

python轻量级性能工具-Locust - yetangjian
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/yetangjian/p/17366389.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Locust基于python的协程机制,打破了线程进程的限制,可以能够在一台测试机上跑高并发
性能测试基础
1.快慢:衡量系统的处理效率:响应时间
2.多少:衡量系统的处理能力:单位时间内能处理多少个事务(tps)
性能测试根据测试需求最常见的分为下面三类
1 负载测试load testing
不断向服务器加压,值得预定的指标或者部分系统资源达到瓶颈,目的是找到系统最大负载的能力
2 压力测试
通过高负载持续长时间,来验证系统是否稳定
3 并发测试:
同时像服务器提交请求,目的发现系统是否存在事务冲突或者锁升级的现象
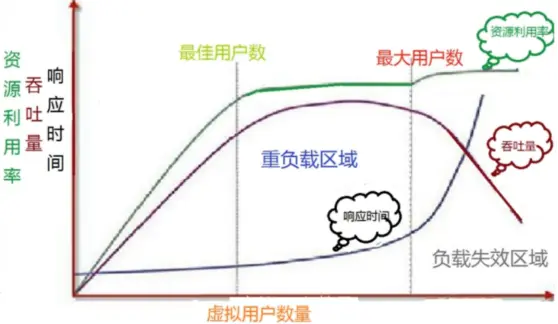
性能负载模型
locust安装
安装存在问题,可以通过豆瓣源下载
pip install locust
locust模板
基本上多数的场景我们都可以基于这个模板read.py去做修改
from locust import HttpUser, TaskSet, task, tag, events
# 启动locust时运行
@events.test_start.add_listener
def setup(environment, **kwargs):
# print("task setup")
# 停止locust时运行
@events.test_stop.add_listener
def teardown(environment, **kwargs):
print("task teardown")
class UserBehavor(TaskSet):
#虚拟用户启用task运行
def on_start(self):
print("start")
locusts_spawned.wait()
#虚拟用户结束task运行
def on_stop(self):
print("stop")
@tag('test1')
@task(2)
def index(self):
self.client.get('/yetangjian/p/17320268.html')
@task(1)
def info(self):
self.client.get("/yetangjian/p/17253215.html")
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
def setup(self):
print("locust setup")
def teardown(self):
print("locust teardown")
host = "https://www.cnblogs.com"
task_set = task(UserBehavor)
min_wait = 3000
max_wait = 5000
注:这里我们给了一个webhost,这样我们可以直接在浏览器中打开locust
集合点lr_rendezvous
当然我们可以把集合点操作放入上述模板的setup中去运行起来
locusts_spawned = Semaphore()
locusts_spawned.acquire()
def on_hatch_complete(**kwargs):
"""
select_task类的钩子函数
:param kwargs:
:return:
"""
locusts_spawned.release()
events.spawning_complete.add_listener(on_hatch_complete)
n = 0
class UserBehavor(TaskSet):
def login(self):
global n
n += 1
print(f"第{n}个用户登陆")
def on_start(self):
self.login()
locusts_spawned.wait()
@task
def test1(self):
#catch_response获取返回
with self.client.get("/yetangjian/p/17253215.html",catch_response=True):
print("查询结束")
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
host = "https://www.cnblogs.com"
task_set = task(UserBehavor)
wait_time = between(1,3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
os.system('locust -f read.py --web-host="127.0.0.1"')
比较常见的用法
在上面两个例子中我们已经看到了一些,例如装饰器events.test_start.add_listener;events.test_stop.add_listener用来在负载测试前后进行一些操作,又例如on_start、on_stop,在task执行前后运行,又例如task,可以用来分配任务的权重
等待时间
# wait between 3.0 and 10.5 seconds after each task #wait_time = between(3.0, 10.5) #固定时间等待 # wait_time = constant(3) #确保每秒运行多少次 constant_throughput(task_runs_per_second) #确保每多少秒运行一次 constant_pacing(wait_time)
同样也可以在User类下发重写wait_time来达到自定义
tag标记
@tag('test1')
@task(2)
def index(self):
self.client.get('/yetangjian/p/17320268.html')
通过对任务打标记,就可以在运行时候执行运行某一些任务:
#只执行标记test1os.system('locust -f read.py --tags test1 --web-host="127.0.0.1"')#不执行标记过的os.system('locust -f read.py --exclude-tags --web-host="127.0.0.1"')#除去test1执行所有os.system('locust -f read.py --exclude-tags test1 --web-host="127.0.0.1"') |
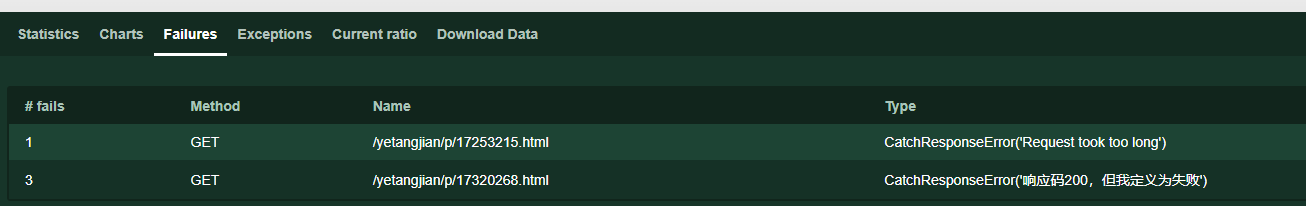
自定义失败
#定义响应时间超过0.1就为失败
with self.client.get("/yetangjian/p/17253215.html", catch_response=True) as response:
if response.elapsed.total_seconds() > 0.1:
response.failure("Request took too long")
#定义响应码是200就为失败
with self.client.get("/yetangjian/p/17320268.html", catch_response=True) as response:
if response.status_code == 200:
response.failure("响应码200,但我定义为失败")
自定义负载形状
自定义一个shape.py通过继承LoadTestShape并重写tick
这个形状类将以100块为单位,20速率的增加用户数,然后在10分钟后停止负载测试(从运行开始的第51秒开始user_count会round到100)
from locust import LoadTestShape
class MyCustomShape(LoadTestShape):
time_limit = 600
spawn_rate = 20
def tick(self):
run_time = self.get_run_time()
if run_time < self.time_limit:
# User count rounded to nearest hundred.
user_count = round(run_time, -2)
return (user_count, self.spawn_rate)
return None
运行图如下所示

通过命令行去触发
os.system('locust -f read.py,shape.py --web-host="127.0.0.1"')
不同时间阶段的例子
from locust import LoadTestShape
class StagesShapeWithCustomUsers(LoadTestShape):
stages = [
{"duration": 10, "users": 10, "spawn_rate": 10},
{"duration": 30, "users": 50, "spawn_rate": 10},
{"duration": 60, "users": 100, "spawn_rate": 10},
{"duration": 120, "users": 100, "spawn_rate": 10}]
def tick(self):
run_time = self.get_run_time()
for stage in self.stages:
if run_time < stage["duration"]:
tick_data = (stage["users"], stage["spawn_rate"])
return tick_data
return None
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK