

JDK 20 Security Enhancements
source link: https://seanjmullan.org/blog/2023/03/22/jdk20
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

JDK 20 Security Enhancements
22 Mar 2023
JDK 20 was released on March 21, 2023! As with my previous blogs, I have compiled a list of what I think are the most interesting and useful security enhancements in this release. I have also grouped them into appropriate categories (crypto, TLS, etc) which should make it easier to find out what has changed in each specific area. The JDK 20 release notes also contain further details on these and other enhancements.
Highlights of this release include further improvements that strengthen the default security of the Java Platform, improved crypto performance, and new JFR events for security monitoring.
One other important JDK 20 feature that is related to security but not part of the security libraries area is the introduction of new system and security properties to control what object factory classes are allowed to reconstruct Java objects from JNDI/LDAP and JNDI/RMI contexts. See the release note for more details on these new properties.
Table of Contents
General
-
New InvalidParameterException constructors that take cause as a parameter
New constructors have been added to the
InvalidParameterExceptionAPI that take a cause (Throwable) as a parameter. This provides a more convenient option than having to separately call theinitCausemethod.For example, you can now throw an
InvalidParameterExceptionas:throw new InvalidParameterException(new NullPointerException())throw new InvalidParameterException("parameter is null", new NullPointerException())Issue: JDK-8296226
-
New service attributes added to the Standard Algorithm Names specification
Four additional service attributes have been added to the Service Attributes section of the Java Security Standard Algorithm Names specification. The attributes are
SupportedKeyClasses,SupportedKeyFormats,SupportedModes, andSupportedPaddings. These attributes were previously defined and used in the JDK security providers, but had not been defined as standard attributes until now.Issue: JDK-8297161
-
An error is now thrown if the java.security file fails to load
An
InternalErroris now thrown at runtime if a security property is retrieved but thejava.securityfile does not exist or fails to load. Prior to this change, if there was a problem loading thejava.securityfile, a subset of critical properties with hard-coded defaults was used.If this issue occurs, you will see an exception stack trace like the following:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.InternalError: Error loading java.security file at java.base/java.security.Security.initialize(Security.java:105) at java.base/java.security.Security.lambda$static$0(Security.java:84) at java.base/java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(AccessController.java:319) at java.base/java.security.Security.<clinit>(Security.java:83) ...Issue: JDK-8155246
Crypto
-
Crypto performance related improvements
Several performance related improvements have been made in the crypto area. Below are details on each of the more significant improvements and a pointer to the corresponding issue.
-
ChaCha20 intrinsics for x86_64 and aarch64 platforms
The SunJCE provider implementation of the ChaCha20 Cipher algorithm now provides an optimized intrinsic for x86_64 and aarch64 platforms, yielding a significant improvement in performance. These optimized routines are designed for x86_64 chipsets that support the AVX, AVX2 and/or AVX512 instruction sets, and aarch64 chips that support the Advanced SIMD instruction set. The intrinsics are enabled by default on the supported platforms, but can be disabled by providing the
-XX:-UseChaCha20Intrinsicscommand-line option to Java. Flags that control intrinsics require the option-XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions.Issue: JDK-8247645
-
Poly1305 intrinsics for ByteBuffers
The x86_64 intrinsic for the SunJCE provider implementation of Poly1305 (used as the authenticator for the ChaCha20
Cipheralgorithm) has been enhanced to also apply toByteBuffers. The intrinsic is now enabled for theCipherSpi.engineUpdate(byte[], ...)andCipherSpi.engineUpdate(ByteBuffer, ...)methods.Issue: JDK-8297379
-
Improved MD5 intrinsics for x86_64 platforms
The performance of the MD5
MessageDigestintrinsic for x86_64 platforms has been significantly improved.Issue: JDK-8296548
-
Improved EC point multiplication for secp256r1 curve
The performance of the elliptic curve point multiplication for the secp256r1 curve has been significantly improved by using pre-computed tables and more efficient algorithms. This performance improvement applies to the SunEC security provider.
Issue: JDK-8295011
-
Improved ECC math operations
Improved BigInteger and curve point operations result in a modest performance improvement for elliptic curve calculations. This performance improvement applies to the SunEC security provider.
Issue: JDK-8294997
-
-
DTLS 1.0 is now disabled by default
The DTLS 1.0 protocol has been disabled by default, improving out of the box security. This protocol has various weaknesses and is no longer recommended. See RFC 8996 for more information.
Applications should be using the more secure DTLS 1.2 protocol, which is supported by the JDK. However, if you encounter issues and need to get your application working, you can (at your own risk), re-enable DTLS 1.0 by removing “DTLSv1.0” from the
jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithmssecurity property in thejava.securityconfiguration file.Issue: JDK-8256660
-
ECDH cipher suites disabled by default
The TLS_ECDH cipher suites have been added to the
jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithmssecurity property and are now disabled by default. These ciphers do not preserve forward secrecy and are rarely used in practice. Some TLS_ECDH cipher suites are already disabled because they use 3DES, RC4, anon, or NULL, which were previously disabled. This action disables all remaining ECDH cipher suites.However, if you encounter issues and need to get your application working, you can (at your own risk), re-enable these cipher suites by removing “ECDH” from the
jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithmssecurity property in thejava.securityconfiguration file.Issue: JDK-8279164
-
New APIs for customizing TLS and DTLS named groups
Two new APIs have been added which allow applications to customize and retrieve the prioritized list of named groups used to negotiate the key exchange mechanism in a TLS or DTLS connection:
javax.net.ssl.SSLParameters::setNamedGroupsandjavax.net.ssl.SSLParameters::getNamedGroups.An example of setting named groups is the following:
SSLParameters params = new SSLParameters(); params.setNamedGroups(new String[] { "x25519", "secp256r1" });Issue: JDK-8281236
Tools
-
New JFR event for recording initial security properties
A new event for recording the initial values of security properties has been added to the Java Flight Recorder tool. This is useful for recording an initial snapshot of the security configuration. The event is named
jdk.InitialSecurityPropertyand is enabled by default. When used together with thejdk.SecurityPropertyModificationevent, JFR will record the initial and subsequent settings for all security properties, which can provide important details of the security environment used by the application.Below is a sample screenshot of the
jdk.InitialSecurityPropertyevent and some of the values captured for each of the security properties.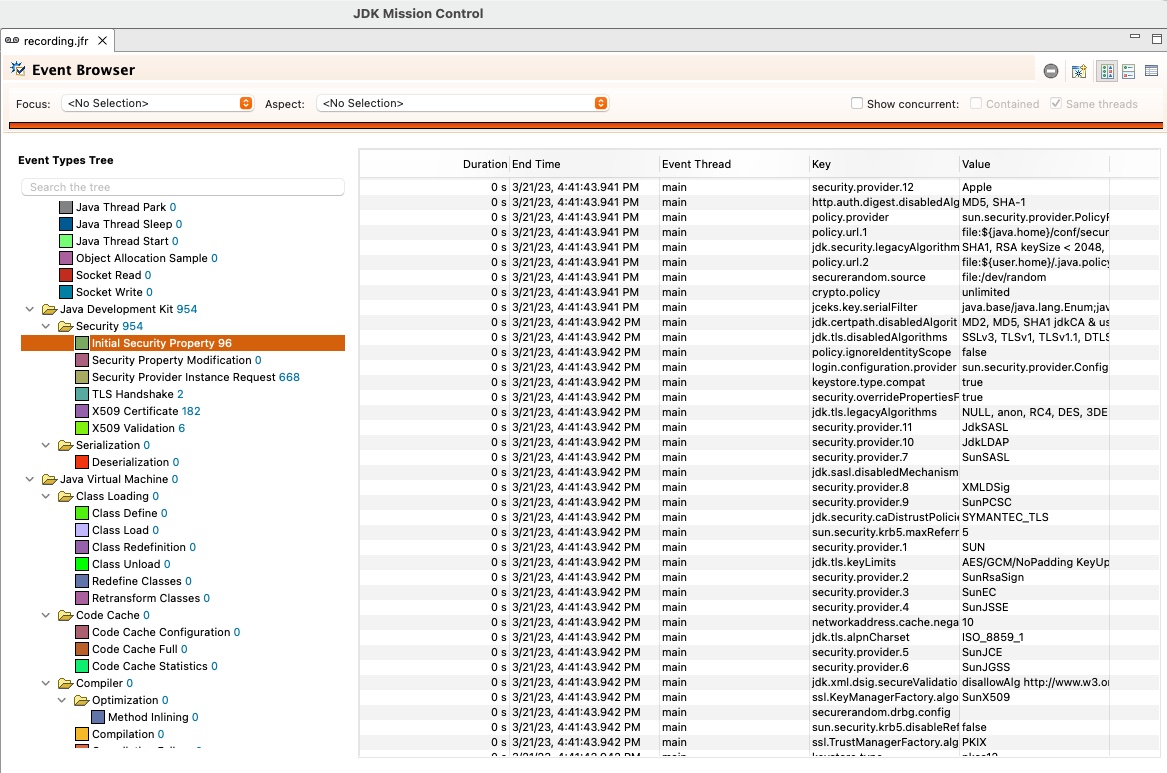
Issue: JDK-8292177
-
New JFR event for security provider usage
A new event has been added to the Java Flight Recorder tool for recording each time a security provider is accessed. This is useful for recording each cryptographic algorithm or service that an application uses, providing additional insight into the security of the application. The event is named
jdk.SecurityProviderServiceand contains three fields for the type of service, the algorithm, and the provider name. This event is disabled by default but can be enabled via the JFR configuration files or standard JFR options.Below is a sample screenshot of the
jdk.SecurityProviderServiceevent and some of the values captured for each algorithms requested.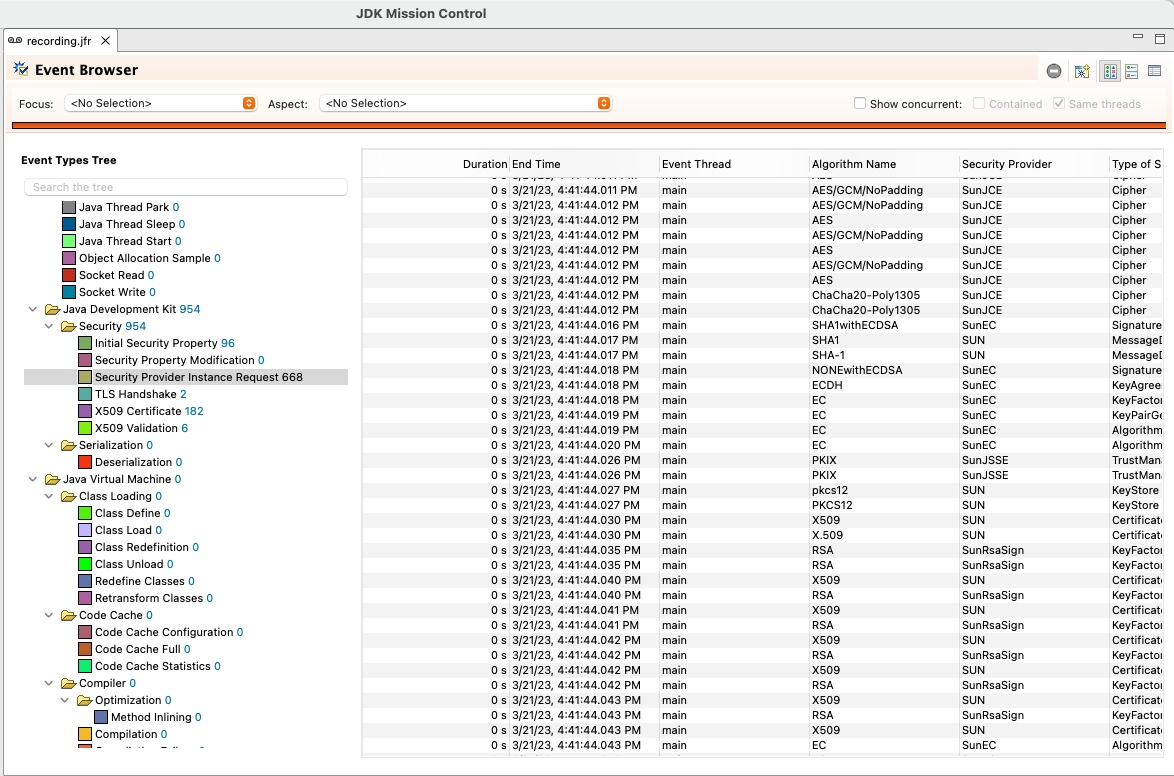
Issue: JDK-8254711
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK