

系统学习rocketmq源码
source link: https://dcbupt.github.io/2020/05/26/blog_article/%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E7%B3%BB%E5%88%97/%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0rocketmq%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.


客户端注册 rocketmq 组件
如果是 sb 应用,rocketmq 提供 starter 方式自动装配 bean,需要引入依赖:rocketmq-spring-boot
spring.factories 文件里指定配置类RocketMQAutoConfiguration,由它注册 producer 和 consumer bean 到 bf
注册 producer
- 通过
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RocketMQProperties.class)注册应用配置绑定 bean:RocketMQProperties,该 bean 包含了应用配置文件里对 rocketmq 的配置信息,producer 和 consumer 在创建过程中都通过该 bean 拿到并注入这些全局配置参数- 应用配置里 rocketmq 必备的配置项是 name-server(ns 地址)
- 如果指定了 producer.group 会创建 producer 实例
- 如果指定了 pull-consumer.group 和 pull-consumer.topic,会创建 consumer 实例
- producer 实例类型是
DefaultMQProducer
@Bean(PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DefaultMQProducer.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "rocketmq", value = {
"name-server",
"producer.group"
}) public DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer(RocketMQProperties rocketMQProperties) {
RocketMQProperties.Producer producerConfig = rocketMQProperties.getProducer();
String nameServer = rocketMQProperties.getNameServer();
String groupName = producerConfig.getGroup();
Assert.hasText(nameServer, "[rocketmq.name-server] must not be null");
Assert.hasText(groupName, "[rocketmq.producer.group] must not be null");
String accessChannel = rocketMQProperties.getAccessChannel();
String ak = rocketMQProperties.getProducer().getAccessKey();
String sk = rocketMQProperties.getProducer().getSecretKey();
boolean isEnableMsgTrace = rocketMQProperties.getProducer().isEnableMsgTrace();
String customizedTraceTopic = rocketMQProperties.getProducer().getCustomizedTraceTopic();
DefaultMQProducer producer = RocketMQUtil.createDefaultMQProducer(groupName, ak, sk, isEnableMsgTrace, customizedTraceTopic);
producer.setNamesrvAddr(nameServer);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(accessChannel)) {
producer.setAccessChannel(AccessChannel.valueOf(accessChannel));
}
producer.setSendMsgTimeout(producerConfig.getSendMessageTimeout());
producer.setRetryTimesWhenSendFailed(producerConfig.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed());
producer.setRetryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed(producerConfig.getRetryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed());
producer.setMaxMessageSize(producerConfig.getMaxMessageSize());
producer.setCompressMsgBodyOverHowmuch(producerConfig.getCompressMessageBodyThreshold());
producer.setRetryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK(producerConfig.isRetryNextServer());
producer.setUseTLS(producerConfig.isTlsEnable());
producer.setNamespace(producerConfig.getNamespace());
producer.setInstanceName(producerConfig.getInstanceName());
log.info(String.format("a producer (%s) init on namesrv %s", groupName, nameServer));
return producer;
}
注册 consumer
- consumer 实例类型是
DefaultLitePullConsumer
@Bean(CONSUMER_BEAN_NAME)@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DefaultLitePullConsumer.class)@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "rocketmq", value = {
"name-server",
"pull-consumer.group",
"pull-consumer.topic"
}) public DefaultLitePullConsumer defaultLitePullConsumer(RocketMQProperties rocketMQProperties) throws MQClientException {
RocketMQProperties.PullConsumer consumerConfig = rocketMQProperties.getPullConsumer();
String nameServer = rocketMQProperties.getNameServer();
String groupName = consumerConfig.getGroup();
String topicName = consumerConfig.getTopic();
Assert.hasText(nameServer, "[rocketmq.name-server] must not be null");
Assert.hasText(groupName, "[rocketmq.pull-consumer.group] must not be null");
Assert.hasText(topicName, "[rocketmq.pull-consumer.topic] must not be null");
String accessChannel = rocketMQProperties.getAccessChannel();
MessageModel messageModel = MessageModel.valueOf(consumerConfig.getMessageModel());
SelectorType selectorType = SelectorType.valueOf(consumerConfig.getSelectorType());
String selectorExpression = consumerConfig.getSelectorExpression();
String ak = consumerConfig.getAccessKey();
String sk = consumerConfig.getSecretKey();
int pullBatchSize = consumerConfig.getPullBatchSize();
boolean useTLS = consumerConfig.isTlsEnable();
DefaultLitePullConsumer litePullConsumer = RocketMQUtil.createDefaultLitePullConsumer(nameServer, accessChannel, groupName, topicName, messageModel, selectorType, selectorExpression, ak, sk, pullBatchSize, useTLS);
litePullConsumer.setEnableMsgTrace(consumerConfig.isEnableMsgTrace());
litePullConsumer.setCustomizedTraceTopic(consumerConfig.getCustomizedTraceTopic());
litePullConsumer.setNamespace(consumerConfig.getNamespace());
litePullConsumer.setInstanceName(consumerConfig.getInstanceName());
log.info(String.format("a pull consumer(%s sub %s) init on namesrv %s", groupName, topicName, nameServer));
return litePullConsumer;
}
注册 RocketMQTemplate
客户端不直接持有 producer 和 consumer,而是通过 RocketMQTemplate,该 bean 注册时从 bf 拿到 producer 和 consumer 实例并注入,然后在初始化阶段调用它们的 start 方法,启动 producer 和 consumer 实例
@Bean(destroyMethod = "destroy")
@Conditional(ProducerOrConsumerPropertyCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = ROCKETMQ_TEMPLATE_DEFAULT_GLOBAL_NAME)
public RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate(RocketMQMessageConverter rocketMQMessageConverter) {
RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate = new RocketMQTemplate();
if (applicationContext.containsBean(PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME)) {
rocketMQTemplate.setProducer((DefaultMQProducer) applicationContext.getBean(PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (applicationContext.containsBean(CONSUMER_BEAN_NAME)) {
rocketMQTemplate.setConsumer((DefaultLitePullConsumer) applicationContext.getBean(CONSUMER_BEAN_NAME));
}
rocketMQTemplate.setMessageConverter(rocketMQMessageConverter.getMessageConverter());
return rocketMQTemplate;
}
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
if (producer != null) {
producer.start();
}
if (Objects.nonNull(consumer)) {
try {
consumer.start();
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to startup PullConsumer for RocketMQTemplate", e);
}
}
}
启动 producer 实例
入口:org.apache.rocketmq.client.producer.DefaultMQProducer#start
调用 start 方法前,已经完成了 DefaultMQProducer 的实例化,在构造函数里设置一些默认的发送者配置信息,同时 new 了一个内部发送者实例DefaultMQProducerImpl,它们互相持有彼此的引用。配置信息包括:
- 发送消息超时时间(默认 3 秒)
- 需要压缩的消息大小阈值(默认 4K)
- 发送消息失败后的重试次数(默认 2 次,不过这可能造成 consumer 收到重复消息)
- 发送消息的最大字节数(默认 4M)
- producerGroupName,作为构造参数传入
- mq 客户端信息,例如实例名、客户端 ip、ns 地址等
- 定义在
ClientConfig,DefaultMQProducer 继承该类
- 定义在
需要注意,通过上面注册阶段的分析可知,发送者配置信息可以被应用配置文件里的配置覆盖。
不过应用配置里一般是定义一些 producer 和 consumer 个性化参数,对于一些敏感信息,例如实例名、客户端 ip、ns 地址等,我们一般沿用 ClientConfig 的实现而不在应用配置文件里指定。
ClientConfig 设置实例名和 ns 地址都通过系统属性获取,我们可以在应用启动脚本里设置这些系统属性
public DefaultMQProducer(String namespace, String producerGroup, RPCHook rpcHook) {
this.log = ClientLogger.getLog();
this.retryResponseCodes = new CopyOnWriteArraySet(Arrays.asList(17, 14, 1, 16, 204, 205));
this.createTopicKey = "TBW102";
this.defaultTopicQueueNums = 4;
this.sendMsgTimeout = 3000;
this.compressMsgBodyOverHowmuch = 4096;
this.retryTimesWhenSendFailed = 2;
this.retryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed = 2;
this.retryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK = false;
this.maxMessageSize = 4194304;
this.traceDispatcher = null;
this.namespace = namespace;
this.producerGroup = producerGroup;
this.defaultMQProducerImpl = new DefaultMQProducerImpl(this, rpcHook);
}
DefaultMQProducer 的 start 方法又会调用内部发送者 DefaultMQProducerImpl 的 start 方法,即 producer 的启动流程实际是启动 DefaultMQProducerImpl
public void start() throws MQClientException {
...
this.defaultMQProducerImpl.start();
...
}
下面具体看 DefaultMQProducerImpl 的 start 流程
处理 mqClient 实例名
ClientConfig 设置了全局的实例名,默认取系统环境变量,缺省值 DEFAULT
private String instanceName = System.getProperty("rocketmq.client.name", "DEFAULT");
sb 应用的配置文件里也可以指定 producer 所属 client 的实例名,该优先级更高。如果没指定,缺省也是 DEFAULT。
如果实例名为 DEFAULT,这里会修改实例名,改成:”{进程 pid}#{时间戳}” 这种格式
public void changeInstanceNameToPID() {
if (this.instanceName.equals("DEFAULT")) {
this.instanceName = UtilAll.getPid() + "#" + System.nanoTime();
}
}
实例化 mqClient
MQClientInstance表示 mqClient 实例。MQClientManager是MQClientInstance的工厂,缓存已创建的MQClientInstance,Key 为{ip}#{mqClient 的实例名},如果没有在环境变量或应用配置里指定 mqClient 实例名,则这里的 key 为:{ip}#{进程 pid}#{时间戳}。注意这时带了时间戳参数,因此有如下结论:
- 如果没有指定 mq 客户端名,每个 producer 实例在启动时都会新建一个 mqClient
- 如果系统配置里指定了 mq 客户端名,所有 producer 共用一个 mqClient
// mQClientFactory的类型就是MQClientInstance
this.mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getOrCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQProducer, rpcHook);
public MQClientInstance getOrCreateMQClientInstance(final ClientConfig clientConfig, RPCHook rpcHook) {
String clientId = clientConfig.buildMQClientId();
MQClientInstance instance = this.factoryTable.get(clientId);
if (null == instance) {
instance = new MQClientInstance(clientConfig.cloneClientConfig(), this.factoryIndexGenerator.getAndIncrement(), clientId, rpcHook);
MQClientInstance prev = this.factoryTable.putIfAbsent(clientId, instance);
if (prev != null) {
instance = prev;
log.warn("Returned Previous MQClientInstance for clientId:[{}]", clientId);
} else {
log.info("Created new MQClientInstance for clientId:[{}]", clientId);
}
}
return instance;
}
producer 注册到 mqClient
DefaultMQProducerImpl注册到MQClientInstance
- mqClient 按 group 维度管理 producer、consumer 实例
boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerProducer(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(), this);
public synchronized boolean registerProducer(String group, DefaultMQProducerImpl producer) {
if (null != group && null != producer) {
MQProducerInner prev = (MQProducerInner) this.producerTable.putIfAbsent(group, producer);
if (prev != null) {
this.log.warn("the producer group[{}] exist already.", group);
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
启动 MQClientInstance
this.mQClientFactory.start();
更新 ns 地址
获取 nameserver 服务器地址(url+端口号)。ns 地址的获取优先级是:
- 优先使用应用配置文件里指定的 ns 地址。在 bean 加载阶段会覆盖 ClientConfig 里 ns 的默认值
@Bean(PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME)@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DefaultMQProducer.class)@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "rocketmq", value = {
"name-server",
"producer.group"
}) public DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer(RocketMQProperties rocketMQProperties) {
RocketMQProperties.Producer producerConfig = rocketMQProperties.getProducer();
String nameServer = rocketMQProperties.getNameServer();
...
producer.setNamesrvAddr(nameServer);
...
}
- 其次使用 ClientConfig 的 ns 默认值。它取了系统环境变量
private String namesrvAddr = NameServerAddressUtils.getNameServerAddresses();
public static String getNameServerAddresses() {
return System.getProperty("rocketmq.namesrv.addr", System.getenv("NAMESRV_ADDR"));
}
- 如果前面都没拿到 ns 地址,向 ns 源服务器地址(也在系统环境变量配置,有缺省值)发起 http 请求,获取 ns 服务器地址
- rocketmq 提供了缺省的 ns 源服务器地址:http://jmenv.tbsite.net:8080/rocketmq/nsaddr
- 拿到 ns 地址更新到 nettyClient
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
}
// 获取系统属性配置的ns源服务器地址
public static String getWSAddr() {
String wsDomainName = System.getProperty("rocketmq.namesrv.domain", DEFAULT_NAMESRV_ADDR_LOOKUP);
String wsDomainSubgroup = System.getProperty("rocketmq.namesrv.domain.subgroup", "nsaddr");
String wsAddr = "http://" + wsDomainName + ":8080/rocketmq/" + wsDomainSubgroup;
if (wsDomainName.indexOf(":") > 0) {
wsAddr = "http://" + wsDomainName + "/rocketmq/" + wsDomainSubgroup;
}
return wsAddr;
}...
// 向ns源服务器地址发起http请求,获取ns服务器地址
String url = this.wsAddr;
HttpTinyClient.HttpResult result = HttpTinyClient.httpGet(url, null, null, "UTF-8", timeoutMills);
if (200 == result.code) {
String responseStr = result.content;
if (responseStr != null) {
return clearNewLine(responseStr);
}
}...
// 注册ns服务器地址到nettyClient
String[] addrArray = addrs.split(";");
List < String > list = Arrays.asList(addrArray);
this.remotingClient.updateNameServerAddressList(list);
启动 MQClientAPIImpl
MQClientAPIImpl封装了通信接口给 mqClient 使用,它内部使用 Netty 通信。它的 start 方法会调用NettyRemotingClient的 start 方法
public void start() {
this.remotingClient.start();
}
NettyRemotingClient 的 start 方法主要做了 2 件事。
初始化 netty 客户端
- 初始化客户端 netty 环境,核心是添加 rocketmq 定义的网络通信 IO 数据的处理类 handler。需要注意的是:
- nioEventLoopGroup 在 NettyRemotingClient 的构造函数里实例化,只指定了一个 nioEventLoop 线程
- 为 IO 数据处理 handler 指定线程池来异步执行,提高 nioEventLoop 的线程利用率
// 为 IO 数据处理 handler 指定线程池来异步执行,提高 nioEventLoop 的线程利用率
this.defaultEventExecutorGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads(), new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "NettyClientWorkerThread_" + this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet());
}
});
// nioEventLoopGroup在NettyRemotingClient的构造函数里实例化,只指定了一个 nioEventLoop 线程
Bootstrap handler = this.bootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupWorker).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true).option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, false).option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis()).option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketSndBufSize()).option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketRcvBufSize()).handler(new ChannelInitializer < SocketChannel > () {@Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
if (nettyClientConfig.isUseTLS()) {
if (null != sslContext) {
pipeline.addFirst(defaultEventExecutorGroup, "sslHandler", sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()));
log.info("Prepend SSL handler");
} else {
log.warn("Connections are insecure as SSLContext is null!");
}
}
pipeline.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup, new NettyEncoder(), new NettyDecoder(), new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, nettyClientConfig.getClientChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()), new NettyConnectManageHandler(), new NettyClientHandler());
}
});
定时清理过期的 ResponseFuture
- 启动一个定时器,每隔 1 秒从 responseTable 移除已经超时的异步结果接收对象 ResponseFuture,并在 callback 线程池里提交任务,执行处理结果的 callback 方法
- nioEventLoop 执行业务 handler 的异步线程里解析响应,然后从 responseTable 根据 reqId 取出 ResponseFuture 并放入响应,再提交任务到线程池,回调 callback 方法处理结果。所以如果长时间没有新消息,responseTable 内存会一直存储接收结果的 ResponseFuture 对象,因此需要定时从 responseTable 清理过期的请求数据
- callback 方法在固定线程数的线程池中执行,线程池数目取 cpu 核数,且最大不超过 4。see:org.apache.rocketmq.remoting.netty.NettyRemotingClient#publicExecutor
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {@Override public void run() {
try {
NettyRemotingClient.this.scanResponseTable();
} catch(Throwable e) {
log.error("scanResponseTable exception", e);
}
}
},
1000 * 3, 1000);
public void scanResponseTable() {
final List < ResponseFuture > rfList = new LinkedList < ResponseFuture > ();
Iterator < Entry < Integer,
ResponseFuture >> it = this.responseTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry < Integer, ResponseFuture > next = it.next();
ResponseFuture rep = next.getValue();
if ((rep.getBeginTimestamp() + rep.getTimeoutMillis() + 1000) <= System.currentTimeMillis()) {
rep.release();
it.remove();
rfList.add(rep);
log.warn("remove timeout request, " + rep);
}
}
for (ResponseFuture rf: rfList) {
try {
executeInvokeCallback(rf);
} catch(Throwable e) {
log.warn("scanResponseTable, operationComplete Exception", e);
}
}
}
private void executeInvokeCallback(final ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
boolean runInThisThread = false;
ExecutorService executor = this.getCallbackExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
try {
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
try {
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch(Throwable e) {
log.warn("execute callback in executor exception, and callback throw", e);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
});
} catch(Exception e) {
runInThisThread = true;
log.warn("execute callback in executor exception, maybe executor busy", e);
}
} else {
runInThisThread = true;
}
if (runInThisThread) {
try {
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch(Throwable e) {
log.warn("executeInvokeCallback Exception", e);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
}
启动定时任务
定时更新 ns 地址
如果应用配置文件和系统环境变量都没有指定 ns 地址,使用单一定时线程池中的线程每隔 2 分钟去 ns 源服务器获取最新的 ns 服务器地址,更新到 nettyClient
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask fetchNameServerAddr exception", e);
}
}
},
1000 * 10, 1000 * 60 * 2, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
定时刷新 topic 消息路由
定时查询并刷新 mq 客户端发布和订阅的 topic 路由信息。获取所有 producer 和 consumer 发布和订阅的 topic,到 ns 查询 topic 的路由信息。执行频率来自配置,默认 30s 执行一次
更新 mqClient 的
brokerAddrTable、topicRouteTable更新 producer 的 topic 路由信息
topicPublishInfoTable- producer 配置时不指定 topic,而是每次发送消息时去 topicPublishInfoTable 拿当前 topic 的路由信息,如果没有会从 ns 查询并更新到 topicPublishInfoTable
更新 consumer 的负载均衡器
RebalanceImpl的 topicSubscribeInfoTable- consumer 订阅的 topic 从 RebalanceImpl 的 SubscriptionData 取出,构建 SubscriptionData 是在 consumer 实例的 start 方法里完成的
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer();
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer exception", e);
}
}
},
10, this.clientConfig.getPollNameServerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
Iterator < Entry < String,
MQConsumerInner >> it = this.consumerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry < String,
MQConsumerInner > entry = it.next();
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
Set < SubscriptionData > subList = impl.subscriptions();
if (subList != null) {
for (SubscriptionData subData: subList) {
topicList.add(subData.getTopic());
}
}
}
}
Iterator < Entry < String,
MQProducerInner >> it = this.producerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry < String,
MQProducerInner > entry = it.next();
MQProducerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
Set < String > lst = impl.getPublishTopicList();
topicList.addAll(lst);
}
}
for (String topic: topicList) {
this.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic);
}
public boolean updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(final String topic) {...topicRouteData = this.mQClientAPIImpl.getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, 1000 * 3);
if (topicRouteData != null) {
TopicRouteData old = this.topicRouteTable.get(topic);
boolean changed = topicRouteDataIsChange(old, topicRouteData);...
if (changed) {
TopicRouteData cloneTopicRouteData = topicRouteData.cloneTopicRouteData();
// 更新存储topic的broker地址
for (BrokerData bd: topicRouteData.getBrokerDatas()) {
this.brokerAddrTable.put(bd.getBrokerName(), bd.getBrokerAddrs());
}
// 更新每个producer发布的topic路由信息,主要是topic的broker路由和MessageQueue信息
{
TopicPublishInfo publishInfo = topicRouteData2TopicPublishInfo(topic, topicRouteData);
publishInfo.setHaveTopicRouterInfo(true);
Iterator < Entry < String,
MQProducerInner >> it = this.producerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry < String,
MQProducerInner > entry = it.next();
MQProducerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
impl.updateTopicPublishInfo(topic, publishInfo);
}
}
}
// 更新每个consumer订阅的topic路由信息,主要是topic的broker路由和MessageQueue信息
{
Set < MessageQueue > subscribeInfo = topicRouteData2TopicSubscribeInfo(topic, topicRouteData);
Iterator < Entry < String,
MQConsumerInner >> it = this.consumerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry < String,
MQConsumerInner > entry = it.next();
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
impl.updateTopicSubscribeInfo(topic, subscribeInfo);
}
}
}
// 更新topic路由信息
this.topicRouteTable.put(topic, cloneTopicRouteData);
return true;
}
}
}
定时向 broker 发送心跳
定时清理不能路由到 topic 的 broker,然后向MQClientInstance的所有可以路由到发布和订阅 topic 的 broker 发送心跳。执行频率来自配置,默认 30s 执行一次
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {@Override public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.cleanOfflineBroker();
MQClientInstance.this.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask sendHeartbeatToAllBroker exception", e);
}
}
},
1000, this.clientConfig.getHeartbeatBrokerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
mqClient 的 brokerAddrTable 中删除已不能路由到 topic 的 broker 机器地址(broker 是主从架构),如果主从架构所有的 broker 机器都路由不到节点,删除 broker 逻辑节点
- brokerAddrTable 维度是 broker 逻辑节点,key=brokerName,value 是 broker 逻辑节点中所有主从架构部署的物理机器地址
ConcurrentHashMap<String, HashMap<Long, String>> updatedTable = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, HashMap<Long, String>>();
Iterator<Entry<String, HashMap<Long, String>>> itBrokerTable = this.brokerAddrTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (itBrokerTable.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, HashMap<Long, String>> entry = itBrokerTable.next();
String brokerName = entry.getKey();
HashMap<Long, String> oneTable = entry.getValue();
HashMap<Long, String> cloneAddrTable = new HashMap<Long, String>();
cloneAddrTable.putAll(oneTable);
Iterator<Entry<Long, String>> it = cloneAddrTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<Long, String> ee = it.next();
String addr = ee.getValue();
if (!this.isBrokerAddrExistInTopicRouteTable(addr)) {
it.remove();
log.info("the broker addr[{} {}] is offline, remove it", brokerName, addr);
}
}
// 如果主从架构所有的broker机器都路由不到节点,删除broker逻辑节点
if (cloneAddrTable.isEmpty()) {
itBrokerTable.remove();
log.info("the broker[{}] name's host is offline, remove it", brokerName);
} else {
updatedTable.put(brokerName, cloneAddrTable);
}
}
if (!updatedTable.isEmpty()) {
this.brokerAddrTable.putAll(updatedTable);
}
private boolean isBrokerAddrExistInTopicRouteTable(final String addr) {
Iterator<Entry<String, TopicRouteData>> it = this.topicRouteTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, TopicRouteData> entry = it.next();
TopicRouteData topicRouteData = entry.getValue();
List<BrokerData> bds = topicRouteData.getBrokerDatas();
for (BrokerData bd : bds) {
if (bd.getBrokerAddrs() != null) {
boolean exist = bd.getBrokerAddrs().containsValue(addr);
if (exist)
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
向可路由到的 broker 物理节点发送心跳
- 心跳信息包括 mq 客户端的 clientId、producerGroupName 和 consumerGroup 的订阅信息
SubscriptionData- broker 按 consumerGroup 维度聚合组订阅信息。客户端拉取消息时,broker 会用到订阅信息来判断消息是否满足过滤条件(tag 过滤 or SQL 过滤)。消息过滤原理后面单独讲
- 如果同 group 中两个 consumer 订阅信息不同,broker 存储的 consumerGroup 订阅信息会被最新一次心跳数据覆盖,被覆盖订阅信息的 consumer 在拉取消息时,broker 可能会找不到 topic 的订阅信息而返回失败
- 如果 mqClient 只有 producer,只需要向 master 节点发送心跳
// 心跳信息包括mq客户端的clientId、所有producer和consumer信息
final HeartbeatData heartbeatData = this.prepareHeartbeatData();
...
// brokerAddrTable是broker逻辑节点维度,每个逻辑节点包含多个broker物理节点,因为broker是主从架构
Iterator<Entry<String, HashMap<Long, String>>> it = this.brokerAddrTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, HashMap<Long, String>> entry = it.next();
String brokerName = entry.getKey();
HashMap<Long, String> oneTable = entry.getValue();
if (oneTable != null) {
// broker物理节点,key=0说明是master物理节点
for (Map.Entry<Long, String> entry1 : oneTable.entrySet()) {
Long id = entry1.getKey();
String addr = entry1.getValue();
if (addr != null) {
// 如果mqClient没有consumer,只需和masterBroker保持心跳
if (consumerEmpty) {
if (id != MixAll.MASTER_ID)
continue;
}
try {
int version = this.mQClientAPIImpl.sendHearbeat(addr, heartbeatData, 3000);
...
}
}
}
}
定时发送 consumer 的消费位点
定时把 consumer 在 messageQueue 的消费位点更新到 broker,目的是消费者集群重启后能继续从 broker 拉取后面未消费过的消息。执行频率来自配置,默认 5s 执行一次
- 注意,只有集群模式才会把消费位点更新到 broker,广播模式只要在本地持久化消费位点即可
- 广播模式只要本机器自己知道在 mq 上消费到哪里即可,宕机重启后也能继续消费后面的消息
- 集群模式如果宕机重启,需要重新负载均衡分配 mq 的消费者机器,所以不能消费者机器本地持久化位点,只有 broker 自己知道 mq 的消费位点,才能给“新的消费者机器”投递后续的消息
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.persistAllConsumerOffset();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask persistAllConsumerOffset exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 10, this.clientConfig.getPersistConsumerOffsetInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
遍历所有 Consumer 实例,然后从内存里获取 consumer 在每个 messageQueue 的当前消费位点
- 当 messageQueue 数目大于 ConsumerGroup 下的实例数,一个 Consumer 实例有可能消费多个 messageQueue
Iterator<Entry<String, MQConsumerInner>> it = this.consumerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, MQConsumerInner> entry = it.next();
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
impl.persistConsumerOffset();
}
for (Map.Entry<MessageQueue, AtomicLong> entry : this.offsetTable.entrySet()) {
MessageQueue mq = entry.getKey();
AtomicLong offset = entry.getValue();
if (offset != null) {
...
// 将consumer对messageQueue的最新消费位点更新到broker
this.updateConsumeOffsetToBroker(mq, offset.get());
}
}
获取 messageQueue 所在 broker 的物理节点地址,更新 consumerGroup 在当前 messageQueue 的消费位点
- messageQueue 在同一个消费组 ConsumerGroup 下只能有一个消费者 Consumer(负载均衡里实现的),所以 messageQueue 记录消费位点是按消费组 ConsumerGroup 维度
public void updateConsumeOffsetToBroker(MessageQueue mq, long offset, boolean isOneway) throws RemotingException,
MQBrokerException, InterruptedException, MQClientException {
// 从messageQueue所在broker获取一个物理节点地址
FindBrokerResult findBrokerResult = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInAdmin(mq.getBrokerName());
if (null == findBrokerResult) {
// 如果找不到broker,去ns获取topic的最新broker路由信息,并更新到本地
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(mq.getTopic());
// 再找一次mq所在的broker的物理节点地址
findBrokerResult = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInAdmin(mq.getBrokerName());
}
if (findBrokerResult != null) {
UpdateConsumerOffsetRequestHeader requestHeader = new UpdateConsumerOffsetRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setTopic(mq.getTopic());
requestHeader.setConsumerGroup(this.groupName);
requestHeader.setQueueId(mq.getQueueId());
requestHeader.setCommitOffset(offset);
// 将mqClient对messageQueue的最新消费位点更新到broker
if (isOneway) {
this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().updateConsumerOffsetOneway(
findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr(), requestHeader, 1000 * 5);
} else {
this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().updateConsumerOffset(
findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr(), requestHeader, 1000 * 5);
}
} else {
throw new MQClientException("The broker[" + mq.getBrokerName() + "] not exist", null);
}
}
启动消息拉取线程
启动一个消息拉取线程,从阻塞队列pullRequestQueue拿消息拉取的 request,向 broker 发送请求批量拉取消息
- 阻塞队列类型:LinkedBlockingQueue
// Start pull service
this.pullMessageService.start();
public void start() {
log.info("Try to start service thread:{} started:{} lastThread:{}", getServiceName(), started.get(), thread);
if (!started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return;
}
stopped = false;
this.thread = new Thread(this, getServiceName());
this.thread.setDaemon(isDaemon);
this.thread.start();
}
...
@Override
public void run() {
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
获取 consumer 实例
通过拉取消息请求所属的 ConsumerGroup,获取 Consumer 实例
- 第一个拉取消息请求是 consumer 的 rebalance 负载均衡后放入的
- 注意,消息拉取请求的维度是 messageQueue,即每个 messageQueue 都会有对应的拉取消息请求
- 后续该 consumer 在 mq 上的消息拉取请求都是复用这个 request
- 这里 Consumer 直接强转成 DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl,说明消息拉取线程使用推模式
// mQClientFactory是MQClientInstance
final MQConsumerInner consumer = this.mQClientFactory.selectConsumer(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup());
if (consumer != null) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl impl = (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl) consumer;
impl.pullMessage(pullRequest);
}
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl 发送拉取消息请求前,会做流控,如果触发流控,会通过一个延时任务,50ms 后再把这个消息拉取请求放入阻塞队列。
满足以下任一条件,触发流控:
- 待处理的消息数超过阈值
- 从 messageQueue 拉取到的消息会放入处理队列 processQueue,每次消费都从该队列取出。所以通过它能判断当前待处理消息数目
- 阈值可以通过配置 consumer 的 pullThresholdForQueue 修改
- 待处理的消息大小超过阈值
- 阈值可以通过配置 consumer 的 pullThresholdSizeForQueue 修改
- 乱序消费 && 处理队列的位点范围超过阈值
// 处理队列缓存的消息数目或消息体大小超过阈值,延时拉取消息
long cachedMessageCount = processQueue.getMsgCount().get();
long cachedMessageSizeInMiB = processQueue.getMsgSize().get() / (1024 * 1024);
if (cachedMessageCount > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdForQueue()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueFlowControlTimes++%1000) == 0) {
log.warn("the cached message count exceeds the threshold {}, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, count={}, size={} MiB, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdForQueue(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), cachedMessageCount, cachedMessageSizeInMiB, pullRequest, queueFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}
if (!this.consumeOrderly) {
// 乱序消费时,处理队列当前待处理消息的位点范围超过阈值(消费速度<生成速度),执行流控,延时拉取消息
if (processQueue.getMaxSpan() > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeConcurrentlyMaxSpan()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueMaxSpanFlowControlTimes++%1000) == 0) {
log.warn("the queue's messages, span too long, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, maxSpan={}, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}", processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), processQueue.getMaxSpan(), pullRequest, queueMaxSpanFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}
}
public void executePullRequestLater(final PullRequest pullRequest, final long timeDelay) {
if (!isStopped()) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Runnable() {@Override public void run() {
PullMessageService.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
},
timeDelay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
log.warn("PullMessageServiceScheduledThread has shutdown");
}
}
public void executePullRequestImmediately(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
try {
this.pullRequestQueue.put(pullRequest);
}
...
}
上报已消费的位点
集群模式下,拉取消息请求里放入 consumer 在 mq 上已消费到的位点 commitOffsetValue,让 broker 做持久化。和定时上报 consumer 消费位点相互配合
// 订阅模式,集群型表示消息在ConsumerGroup中只能被消费一次,广播型表示消息可以被ConsumerGroup中的每个Consumer消费一次
// 集群订阅模式,拉取消息时传入commitOffsetValue,应该是告知broker,当前ConsumerGroup已经消费到该位点了,位点前的消息不能再被拉取
if (MessageModel.CLUSTERING == this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
commitOffsetValue = this.offsetStore.readOffset(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), ReadOffsetType.READ_FROM_MEMORY);
if (commitOffsetValue > 0) {
commitOffsetEnable = true;
}
}
注意拉取请求的起始位点 nextOffset 不是 commitOffsetValue。而是从 broker 拿到的响应 pullResult 里取出的,即 broker 会在响应里告诉 consumer,下一次消息拉取的起始位点
- 首次拉取请求的 nextOffset 为 null,这时 broker 就会用到 consumer 上报的 commitOffsetValue
long prevRequestOffset = pullRequest.getNextOffset();
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
获取 broker 地址
获取 messageQueue 所在的 broker 地址,然后调用 pullMessageAsync 异步拉取消息
- 传入 Consumer 的 callback 接口用于收到消息后回调,消费批量拉取到的消息
FindBrokerResult findBrokerResult =
// 挑选要从messageQueue所在的物理broker拉取消息,可能是master也可能是slave
this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(mq.getBrokerName(),
this.recalculatePullFromWhichNode(mq), false);
if (null == findBrokerResult) {
// 找不到broker,重新从ns刷一遍路由信息到内存,然后再找一遍
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(mq.getTopic());
findBrokerResult =
this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(mq.getBrokerName(),
this.recalculatePullFromWhichNode(mq), false);
}
if (findBrokerResult != null) {
...
PullMessageRequestHeader requestHeader = new PullMessageRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setConsumerGroup(this.consumerGroup);
requestHeader.setTopic(mq.getTopic());
requestHeader.setQueueId(mq.getQueueId());
requestHeader.setQueueOffset(offset); // pullRequest.getNextOffset(),拉取该位点后面的消息
requestHeader.setMaxMsgNums(maxNums); // 批量拉取的最大消息数
requestHeader.setSysFlag(sysFlagInner);
requestHeader.setCommitOffset(commitOffset);
requestHeader.setSuspendTimeoutMillis(brokerSuspendMaxTimeMillis);
requestHeader.setSubscription(subExpression);
requestHeader.setSubVersion(subVersion);
requestHeader.setExpressionType(expressionType);
String brokerAddr = findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr();
if (PullSysFlag.hasClassFilterFlag(sysFlagInner)) {
brokerAddr = computePullFromWhichFilterServer(mq.getTopic(), brokerAddr);
}
...
// 批量拉取消息,推模式异步拉取消息,提供callback接口,异步future结果返回后,通过注册在future的监听器回调callback方法消费批量拉取的消息
RemotingCommand request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.PULL_MESSAGE, requestHeader);
switch (communicationMode) {
case ONEWAY:
assert false;
return null;
case ASYNC:
this.pullMessageAsync(addr, request, timeoutMillis, pullCallback);
return null;
case SYNC:
return this.pullMessageSync(addr, request, timeoutMillis);
default:
assert false;
break;
}
}
定义 netty 响应的回调 callback
调用底层 netty 发送异步消息拉取请求前,又定义了一个 callback,用于将 netty 的响应结果转成 PullResult,然后回调外层 Consumer 提供的 callback,真正消费批量消息
- 体现了分层和单一职责的思想
this.remotingClient.invokeAsync(addr, request, timeoutMillis, new InvokeCallback() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
RemotingCommand response = responseFuture.getResponseCommand();
if (response != null) {
try {
PullResult pullResult = MQClientAPIImpl.this.processPullResponse(response, addr);
assert pullResult != null;
pullCallback.onSuccess(pullResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
pullCallback.onException(e);
}
}
}
}
建立和 broker 的 tcp 连接
netty 在发送异步请求前,会到 channelTable 拿这个 broker 地址对应的 channel 连接通道。如果没有(第一次发送请求),会调用 connect 方法建立与 broker 的 tcp 连接,然后再把通道 channel 缓存到 channelTable
private Channel getAndCreateChannel(final String addr) throws RemotingConnectException,
InterruptedException {
if (null == addr) {
return getAndCreateNameserverChannel();
}
ChannelWrapper cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
if (cw != null && cw.isOK()) {
return cw.getChannel();
}
return this.createChannel(addr);
}
private Channel createChannel(final String addr) throws InterruptedException {
ChannelWrapper cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
if (cw != null && cw.isOK()) {
return cw.getChannel();
}
if (this.lockChannelTables.tryLock(LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
try {
boolean createNewConnection;
cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
if (cw != null) {
if (cw.isOK()) {
return cw.getChannel();
} else if (!cw.getChannelFuture().isDone()) {
createNewConnection = false;
} else {
this.channelTables.remove(addr);
createNewConnection = true;
}
} else {
createNewConnection = true;
}
if (createNewConnection) {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = this.bootstrap.connect(RemotingHelper.string2SocketAddress(addr));
log.info("createChannel: begin to connect remote host[{}] asynchronously", addr);
cw = new ChannelWrapper(channelFuture);
this.channelTables.put(addr, cw);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("createChannel: create channel exception", e);
} finally {
this.lockChannelTables.unlock();
}
} else {
log.warn("createChannel: try to lock channel table, but timeout, {}ms", LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
}
if (cw != null) {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = cw.getChannelFuture();
if (channelFuture.awaitUninterruptibly(this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis())) {
if (cw.isOK()) {
log.info("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] success, {}", addr, channelFuture.toString());
return cw.getChannel();
} else {
log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[" + addr + "] failed, " + channelFuture.toString(), channelFuture.cause());
}
} else {
log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] timeout {}ms, {}", addr, this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis(), channelFuture.toString());
}
}
return null;
}
通过 netty 发送请求
使用 netty 发送消息异步拉取请求到 broker
- 创建这次请求的
ResponseFuture对象,封装这次请求的异步响应上下文,包括异步消息响应(收到响应后 set 进去)、reqId、callback 函数等 - 缓存 ResponseFuture,key 是 reqId
- reqId 的生成规则是一个全局自增数
- 拿到响应后通过 reqId 拿到
ResponseFuture,填充响应结果,然后在 callback 线程池里回调内层 callback 转换响应结果,再回调外层 callback 处理消息 - 通过 reqId 关联请求和响应,是实现异步拉取消息(推模式)的关键点
// 创建这次请求的`ResponseFuture`对象,封装这次请求的响应上下文,包括从netty通道获取的响应结果、处理响应结果的回调方法等
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis - costTime, invokeCallback, once);
// 缓存ResponseFuture,key是请求id,生成规则是一个全局自增数。拿到响应后通过请求id拿到`ResponseFuture`,填充响应结果,然后执行回调方法处理响应结果
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
try {
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
}
requestFail(opaque);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <{}> failed.", RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel));
}
});
}
// 拿到响应后通过请求id拿到`ResponseFuture`,填充响应结果
// 回调内层callback处理响应结果,最终回调外层callback消费消息
public void processResponseCommand(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand cmd) {
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = responseTable.get(opaque);
if (responseFuture != null) {
responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);
responseTable.remove(opaque);
if (responseFuture.getInvokeCallback() != null) {
executeInvokeCallback(responseFuture);
} else {
responseFuture.putResponse(cmd);
responseFuture.release();
}
}
}
private void executeInvokeCallback(final ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
boolean runInThisThread = false;
ExecutorService executor = this.getCallbackExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
try {
executor.submit(new Runnable() {@Override public void run() {
try {
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch(Throwable e) {
log.warn("execute callback in executor exception, and callback throw", e);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
});
} catch(Exception e) {
runInThisThread = true;
log.warn("execute callback in executor exception, maybe executor busy", e);
}
} else {
runInThisThread = true;
}
if (runInThisThread) {
try {
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch(Throwable e) {
log.warn("executeInvokeCallback Exception", e);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
}
如果是同步拉取消息
以上说的都是异步拉取消息的方式,即推 Push 模式。如果是拉 Pull 模式,区别就是从异步拉取消息改为同步拉取消息。具体实现方式为:
- ResponseFuture 放入 table,然后通过和 broker 建连的 channel 发送请求,这和异步方式没差别
- 调用 CDL 的 await 方法,让拉取消息线程阻塞等待响应结果
- 注意是带最长阻塞时间的
- 收到响应后,通过 reqId 拿到 ResponseFuture,因为同步方式 ResponseFuture 不会包含 callback 函数,所以走 putResponse 方法,set 响应数据并执行 countDown。这会唤醒拉取消息线程,拿到响应数据开始执行消费逻辑。这也是同步和异步最大的区别
public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
try {
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
} else {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
}
responseTable.remove(opaque);
responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
}
});
// 同步拉取消息,线程hold一定时间等待response
RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
if (null == responseCommand) {
if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), timeoutMillis,
responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
return responseCommand;
} finally {
this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
}
}
public RemotingCommand waitResponse(final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException {
this.countDownLatch.await(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this.responseCommand;
}
public void processResponseCommand(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand cmd) {
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = responseTable.get(opaque);
if (responseFuture != null) {
responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);
responseTable.remove(opaque);
if (responseFuture.getInvokeCallback() != null) {
executeInvokeCallback(responseFuture);
} else {
responseFuture.putResponse(cmd);
responseFuture.release();
}
} else {
log.warn("receive response, but not matched any request, " + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()));
log.warn(cmd.toString());
}
}
消费拉取到的消息
收到异步响应后 netty 回调业务 handler 处理消息,see:org.apache.rocketmq.remoting.netty.NettyRemotingClient.NettyClientHandler#channelRead0
在业务 handler 里通过 reqId 拿到对应 ResponseFuture 并把消息体赋给它。然后提交任务到 callback 线程池,异步调用 callback 线程来处理新消息
callback 线程将消息体转义为 pullResult 对象,然后回调业务 callback 的 onSuccess 方法开始真正处理新消息。
下面介绍的都是拿到了新消息后的逻辑,如果没拉取到新消息会立刻将请求放入阻塞队列
设置下次拉取消息的起始位点
读取在 messageQueue 上的消息拉取响应里返回的位点,作为下次拉取消息的起始位点
// 读取messageQueue在消息拉取的响应里返回的位点,作为下次拉取消息的起始位点
long prevRequestOffset = pullRequest.getNextOffset();
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
消息放入 processQueue
拉取到的消息放入 processQueue
// 消息List放入处理队列
boolean dispatchToConsume = processQueue.putMessage(pullResult.getMsgFoundList());
异步消费消息
提交消费任务到线程池异步执行。按消费模式的不同,乱序(并发)消费使用 ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService,顺序消费使用 ConsumeMessageOrderlyService
// 创建消费任务,提交到线程池执行
// 如果是并发消费,消息list按最大批量消费数阈值分片后,提交并发消费任务到线程池 ✨
// 如果是顺序消费,提交顺序消费任务到线程池 ✨
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.consumeMessageService.submitConsumeRequest(
pullResult.getMsgFoundList(),
processQueue,
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
dispatchToConsume);
如果是乱序消费,消息 list 按单次消费消息数阈值分片后,提交多个并发消费任务到线程池
- 消费阈值默认为 1,定义在 org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumer#consumeMessageBatchMaxSize
- 一般我们不改这个值,因为 listener 消费接口返回消费结果状态,如果多条消息一起消费,它们只能一起消费成功或失败
final int consumeBatchSize = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeMessageBatchMaxSize();
if (msgs.size() <= consumeBatchSize) {
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgs, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
} else {
for (int total = 0; total < msgs.size(); ) {
List<MessageExt> msgThis = new ArrayList<MessageExt>(consumeBatchSize);
for (int i = 0; i < consumeBatchSize; i++, total++) {
if (total < msgs.size()) {
msgThis.add(msgs.get(total));
} else {
break;
}
}
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgThis, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
for (; total < msgs.size(); total++) {
msgThis.add(msgs.get(total));
}
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
}
}
执行并发消费消息任务,先调用前置 hook
- hook 函数是调用 org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#registerConsumeMessageHook 方法注册到 consumer 的
if (ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.hasHook()) {
consumeMessageContext = new ConsumeMessageContext();
consumeMessageContext.setNamespace(defaultMQPushConsumer.getNamespace());
consumeMessageContext.setConsumerGroup(defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
consumeMessageContext.setProps(new HashMap<String, String>());
consumeMessageContext.setMq(messageQueue);
consumeMessageContext.setMsgList(msgs);
consumeMessageContext.setSuccess(false);
ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.executeHookBefore(consumeMessageContext);
}
再调用业务方 listener 消费批量消息
status = listener.consumeMessage(Collections.unmodifiableList(msgs), context);
最后调用后置 hook
if (ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.hasHook()) {
consumeMessageContext.setStatus(status.toString());
consumeMessageContext.setSuccess(ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS == status);
// 调用后置hook
ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.executeHookAfter(consumeMessageContext);
}
处理消费结果
- 如果 listener 返回的消费状态为重试(消费失败了),消息发送回 broker,并传入消息重投最大次数和重投时间间隔
- 重投次数由 org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumer#maxReconsumeTimes 控制,默认为-1,然后被转成 16,即默认重投 16 次
- 重投时间间隔由 org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.listener.ConsumeConcurrentlyContext#delayLevelWhenNextConsume 控制。-1 表示直接投递到 DLQ 死信队列不重新消费了,0 表示由 broker 控制重投间隔,大于 0 表示客户端控制重投间隔。默认为 0
- ConsumeConcurrentlyContext 作为入参传递给 listener,业务方可以修改默认值控制消息的重投间隔
- 如果消息发回 broker 失败,会本地提交一个延时任务,5 秒后重新消费消息
- 从处理队列 ProcessQueue 移除消费完的消息
- 从 processQueue 获取下一个待消费消息的 offset,更新到 offsetTable
- offsetTable 按 messageQueue 维度存储将要消费的下一条消息位点。集群模式下定时上报到 broker,目的是 consumerGroup 重新负载均衡后(例如 consumerGroup 集群重启),broker 能知道 consumerGroup 在 messageQueue 上需要从哪条消息开始继续消费
case RECONSUME_LATER:
ackIndex = -1;
...
case CLUSTERING:
List < MessageExt > msgBackFailed = new ArrayList < MessageExt > (consumeRequest.getMsgs().size());
for (int i = ackIndex + 1; i < consumeRequest.getMsgs().size(); i++) {
MessageExt msg = consumeRequest.getMsgs().get(i);
// 集群模式,批量消息消费失败,重投递消息到broker的消费队列,指定下次延迟发送时间 ✨
boolean result = this.sendMessageBack(msg, context);
if (!result) {
msg.setReconsumeTimes(msg.getReconsumeTimes() + 1);
msgBackFailed.add(msg);
}
}
if (!msgBackFailed.isEmpty()) {
consumeRequest.getMsgs().removeAll(msgBackFailed);
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(msgBackFailed, consumeRequest.getProcessQueue(), consumeRequest.getMessageQueue());
}
break;
...
// 消费完的消息,从处理队列(实际就是一个map,key=offset,value=消息)移除,返回移除后队列下一条待消费的消息offset
long offset = consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().removeMessage(consumeRequest.getMsgs());
// 更新下一个待消费消息的offset到内存offsetTable
if (offset >= 0 && !consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().isDropped()) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.getOffsetStore().updateOffset(consumeRequest.getMessageQueue(), offset, true);
}
如果业务方使用的 listener 是 MessageListenerOrderly,则表示顺序消费 mq 上的消息,consumer 实例创建的消费服务就是 ConsumeMessageOrderlyService
顺序消费基本流程和并发消费类似,只说区别
1、如果 mqClient 还没有给 messageQueue 加锁,或加锁过期了,则加锁后再延迟消费消息
- mqClient 通知 broker 给 mq 加锁的目的是为了严格保证 mq 与消费者实例唯一绑定,确保 mq 上的消息在集群模式下被顺序消费
- 只有当 mqClient 关闭时,才会 unLock 所有 messageQueue
- ConsumeMessageOrderlyService 的 start 方法会开启一个定时任务,发送 mq 加锁请求给负载均衡分配的 mq 所在的 broker。加锁成功后会置 mq 对应的 processQueue 的 locked 字段为 true
// processQueue的locked状态和messageQueue是一致的,通过本地processQueue的锁定状态和锁定时间判断messageQueue是否锁定或过期,如果过期,需要重新让consumer所在的mqClient锁定messageQueue
// 锁定messageQueue的作用我认为应该是为了通知broker,messageQueue已被consumerGroup中的当前client占据,防止极端情况组内其他client也去messageQueue拉取消息,造成乱序消费
// 只有当mqClient关闭时,才会unLock所有messageQueue
if (MessageModel.BROADCASTING.equals(ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.messageModel())
|| (this.processQueue.isLocked() && !this.processQueue.isLockExpired())) {
...
} else {
ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.tryLockLaterAndReconsume(this.messageQueue, this.processQueue, 100);
}
public boolean lock(final MessageQueue mq) {
FindBrokerResult findBrokerResult = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(mq.getBrokerName(), MixAll.MASTER_ID, true);
if (findBrokerResult != null) {
LockBatchRequestBody requestBody = new LockBatchRequestBody();
requestBody.setConsumerGroup(this.consumerGroup);
requestBody.setClientId(this.mQClientFactory.getClientId());
requestBody.getMqSet().add(mq);
try {
// ConsumerGroup中的当前mqClient锁住它对应broker中的messageQueue
// 所谓锁住,实际是在broker中标记messageQueue被consumerGroup的哪个mqClient占有
Set<MessageQueue> lockedMq =
this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().lockBatchMQ(findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr(), requestBody, 1000);
for (MessageQueue mmqq : lockedMq) {
ProcessQueue processQueue = this.processQueueTable.get(mmqq);
if (processQueue != null) {
// 缓存队列locked,说明它对应的messageQueue已被当前ConsumerGroup的mqClient锁住
processQueue.setLocked(true);
processQueue.setLastLockTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
...
}
}
if (lockOK) {
ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.submitConsumeRequestLater(processQueue, mq, 10);
} else {
ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.submitConsumeRequestLater(processQueue, mq, 3000);
}
2、从 processQueue 按位点顺序取不超过批量消费消息阈值数的消息进行消费
- 并发消费时,直接切分收到的消息 list,每个切分后的子消息 list 创建一个线程消费
- 从 processQueue 取消息 && 调用业务 Listener 顺序消费时,都加了互斥锁,确保 processQueue 的 msgs 不被并发访问消费,即保证了顺序性
// 批量消费消息数阈值
final int consumeBatchSize = ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeMessageBatchMaxSize();
// 从缓存队列批量顺序取待消费消息,不超过批量消费消息数阈值
List<MessageExt> msgs = this.processQueue.takeMessages(consumeBatchSize);
try {
// 调用业务Listener顺序消费时加锁,防止在任务并发执行时,并发调用listener消费消息,产生消费乱序
this.processQueue.getLockConsume().lock();
// 批量消费消息
status = messageListener.consumeMessage(Collections.unmodifiableList(msgs), context);
} catch (Throwable e) {
...
} finally {
// 解锁
this.processQueue.getLockConsume().unlock();
}
3、顺序消费失败,如果超过最大重试次数,发送到死信队列,跳过消息。否则,将 msgs 重新放回 processQueue,延迟提交该 processQueue 上的顺序消费任务到线程池
- 最大重试次数取 org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumer#maxReconsumeTimes,默认-1,会转成 Integer.MAX_VALUE,表示会一直重试
- 本地延迟消费的延时时间默认 1s,取 org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumer#suspendCurrentQueueTimeMillis。可以通过 org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.listener.ConsumeOrderlyContext#suspendCurrentQueueTimeMillis 字段修改
- 并发消费失败的消息,重投递回 broker,不是提交延时任务本地重新消费
case SUSPEND_CURRENT_QUEUE_A_MOMENT:
this.getConsumerStatsManager().incConsumeFailedTPS(consumerGroup, consumeRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), msgs.size());
if (checkReconsumeTimes(msgs)) {
consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().makeMessageToConsumeAgain(msgs);
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(
consumeRequest.getProcessQueue(),
consumeRequest.getMessageQueue(),
context.getSuspendCurrentQueueTimeMillis());
continueConsume = false;
} else {
commitOffset = consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().commit();
}
break;
拉取消息请求放回阻塞队列
提交消费任务后,消息拉取请求放到阻塞队列,由拉取线程从阻塞队列取出请求,再次向 broker 发起请求
// 消息拉取请求放到阻塞队列,由拉取线程轮询阻塞队列再次向broker发起请求
if (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval() > 0) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest,DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval());
} else {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
启动负载均衡线程
负载均衡线程默认每隔 20s 执行一次负载 mq 的负载均衡
@Override public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
this.waitForRunning(waitInterval);
this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance();
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
按 consumer 实例订阅的 topic 所属 mq 维度执行负载均衡策略
public void doRebalance() {
for (Map.Entry<String, MQConsumerInner> entry : this.consumerTable.entrySet()) {
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
try {
impl.doRebalance();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("doRebalance exception", e);
}
}
}
}
public void doRebalance(final boolean isOrder) {
Map<String, SubscriptionData> subTable = this.getSubscriptionInner();
if (subTable != null) {
for (final Map.Entry<String, SubscriptionData> entry : subTable.entrySet()) {
final String topic = entry.getKey();
try {
this.rebalanceByTopic(topic, isOrder);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("rebalanceByTopic Exception", e);
}
}
}
}
}
获取存储 topic 消息的所有 messageQueue
- topic 的路由信息是定时请求 ns 获取到的
// topicSubscribeInfoTable存储的是定时从ns拿到的topic路由信息,即存储topic消息的所有messageQueue
Set<MessageQueue> mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
随机请求存储 topic 消息的一台 broker,获取同 consumerGroup 下所有客户端的 clientId
- 所有订阅该 topic 的 consumer 都会通过心跳消息向所有存储 topic 消息的 broker 上报 ConsumerGroup 信息,因此通过 broker 能拿到 ConsumerGroup 中的所有 clientId
// 随机取存储topic消息的一个broker,通过它获取当前consumer所在Group中所有consumer客户端的clientId
List<String> cidAll = this.mQClientFactory.findConsumerIdList(topic, consumerGroup);
按 mqClient 均分的方式为 consumer 消费的 topic 分配 messageQueue
/**
* 均分算法,如果consumer数量超过messageQueue数量,超过部分的consumer实例不消费messageQueue
* 返回分配到的messageQueue
*/
int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);
int mod = mqAll.size() % cidAll.size();
int averageSize = mqAll.size() <= cidAll.size() ? 1 : (mod > 0 && index < mod ? mqAll.size() / cidAll.size() + 1 : mqAll.size() / cidAll.size());
int startIndex = (mod > 0 && index < mod) ? index * averageSize: index * averageSize + mod;
int range = Math.min(averageSize, mqAll.size() - startIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++) {
result.add(mqAll.get((startIndex + i) % mqAll.size()));
}
return result;
如果负载均衡分配的 messageQueue 在 mqClient 上还没有 processQueue,创建与 messageQueue 映射的 processQueue,然后构建该 messageQueue 上的消息拉取请求,放入阻塞队列
- 如果之前已经缓存了该 topic 的 messageQueue,会比对之前的 messageQueue 是否依然在该 topic 新分配的 messageQueue 里,如果不在,认为之前分配的 messageQueue 失效并 remove,同时 drop 对应的 processQueue
- 如果 consumerGroup 顺序消费 topic 消息,创建 ProcessQueue 前,一定要用 ConsumerGroup 中的当前 client 锁住 messageQueue,否则不能拉取消息。应该是担心万一 messageQueue 已被别的 consumerClient 占据,造成多个 consumer 同时消费一个 messageQueue 产生乱序消费
Iterator<Entry<MessageQueue, ProcessQueue>> it = this.processQueueTable.entrySet().iterator();
...
// messageQueue的topic与consumer订阅的topic相同,说明是之前已经负载均衡后给consumer分配的messageQueue
// 但messageQueue不在最新负载均衡分配的mqs里,说明broker上的messageQueue有调整,之前的messageQueue失效,需要remove,并drop对应的processQueue
if (mq.getTopic().equals(topic)) {
if (!mqSet.contains(mq)) {
pq.setDropped(true);
if (this.removeUnnecessaryMessageQueue(mq, pq)) {
it.remove();
}
}
...
// mqSet:负载均衡器给当前consumer实例分配的messageQueueSet
for (MessageQueue mq : mqSet) {
// 如果最新负载均衡分配的messageQueue在mqClient没有对应的processQueue,初始化processQueue,然后构建消息拉取请求,拉取messageQueue里的消息
if (!this.processQueueTable.containsKey(mq)) {
ProcessQueue pq = new ProcessQueue();
// 获取从messageQueue拉取消息的起始位点
long nextOffset = this.computePullFromWhere(mq);
if (nextOffset >= 0) {
// 初始化缓存队列,映射分配的messageQueue
ProcessQueue pre = this.processQueueTable.putIfAbsent(mq, pq);
if (pre != null) {
log.info("doRebalance, {}, mq already exists, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
} else {
// 初始化后,构建消息拉取请求,拉取messageQueue里的消息
log.info("doRebalance, {}, add a new mq, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest();
pullRequest.setConsumerGroup(consumerGroup);
pullRequest.setNextOffset(nextOffset);
pullRequest.setMessageQueue(mq);
pullRequest.setProcessQueue(pq);
pullRequestList.add(pullRequest);
changed = true;
}
}
}
}
// 消息拉取请求放入阻塞队列
this.dispatchPullRequest(pullRequestList);
更新 mqClient 的状态
producer 所属 mqClient 的 serviceState 变为 RUNNING,表示 producer 实例启动成功
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
启动 consumer 实例
启动 consumer 实例和启动 producer 实例基本类似。启动方法入口:org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start
构建 SubscriptionData
构建 consumer 的订阅信息 SubscriptionData,放入它的负载均衡器 RebalanceImpl
private void copySubscription() throws MQClientException {
try {
Map < String,
String > sub = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getSubscription();
if (sub != null) {
for (final Map.Entry < String, String > entry: sub.entrySet()) {
final String topic = entry.getKey();
final String subString = entry.getValue();
SubscriptionData subscriptionData = FilterAPI.buildSubscriptionData(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), topic, subString);
this.rebalanceImpl.getSubscriptionInner().put(topic, subscriptionData);
}
}
...
}
实例化 mqClient
同 producer
实例化 offsetStore
实例化 offsetStore,存储在 mq 上的下一条待消费消息的 offset。如果是广播模式,本地持久化 offset 即可,如果是集群模式,需要同步给 broker,目的是重新负载均衡新的消费者机器绑定 mq 后,broker 能知道该从哪个消息开始继续消费
switch (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
case BROADCASTING:
this.offsetStore = new LocalFileOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
case CLUSTERING:
this.offsetStore = new RemoteBrokerOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
default:
break;
}
实例化消息消费服务
根据业务 listener 是并发消费类型还是顺序消费类型,创建对应的消息消费服务
if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerOrderly) {
this.consumeOrderly = true;
this.consumeMessageService = new ConsumeMessageOrderlyService(this, (MessageListenerOrderly) this.getMessageListenerInner());
} else if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerConcurrently) {
this.consumeOrderly = false;
this.consumeMessageService = new ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService(this, (MessageListenerConcurrently) this.getMessageListenerInner());
}
启动消息消费服务的定时任务
针对消费服务,启动辅助的定时任务
并发消费的定时任务
该定时任务延时 15 分钟后,每隔 15 分钟执行一次。该任务定时清理消费超时的消息,消费超时阈值默认 15 分钟,所以定时任务的周期如此设置
- 消费超时的阈值由 org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumer#consumeTimeout 控制,默认 15 分钟
public void start() {
this.cleanExpireMsgExecutors.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
cleanExpireMsg();
}
},
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeTimeout(), this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeTimeout(), TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
清理消费超时消息的具体流程:
遍历 processQueue 里的消息,如果业务 listener 对消息的消费时间超过阈值,默认 15 分钟,将消息发回 broker 做延时投递重新消费,然后从 processQueue 里移除
public void cleanExpiredMsg(DefaultMQPushConsumer pushConsumer) {
if (pushConsumer.getDefaultMQPushConsumerImpl().isConsumeOrderly()) {
return;
}
int loop = msgTreeMap.size() < 16 ? msgTreeMap.size() : 16;
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
MessageExt msg = null;
try {
this.lockTreeMap.readLock().lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 如果业务listener消费消息的时间超过了阈值,将消息发回broker
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty() && System.currentTimeMillis() - Long.parseLong(MessageAccessor.getConsumeStartTimeStamp(msgTreeMap.firstEntry().getValue())) > pushConsumer.getConsumeTimeout() * 60 * 1000) {
msg = msgTreeMap.firstEntry().getValue();
} else {
break;
}
} finally {
this.lockTreeMap.readLock().unlock();
}
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
log.error("getExpiredMsg exception", e);
}
try {
pushConsumer.sendMessageBack(msg, 3);
log.info("send expire msg back. topic={}, msgId={}, storeHost={}, queueId={}, queueOffset={}", msg.getTopic(), msg.getMsgId(), msg.getStoreHost(), msg.getQueueId(), msg.getQueueOffset());
try {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().lockInterruptibly();
try {
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty() && msg.getQueueOffset() == msgTreeMap.firstKey()) {
try {
removeMessage(Collections.singletonList(msg));
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("send expired msg exception", e);
}
}
} finally {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().unlock();
}
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
log.error("getExpiredMsg exception", e);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("send expired msg exception", e);
}
}
}
顺序消费的定时任务
默认 20s 执行一次,定时对 broker 上的 messageQueue 发起加锁请求,加锁成功的 mq 对应的 processQueue,置 locked 字段为 true。这么做是为了确保 mqClient 和 mq 的唯一绑定关系,确保 mq 上的消息在 consumerGroup 能被顺序消费
public void start() {
// 集群模式顺序消费时,client定时对broker上的messageQueue加锁,对加锁成功的mq对应的processQueue,置locked字段为true
if (MessageModel.CLUSTERING.equals(ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.messageModel())) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {@Override public void run() {
ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.lockMQPeriodically();
}
},
1000 * 1, ProcessQueue.REBALANCE_LOCK_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
public void lockAll() {
HashMap < String,
Set < MessageQueue >> brokerMqs = this.buildProcessQueueTableByBrokerName();
Iterator < Entry < String,
Set < MessageQueue >>> it = brokerMqs.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry < String,
Set < MessageQueue >> entry = it.next();
final String brokerName = entry.getKey();
final Set < MessageQueue > mqs = entry.getValue();
if (mqs.isEmpty()) continue;
FindBrokerResult findBrokerResult = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(brokerName, MixAll.MASTER_ID, true);
if (findBrokerResult != null) {
LockBatchRequestBody requestBody = new LockBatchRequestBody();
requestBody.setConsumerGroup(this.consumerGroup);
requestBody.setClientId(this.mQClientFactory.getClientId());
requestBody.setMqSet(mqs);
try {
Set < MessageQueue > lockOKMQSet = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().lockBatchMQ(findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr(), requestBody, 1000);
for (MessageQueue mq: lockOKMQSet) {
ProcessQueue processQueue = this.processQueueTable.get(mq);
if (processQueue != null) {
if (!processQueue.isLocked()) {
log.info("the message queue locked OK, Group: {} {}", this.consumerGroup, mq);
}
processQueue.setLocked(true);
processQueue.setLastLockTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
for (MessageQueue mq: mqs) {
if (!lockOKMQSet.contains(mq)) {
ProcessQueue processQueue = this.processQueueTable.get(mq);
if (processQueue != null) {
processQueue.setLocked(false);
log.warn("the message queue locked Failed, Group: {} {}", this.consumerGroup, mq);
}
}
}
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error("lockBatchMQ exception, " + mqs, e);
}
}
}
}
consumer 注册到 mqClient
同 producer
启动 MQClientInstance
同 producer
Broker
Broker 如何做消息持久化
先说结论:
- 消息持久化的流程是:先写内核缓冲区 PageCache–>再把数据刷盘到文件
- broker 将消息顺序写入 commitLog 文件。超过 1G 后自动创建新文件,文件名为当前偏移量 offset
- 写入 commitLog 后,broker 会把消息的索引信息放到 messageQueue 里。索引信息包括:commitLogOffset+msgSize+tagsHashCode,共 20 字节
- broker 处理 consumer 的消息拉取请求时,如果 messageQueue 里存在 request.nextOffset 偏移量后面的消息,且消息的 tagsHashCode 在 group 的订阅信息里,或者消息满足 consumer 端的 sql 表达式,则通过 commitLogOffset+msgSize 到 commitLog 里取出消息体,发送给 consumer
- 获取消息需要先读 messageQueue 再读 commitLog,但不会影响性能。因为 Linux 的 PageCache 技术,读写磁盘文件的数据都会缓存到 PageCache 缓存,且 messageQueue 只包含索引信息,占用的字节更少(每个消息 20 字节),所以 PageCache 可以缓存更多的 messageQueue,对它的读取接近直接从内存获取
消息持久化的入口:
org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile#appendMessagesInner
写入内核缓冲区
先将消息写入内核缓冲区 PageCache
byteBuffer.put(this.msgStoreItemMemory.array(), 0, msgLen);
这里需要说明的是,buteBuffer 使用了 java nio 里的 DirectByteBuffer,该对象是 java 程序对内核缓冲区的引用,通过它可以直接操作内核缓冲区,减少了用户空间(java 堆内存)到内核缓冲区的数据拷贝,提高了 io 读写性能。这也是我们常说的零拷贝技术。
public void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(fileSize);
final long address = ((DirectBuffer) byteBuffer).address();
Pointer pointer = new Pointer(address);
LibC.INSTANCE.mlock(pointer, new NativeLong(fileSize));
availableBuffers.offer(byteBuffer);
}
}
刷盘即 PageCache 缓存的数据刷入磁盘文件。有两种实现方式:
- 将 DirectByteBuffer 指向的 PageCache 的数据提交到 FileChannel。FileChannel 把数据给到操作系统进行文件修改
- 调用 java.nio.MappedByteBuffer#force,不通过 FileChannel 直接将 PageCache 的数据映射到文件,这种是针对超大文件的一种优化。还不太了解原理
刷盘策略也分为同步刷盘和异步刷盘,他们的共同点都是唤醒异步刷盘线程执行刷盘操作,区别是同步刷盘阻塞等待刷盘线程的结果,异步刷盘只唤醒刷盘线程就结束了
- GroupCommitService:同步刷盘,基于 MappedByteBuffer
- 同步刷盘的线程阻塞在 flushOkFuture.get 方法,等待刷盘结果再返回
- CommitRealTimeService:异步刷盘,基于 DirectByteBuffer
- 异步刷盘只是 wakeUp 刷盘线程,底层 countDown 唤醒,开始刷盘
- FlushRealTimeService:异步刷盘,基于 MappedByteBuffer
- 异步刷盘只是 wakeUp 刷盘线程,底层 countDown 唤醒,开始刷盘
public void handleDiskFlush(AppendMessageResult result, PutMessageResult putMessageResult, MessageExt messageExt) {
// Synchronization flush
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
final GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;
if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {
GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes());
service.putRequest(request);
CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> flushOkFuture = request.future();
PutMessageStatus flushStatus = null;
try {
flushStatus = flushOkFuture.get(this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
//flushOK=false;
}
if (flushStatus != PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK) {
log.error("do groupcommit, wait for flush failed, topic: " + messageExt.getTopic() + " tags: " + messageExt.getTags()
+ " client address: " + messageExt.getBornHostString());
putMessageResult.setPutMessageStatus(PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
}
} else {
service.wakeup();
}
}
// Asynchronous flush
else {
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
// FlushRealTimeService
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
// CommitRealTimeService
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
}
}
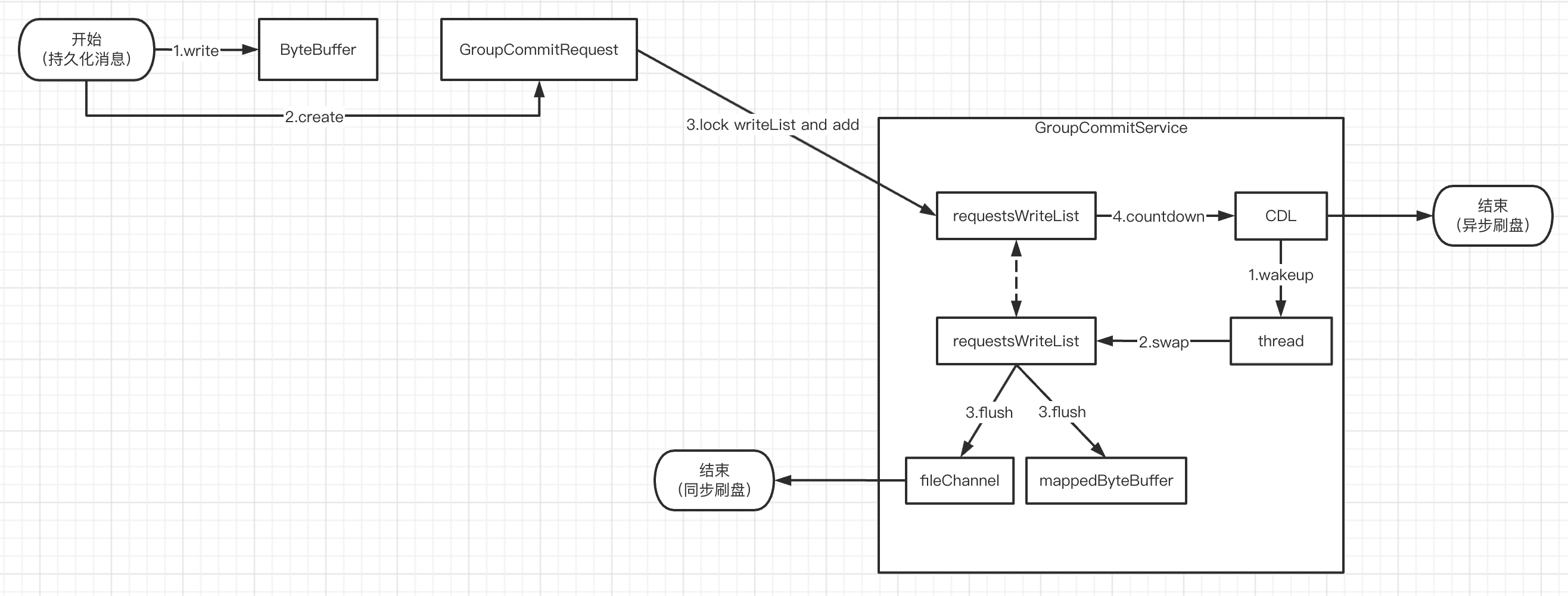
如果是同步刷盘策略,会把一个组提交 GroupCommitRequest 请求放到 GroupCommitService 的写列表里。然后执行 countDown 方法唤醒同步刷盘线程
- GroupCommitRequest 指定了消息在 PageCache 的 offset,该 offset 之前的数据都可以刷到磁盘里
- GroupCommitService 是一个守护线程,负责执行列表里的组提交刷盘请求
private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsWrite = new ArrayList<GroupCommitRequest>();
private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsRead = new ArrayList<GroupCommitRequest>();
public synchronized void putRequest(final GroupCommitRequest request) {
synchronized (this.requestsWrite) {
this.requestsWrite.add(request);
}
this.wakeup();
}
public void wakeup() {
if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
waitPoint.countDown(); // notify
}
}
唤醒线程后,先交换 GroupCommitService 的读写列表。相当于清空了写列表,它可以继续添加新的组提交请求。刷盘遍历的是读列表里的组提交请求,然后执行底层的刷盘操作
- 两个列表交替使用,读列表被加锁刷盘时,写列表可以继续用于添加请求。效率较高
- 刷盘结束条件:刷两次或者刷盘请求指定的 offset 位置已经刷到磁盘了
private void swapRequests() {
List<GroupCommitRequest> tmp = this.requestsWrite;
this.requestsWrite = this.requestsRead;
this.requestsRead = tmp;
}
private void doCommit() {
synchronized (this.requestsRead) {
if (!this.requestsRead.isEmpty()) {
for (GroupCommitRequest req : this.requestsRead) {
// There may be a message in the next file, so a maximum of
// two times the flush
boolean flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
for (int i = 0; i < 2 && !flushOK; i++) {
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
}
req.wakeupCustomer(flushOK ? PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK : PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
}
long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
this.requestsRead.clear();
} else {
// Because of individual messages is set to not sync flush, it
// will come to this process
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
}
}
}
public int flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) {
if (this.hold()) {
int value = getReadPosition();
try {
//We only append data to fileChannel or mappedByteBuffer, never both.
if (writeBuffer != null || this.fileChannel.position() != 0) {
this.fileChannel.force(false);
} else {
this.mappedByteBuffer.force();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when force data to disk.", e);
}
this.flushedPosition.set(value);
this.release();
} else {
log.warn("in flush, hold failed, flush offset = " + this.flushedPosition.get());
this.flushedPosition.set(getReadPosition());
}
}
return this.getFlushedPosition();
}
Broker 处理 Consumer 拉取消息请求
入口:org.apache.rocketmq.broker.processor.PullMessageProcessor#processRequest(io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext, org.apache.rocketmq.remoting.protocol.RemotingCommand)
构建 MessageFilter
根据 request 里的 consumerGroup 订阅信息构建消息过滤 MessageFilter 对象。该对象主要包含 2 个用于消息过滤的成员变量:
- SubscriptionData,它包含了 tagsHashCodeSet,通过它完成基于 tag 的过滤
- ConsumerFilterData,它使用布隆过滤器存储 consumerGroup+topic 映射的 bit 数组。通过它做基于 sql 表达式的过滤
- 每条消息在 messageQueue 扩展队列里会存储所有通过 sql 校验的 consumerGroup 组成的布隆过滤器 bit 数组。这个大 bit 数组是在消息持久化过程中计算并存储到 messageQueue 的扩展队列
- 如果当前 bit 数组不包含在这个大数组中,说明这条消息一定不能满足 sql 表达式
- 如果包含,说明这条消息可能满足 sql 表达式(因为布隆过滤器可能误判),再执行一次 sql 表达式来验证。通过布隆过滤器,能提升 consumer 消息拉取的性能,不用每条消息都执行一遍 sql 表达式来验证
- 每条消息在 messageQueue 扩展队列里会存储所有通过 sql 校验的 consumerGroup 组成的布隆过滤器 bit 数组。这个大 bit 数组是在消息持久化过程中计算并存储到 messageQueue 的扩展队列
MessageFilter messageFilter;
if (this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isFilterSupportRetry()) {
messageFilter = new ExpressionForRetryMessageFilter(subscriptionData, consumerFilterData,
this.brokerController.getConsumerFilterManager());
} else {
messageFilter = new ExpressionMessageFilter(subscriptionData, consumerFilterData,
this.brokerController.getConsumerFilterManager());
}
找到 MessageQueue
实际要找的是:存储 MessageQueue 的所有文件在内存 PageCache 里的映射对象
broker 为每个 topic 创建多个 messageQueue。每个 MessageQueue 对应一个包含 topic+messageQueueId 的路径,该路径下会创建多个文件,存储消息的索引和过滤信息
- 每条消息在 messageQueue 上占 20 字节:commitLogOffset、msgSize、消息在 MessageQueue 扩展队列的地址
- 每个文件大小 mappedFileSize 默认为 20 字节*30W,即每个文件最多存储 30W 条消息
- 每条消息在扩展对列上存储:所有通过 sql 校验的 consumerGroup 组成的布隆过滤器 bit 数组、消息的 tagsHashCode
按 topic+queueId 查内存,获取 MessageQueue。它主要封装了 MappedFileQueue,表示实际存储 MessageQueue 的路径下所有文件的 PageCache 缓存
public class ConsumeQueue {
private static final InternalLogger log = InternalLoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggerName.STORE_LOGGER_NAME);
// messageQueue上的每条消息的大小,20字节=commitLogOffset+msgSize+tagsHashCode
public static final int CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE = 20;
private final MappedFileQueue mappedFileQueue;
private final String topic;
private final int queueId;
private final String storePath;
// 默认20字节*30W,即一个MessageQueue最多存储30W条消息
private final int mappedFileSize;
public ConsumeQueue(final String topic, final int queueId, final String storePath, final int mappedFileSize, final DefaultMessageStore defaultMessageStore) {
this.storePath = storePath;
this.mappedFileSize = mappedFileSize;
this.defaultMessageStore = defaultMessageStore;
this.topic = topic;
this.queueId = queueId;
String queueDir = this.storePath + File.separator + topic + File.separator + queueId;
this.mappedFileQueue = new MappedFileQueue(queueDir, mappedFileSize, null);
this.byteBufferIndex = ByteBuffer.allocate(CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
if (defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isEnableConsumeQueueExt()) {
this.consumeQueueExt = new ConsumeQueueExt(topic, queueId, StorePathConfigHelper.getStorePathConsumeQueueExt(defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getStorePathRootDir()), defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getMappedFileSizeConsumeQueueExt(), defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getBitMapLengthConsumeQueueExt());
}
}
... ...
}
public ConsumeQueue findConsumeQueue(String topic, int queueId) {
ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> map = consumeQueueTable.get(topic);
if (null == map) {
ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> newMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue>(128);
ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> oldMap = consumeQueueTable.putIfAbsent(topic, newMap);
if (oldMap != null) {
map = oldMap;
} else {
map = newMap;
}
}
ConsumeQueue logic = map.get(queueId);
… …
return logic;
}
定位在 MessageQueue 的起始消费位置
根据 request 传入的起始消息 offset,先定位具体存储该条消息的文件的 PageCache,再计算 offset 在该文件的起始字节位置,返回从该位置开始的 ByteBuffer
public SelectMappedBufferResult getIndexBuffer(final long startIndex) {
int mappedFileSize = this.mappedFileSize;
long offset = startIndex * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
if (offset >= this.getMinLogicOffset()) {
// 根据offset到MassageQueue的文件列表里拿到存储该条消息的文件,返回该文件映射的PageCache对象MappedFile
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.findMappedFileByOffset(offset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
// offset % mappedFileSize 是该条消息在文件里的起始字节位置,返回从该位置开始的ByteBuffer
SelectMappedBufferResult result = mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer((int) (offset % mappedFileSize));
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
定位是哪个文件其实很简单,根据 offset 计算消息存储在哪个字节处(offset*20,20 为每条消息的存储空间),然后除每个文件的最大字节数(20 字节*30W)
long offset = startIndex * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
... ...
int index = (int) ((offset / this.mappedFileSize) - (firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() / this.mappedFileSize));
定位在文件上的起始字节位置也同理,对单个文件最大字节数取余即可
SelectMappedBufferResult result = mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer((int) (offset % mappedFileSize));
拿到起始位置的 ByteBuffer 后,每 20 字节开始读取消息在 ByteBuffer 上的索引和过滤信息
- 注意,tagsCode 实际为消息在扩展队列的地址,tagsCode 和所有通过 sql 过滤的布隆过滤器 bit 数组都存储在扩展队列
- 最多读取消息数可以在 request 里指定,如果不指定默认为 16000/20 = 800。当然还没读到这些消息 messageQueue 就读完了也会退出
final int maxFilterMessageCount = Math.max(16000, maxMsgNums * ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
... ...
for (; i < bufferConsumeQueue.getSize() && i < maxFilterMessageCount; i += ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE) {
long offsetPy = bufferConsumeQueue.getByteBuffer().getLong();
int sizePy = bufferConsumeQueue.getByteBuffer().getInt();
long tagsCode = bufferConsumeQueue.getByteBuffer().getLong();
... ...
}
调用此次消息拉取请求的消息过滤器 MessageFilter,判断消息是否满足过滤条件。实际调用方法为:org.apache.rocketmq.broker.filter.ExpressionMessageFilter#isMatchedByConsumeQueue
if (messageFilter != null
// 消息是否满足tag过滤和sql过滤
&& !messageFilter.isMatchedByConsumeQueue(isTagsCodeLegal ? tagsCode : null, extRet ? cqExtUnit : null)) {
if (getResult.getBufferTotalSize() == 0) {
status = GetMessageStatus.NO_MATCHED_MESSAGE;
}
continue;
}
基于 tag 或者基于 sql 的消息过滤规则上面说过了,代码也很清晰
public boolean isMatchedByConsumeQueue(Long tagsCode, ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit cqExtUnit) {
if (null == subscriptionData) {
return true;
}
if (subscriptionData.isClassFilterMode()) {
return true;
}
// by tags code.
if (ExpressionType.isTagType(subscriptionData.getExpressionType())) {
if (tagsCode == null) {
return true;
}
if (subscriptionData.getSubString().equals(SubscriptionData.SUB_ALL)) {
return true;
}
return subscriptionData.getCodeSet().contains(tagsCode.intValue());
} else {
// no expression or no bloom
if (consumerFilterData == null || consumerFilterData.getExpression() == null
|| consumerFilterData.getCompiledExpression() == null || consumerFilterData.getBloomFilterData() == null) {
return true;
}
// message is before consumer
if (cqExtUnit == null || !consumerFilterData.isMsgInLive(cqExtUnit.getMsgStoreTime())) {
log.debug("Pull matched because not in live: {}, {}", consumerFilterData, cqExtUnit);
return true;
}
byte[] filterBitMap = cqExtUnit.getFilterBitMap();
BloomFilter bloomFilter = this.consumerFilterManager.getBloomFilter();
if (filterBitMap == null || !this.bloomDataValid
|| filterBitMap.length * Byte.SIZE != consumerFilterData.getBloomFilterData().getBitNum()) {
return true;
}
BitsArray bitsArray = null;
try {
bitsArray = BitsArray.create(filterBitMap);
// 如果consumerGroup的布隆过滤bit数组在所有满足sql的consumerGroup组成的布隆过滤bit数组中,则认为sql过滤通过
// (可能误判,还需要实际执行sql表达式来判断是否满足)
boolean ret = bloomFilter.isHit(consumerFilterData.getBloomFilterData(), bitsArray);
log.debug("Pull {} by bit map:{}, {}, {}", ret, consumerFilterData, bitsArray, cqExtUnit);
return ret;
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("bloom filter error, sub=" + subscriptionData
+ ", filter=" + consumerFilterData + ", bitMap=" + bitsArray, e);
}
}
return true;
}
如果 MessageFilter 过滤通过了,从 commitLog 里取出实际的消息体内存映射 MappedByteBuffer。取的逻辑和上面 MessageQueue 一样,先根据 commitLogOffset 做除法定位文件,然后取余定位具体内存位置
- CommitLog 每个文件大小默认为 1G
SelectMappedBufferResult selectResult = this.commitLog.getMessage(offsetPy, sizePy);
public SelectMappedBufferResult getMessage(final long offset, final int size) {
int mappedFileSize = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getMappedFileSizeCommitLog();
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.findMappedFileByOffset(offset, offset == 0);
if (mappedFile != null) {
int pos = (int) (offset % mappedFileSize);
return mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer(pos, size);
}
return null;
}
拿到实际消息体后,如果按 sql 过滤,还要实际执行一遍 sql 表达式来确认是否满足,因为布隆过滤器可能误判
public boolean isMatchedByCommitLog(ByteBuffer msgBuffer, Map<String, String> properties) {
if (subscriptionData == null) {
return true;
}
if (subscriptionData.isClassFilterMode()) {
return true;
}
if (ExpressionType.isTagType(subscriptionData.getExpressionType())) {
return true;
}
ConsumerFilterData realFilterData = this.consumerFilterData;
Map<String, String> tempProperties = properties;
// no expression
if (realFilterData == null || realFilterData.getExpression() == null
|| realFilterData.getCompiledExpression() == null) {
return true;
}
if (tempProperties == null && msgBuffer != null) {
tempProperties = MessageDecoder.decodeProperties(msgBuffer);
}
Object ret = null;
try {
MessageEvaluationContext context = new MessageEvaluationContext(tempProperties);
// 执行sql表达式判断消息是否真的满足过滤条件,因为布隆过滤器可能误判
ret = realFilterData.getCompiledExpression().evaluate(context);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Message Filter error, " + realFilterData + ", " + tempProperties, e);
}
log.debug("Pull eval result: {}, {}, {}", ret, realFilterData, tempProperties);
if (ret == null || !(ret instanceof Boolean)) {
return false;
}
return (Boolean) ret;
}
设置下次 consumer 拉取消息的起始 offset。i 为这次读到的内存位置
// 更新下次消息拉取的起始offset。for循环读取messageQueue消息时做了计数,所以下次拉取消息的offset就是这次的offset加上计数器的值
nextBeginOffset = offset + (i / ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
遍历完 MessageQueue 后,把满足条件的消息从 MappedByteBuffer 移到堆内存,然后转成字节数组赋值给 response
// 把消息在PageCache的缓存数据读取到堆内存,转成字节数组,放到响应的body里
final byte[] r = this.readGetMessageResult(getMessageResult, requestHeader.getConsumerGroup(), requestHeader.getTopic(), requestHeader.getQueueId());
如果没拉取到消息
遍历完 MessageQueue 后如果没有符合过滤条件的消息,broker 会把请求挂起,这时不会发送响应给 consumer。
如果 broker 支持长轮训,挂起的时间为 consumer 发送请求时指定的时间。如果不支持长轮训,则使用短轮训,默认挂起 1s。
- 所谓挂起,是把 consumerGroup 在该 messageQueue 上的消息拉取请求存到 map 里
// 如果没有满足条件的新消息,把consumer的请求缓存起来,然后返回null,此时不会给consumer发送响应
this.brokerController.getPullRequestHoldService().suspendPullRequest(topic, queueId, pullRequest);
public void suspendPullRequest(final String topic, final int queueId, final PullRequest pullRequest) {
String key = this.buildKey(topic, queueId);
ManyPullRequest mpr = this.pullRequestTable.get(key);
if (null == mpr) {
mpr = new ManyPullRequest();
ManyPullRequest prev = this.pullRequestTable.putIfAbsent(key, mpr);
if (prev != null) {
mpr = prev;
}
}
mpr.addPullRequest(pullRequest);
}
broker 会有一个守护线程 PullRequestHoldService,如果支持长轮训,5s 执行一次,处理所有挂起的请求,如果是短轮询,1s 执行一次
public void run() {
log.info("{} service started", this.getServiceName());
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
if (this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isLongPollingEnable()) {
this.waitForRunning(5 * 1000);
} else {
this.waitForRunning(this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().getShortPollingTimeMills());
}
long beginLockTimestamp = this.systemClock.now();
this.checkHoldRequest();
long costTime = this.systemClock.now() - beginLockTimestamp;
if (costTime > 5 * 1000) {
log.info("[NOTIFYME] check hold request cost {} ms.", costTime);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
log.info("{} service end", this.getServiceName());
}
处理挂起请求的逻辑是:
如果 messageQueue 在 hold 开始后又有新消息,或者超过最大 hold 时长,发送消息拉取结果给 consumer,让它发送新的请求过来,从新的 beginOffset 开始继续拉取消息
if (newestOffset > request.getPullFromThisOffset()) {
… …
try {
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor().executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() >= (request.getSuspendTimestamp() + request.getTimeoutMillis())) {
try {
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor().executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK