

干货 | BitSail Connector 开发详解系列一:Source - 字节跳动数据平台
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/bytedata/p/17223850.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

更多技术交流、求职机会,欢迎关注字节跳动数据平台微信公众号,回复【1】进入官方交流群
BitSail 是字节跳动自研的数据集成产品,支持多种异构数据源间的数据同步,并提供离线、实时、全量、增量场景下全域数据集成解决方案。本系列聚焦 BitSail Connector 开发模块,为大家带来详细全面的开发方法与场景示例,本篇将主要介绍 Source 接口部分。
持续关注,BitSail Connector 开发详解将分为四篇呈现。
-
BitSail Connector 开发详解系列一:Source
-
BitSail Connector 开发详解系列二:SourceSplitCoordinator
-
BitSail Connector 开发详解系列三:SourceReader
-
BitSail Connector 开发详解系列四:Sink、Writer
Source Connector
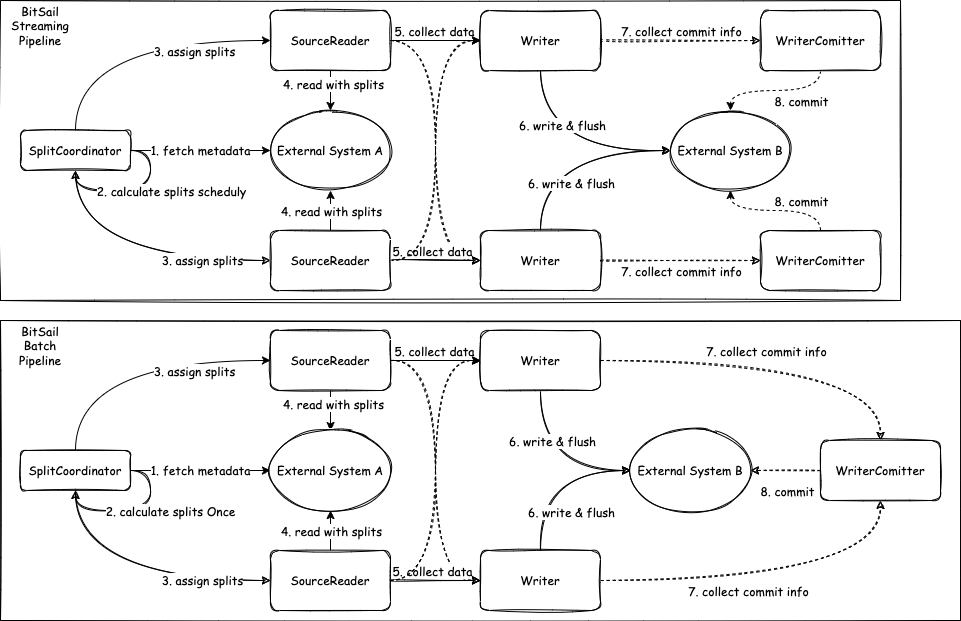
本文将主要介绍 Source 接口部分:
-
Source: 参与数据读取组件的生命周期管理,主要负责和框架的交互,构架作业,不参与作业真正的执行。
-
SourceSplit: 数据读取分片,大数据处理框架的核心目的就是将大规模的数据拆分成为多个合理的 Split 并行处理。
-
State:作业状态快照,当开启 checkpoint 之后,会保存当前执行状态。
Source
数据读取组件的生命周期管理,主要负责和框架的交互,构架作业,它不参与作业真正的执行。
以 RocketMQSource 为例:Source 方法需要实现 Source 和 ParallelismComputable 接口。
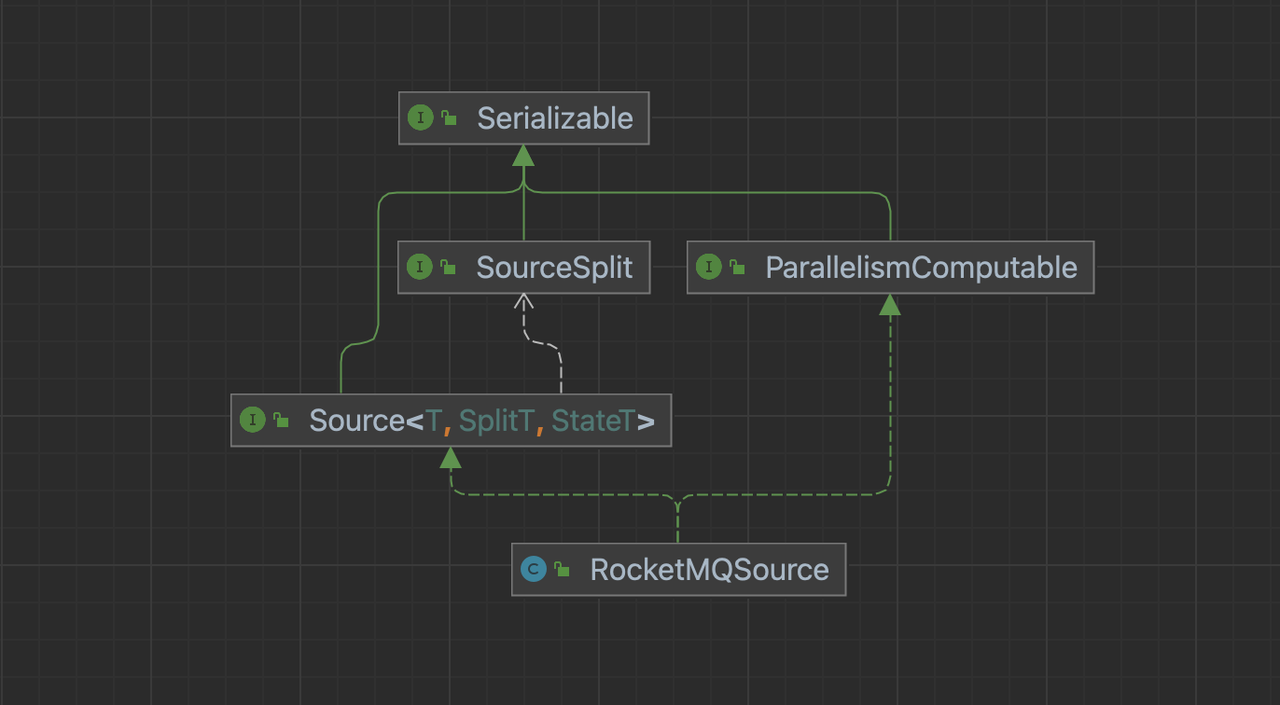
Source 接口
public interface Source<T, SplitT extends SourceSplit, StateT extends Serializable>
extends Serializable, TypeInfoConverterFactory {
/**
* Run in client side for source initialize;
*/
void configure(ExecutionEnviron execution, BitSailConfiguration readerConfiguration) throws IOException;
/**
* Indicate the Source type.
*/
Boundedness getSourceBoundedness();
/**
* Create Source Reader.
*/
SourceReader<T, SplitT> createReader(SourceReader.Context readerContext);
/**
* Create split coordinator.
*/
SourceSplitCoordinator<SplitT, StateT> createSplitCoordinator(SourceSplitCoordinator.Context<SplitT, StateT> coordinatorContext);
/**
* Get Split serializer for the framework,{@link SplitT}should implement from {@link Serializable}
*/
default BinarySerializer<SplitT> getSplitSerializer() {
return new SimpleBinarySerializer<>();
}
/**
* Get State serializer for the framework, {@link StateT}should implement from {@link Serializable}
*/
default BinarySerializer<StateT> getSplitCoordinatorCheckpointSerializer() {
return new SimpleBinarySerializer<>();
}
/**
* Create type info converter for the source, default value {@link BitSailTypeInfoConverter}
*/
default TypeInfoConverter createTypeInfoConverter() {
return new BitSailTypeInfoConverter();
}
/**
* Get Source' name.
*/
String getReaderName();
}
configure 方法
主要去做一些客户端的配置的分发和提取,可以操作运行时环境 ExecutionEnviron 的配置和 readerConfiguration 的配置。
@Override
public void configure(ExecutionEnviron execution, BitSailConfiguration readerConfiguration) {
this.readerConfiguration = readerConfiguration;
this.commonConfiguration = execution.getCommonConfiguration();
}
getSourceBoundedness 方法
设置作业的处理方式,是采用流式处理方法、批式处理方法,或者是流批一体的处理方式,在流批一体的场景中,我们需要根据作业的不同类型设置不同的处理方式。
具体对应关系如下:
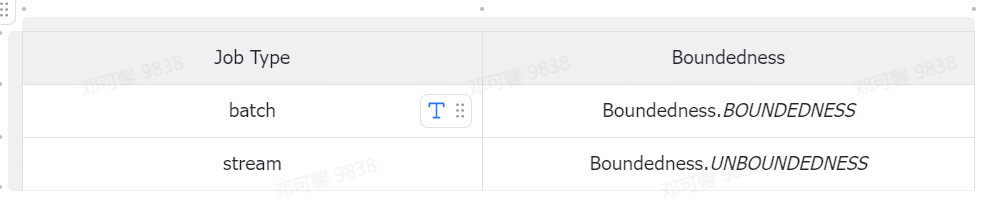
流批一体场景示例
@Override
public Boundedness getSourceBoundedness() {
return Mode.BATCH.equals(Mode.getJobRunMode(commonConfiguration.get(CommonOptions.JOB_TYPE))) ?
Boundedness.BOUNDEDNESS :
Boundedness.UNBOUNDEDNESS;
}
流批一体场景示例
@Override
public Boundedness getSourceBoundedness() {
return Mode.BATCH.equals(Mode.getJobRunMode(commonConfiguration.get(CommonOptions.JOB_TYPE))) ?
Boundedness.BOUNDEDNESS :
Boundedness.UNBOUNDEDNESS;
}
createTypeInfoConverter 方法
用于指定 Source 连接器的类型转换器;我们知道大多数的外部数据系统都存在着自己的类型定义,它们的定义与 BitSail 的类型定义不会完全一致;为了简化类型定义的转换,我们支持了通过配置文件来映射两者之间的关系,进而来简化配置文件的开发。
在行为上表现为对任务描述 Json 文件中reader部分的columns的解析,对于columns中不同字段的 type 会根据上面描述文件从ClickhouseReaderOptions.COLUMNS字段中解析到readerContext.getTypeInfos()中。
-
BitSailTypeInfoConverter默认的
TypeInfoConverter,直接对ReaderOptions.COLUMNS字段进行字符串的直接解析,COLUMNS字段中是什么类型,TypeInfoConverter中就是什么类型。 -
FileMappingTypeInfoConverter会在 BitSail 类型系统转换时去绑定
{readername}-type-converter.yaml文件,做数据库字段类型和 BitSail 类型的映射。ReaderOptions.COLUMNS字段在通过这个映射文件转换后才会映射到TypeInfoConverter中。
FileMappingTypeInfoConverter
通过 JDBC 方式连接的数据库,包括 MySql、Oracle、SqlServer、Kudu、ClickHouse 等。这里数据源的特点是以java.sql.ResultSet的接口形式返回获取的数据,对于这类数据库,我们往往将TypeInfoConverter对象设计为FileMappingTypeInfoConverter,这个对象会在 BitSail 类型系统转换时去绑定{readername}-type-converter.yaml文件,做数据库字段类型和 BitSail 类型的映射。
@Override
public TypeInfoConverter createTypeInfoConverter() {
return new FileMappingTypeInfoConverter(getReaderName());
}
对于{readername}-type-converter.yaml文件的解析,以clickhouse-type-converter.yaml为例。
# Clickhouse Type to BitSail Type
engine.type.to.bitsail.type.converter:
- source.type: int32
target.type: int
- source.type: float64
target.type: double
- source.type: string
target.type: string
- source.type: date
target.type: date.date
- source.type: null
target.type: void
# BitSail Type to Clickhouse Type
bitsail.type.to.engine.type.converter:
- source.type: int
target.type: int32
- source.type: double
target.type: float64
- source.type: date.date
target.type: date
- source.type: string
target.type: string
这个文件起到的作用是进行 job 描述 json 文件中reader部分的columns的解析,对于columns中不同字段的 type 会根据上面描述文件从ClickhouseReaderOptions.COLUMNS字段中解析到readerContext.getTypeInfos()中。
"reader": {
"class": "com.bytedance.bitsail.connector.clickhouse.source.ClickhouseSource",
"jdbc_url": "jdbc:clickhouse://localhost:8123",
"db_name": "default",
"table_name": "test_ch_table",
"split_field": "id",
"split_config": "{\"name\": \"id\", \"lower_bound\": 0, \"upper_bound\": \"10000\", \"split_num\": 3}",
"sql_filter": "( id % 2 == 0 )",
"columns": [
{
"name": "id",
"type": "int64"
},
{
"name": "int_type",
"type": "int32"
},
{
"name": "double_type",
"type": "float64"
},
{
"name": "string_type",
"type": "string"
},
{
"name": "p_date",
"type": "date"
}
]
},
这种方式不仅仅适用于数据库,也适用于所有需要在类型转换中需要引擎侧和 BitSail 侧进行类型映射的场景。
BitSailTypeInfoConverter
通常采用默认的方式进行类型转换,直接对ReaderOptions.COLUMNS字段进行字符串的直接解析。
@Override
public TypeInfoConverter createTypeInfoConverter() {
return new BitSailTypeInfoConverter();
}
以 Hadoop 为例:
"reader": {
"class": "com.bytedance.bitsail.connector.hadoop.source.HadoopSource",
"path_list": "hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/test_namespace/source/test.json",
"content_type":"json",
"reader_parallelism_num": 1,
"columns": [
{
"name":"id",
"type": "int"
},
{
"name": "string_type",
"type": "string"
},
{
"name": "map_string_string",
"type": "map<string,string>"
},
{
"name": "array_string",
"type": "list<string>"
}
]
}

createSourceReader 方法
书写具体的数据读取逻辑,负责数据读取的组件,在接收到 Split 后会对其进行数据读取,然后将数据传输给下一个算子。
具体传入构造 SourceReader 的参数按需求决定,但是一定要保证所有参数可以序列化。如果不可序列化,将会在 createJobGraph 的时候出错。
public SourceReader<Row, RocketMQSplit> createReader(SourceReader.Context readerContext) {
return new RocketMQSourceReader(
readerConfiguration,
readerContext,
getSourceBoundedness());
}
createSplitCoordinator 方法
书写具体的数据分片、分片分配逻辑,SplitCoordinator 承担了去创建、管理 Split 的角色。
具体传入构造 SplitCoordinator 的参数按需求决定,但是一定要保证所有参数可以序列化。如果不可序列化,将会在 createJobGraph 的时候出错。
public SourceSplitCoordinator<RocketMQSplit, RocketMQState> createSplitCoordinator(SourceSplitCoordinator
.Context<RocketMQSplit, RocketMQState> coordinatorContext) {
return new RocketMQSourceSplitCoordinator(
coordinatorContext,
readerConfiguration,
getSourceBoundedness());
}
ParallelismComputable 接口
public interface ParallelismComputable extends Serializable {
/**
* give a parallelism advice for reader/writer based on configurations and upstream parallelism advice
*
* @param commonConf common configuration
* @param selfConf reader/writer configuration
* @param upstreamAdvice parallelism advice from upstream (when an operator has no upstream in DAG, its upstream is
* global parallelism)
* @return parallelism advice for the reader/writer
*/
ParallelismAdvice getParallelismAdvice(BitSailConfiguration commonConf,
BitSailConfiguration selfConf,
ParallelismAdvice upstreamAdvice) throws Exception;
}
getParallelismAdvice 方法
用于指定下游 reader 的并行数目。一般有以下的方式:
可以选择selfConf.get(ClickhouseReaderOptions.READER_PARALLELISM_NUM)来指定并行度。
也可以自定义自己的并行度划分逻辑。
比如在 RocketMQ 中,我们可以定义每 1 个 reader 可以处理至多 4 个队列DEFAULT_ROCKETMQ_PARALLELISM_THRESHOLD= 4
通过这种自定义的方式获取对应的并行度。
public ParallelismAdvice getParallelismAdvice(BitSailConfiguration commonConfiguration,
BitSailConfiguration rocketmqConfiguration,
ParallelismAdvice upstreamAdvice) throws Exception {
String cluster = rocketmqConfiguration.get(RocketMQSourceOptions.CLUSTER);
String topic = rocketmqConfiguration.get(RocketMQSourceOptions.TOPIC);
String consumerGroup = rocketmqConfiguration.get(RocketMQSourceOptions.CONSUMER_GROUP);
DefaultLitePullConsumer consumer = RocketMQUtils.prepareRocketMQConsumer(rocketmqConfiguration, String.format(SOURCE_INSTANCE_NAME_TEMPLATE,
cluster,
topic,
consumerGroup,
UUID.randomUUID()
));
try {
consumer.start();
Collection<MessageQueue> messageQueues = consumer.fetchMessageQueues(topic);
int adviceParallelism = Math.max(CollectionUtils.size(messageQueues) / DEFAULT_ROCKETMQ_PARALLELISM_THRESHOLD, 1);
return ParallelismAdvice.builder()
.adviceParallelism(adviceParallelism)
.enforceDownStreamChain(true)
.build();
} finally {
consumer.shutdown();
}
}
}
SourceSplit
数据源的数据分片格式,需要我们实现 SourceSplit 接口。

SourceSplit 接口
要求我们实现一个实现一个获取 splitId 的方法。
public interface SourceSplit extends Serializable {
String uniqSplitId();
}
对于具体切片的格式,开发者可以按照自己的需求进行自定义。
JDBC 类存储
一般会通过主键,来对数据进行最大、最小值的划分;对于无主键类则通常会将其认定为一个 split,不再进行拆分,所以 split 中的参数包括主键的最大最小值,以及一个布尔类型的readTable,如果无主键类或是不进行主键的切分则整张表会视为一个 split,此时readTable为true,如果按主键最大最小值进行切分,则设置为false。
以 ClickhouseSourceSplit 为例:
@Setter
public class ClickhouseSourceSplit implements SourceSplit {
public static final String SOURCE_SPLIT_PREFIX = "clickhouse_source_split_";
private static final String BETWEEN_CLAUSE = "( `%s` BETWEEN ? AND ? )";
private final String splitId;
/**
* Read whole table or range [lower, upper]
*/
private boolean readTable;
private Long lower;
private Long upper;
public ClickhouseSourceSplit(int splitId) {
this.splitId = SOURCE_SPLIT_PREFIX + splitId;
}
@Override
public String uniqSplitId() {
return splitId;
}
public void decorateStatement(PreparedStatement statement) {
try {
if (readTable) {
lower = Long.MIN_VALUE;
upper = Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
statement.setObject(1, lower);
statement.setObject(2, upper);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw BitSailException.asBitSailException(CommonErrorCode.RUNTIME_ERROR, "Failed to decorate statement with split " + this, e.getCause());
}
}
public static String getRangeClause(String splitField) {
return StringUtils.isEmpty(splitField) ? null : String.format(BETWEEN_CLAUSE, splitField);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format(
"{\"split_id\":\"%s\", \"lower\":%s, \"upper\":%s, \"readTable\":%s}",
splitId, lower, upper, readTable);
}
}
一般按照消息队列中 topic 注册的 partitions 的数量进行 split 的划分,切片中主要应包含消费的起点和终点以及消费的队列。
以 RocketMQSplit 为例:
@Builder
@Getter
public class RocketMQSplit implements SourceSplit {
private MessageQueue messageQueue;
@Setter
private long startOffset;
private long endOffset;
private String splitId;
@Override
public String uniqSplitId() {
return splitId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RocketMQSplit{" +
"messageQueue=" + messageQueue +
", startOffset=" + startOffset +
", endOffset=" + endOffset +
'}';
}
}
一般会按照文件作为最小粒度进行划分,同时有些格式也支持将单个文件拆分为多个子 Splits。文件系统 split 中需要包装所需的文件切片。
以 FtpSourceSplit 为例:
public class FtpSourceSplit implements SourceSplit {
public static final String FTP_SOURCE_SPLIT_PREFIX = "ftp_source_split_";
private final String splitId;
@Setter
private String path;
@Setter
private long fileSize;
public FtpSourceSplit(int splitId) {
this.splitId = FTP_SOURCE_SPLIT_PREFIX + splitId;
}
@Override
public String uniqSplitId() {
return splitId;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (obj instanceof FtpSourceSplit) && (splitId.equals(((FtpSourceSplit) obj).splitId));
}
}
特别的,在 Hadoop 文件系统中,我们也可以利用对org.apache.hadoop.mapred.InputSplit类的包装来自定义我们的 Split。
public class HadoopSourceSplit implements SourceSplit {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final Class<? extends InputSplit> splitType;
private transient InputSplit hadoopInputSplit;
private byte[] hadoopInputSplitByteArray;
public HadoopSourceSplit(InputSplit inputSplit) {
if (inputSplit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Hadoop input split must not be null");
}
this.splitType = inputSplit.getClass();
this.hadoopInputSplit = inputSplit;
}
public InputSplit getHadoopInputSplit() {
return this.hadoopInputSplit;
}
public void initInputSplit(JobConf jobConf) {
if (this.hadoopInputSplit != null) {
return;
}
checkNotNull(hadoopInputSplitByteArray);
try {
this.hadoopInputSplit = (InputSplit) WritableFactories.newInstance(splitType);
if (this.hadoopInputSplit instanceof Configurable) {
((Configurable) this.hadoopInputSplit).setConf(jobConf);
} else if (this.hadoopInputSplit instanceof JobConfigurable) {
((JobConfigurable) this.hadoopInputSplit).configure(jobConf);
}
if (hadoopInputSplitByteArray != null) {
try (ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(hadoopInputSplitByteArray))) {
this.hadoopInputSplit.readFields(objectInputStream);
}
this.hadoopInputSplitByteArray = null;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate Hadoop InputSplit", e);
}
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
if (hadoopInputSplit != null) {
try (
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream)
) {
this.hadoopInputSplit.write(objectOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.flush();
this.hadoopInputSplitByteArray = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
}
}
out.defaultWriteObject();
}
@Override
public String uniqSplitId() {
return hadoopInputSplit.toString();
}
}
State
在需要做 checkpoint 的场景下,通常我们会通过 Map 来保留当前的执行状态
流批一体场景
在流批一体场景中,我们需要保存状态以便从异常中断的流式作业恢复
以 RocketMQState 为例:
public class RocketMQState implements Serializable {
private final Map<MessageQueue, String> assignedWithSplitIds;
public RocketMQState(Map<MessageQueue, String> assignedWithSplitIds) {
this.assignedWithSplitIds = assignedWithSplitIds;
}
public Map<MessageQueue, String> getAssignedWithSplits() {
return assignedWithSplitIds;
}
}
对于批式场景,我们可以使用EmptyState不存储状态,如果需要状态存储,和流批一体场景采用相似的设计方案。
public class EmptyState implements Serializable {
public static EmptyState fromBytes() {
return new EmptyState();
}
}
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK