

Hive执行计划之hive依赖及权限查询和常见使用场景 - 鲁边
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/lubians/p/17464519.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Hive查看执行计划的命令中还有两个不怎么常用但很重要的命令,接下来详细介绍一下。
有一个问题:如何在hiveSQL执行之前就探查到这段逻辑的血缘依赖关系?
hive血缘是很多生产级数仓必须要提供的功能,大多数解决方案都是使用hive hooks的方法通过SQL执行后解析得到hive表的依赖关系。
这个方案能细粒度到字段级依赖,属于很完善的一个解决方案,但有很多场景我们需要在SQL执行之前就得到依赖关系,那么如何解决的呢?
1.explain dependency的查询与使用
explain dependency 提供了这样的一个解决方案,它可以查询一段SQL需要的数据来源,以JSON的形式展现结果数据。里面主要包含两部分内容:
-
input_tables:描述一段SQL依赖的数据来源表,里面存储的是hive表名的列表,格式如下:
{"tablename":"库名@表名","tabletype":"表的类型(外部表/内部表)"} -
input_partitions:描述一段SQL依赖的数据来源表分区,里面存储的是分区名称的列表,格式如下:
{"partitionName":"库名@表名@分区列=分区列的值"}如果查询的表为非分区表,则显示为空。
可以通过以下例子来进行比对,其中例1是查询非分区普通表SQL的explain dependency,例2是查询分区表SQL的explain dependency。
例1 使用explain dependency查看SQL非分区普通表。
explain dependency
-- 统计年龄小于30岁各个年龄里,昵称里带“小”的人数
select age,count(0) as num from temp.user_info_all_no
where age < 30 and nick like '%小%'
group by age;
输出结果内容:
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all_no","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[]}
例2 使用explain dependency查看SQL查询分区表。
explain dependency
-- 统计年龄小于30岁各个年龄里,昵称里带“小”的人数,其中ymd字段为分区字段
select age,count(0) as num from temp.user_info_all where ymd >= '20230501'
and age < 30 and nick like '%小%'
group by age;
输出结果内容:
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230504"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230505"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230529"}]}
2.借助explain dependency解决一些常见问题
explain dependency的使用场景有以下几个:
场景一,快速排除。快速排除因为读不到相应分区的数据而导致任务数据输出异常。例如,在一个以天为分区的任务中,上游任务因为生产过程不可控因素出现异常或者空跑,导致下游任务引发异常。通过这种方式,可以快速查看SQL读取的分区是否出现异常。
场景二,理清表的输入,帮助理解程序的运行,特别是有助于理解有多重子查询,多表连接的依赖输入。
场景三,提前通过解析hiveSQL脚本进行血缘依赖解析,用于一些定制化数据平台工具开发中的血缘构建。
explain dependency的使用能帮助开发者解决哪些问题呢?
2.1.识别看似等价的SQL代码实际上是不等价的:
对于接触SQL不久的程序员来说,很多人容易将
select * from a left join b on a.no=b.no and a.f>1 and a.f<3;
这段逻辑等价于 select * from a left join b on a.no=b.no where a.f>1 and a.f<3;
这两段的逻辑的区别是在多表left join的时候where 后加条件是否等价与on后面加条件。
我们通过实例来看看其中的区别:
例3 使用explain dependency识别看似等价的SQL代码。
-- 代码1
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd and a.ymd >= '20230501' and a.ymd <= '20230502';
-- 代码2
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd
where a.ymd >= '20230501' and a.ymd <= '20230502';
输出结果内容:
// 代码1输出结果
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230430"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230504"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230505"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230529"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230606"}]}
// 代码2输出结果
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"}]}
通过以上输出结果可以看出,上面例子里的两段SQL其实并不等价。在left join(left outer join)的连接条件中加入非等值的过滤条件后,这里特指作用于a表,也就是连接的基表,并没有将左外连接的左右两个表按照过滤条件进行过滤,左外连接在执行时会读取所有分区数据,然后进行关联数据过滤操作。
left outer join 针对左表非等值条件on和where查询数据on条件查询数据大于where条件查询数据。
下面查看left outer join对右表的过滤条件实例:
例4 使用explain dependency识别left outer join 右表过滤非等值条件区别
-- 代码1
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd and b.ymd >= '20230501' and b.ymd <= '20230502';
-- 代码2
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd
where b.ymd >= '20230501' and b.ymd <= '20230502';
输出结果内容:
// 代码1输出结果,on后跟非等值条件
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230430"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230504"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230505"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230529"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"}]}
// 代码2输出结果,where后跟非等值条件
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230430"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230504"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230505"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230529"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230606"}]}
可以看到left outer join 针对右表非等值条件on和where查询数据左表都是全表扫描,右表on条件是条件过滤,where条件是全表扫描。
接下来对inner join,right outer join,full outer join进行测试。会发现
inner join 的类似针对左右表非等值条件on和where查询数据是等价的。
right outer join和left join相反。
full outer join都是全表扫描。
那么可以很好的判断出一下两段SQL的过滤条件数据读取范围是完全不一样的。就不贴执行结果了。
例5 left outer join下的对左表和右表不等值条件过滤。
-- 代码1
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd and a.ymd >= '20230501' and a.ymd <= '20230502';
-- 代码2
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd and b.ymd >= '20230501' and b.ymd <= '20230502';
以上不同join类型数据查询范围不一致主要原因和hive对join和where的谓词下推支持不同有关。通过explain dependency可以直接验证hive对join和where进行谓词下推规则的验证。
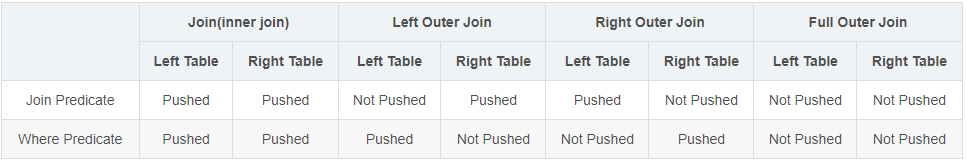
谓词下推可详细查看什么是谓词下推,看这一篇就够了
2.2 通过explain dependency验证将过滤条件在不同位置的查询区别
如果要使用外连接并需要对左右两个表进行条件过滤,做好的方式是将过滤条件放到就近处,即如果已经知道表数据过滤筛选条件,那么在使用该表前,就先用过滤条件进行过滤,然后进行其他操作。
一些SQL内置优化器会做一些过滤下推优化,但部分条件还是不会进行下推。所以我们在写SQL时尽量养成先过滤而后进行其他操作(聚合,关联)的习惯。
可以看如下实例:
例6 left outer join对左表过滤数据的优化对比。
-- 代码1
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd
where a.ymd >= '20230501' and a.ymd <= '20230502';
-- 代码2
explain dependency
select a.uid from (
select uid,ymd from temp.user_info_all
-- 在子查询内部进行过滤
where ymd >= '20230501' and ymd <= '20230502'
) a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd;
-- 代码3
explain dependency
select a.uid from (
select uid,ymd from temp.user_info_all
-- 在子查询内部进行过滤
where ymd >= '20230501' and ymd <= '20230502'
) a
left outer join (
select uid,ymd from temp.user_act_info
where ymd >= '20230501' and ymd <= '20230502'
) b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd;
执行结果:
//代码1,左右表都进行了过滤
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"}]}
//代码2,右表进行了全表扫描
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230606"}]}
//代码3,左右表都进行了过滤
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"}]}
可以看到left outer join对左表过滤数据的优化中代码1片段等价于代码3片段,即两表都在就近处都过滤。
例7 left outer join对右表过滤数据的优化对比。
-- 代码1
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd
where b.ymd >= '20230501' and b.ymd <= '20230502';
-- 代码2
explain dependency
select a.uid from (
select uid,ymd from temp.user_info_all
-- 在子查询内部进行过滤
where ymd >= '20230501' and ymd <= '20230502'
) a
left outer join (
select uid,ymd from temp.user_act_info
where ymd >= '20230501' and ymd <= '20230502'
) b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd;
-- 代码3
explain dependency
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join (
select uid,ymd from temp.user_act_info
where ymd >= '20230501' and ymd <= '20230502'
) b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd;
执行结果内容:
// 代码1 ,左右表都进行了全表扫描
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230430"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230504"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230505"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230529"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230606"}]}
//代码2,左右表都进行了过滤
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"}]}
//代码3,右表都进行了过滤
{"input_tables":[{"tablename":"temp@user_info_all","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"},{"tablename":"temp@user_act_info","tabletype":"MANAGED_TABLE"}],"input_partitions":[{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230430"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230503"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230504"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230505"},{"partitionName":"temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230529"}]}
可以看到left outer join对右表过滤数据的优化中代码2是最优,代码3次之,代码1最差。
3.查看SQL操作涉及到的相关权限信息
通过explain authorization可以知道当前SQL访问的数据来源(INPUTS) 和数据输出(OUTPUTS),以及当前Hive的访问用户 (CURRENT_USER)和操作(OPERATION)。
可以看以下实例:
例8 使用explain authorization查看权限相关信息。
explain authorization
select a.uid from temp.user_info_all a
left outer join temp.user_act_info b
on a.uid = b.uid and a.ymd = b.ymd
where a.ymd >= '20230501' and a.ymd <= '20230502';
执行结果:
INPUTS:
temp@user_info_all
temp@user_act_info
temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230501
temp@user_info_all@ymd=20230502
temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230501
temp@user_act_info@ymd=20230502
OUTPUTS:
hdfs://nameservice1/tmp/hive/hdfs/a88cc133-c310-4129-bfa0-28011ac23904/hive_2023-06-07_19-42-55_464_2777807904847671424-1/-mr-10000
CURRENT_USER:
hdfs
OPERATION:
QUERY
AUTHORIZATION_FAILURES:
Permission denied: Principal [name=hdfs, type=USER] does not have following privileges for operation QUERY [[SELECT] on Object [type=TABLE_OR_VIEW, name=temp.user_act_info], [SELECT] on Object [type=TABLE_OR_VIEW, name=temp.user_info_all]]
从上面的信息可知:
上面案例的数据来源是temp数据库中的 user_info_all表和user_act_info表;
数据的输出路径是hdfs://nameservice1/tmp/hive/hdfs/a88cc133-c310-4129-bfa0-28011ac23904/hive_2023-06-07_19-42-55_464_2777807904847671424-1/-mr-10000;
当前的操作用户是hdfs,操作是查询(QUERY);
观察上面的信息我们还会看到AUTHORIZATION_FAILURES信息,提示对当前的输入没有查询权限,但如果运行上面的SQL的话也能够正常运行。为什么会出现这种情况?Hive在默认不配置权限管理的情况下不进行权限验证,所有的用户在Hive里面都是超级管理员,即使不对特定的用户进行赋权,也能够正常查询。
通过上面对explain相关参数的介绍,可以发现explain中有很多值得我们去研究的内容,读懂 explain 的执行计划有利于我们优化Hive SQL,同时也能提升我们对SQL的掌控力。
下一期:Hive执行计划之什么是hiveSQL向量化模式及优化详解
按例,欢迎点击此处关注我的个人公众号,交流更多知识。
后台回复关键字 hive,随机赠送一本鲁边备注版珍藏大数据书籍。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK