

OpenHarmony源码解析之系统服务管理子系统
source link: https://www.51cto.com/article/751877.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

1、预备知识
Linux中主要的IPC机制有:管道(pipe)、信号(signal)、信号量(semophore)、消息队列(Message)、共享内存(Share Memory)、套接字(Socket)等。Openharmony基于binder驱动封装了一套ipc机制(foundation\communication\ipc)用于实现设备内的跨进程通信。
Binder机制通常采用客户端-服务器(Client-Server)模型,服务请求方(Client)可获取服务提供方(Server)的代理 (Proxy),并通过此代理读写数据来实现进程间的数据通信。通常,系统能力(SystemAbility)Server侧会先注册到系统能力管理者(System Ability Manager,缩写SAMgr)中,SAMgr负责管理这些SA并向Client提供相关的接口(添加,查询,获取,删除等)。Client要和某个具体的SA通信,必须先从SAMgr中获取该SA的代理,然后使用代理和SA通信。
注:SAMgr本身也是IPC的Server端,Client通过SAMgr的代理,调用SAMgr的接口。
(1)binder机制架构图
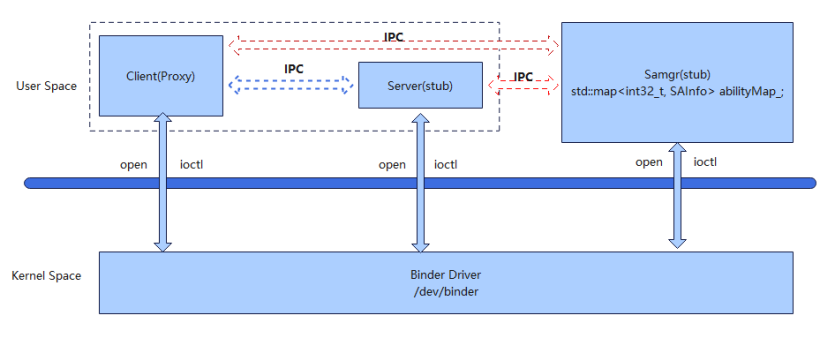
SAMgr中保存了一个map,key为saId, value为SAInfo。SAInfo结构体定义如下:
struct SAInfo {
sptr<IRemoteObject> remoteObj;
bool isDistributed = false;
std::u16string capability;
std::string permission;
};(2)实现IPC的基本步骤
- 定义接口类
接口类继承IRemoteBroker,定义描述符、业务函数和消息码。 - 实现服务提供端(Stub)
Stub继承IRemoteStub,除了接口类中未实现方法外,还需要实现OnRemoteRequest方法。 - 实现服务请求端(Proxy)
Proxy继承IRemoteProxy,封装业务函数,调用SendRequest将请求发送到Stub。 - 服务端进程注册SA
服务提供方所在进程启动后,申请SA的唯一标识,将Stub注册到SAMgr。 - 客户端进程通过SA的标识(saId),从SAMgr获取Proxy,通过Proxy实现与Stub的跨进程通信。
ohos中的SystemAbility可以运行在独立的进程中,也可以多个SystemAbility同时依附在某个进程内(如 foundation进程),通过这个进程对外提供服务。其他进程通过IPC(binder机制)使用这些服务提供的接口。
2、系统服务管理子系统简介
系统服务管理子系统由两部分构成。
系统服务框架组件(safwk):定义了SystemAbility的实现方法,并提供启动、发布等接口实现。
系统服务管理组件(samgr): 提供系统服务注册、查询等功能。
架构图如下:

代码目录:
/foundation/systemabilitymgr
│── safwk # 组件目录
│ ├── bundle.json # 组件描述及编译脚本
│ ├── etc # 配置文件
│ ├── interfaces # 对外接口目录
│ ├── services # 框架实现
│ ├── test # 测试用例
├── samgr
│ ├── bundle.json # 部件描述及编译文件
│ ├── frameworks # 框架实现存在目录
│ ├── interfaces # 接口目录
│ ├── services # 组件服务端目录
│ ├── test # 测试代码存放目录
│ ├── utils # 工具类目录3、系统服务框架组件
SystemAbility实现一般采用XXX.cfg + saId.xml + libXXX.z.so的方式由init进程解析对应的XXX.cfg文件拉起SystemAbility所依赖的进程。(注:多个系统服务可能跑在同一个进程里。比如AbilityManagerService、BatteryService、WindowManagerService都在foundation进程,MMIService在独立的进程multimodalinput中。)
SystemAbility类图如下:
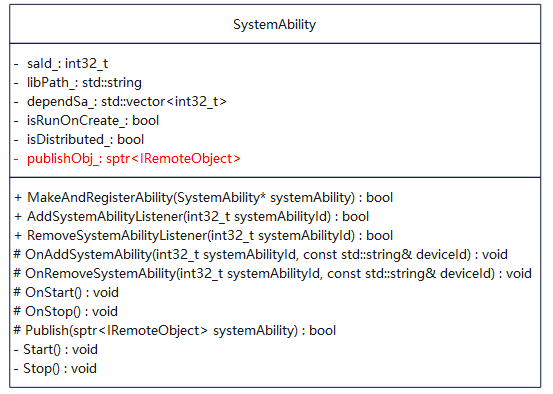
SystemAbility子类需要重写OnStart()和OnStop()方法,并且在OnStart()方法中调用Publish(sptr<IRemoteObject> systemAbility)方法把系统服务发布出去。
(1)系统服务实现步骤
下面以AbilityManagerService为例说明SystemAbility的实现。
定义IPC对外接口IXXX
定义该服务对外提供的能力集合函数,统一继承IPC接口类IRemoteBroker;同时声明该IPC对外接口唯一标识符DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR(XXX);该标识符用于IPC通信的校验等目的。
foundation\ability\ability_runtime\interfaces\inner_api\ability_manager\include\ability_manager_interface.h。
class IAbilityManager : public OHOS::IRemoteBroker {
public:
DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR(u"ohos.aafwk.AbilityManager")
/**
* StartAbility with want, send want to ability manager service.
*
* @param want, the want of the ability to start.
* @param userId, Designation User ID.
* @param requestCode, Ability request code.
* @return Returns ERR_OK on success, others on failure.
*/
virtual int StartAbility(
const Want &want,
int32_t userId = DEFAULT_INVAL_VALUE,
int requestCode = DEFAULT_INVAL_VALUE) = 0;
//...此处省略若干行
}定义客户端代码XXXProxy
foundation\ability\ability_runtime\services\abilitymgr\include\ability_manager_proxy.h。
class AbilityManagerProxy : public IRemoteProxy<IAbilityManager> {
public:
explicit AbilityManagerProxy(const sptr<IRemoteObject> &impl) : IRemoteProxy<IAbilityManager>(impl)
{}
virtual ~AbilityManagerProxy()
{}
/**
* StartAbility with want, send want to ability manager service.
*
* @param want, the want of the ability to start.
* @param requestCode, Ability request code.
* @param userId, Designation User ID.
* @return Returns ERR_OK on success, others on failure.
*/
virtual int StartAbility(
const Want &want,
int32_t userId = DEFAULT_INVAL_VALUE,
int requestCode = DEFAULT_INVAL_VALUE) override;
//...此处省略若干行
private:
static inline BrokerDelegator<AbilityManagerProxy> delegator_;
};foundation\ability\ability_runtime\services\abilitymgr\src\ability_manager_proxy.cpp。
int AbilityManagerProxy::StartAbility(const Want &want, int32_t userId, int requestCode)
{
int error;
MessageParcel data;
MessageParcel reply;
MessageOption option;
if (!WriteInterfaceToken(data)) {
return INNER_ERR;
}
if (!data.WriteParcelable(&want)) {
HILOG_ERROR("want write failed.");
return INNER_ERR;
}
if (!data.WriteInt32(userId)) {
HILOG_ERROR("userId write failed.");
return INNER_ERR;
}
if (!data.WriteInt32(requestCode)) {
HILOG_ERROR("requestCode write failed.");
return INNER_ERR;
}
error = Remote()->SendRequest(IAbilityManager::START_ABILITY, data, reply, option);
if (error != NO_ERROR) {
HILOG_ERROR("Send request error: %{public}d", error);
return error;
}
return reply.ReadInt32();
}AbilityManagerProxy::StartAbility()实现代码中会调用Remote()->SendRequest(IAbilityManager::START_ABILITY, data, reply, option);把消息码和数据发送给服务端。
定义服务端代码XXXStub
foundation\ability\ability_runtime\services\abilitymgr\include\ability_manager_stub.h。
class AbilityManagerStub : public IRemoteStub<IAbilityManager> {
public:
AbilityManagerStub();
~AbilityManagerStub();
virtual int OnRemoteRequest(
uint32_t code, MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option) override;
//...此处省略若干行
};foundation\ability\ability_runtime\services\abilitymgr\src\ability_manager_stub.cpp。
int AbilityManagerStub::OnRemoteRequest(uint32_t code, MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option)
{
std::u16string descriptor = AbilityManagerStub::GetDescriptor();
std::u16string remoteDescriptor = data.ReadInterfaceToken();
if (descriptor != remoteDescriptor) {
HILOG_INFO("local descriptor is not equal to remote");
return ERR_INVALID_STATE;
}
auto itFunc = requestFuncMap_.find(code);
if (itFunc != requestFuncMap_.end()) {
auto requestFunc = itFunc->second;
if (requestFunc != nullptr) {
return (this->*requestFunc)(data, reply);
}
}
HILOG_WARN("default case, need check.");
return IPCObjectStub::OnRemoteRequest(code, data, reply, option);
}requestFuncMap_[START_ABILITY] = &AbilityManagerStub::StartAbilityInner。
消息码START_ABILITY对应的函数为AbilityManagerStub::StartAbilityInner。
int AbilityManagerStub::StartAbilityInner(MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply)
{
Want *want = data.ReadParcelable<Want>();
if (want == nullptr) {
HILOG_ERROR("want is nullptr");
return ERR_INVALID_VALUE;
}
int32_t userId = data.ReadInt32();
int requestCode = data.ReadInt32();
int32_t result = StartAbility(*want, userId, requestCode);
reply.WriteInt32(result);
delete want;
return NO_ERROR;
}StartAbility()的实现在AbilityManagerStub的实现类AbilityManagerService中。
SystemAbility的实现类
foundation\ability\ability_runtime\services\abilitymgr\include\ability_manager_service.h。
class AbilityManagerService : public SystemAbility,
public AbilityManagerStub,
public AppStateCallback,
public std::enable_shared_from_this<AbilityManagerService> {
DECLARE_DELAYED_SINGLETON(AbilityManagerService)
DECLEAR_SYSTEM_ABILITY(AbilityManagerService)
public:
void OnStart() override;
void OnStop() override;
ServiceRunningState QueryServiceState() const;
/**
* StartAbility with want, send want to ability manager service.
*
* @param want, the want of the ability to start.
* @param requestCode, Ability request code.
* @param userId, Designation User ID.
* @return Returns ERR_OK on success, others on failure.
*/
virtual int StartAbility(
const Want &want, int32_t userId = DEFAULT_INVAL_VALUE, int requestCode = DEFAULT_INVAL_VALUE) override;
// ...此处省略若干行
}AbilityManagerService同时继承了SystemAbility和AbilityManagerStub。
在重写的SystemAbility的接口函数OnStart()中,调用Publish(instance_)把自己发布出去。
void AbilityManagerService::OnStart()
{
//...此处省略若干行
/* Publish service maybe failed, so we need call this function at the last,
* so it can't affect the TDD test program */
instance_ = DelayedSingleton<AbilityManagerService>::GetInstance().get();
if (instance_ == nullptr) {
HILOG_ERROR("AMS enter OnStart, but instance_ is nullptr!");
return;
}
bool ret = Publish(instance_);
if (!ret) {
HILOG_ERROR("Publish AMS failed!");
return;
}
//...此处省略若干行
}注:在实现SystemAbility的时候,必须调用宏REGISTER_SYSTEM_ABILITY_BY_ID或者SystemAbility::MakeAndRegisterAbility()把SystemAbility注册到LocalAbilityManager中。
可参考如下代码:
const bool REGISTER_RESULT =
SystemAbility::MakeAndRegisterAbility(DelayedSingleton<AbilityManagerService>::GetInstance().get());REGISTER_SYSTEM_ABILITY_BY_ID(AppMgrService, APP_MGR_SERVICE_ID, true);SystemAbility配置
以c++实现的SA必须配置相关SystemAbility的profile配置文件才会完成SA的自动加载注册逻辑,否则没有编写配置文件的SystemAbility不会完成自动加载注册。配置方法如下:
在子系统的根目录新建一个以sa_profile为名的文件夹,然后在此文件夹中新建两个文件:一个以saId为前缀的xml文件,另外一个为BUILD.gn文件。
比如AbilityManagerService,saId为ABILITY_MGR_SERVICE_ID(即180),对应的配置文件为180.xml。内容如下:
<info>
<process>foundation</process>
<systemability>
<name>180</name>
<libpath>libabilityms.z.so</libpath>
<run-on-create>true</run-on-create>
<distributed>false</distributed>
<dump-level>1</dump-level>
</systemability>
</info>BUILD.gn内容如下:
ohos_sa_profile("ams_sa_profile") {
sources = [
"180.xml",
"182.xml",
"183.xml",
"184.xml",
"501.xml",
]
part_name = "ability_runtime"
}- 进程名字即该SystemAbility要运行的进程空间,此字段是必填选项。上例中,AbilityManagerService跑在foundation进程中。
- 一个SystemAbility配置文件只能配置一个SystemAbility节点,配置多个会导致编译失败。
- SystemAbility的name为对应的saId必须与代码中注册的saId保持一致,必配项。
- libpath为SystemAbility的加载路径,必配项。
- run-on-create:true表示进程启动后即向samgr组件注册该SystemAbility;false表示按需启动,即在其他模块访问到该SystemAbility时启动,必配项。
- distributed:true表示该SystemAbility为分布式SystemAbility,支持跨设备访问;false表示只有本地跨进程访问。
- bootphase:可不设置;可以设置的值有三种:BootStartPhase、CoreStartPhase、OtherStartPhase(默认类型),三种优先级依次降低,在同一个进程中,会优先拉起注册配置BootStartPhase的SystemAbility,然后是配置了CoreStartPhase的SystemAbility,最后是OtherStartPhase;当高优先级的SystemAbility全部启动注册完毕才会启动下一级的SystemAbility的注册启动。
- dump-level:表示systemdumper支持的level等级,默认配置1。
- BUILD.gn中part_name为相应部件名称;sources表示当前子系统需要配置的SystemAbility列表,可支持配置多个SystemAbility。
以上步骤完成后,全量编译代码后会在out路径下生成一个以进程名为前缀的xml文件(比如foundation.xml),路径为:out\…\system\profile\foundation.xml。该文件整合了所有需要在该进程中运行的SA的saId.xml文件内容。(比如AbilityManagerService,WindowManagerService,PowerManagerService等SA的配置文件都会被集成到foundation.xml中)。
Cfg配置文件
cfg配置文件为linux提供的native进程拉起策略,开机启动阶段由init进程解析cfg文件把目标进程拉起(动态加载的除外)。
foundation进程的配置文件在systemabilitymgr子系统中。
foundation\systemabilitymgr\safwk\etc\profile\foundation.cfg。
"services" : [{
"name" : "foundation",
"path" : ["/system/bin/sa_main", "/system/profile/foundation.xml"],
"importance" : -20,
"uid" : "foundation",
//...此处省略若干行
}
](2)SystemAbility所在进程启动时序图
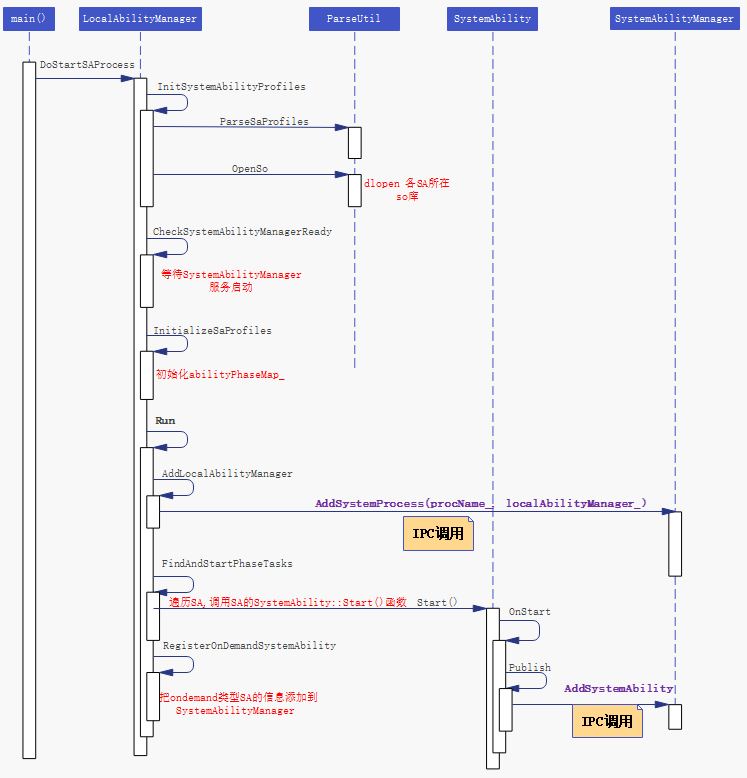
该流程即为/system/bin/sa_main可执行文件的启动流程,main()函数(代码路径foundation\systemabilitymgr\safwk\services\safwk\src\main.cpp)在调用LocalAbilityManager::GetInstance().DoStartSAProcess(profilePath, saId)之前会把进程改名为saId.xml配置文件中指定的进程名。
3、系统服务管理组件
SystemAbilityManager本身是IPC接口ISystemAbilityManager的服务端。提供了添加、删除、查询系统服务,以及订阅系统服务状态等接口。IPCSkeleton::SetContextObject()通过该方法告诉binder我是服务管理器,我是0号选手。
constexpr int REGISTRY_HANDLE = 0。
foundation\systemabilitymgr\samgr\services\samgr\native\source\main.cpp。
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
HILOGI("%{public}s called, enter System Ability Manager ", __func__);
OHOS::sptr<OHOS::SystemAbilityManager> manager = OHOS::SystemAbilityManager::GetInstance();
manager->Init();
OHOS::sptr<OHOS::IRemoteObject> serv = manager->AsObject();
if (!IPCSkeleton::SetContextObject(serv)) {
HILOGE("set context fail!"); // add log for dfx
}
int result = SetParameter("bootevent.samgr.ready", "true");
HILOGI("set samgr ready ret : %{public}s", result == 0 ? "succeed" : "failed");
manager->StartDfxTimer();
OHOS::IPCSkeleton::JoinWorkThread();
return -1;
}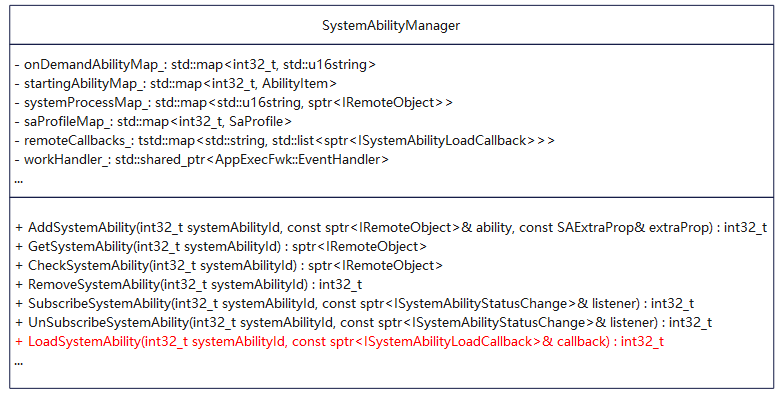
标红的方法LoadSystemAbility适用于动态加载系统服务进程的场景。
前面章节讲的AbilityManagerService所在的foundation进程,开机即被init进程拉起。
有些系统服务进程需要动态加载,比如QuickFixManagerService所在的quick_fix进程。
foundation\ability\ability_runtime\services\quickfixmgr\quick_fix.cfg。
{
"services" : [{
"name" : "quick_fix",
"path" : ["/system/bin/sa_main", "/system/profile/quick_fix.xml"],
"ondemand" : true,
"uid" : "quickfixserver",
"gid" : ["system"],
"secon" : "u:r:quick_fix:s0"
}
]
}cfg文件指定了"ondemand"为 true,说明quick_fix进程要按需启动。拉起quick_fix进程的关键在于SystemAbilityManager::LoadSystemAbility方法。
foundation\ability\ability_runtime\interfaces\inner_api\quick_fix\src\quick_fix_manager_client.cpp。
bool QuickFixManagerClient::LoadQuickFixMgrService()
{
// ...此处省略若干行
sptr<QuickFixLoadCallback> loadCallback = new (std::nothrow) QuickFixLoadCallback();
if (loadCallback == nullptr) {
HILOG_ERROR("Create load callback failed.");
return false;
}
auto ret = systemAbilityMgr->LoadSystemAbility(QUICK_FIX_MGR_SERVICE_ID, loadCallback);
if (ret != 0) {
HILOG_ERROR("Load system ability %{public}d failed with %{public}d.", QUICK_FIX_MGR_SERVICE_ID, ret);
return false;
}
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(loadSaMutex_);
auto waitStatus = loadSaCondation_.wait_for(lock, std::chrono::milliseconds(LOAD_SA_TIMEOUT_MS),
[this]() {
return loadSaFinished_;
});
if (!waitStatus) {
HILOG_ERROR("Wait for load sa timeout.");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}SystemAbilityManager::LoadSystemAbility()中,会先判断目标SA是否已存在,如不存在,则调用StartDynamicSystemProcess()函数把目标SA所在进程拉起。(SystemAbilityManager在初始化的时候会遍历/system/profile/目录下的文件并解析,把所有SA的配置信息保存到saProfileMap_中。所以目标SA所在的进程名,SystemAbilityManager都有保存。)
int32_t SystemAbilityManager::StartDynamicSystemProcess(const std::u16string& name, int32_t systemAbilityId)
{
std::string strExtra = std::to_string(systemAbilityId);
auto extraArgv = strExtra.c_str();
auto result = ServiceControlWithExtra(Str16ToStr8(name).c_str(), ServiceAction::START, &extraArgv, 1);
HILOGI("StartDynamicSystemProcess call ServiceControlWithExtra result:%{public}d!", result);
return (result == 0) ? ERR_OK : ERR_INVALID_VALUE;
}ServiceControlWithExtra()函数的实现在base\startup\init\interfaces\innerkits\service_control\service_control.c文件中,实际就是通知init进程把目标进程拉起。目标进程被拉起之后会再走一遍时序图1的流程。跟开机启动的系统服务进程的不同点在于,动态加载的系统服务进程main()函数参数多了目标saId。
4、系统服务接口使用方法
foundation\systemabilitymgr\samgr\interfaces\innerkits\samgr_proxy\include\system_ability_definition.h 定义了所有系统服务的saId。
比如要使用AbilityManagerService的StartAbility()接口。
- 包含头文件
#include "ability_manager_interface.h"
#include "if_system_ability_manager.h"
#include "ipc_skeleton.h"
#include "iservice_registry.h"
#include "system_ability_definition.h"- 获取系统服务,调用接口
OHOS::sptr<OHOS::ISystemAbilityManager> systemAbilityManager =
OHOS::SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
OHOS::sptr<OHOS::IRemoteObject> abilityObject =
systemAbilityManager->GetSystemAbility(OHOS::ABILITY_MGR_SERVICE_ID);
auto abms = OHOS::iface_cast<OHOS::AAFwk::IAbilityManager>(abilityObject);
abms->StartAbility(want, userId, requestCode);5、系统服务不配置saId.xml,不走自动加载注册流程行不行?
答案是可以的。
参考SysEventServiceOhos,是SystemAbility,但没有配置saId.xml,直接在hiview进程中初始化并注册。
SysEventService::OnLoad() => (hiview进程加载SysEventService插件)
SysEventServiceAdapter::StartService() =>
OHOS::HiviewDFX::SysEventServiceOhos::StartService() =>
samgr->AddSystemAbility(DFX_SYS_EVENT_SERVICE_ABILITY_ID, instance)
本文详细讲解了系统服务的实现方法和注意事项。通过这篇文章相信大家对系统服务管理子系统有了一定的了解。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK