

Supervisor启动并管理Celery相关进程 - huxiaofeng
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/huxiaofeng1029/p/17483637.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Supervisor启动并管理Celery相关进程
关于celery在运行过程中, 默认情况下是无法在关机以后自动重启的。所以我们一般开发中会使用supervisor进程监控来对celery程序进行运行监控!当celery没有启动的情况下,supervisor会自动启动celery,所以我们需要安装supervisor并且编写一个supervisor的控制脚本,在脚本中编写对celery进行启动的命令即可。
1. 安装和启动celery任务监控器
针对celery中的任务执行过程,我们也可以安装一个flower的工具来进行监控。
pip install flower
cd /home/moluo/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi
# 保证celery在启动中
celery -A luffycityapi worker -l INFO
# 再启动celery-flower
celery -A luffycityapi flower --port=5555
http://localhost:5555
attention: 这里启动了测试之后就可以关掉了, 因为后面会使用supervisor启动flower, 防止占用端口
2. supervisor启动celery&flower
Supervisor是用Python开发的一套通用的进程管理程序,能将一个普通的命令行进程变为系统守护进程daemon,并监控进程状态,异常退出时能自动重启。
pip install supervisor
# 注意:如果supervisor是安装在虚拟环境的,则每次使用supervisor务必在虚拟环境中进行后面所有的操作
# conda activate luffycity
supervisor配置文档:http://supervisord.org/configuration.html
对Supervisor初始化配置
# 在项目根目录下创建存储supervisor配置目录,在luffycityapi创建scripts目录,已经创建则忽略
conda activate luffycity
cd /home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi
mkdir -p scripts && cd scripts
# 生成初始化supervisor核心配置文件,echo_supervisord_conf是supervisor安装成功以后,自动附带的。
echo_supervisord_conf > supervisord.conf
# 可以通过 ls 查看scripts下是否多了supervisord.conf这个文件,表示初始化配置生成了。
# 在编辑器中打开supervisord.conf,并去掉最后一行的注释分号。
# 修改如下,表示让supervisor自动加载当前supervisord.conf所在目录下所有ini配置文件
supervisord/conf.py,主要修改文件中的39, 40,75,76,169,170行去掉左边注释,其中170修改成当前目录。配置代码:
; Sample supervisor config file.
;
; For more information on the config file, please see:
; http://supervisord.org/configuration.html
;
; Notes:
; - Shell expansion ("~" or "$HOME") is not supported. Environment
; variables can be expanded using this syntax: "%(ENV_HOME)s".
; - Quotes around values are not supported, except in the case of
; the environment= options as shown below.
; - Comments must have a leading space: "a=b ;comment" not "a=b;comment".
; - Command will be truncated if it looks like a config file comment, e.g.
; "command=bash -c 'foo ; bar'" will truncate to "command=bash -c 'foo ".
;
; Warning:
; Paths throughout this example file use /tmp because it is available on most
; systems. You will likely need to change these to locations more appropriate
; for your system. Some systems periodically delete older files in /tmp.
; Notably, if the socket file defined in the [unix_http_server] section below
; is deleted, supervisorctl will be unable to connect to supervisord.
[unix_http_server]
file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; the path to the socket file
;chmod=0700 ; socket file mode (default 0700)
;chown=nobody:nogroup ; socket file uid:gid owner
;username=user ; default is no username (open server)
;password=123 ; default is no password (open server)
; Security Warning:
; The inet HTTP server is not enabled by default. The inet HTTP server is
; enabled by uncommenting the [inet_http_server] section below. The inet
; HTTP server is intended for use within a trusted environment only. It
; should only be bound to localhost or only accessible from within an
; isolated, trusted network. The inet HTTP server does not support any
; form of encryption. The inet HTTP server does not use authentication
; by default (see the username= and password= options to add authentication).
; Never expose the inet HTTP server to the public internet.
[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default
port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface
;username=user ; default is no username (open server)
;password=123 ; default is no password (open server)
[supervisord]
logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ; main log file; default $CWD/supervisord.log
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; max main logfile bytes b4 rotation; default 50MB
logfile_backups=10 ; # of main logfile backups; 0 means none, default 10
loglevel=info ; log level; default info; others: debug,warn,trace
pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ; supervisord pidfile; default supervisord.pid
nodaemon=false ; start in foreground if true; default false
silent=false ; no logs to stdout if true; default false
minfds=1024 ; min. avail startup file descriptors; default 1024
minprocs=200 ; min. avail process descriptors;default 200
;umask=022 ; process file creation umask; default 022
;user=supervisord ; setuid to this UNIX account at startup; recommended if root
;identifier=supervisor ; supervisord identifier, default is 'supervisor'
;directory=/tmp ; default is not to cd during start
;nocleanup=true ; don't clean up tempfiles at start; default false
;childlogdir=/tmp ; 'AUTO' child log dir, default $TEMP
;environment=KEY="value" ; key value pairs to add to environment
;strip_ansi=false ; strip ansi escape codes in logs; def. false
; The rpcinterface:supervisor section must remain in the config file for
; RPC (supervisorctl/web interface) to work. Additional interfaces may be
; added by defining them in separate [rpcinterface:x] sections.
[rpcinterface:supervisor]
supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface
; The supervisorctl section configures how supervisorctl will connect to
; supervisord. configure it match the settings in either the unix_http_server
; or inet_http_server section.
[supervisorctl]
; serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket
serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; use an http:// url to specify an inet socket
;username=chris ; should be same as in [*_http_server] if set
;password=123 ; should be same as in [*_http_server] if set
;prompt=mysupervisor ; cmd line prompt (default "supervisor")
;history_file=~/.sc_history ; use readline history if available
; The sample program section below shows all possible program subsection values.
; Create one or more 'real' program: sections to be able to control them under
; supervisor.
;[program:theprogramname]
;command=/bin/cat ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1)
;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999)
;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true)
;startsecs=1 ; # of secs prog must stay up to be running (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures when starting (default 3)
;autorestart=unexpected ; when to restart if exited after running (def: unexpected)
;exitcodes=0 ; 'expected' exit codes used with autorestart (default 0)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false)
;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=true ; redirect proc stderr to stdout (default false)
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stdout_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false)
;stdout_syslog=false ; send stdout to syslog with process name (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stderr_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;stderr_syslog=false ; send stderr to syslog with process name (default false)
;environment=A="1",B="2" ; process environment additions (def no adds)
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils)
; The sample eventlistener section below shows all possible eventlistener
; subsection values. Create one or more 'real' eventlistener: sections to be
; able to handle event notifications sent by supervisord.
;[eventlistener:theeventlistenername]
;command=/bin/eventlistener ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1)
;events=EVENT ; event notif. types to subscribe to (req'd)
;buffer_size=10 ; event buffer queue size (default 10)
;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=-1 ; the relative start priority (default -1)
;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true)
;startsecs=1 ; # of secs prog must stay up to be running (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures when starting (default 3)
;autorestart=unexpected ; autorestart if exited after running (def: unexpected)
;exitcodes=0 ; 'expected' exit codes used with autorestart (default 0)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false)
;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=false ; redirect_stderr=true is not allowed for eventlisteners
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false)
;stdout_syslog=false ; send stdout to syslog with process name (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;stderr_syslog=false ; send stderr to syslog with process name (default false)
;environment=A="1",B="2" ; process environment additions
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils)
; The sample group section below shows all possible group values. Create one
; or more 'real' group: sections to create "heterogeneous" process groups.
;[group:thegroupname]
;programs=progname1,progname2 ; each refers to 'x' in [program:x] definitions
;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999)
; The [include] section can just contain the "files" setting. This
; setting can list multiple files (separated by whitespace or
; newlines). It can also contain wildcards. The filenames are
; interpreted as relative to this file. Included files *cannot*
; include files themselves.
[include]
files = *.ini
创建luffycity_celery_worker.ini文件,启动我们项目worker主进程
cd /home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/scripts
touch luffycity_celery_worker.ini
[program:luffycity_celery_worker]
# 启动命令 conda env list
command=/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin/celery -A luffycityapi worker -l info -n worker1
# 项目根目录的绝对路径[manage.py所在目录路径],通过pwd查看
directory=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi
# 项目虚拟环境
enviroment=PATH="/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin"
# 运行日志绝对路径
stdout_logfile=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/logs/celery.worker.info.log
# 错误日志绝对路径
stderr_logfile=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/logs/celery.worker.error.log
# 自动启动,开机自启
autostart=true
# 启动当前命令的用户名
user=ifeng
# 重启
autorestart=true
# 进程启动后跑了几秒钟,才被认定为成功启动,默认1
startsecs=10
# 进程结束后60秒才被认定结束
stopwatisecs=60
# 优先级,值小的优先启动
priority=990
创建luffycity_celery_beat.ini文件,来触发我们的beat定时计划任务
cd /home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/scripts
touch luffycity_celery_beat.ini
[program:luffycity_celery_beat]
# 启动命令 conda env list
command=/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin/celery -A luffycityapi beat -l info
# 项目根目录的绝对路径,通过pwd查看
directory=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi
# 项目虚拟环境
enviroment=PATH="/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin"
# 运行日志绝对路径
stdout_logfile=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/logs/celery.beat.info.log
# 错误日志绝对路径
stderr_logfile=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/logs/celery.beat.error.log
# 自动启动,开机自启
autostart=true
# 重启
autorestart=true
# 进程启动后跑了几秒钟,才被认定为成功启动,默认1
startsecs=10
# 进程结束后60秒才被认定结束
stopwatisecs=60
# 优先级,值小的优先启动
priority=998
创建luffycity_celery_flower.ini文件,来启动我们的celery监控管理工具
cd /home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/scripts
touch luffycity_celery_flower.ini
[program:luffycity_celery_flower]
# 启动命令 conda env list
command=/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin/celery -A luffycityapi flower --port=5555
# 项目根目录的绝对路径,通过pwd查看
directory=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi
# 项目虚拟环境
enviroment=PATH="/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin"
# 输出日志绝对路径
stdout_logfile=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/logs/celery.flower.info.log
# 错误日志绝对路径
stderr_logfile=/home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/logs/celery.flower.error.log
# 自动启动,开机自启
autostart=true
# 重启
autorestart=true
# 进程启动后跑了几秒钟,才被认定为成功启动,默认1
startsecs=10
# 进程结束后60秒才被认定结束
stopwatisecs=60
# 优先级
priority=999
启动supervisor,确保此时你在项目路径下
cd ~/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi
supervisord -c scripts/supervisord.conf
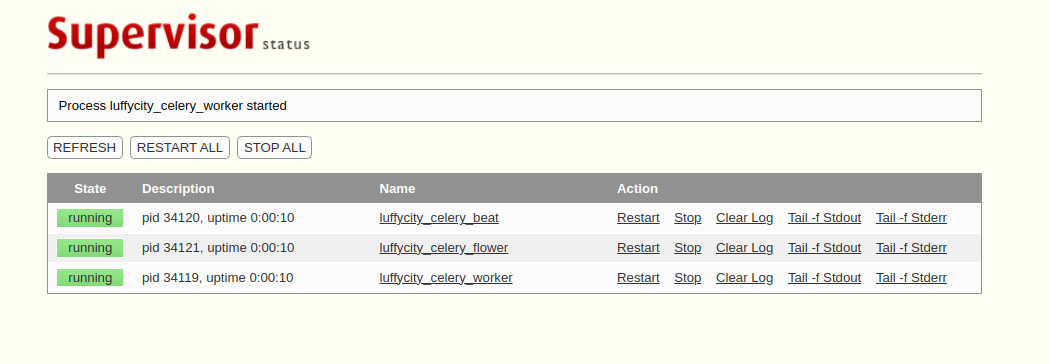
通过浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:9001
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
supervisorctl stop program |
停止某一个进程,program 就是进程名称,例如在ini文件首行定义的[program:进程名称] |
supervisorctl stop all |
停止全部进程 |
| supervisorctl start program | 启动某个进程,program同上,也支持启动所有的进程 |
| supervisorctl restart program | 重启某个进程,program同上,也支持重启所有的进程 |
supervisorctl reload |
载入最新的配置文件,停止原有进程并按新的配置启动、管理所有进程 注意:start、restart、stop 等都不会载入最新的配置文件 |
| supervisorctl update | 根据最新的配置文件,启动新配置或有改动的进程,配置没有改动的进程不会受影响而重启 |
| ps aux | grep supervisord | 查看supervisor是否启动 |
把supervisor注册到ubuntu系统服务中并设置开机自启
cd /home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/scripts
touch supervisor.service
supervisor.service,配置内容,并保存。需要通过conda env list 查看当前的虚拟环境路径
[Unit]
Description=supervisor
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin/supervisord -n -c /home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/scripts/supervisord.conf
ExecStop=/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin/supervisorctl $OPTIONS shutdown
ExecReload=/home/ifeng/anaconda3/envs/luffycity/bin/supervisorctl $OPTIONS reload
KillMode=process
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=42s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
设置开机自启
# 创建日志文件
sudo chmod 766 /tmp/supervisord.log
cd /home/ifeng/Desktop/luffycity/luffycityapi/scripts
# 赋予权限
chmod 766 supervisor.service
# 复制到系统开启服务目录下
sudo cp supervisor.service /lib/systemd/system/
# 设置允许开机自启
systemctl enable supervisor.service
# 判断是否已经设置为开机自启了
systemctl is-enabled supervisor.service
# 通过systemctl查看supervisor运行状态
systemctl status supervisor.service
# 如果查看服务状态时无法启动,则可以通过重启linux系统来测试是否因为前面的终端已经运行了supervisor导致的。当然,也可以手动关闭supervisor以及相关的服务。
# supervisorctl stop all
# ps aux | grep supervisord
# kill -9 51564 # 注意: 9068是举例的,具体看上一行的查询结果
效果图:
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK