Tomcat 系列篇一-介绍下 connector
source link: https://nicksxs.me/2023/09/10/Tomcat-%E7%B3%BB%E5%88%97%E7%AF%87%E4%B8%80-%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D%E4%B8%8B-connector/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Tomcat 系列篇一-介绍下 connector
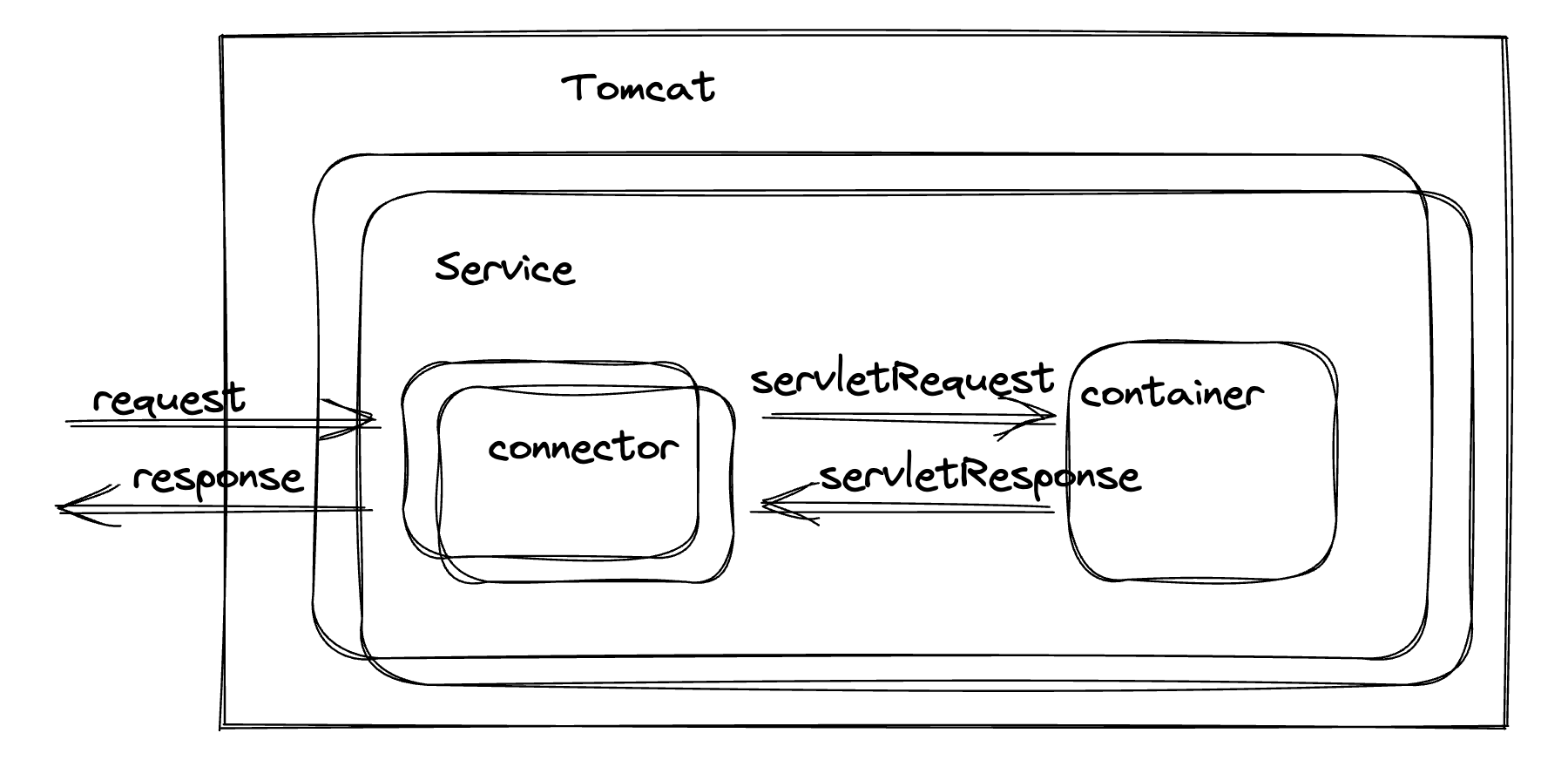
tomcat的主体架构里,connector 作为核心的连接器
这也是个架构的优化,将连接跟请求处理分开,可以适配各种连接协议
连接器的初始化逻辑,是在初始化 WebServer 的时候调用org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory#getWebServer
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory : this.createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
// 这里就是创建 Connector
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
this.customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);而 connector 中最重要的就是 ProtocolHandler ,初始化代码中org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector#Connector(java.lang.String)
public Connector(String protocol) {
boolean apr = AprStatus.getUseAprConnector() && AprStatus.isInstanceCreated()
&& AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable();
ProtocolHandler p = null;
try {
p = ProtocolHandler.create(protocol, apr);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e);
}
if (p != null) {
protocolHandler = p;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocolHandler.getClass().getName();
} else {
protocolHandler = null;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocol;
}
// Default for Connector depends on this system property
setThrowOnFailure(Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"));
}这里就调用了org.apache.coyote.ProtocolHandler#create
根据协议来生成对应的,我们这里默认就是org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol
public static ProtocolHandler create(String protocol, boolean apr)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
if (protocol == null || "HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol)
|| (!apr && org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))
|| (apr && org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))) {
if (apr) {
return new org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol();
} else {
return new org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol();
}
} else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)
|| (!apr && org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))
|| (apr && org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))) {
if (apr) {
return new org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol();
} else {
return new org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol();
}
} else {
// Instantiate protocol handler
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocol);
return (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
}
}而这个初始化就主要做的是初始化 EndPoint
public Http11NioProtocol() {
super(new NioEndpoint());
}这个调用父类的方法是调用的org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Protocol#AbstractHttp11Protocol
public AbstractHttp11Protocol(AbstractEndpoint<S,?> endpoint) {
super(endpoint);
setConnectionTimeout(Constants.DEFAULT_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT);
ConnectionHandler<S> cHandler = new ConnectionHandler<>(this);
setHandler(cHandler);
getEndpoint().setHandler(cHandler);
}而后在 Tomcat 启动后,在启动 connector 的时候
是在StandardService 添加 connector 时,启动了 connectororg.apache.catalina.core.StandardService#addConnector
@Override
public void addConnector(Connector connector) {
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
connector.setService(this);
Connector results[] = new Connector[connectors.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(connectors, 0, results, 0, connectors.length);
results[connectors.length] = connector;
connectors = results;
}
try {
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
connector.start();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
sm.getString("standardService.connector.startFailed", connector), e);
}
// Report this property change to interested listeners
support.firePropertyChange("connector", null, connector);
}而后就会调用到 Connector 的 initInternal 方法org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector#initInternal
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (protocolHandler == null) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"));
}
// Initialize adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
if (service != null) {
protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
// Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default
if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) {
setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods());
}
if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprStatus.isInstanceCreated()) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprListener",
getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
}
if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprStatus.isAprAvailable()) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprLibrary",
getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
}
if (AprStatus.isAprAvailable() && AprStatus.getUseOpenSSL() &&
protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol) {
AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler =
(AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?>) protocolHandler;
if (jsseProtocolHandler.isSSLEnabled() &&
jsseProtocolHandler.getSslImplementationName() == null) {
// OpenSSL is compatible with the JSSE configuration, so use it if APR is available
jsseProtocolHandler.setSslImplementationName(OpenSSLImplementation.class.getName());
}
}
try {
protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
}
}这里继续往下走就是 protocolHandler 的 init 方法
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.init", getName()));
logPortOffset();
}
if (oname == null) {
// Component not pre-registered so register it
oname = createObjectName();
if (oname != null) {
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null);
}
}
if (this.domain != null) {
ObjectName rgOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=" + getName());
this.rgOname = rgOname;
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(
getHandler().getGlobal(), rgOname, null);
}
String endpointName = getName();
endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length()-1));
endpoint.setDomain(domain);
endpoint.init();
}看一下继承关系
然后就看到这里调用了 endpoint.init() ,走的也是父类的初始化方法,org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint#init
public final void init() throws Exception {
if (bindOnInit) {
bindWithCleanup();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_INIT;
}
if (this.domain != null) {
// Register endpoint (as ThreadPool - historical name)
oname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=ThreadPool,name=\"" + getName() + "\"");
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null);
ObjectName socketPropertiesOname = new ObjectName(domain +
":type=SocketProperties,name=\"" + getName() + "\"");
socketProperties.setObjectName(socketPropertiesOname);
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(socketProperties, socketPropertiesOname, null);
for (SSLHostConfig sslHostConfig : findSslHostConfigs()) {
registerJmx(sslHostConfig);
}
}
}然后接着调用了org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint#bindWithCleanup
private void bindWithCleanup() throws Exception {
try {
bind();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Ensure open sockets etc. are cleaned up if something goes
// wrong during bind
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
unbind();
throw t;
}
}这里的 bind 方法调用的是org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint#bind
@Override
public void bind() throws Exception {
initServerSocket();
setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(1));
// Initialize SSL if needed
initialiseSsl();
}这里的 initServerSocket是后面抽出来的,方便扩展,主要就是开启 ServerSocketChannel,绑定端口
// Separated out to make it easier for folks that extend NioEndpoint to
// implement custom [server]sockets
protected void initServerSocket() throws Exception {
if (getUseInheritedChannel()) {
// Retrieve the channel provided by the OS
Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel();
if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) {
serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel) ic;
}
if (serverSock == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited"));
}
} else if (getUnixDomainSocketPath() != null) {
SocketAddress sa = JreCompat.getInstance().getUnixDomainSocketAddress(getUnixDomainSocketPath());
serverSock = JreCompat.getInstance().openUnixDomainServerSocketChannel();
serverSock.bind(sa, getAcceptCount());
if (getUnixDomainSocketPathPermissions() != null) {
Path path = Paths.get(getUnixDomainSocketPath());
Set<PosixFilePermission> permissions =
PosixFilePermissions.fromString(getUnixDomainSocketPathPermissions());
if (path.getFileSystem().supportedFileAttributeViews().contains("posix")) {
FileAttribute<Set<PosixFilePermission>> attrs = PosixFilePermissions.asFileAttribute(permissions);
Files.setAttribute(path, attrs.name(), attrs.value());
} else {
java.io.File file = path.toFile();
if (permissions.contains(PosixFilePermission.OTHERS_READ) && !file.setReadable(true, false)) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.perms.readFail", file.getPath()));
}
if (permissions.contains(PosixFilePermission.OTHERS_WRITE) && !file.setWritable(true, false)) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.perms.writeFail", file.getPath()));
}
}
}
} else {
serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open();
socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket());
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(), getPortWithOffset());
serverSock.bind(addr, getAcceptCount());
}
serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior
}接着我们来看下 start 方法,这里多数是复用的 父类的方法org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint#start
public final void start() throws Exception {
if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) {
bindWithCleanup();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
startInternal();
}startInternal 才是 NioEndPoint 中的处理
/**
* Start the NIO endpoint, creating acceptor, poller threads.
*/
@Override
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
if (socketProperties.getProcessorCache() != 0) {
processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
}
if (socketProperties.getEventCache() != 0) {
eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getEventCache());
}
if (socketProperties.getBufferPool() != 0) {
nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getBufferPool());
}
// Create worker collection
if (getExecutor() == null) {
createExecutor();
}
initializeConnectionLatch();
// Start poller thread
poller = new Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(poller, getName() + "-Poller");
pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
startAcceptorThread();
}
}上面是启动了一个 Poller 线程,在startAcceptorThread 里是启动了 acceptor
protected void startAcceptorThread() {
acceptor = new Acceptor<>(this);
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor";
acceptor.setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptor, threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
}启动后运行的代码
@Override
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
try {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (!stopCalled) {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (endpoint.isPaused() && !stopCalled) {
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (stopCalled) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
//if we have reached max connections, wait
endpoint.countUpOrAwaitConnection();
// Endpoint might have been paused while waiting for latch
// If that is the case, don't accept new connections
if (endpoint.isPaused()) {
continue;
}
U socket = null;
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();
} catch (Exception ioe) {
// We didn't get a socket
endpoint.countDownConnection();
if (endpoint.isRunning()) {
// Introduce delay if necessary
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
// re-throw
throw ioe;
} else {
break;
}
}
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
// Configure the socket
if (!stopCalled && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to
// an appropriate processor if successful
if (!endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)) {
endpoint.closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
endpoint.destroySocket(socket);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
String msg = sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail");
// APR specific.
// Could push this down but not sure it is worth the trouble.
if (t instanceof Error) {
Error e = (Error) t;
if (e.getError() == 233) {
// Not an error on HP-UX so log as a warning
// so it can be filtered out on that platform
// See bug 50273
log.warn(msg, t);
} else {
log.error(msg, t);
}
} else {
log.error(msg, t);
}
}
}
} finally {
stopLatch.countDown();
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}这行socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();是 accept 等待线程进来,进来以后调用
@Override
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = null;
try {
// Allocate channel and wrapper
NioChannel channel = null;
if (nioChannels != null) {
channel = nioChannels.pop();
}
if (channel == null) {
SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler(
socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(),
socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(),
socketProperties.getDirectBuffer());
if (isSSLEnabled()) {
channel = new SecureNioChannel(bufhandler, this);
} else {
channel = new NioChannel(bufhandler);
}
}
NioSocketWrapper newWrapper = new NioSocketWrapper(channel, this);
channel.reset(socket, newWrapper);
connections.put(socket, newWrapper);
socketWrapper = newWrapper;
// Set socket properties
// Disable blocking, polling will be used
socket.configureBlocking(false);
if (getUnixDomainSocketPath() == null) {
socketProperties.setProperties(socket.socket());
}
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
socketWrapper.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
poller.register(socketWrapper);
return true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.socketOptionsError"), t);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
if (socketWrapper == null) {
destroySocket(socket);
}
}
// Tell to close the socket if needed
return false;
}这里就是最重要的封装了 NioSocketWrapper, 然后注册到 Poller,
我们再来看 Poller 代码,注册其实是添加事件 event
public void register(final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper) {
socketWrapper.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into.
PollerEvent event = null;
if (eventCache != null) {
event = eventCache.pop();
}
if (event == null) {
event = new PollerEvent(socketWrapper, OP_REGISTER);
} else {
event.reset(socketWrapper, OP_REGISTER);
}
addEvent(event);
}然后Poller 的运行方法会处理这些 event
@Override
public void run() {
// Loop until destroy() is called
while (true) {
boolean hasEvents = false;
try {
if (!close) {
hasEvents = events();
if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {
// If we are here, means we have other stuff to do
// Do a non blocking select
keyCount = selector.selectNow();
} else {
keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);
}
wakeupCounter.set(0);
}
if (close) {
events();
timeout(0, false);
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe);
}
break;
}
// Either we timed out or we woke up, process events first
if (keyCount == 0) {
hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
}
} catch (Throwable x) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorLoopError"), x);
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
// Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch
// any active event.
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) sk.attachment();
// Attachment may be null if another thread has called
// cancelledKey()
if (socketWrapper != null) {
processKey(sk, socketWrapper);
}
}
// Process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
}
getStopLatch().countDown();
}如果 events 方法返回了 true 代表有事件,就会跑到processKey(sk, socketWrapper); 来处理这个事件
而这里的 processKey 也比较复杂,
protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper) {
try {
if (close) {
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
} else if (sk.isValid()) {
if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable()) {
if (socketWrapper.getSendfileData() != null) {
processSendfile(sk, socketWrapper, false);
} else {
unreg(sk, socketWrapper, sk.readyOps());
boolean closeSocket = false;
// Read goes before write
if (sk.isReadable()) {
if (socketWrapper.readOperation != null) {
if (!socketWrapper.readOperation.process()) {
closeSocket = true;
}
} else if (socketWrapper.readBlocking) {
synchronized (socketWrapper.readLock) {
socketWrapper.readBlocking = false;
socketWrapper.readLock.notify();
}
} else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) {
closeSocket = true;
}
}
if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) {
if (socketWrapper.writeOperation != null) {
if (!socketWrapper.writeOperation.process()) {
closeSocket = true;
}
} else if (socketWrapper.writeBlocking) {
synchronized (socketWrapper.writeLock) {
socketWrapper.writeBlocking = false;
socketWrapper.writeLock.notify();
}
} else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) {
closeSocket = true;
}
}
if (closeSocket) {
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
}
}
}
} else {
// Invalid key
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.keyProcessingError"), t);
}
}正常请求回到这else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true))
然后调用processSocket 进行处理,
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if (socketWrapper == null) {
return false;
}
SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = null;
if (processorCache != null) {
sc = processorCache.pop();
}
if (sc == null) {
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);
} else {
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
}
Executor executor = getExecutor();
if (dispatch && executor != null) {
executor.execute(sc);
} else {
sc.run();
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}这里就会调用 createSocketProcessor 进行处理了,不过这是下一篇的内容了。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK