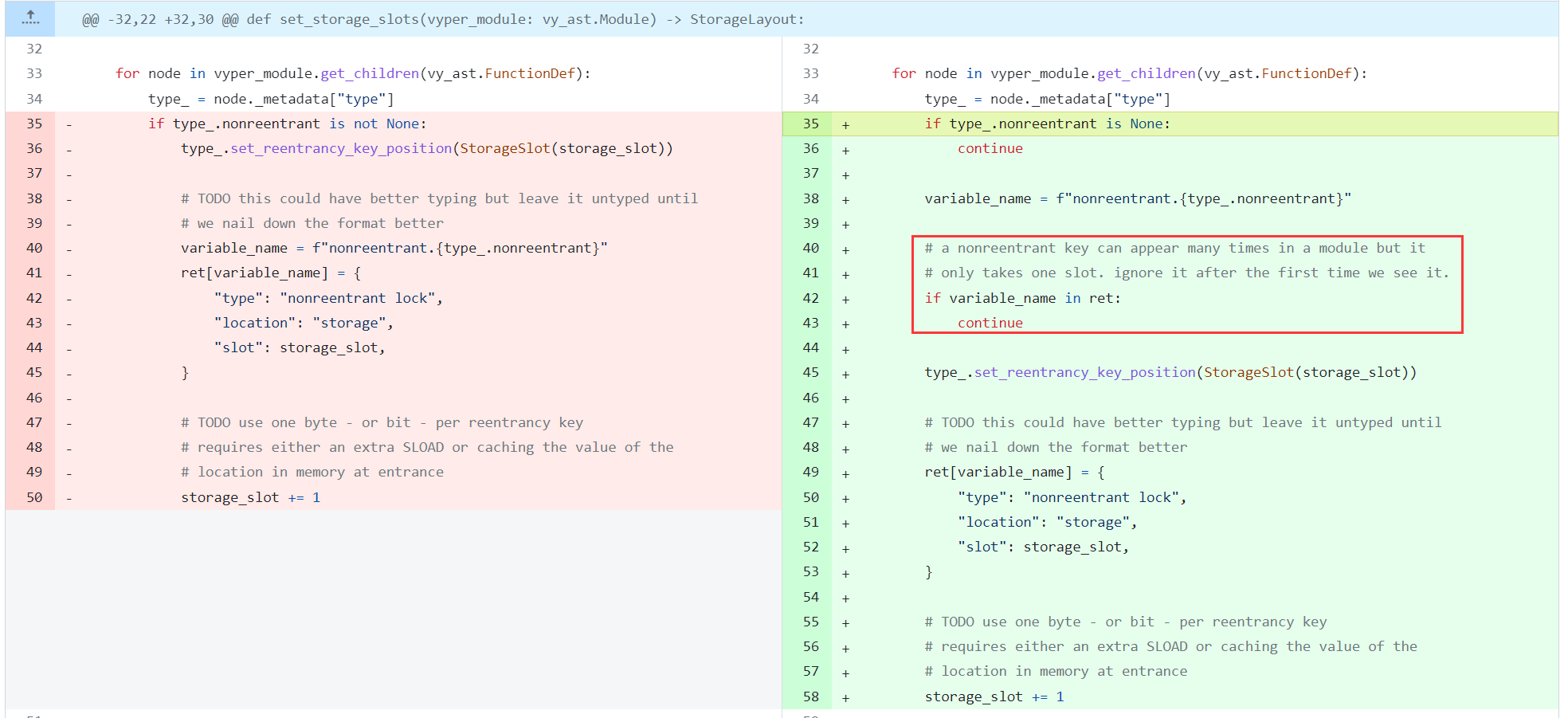
4. 漏洞修复
漏洞补丁很简单,只允许在出现不同名的重入锁时才使用新的 slot:
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK