

玩转SpringBoot—启动源码及外部化配置
source link: https://www.51cto.com/article/768754.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

玩转SpringBoot—启动源码及外部化配置

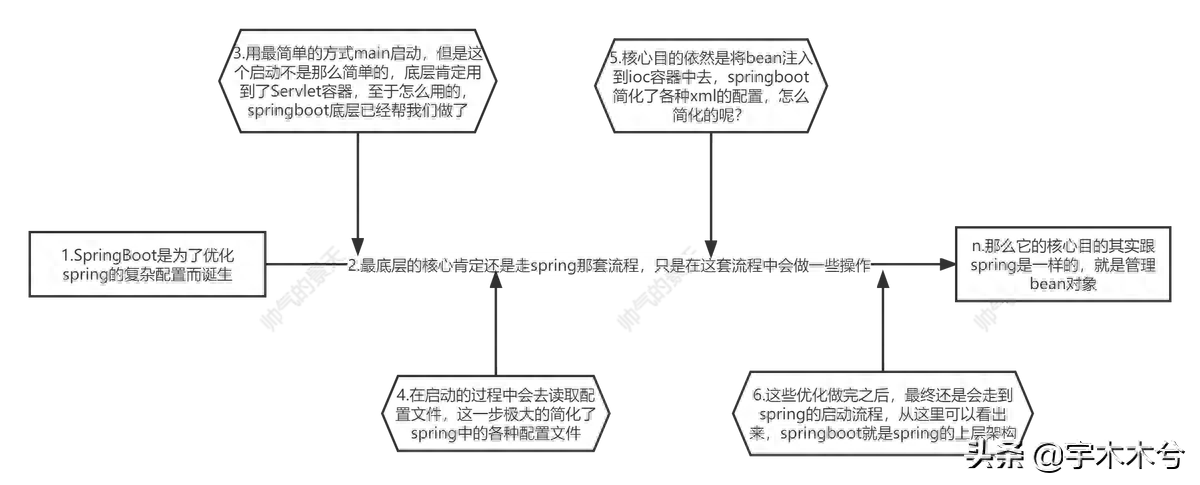
- 理解springboot的总体启动流程,并能口述大概
- 理清配置文件的加载流程
第1章 main入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
//代码很简单SpringApplication.run();
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApp.class, args);
}public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource,
String... args) {
//这个里面调用了run() 方法,我们转到定义
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
//这个run方法代码也很简单,就做了两件事情
//1、new了一个SpringApplication() 这么一个对象
//2、执行new出来的SpringApplication()对象的run()方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}上面代码主要做了两件事情。
- 第一步new了一个SpringApplication对象
- 第二步调用了run()方法。
一、SpringApplication
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//1、先把主类保存起来
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//2、判断运行项目的类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//3、扫描当前路径下META-INF/spring.factories文件的,加载ApplicationContextInitializer接口实例
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//4、扫描当前路径下META-INF/spring.factories文件的,加载ApplicationListener接口实例
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}1、判断运行环境
构造方法内会调用枚举WebApplicationType的deduceFromClasspath方法获得应用类型并设置当前应用是普通web应用、响应式web应用还是非web应用。
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();deduceFromClasspath方法由枚举WebApplicationType提供,具体实现如下:
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
//当classpath下只存在org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler,
//且不存在org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet,也不存在
//org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer则运行环境为reactive,该模式是非阻塞模式
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}推断的过程中重点调用了ClassUtils.isPresent()方法,用来判断指定类名的类是否存在,是否可以进行加载。ClassUtils.isPresent()方法源代码如下:
public static boolean isPresent(String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
forName(className, classLoader);
return true;
}
catch (IllegalAccessError err) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Readability mismatch in inheritance hierarchy of class [" +
className + "]: " + err.getMessage(), err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Typically ClassNotFoundException or NoClassDefFoundError...
return false;
}
}isPresent()方法调用了forName()方法,如果在调用forName()方法的过程中出现异常则返回false,也就是目标类不存在。否则,返回true。
看一下forName()方法的部分代码:
public static Class<?> forName(String name, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ClassNotFoundException, LinkageError {
// 此处省略一些非空和基础类型的判断逻辑代码
ClassLoader clToUse = classLoader;
if (clToUse == null) {
//如果为空则获取默认classLoader
clToUse = getDefaultClassLoader();
}
try {
// 返回加载户的Class。
return Class.forName(name, false, clToUse);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// 如果直接加载类出现异常,则尝试加载内部类。
int lastDotIndex = name.lastIndexOf(PACKAGE_SEPARATOR);
if (lastDotIndex != -1) {
// 拼接内部类
String innerClassName =
name.substring(0, lastDotIndex) + INNER_CLASS_SEPARATOR + name.substring(lastDotIndex + 1);
try {
return Class.forName(innerClassName, false, clToUse);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex2) {
// Swallow - let original exception get through
}
}
throw ex;
}
}通过以上核心代码,可得知forName()方法主要做的事情就是获得类加载器,尝试直接加载类,如果失败则尝试加载该类的内部类,如果依旧失败,则抛出异常。
因此,整个应用类型的推断分以下步骤:
- SpringBoot调用SpringApplication构造方法;
- SpringApplication构造方法调用枚举类的类型推断方法deduceFromClasspath()。
- deduceFromClasspath()方法通过ClassUtils.isPresent()返回结果为true或false来确定是否加载成功指定的类。
- ClassUtils.isPresent()方法通过调用forName()方法并捕获异常来确定是否能够成功加载该类。
- forName()方法通过尝试加载指定类和指定类的内部类来确定该类是否存在,存在则返回该类,不存在则抛异常。
在类型推断的过程中枚举类WebApplicationType定义了具体去加载哪些类:
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org."
+ "springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";- 如果应用程序存在DispatcherHandler并且不存在DispatcherServlet和ServletContainer则为响应式web应用,需加载并启动内嵌的响应式web服务。
- 如果应用程序不包含Servlet和ConfigurableWebApplicationContext则为普通应用程序。
- 其他情况则为基于servlet的web应用,需加载并启动内嵌的web服务。
2、初始化器和监听器
利用SPI机制扫描 META-INF/spring.factories 这个文件,并且加载ApplicationContextInitializer、ApplicationListener 接口实例。
- ApplicationContextInitializer 这个类当springboot上下文Context初始化完成后会调用。
- ApplicationListener 当springboot启动时事件change后都会触发。
总结:上面就是SpringApplication初始化的代码,new SpringApplication()没做啥事情 ,利用SPI机制主要加载了META-INF/spring.factories 下面定义的事件监听器接口实现类。
二、执行run方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
<!--1、这个是一个计时器,没什么好说的-->
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
<!--2、这个也不是重点,就是设置了一些环境变量-->
configureHeadlessProperty();
<!--3、获取事件监听器SpringApplicationRunListener类型,并且执行starting()方法-->
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
<!--4、把参数args封装成DefaultApplicationArguments,这个了解一下就知道-->
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
<!--5、这个很重要准备环境了,并且把环境跟spring上下文绑定好,并且执行environmentPrepared()方法-->
//准备容器环境、这里会加载配置文件。在这个方法里面会调用所有监听器Listener的onApplicationEvent(event);
// 此时有一个与配置文件相关的监听器就会被加载`ConfigFileApplicationListener`
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments);
<!--6、判断一些环境的值,并设置一些环境的值-->
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
<!--7、打印banner-->
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
<!--8、创建上下文,根据项目类型创建上下文-->
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
<!--9、准备上下文,执行完成后调用contextPrepared()方法,contextLoaded()方法-->
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
<!--10、这个是spring启动的代码了,这里就回去里面就回去扫描并且初始化单实列bean了-->
//这个refreshContext()加载了bean,还启动了内置web容器,需要细细的去看看
refreshContext(context);
<!--11、啥事情都没有做-->
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
<!--12、执行ApplicationRunListeners中的started()方法-->
listeners.started(context);
<!--执行Runner(ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner)-->
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}第2章 环境变量及配置
一、prepareEnvironment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 创建和配置环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}二、getOrCreateEnvironment
/**
* 该方法根据webApplicationType判断当前项目是什么类型项目
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
//webApplicationType是在new SpringApplication方法中通过WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath()进行赋值枚举WebApplicationType中定义了三个应用类型:
- NONE:应用程序不作为web应用启动,不启动内嵌的服务。
- SERVLET:应用程序以基于servlet的web应用启动,需启动内嵌servlet web服务。
- REACTIVE:应用程序以响应式web应用启动,需启动内嵌的响应式web服务。
这里调用newStandardServletEnvironment()方法。
StandardServletEnvironment继承了StandardEnvironment方法,StandardEnvironment又继承了AbstractEnvironment方法;在AbstractEnvironment方法中调用了customizePropertySources方法。
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
}customizePropertySources方法会回调StandardServletEnvironment方法中的customizePropertySources方法。
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
//在这里又调用了父类StandardEnvironment的方法
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}到这里为止propertySources里面就加载了servletConfigInitParams、servletContextInitParams、systemProperties、systemEnvironment。
然后回到prepareEnvironment方法中,在listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);方法中去进行监听。
三、environmentPrepared
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}
}继续进入environmentPrepared方法,会进入到SpringApplicationRunListener接口,这个接口在run方法中的getRunListeners里面获取,最终是在sprin.factories里面进行加载实现类EventPublishingRunListener,执行的是EventPublishingRunListener类中的environmentPrepared方法。
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
}multicastEvent
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}invokeListener
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}doInvokeListener
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}进入ConfigFileApplicationListener实现类中的onApplicationEvent方法。
onApplicationEvent
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
//在这个方法里面读取配置文件
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
//进入
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
//进入
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
//load方法是读取配置文件的核心方法
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}void load() {
FilteredPropertySource.apply(this.environment, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, LOAD_FILTERED_PROPERTY,
(defaultProperties) -> {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (isDefaultProfile(profile)) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter,
addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
addLoadedPropertySources();
applyActiveProfiles(defaultProperties);
});
}createApplicationContext
一起来看下context = createApplicationContext(); 这段代码,这段代码主要是根据项目类型创建上下文,并且会注入几个核心组件类。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
//1:会去注入一些spring核心组件
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}Web类型项目创建上下文对象AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 。这里会把 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 等一些核心组件加入到Spring容器。
五、refreshContext
下面一起来看下refreshContext(context) 这个方法,这个方法启动spring的代码加载了bean,还启动了内置web容器。
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 转到定义看看
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
//看看refresh()方法去
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}转到AbstractApplicationContext - >refresh()方法里面发现这是spring容器启动代码。
/**
* 加载或刷新一个持久化的配置,可能是XML文件、属性文件或关系数据库模式。
* 由于这是一种启动方法,如果失败,应该销毁已经创建的单例,以避免悬空资源。
* 换句话说,在调用该方法之后,要么全部实例化,要么完全不实例化。
* @throws 如果bean工厂无法初始化,则抛出 BeansException 异常
* @throws 如果已经初始化且不支持多次刷新,则会抛出 IllegalStateException 异常
*/
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
//加载或刷新配置前的同步处理
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 为刷新而准备此上下文
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类去刷新内部bean工厂。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备好bean工厂,以便在此上下文中使用。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行后置处理。
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用在上下文中注册为bean的工厂处理器。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册拦截bean创建的bean处理器。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化此上下文的 message resource 消息资源。
initMessageSource();
// 为这个上下文初始化事件多路广播器。
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化特定上下文子类中的其他特殊bean。
onRefresh();
// 注册监听器(检查监听器的bean并注册它们)。
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余的(非 lazy-init 懒初始化的)单例。
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后一步: 发布相应的事件。
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 销毁已经创建的单例,以避免悬空资源。
destroyBeans();
// 重置 'active' 表示.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// 将异常传播给调用者。
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 重置Spring内核中的共用的缓存,因为我们可能再也不需要单例bean的元数据了……
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK