

Openfoam Pstream类探索 - TJUHE
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/heloveHe/p/17148332.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Openfoam Pstream类探索
对于数值仿真而言,无论是商软或者开源软件,并行计算都是非常重要的,
作为一名仿真工程师,如果想把自身数值仿真能力提升一个层次,需要对并行计算有很好的理解与应用
openfoam并行通信主要通过Pstream类完成
Pstream类,类如其名,parallel_stream,并行计算时使用的信息流
Openfoam对其的介绍是:
Inter-processor communications stream.
处理器间交换信息流
类似的命名方法我们在c++文件读取时说过,std有fstream类读取写入文件/二进制文件,比如说我们要读取文件,会把读取内容放入缓存区内进行操作
#include <iostream>#include <fstream> // ifstream类需要包含的头文件。#include <string> // getline()函数需要包含的头文件。using namespace std; int main(){ string filename = R"(./test.txt)"; //ifstream fin(filename, ios::in); ifstream fin; fin.open(filename , ios::in); // 判断打开文件是否成功。 // 失败的原因主要有:1)目录不存在;2)文件不存在;3)没有权限,Linux平台下很常见。 if (fin.is_open() == false) { cout << "打开文件" << filename << "失败。\n"; return 0; } string buffer; while (fin >> buffer) { cout << buffer << endl; } fin.close(); // 关闭文件,fin对象失效前会自动调用close()。 cout << "操作文件完成。\n";}
类似的openfoam也有PstreamBuffers类进行并行通信缓冲
可以这样使用:
PstreamBuffers pBuffers(Pstream::commsTypes::nonBlocking); for (label proci = 0; proci < Pstream::nProcs(); proci++) { if (proci != Pstream::myProcNo()) { someObject vals; UOPstream str(proci, pBuffers); str << vals; } } pBuffers.finishedSends(); // no-op for blocking for (label proci = 0; proci < Pstream::nProcs(); proci++) { if (proci != Pstream::myProcNo()) { UIPstream str(proci, pBuffers); someObject vals(str); } }
上面这个程序可以看到,先后使用UOPstream与UIPstream进行缓冲区的文件输出与读取,这就很像ofstream类与ifstream类,甚至命名方式上都有几分相似,我们打开相应的继承关系图
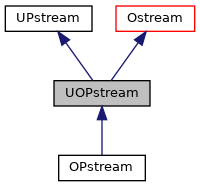
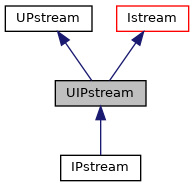
二者分别服务于IPstream类与OPstream类,我们再打开今天文章的主角,Pstream类继承关系图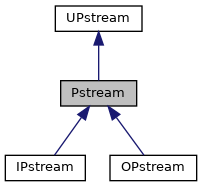
发现IPstream类与OPstream类是Pstream类的衍生类,Pstream类是其基础
打开Pstream类的源码:
点击查看代码
namespace Foam{ /*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*\ Class Pstream Declaration\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ class Pstream: public UPstream{ protected: // Protected data //- Transfer buffer DynamicList<char> buf_; public: // Declare name of the class and its debug switch ClassName("Pstream"); // Constructors //- Construct given optional buffer size Pstream ( const commsTypes commsType, const label bufSize = 0 ) : UPstream(commsType), buf_(0) { if (bufSize) { buf_.setCapacity(bufSize + 2*sizeof(scalar) + 1); } } // Gather and scatter //- Gather data. Apply bop to combine Value // from different processors template<class T, class BinaryOp> static void gather ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, T& Value, const BinaryOp& bop, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T, class BinaryOp> static void gather ( T& Value, const BinaryOp& bop, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = Pstream::worldComm ); //- Scatter data. Distribute without modification. Reverse of gather template<class T> static void scatter ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, T& Value, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T> static void scatter ( T& Value, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = Pstream::worldComm ); // Combine variants. Inplace combine values from processors. // (Uses construct from Istream instead of <<) template<class T, class CombineOp> static void combineGather ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, T& Value, const CombineOp& cop, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T, class CombineOp> static void combineGather ( T& Value, const CombineOp& cop, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = Pstream::worldComm ); //- Scatter data. Reverse of combineGather template<class T> static void combineScatter ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, T& Value, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T> static void combineScatter ( T& Value, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = Pstream::worldComm ); // Combine variants working on whole List at a time. template<class T, class CombineOp> static void listCombineGather ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, List<T>& Value, const CombineOp& cop, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T, class CombineOp> static void listCombineGather ( List<T>& Value, const CombineOp& cop, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = Pstream::worldComm ); //- Scatter data. Reverse of combineGather template<class T> static void listCombineScatter ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, List<T>& Value, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T> static void listCombineScatter ( List<T>& Value, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = Pstream::worldComm ); // Combine variants working on whole map at a time. Container needs to // have iterators and find() defined. template<class Container, class CombineOp> static void mapCombineGather ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, Container& Values, const CombineOp& cop, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class Container, class CombineOp> static void mapCombineGather ( Container& Values, const CombineOp& cop, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm ); //- Scatter data. Reverse of combineGather template<class Container> static void mapCombineScatter ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, Container& Values, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class Container> static void mapCombineScatter ( Container& Values, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm ); // Gather/scatter keeping the individual processor data separate. // Values is a List of size UPstream::nProcs() where // Values[UPstream::myProcNo()] is the data for the current processor. //- Gather data but keep individual values separate template<class T> static void gatherList ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, List<T>& Values, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T> static void gatherList ( List<T>& Values, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm ); //- Scatter data. Reverse of gatherList template<class T> static void scatterList ( const List<commsStruct>& comms, List<T>& Values, const int tag, const label comm ); //- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication template<class T> static void scatterList ( List<T>& Values, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm ); // Exchange //- Helper: exchange contiguous data. Sends sendData, receives into // recvData. If block=true will wait for all transfers to finish. template<class Container, class T> static void exchange ( const UList<Container>& sendData, const labelUList& recvSizes, List<Container>& recvData, const int tag = UPstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm, const bool block = true ); //- Helper: exchange sizes of sendData. sendData is the data per // processor (in the communicator). Returns sizes of sendData // on the sending processor. template<class Container> static void exchangeSizes ( const Container& sendData, labelList& sizes, const label comm = UPstream::worldComm ); //- Exchange contiguous data. Sends sendData, receives into // recvData. Determines sizes to receive. // If block=true will wait for all transfers to finish. template<class Container, class T> static void exchange ( const UList<Container>& sendData, List<Container>& recvData, const int tag = UPstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm, const bool block = true );};
我们看到Pstream类有一个构造函数,剩下的都是静态成员函数,而这些成员函数就是并行通讯的工具箱
这里多问一句,为什么工具箱的函数都是静态成员函数
为什么这里用静态成员函数呢
用静态成员可以变量实现多个对象间的数据共享,比全局变量更安全
这里我详细说下,举个例子
Time mytime1;mytime1.hour=2;Time mytime2;mytime2.hour=4;
这段程序中成员变量是跟着对象走的,他们的对象各自占用不同的内存地址,彼此互不影响
那我们想做类内的全局变量满足相互通信需求,在不同对象mytime1和mytime2中共享一个副本,怎么办
这时static关键字就派上用场了,增加了static关键字或成员函数不隶属整个对象,而隶属于整个类
因为这个变量跟着类走,所以调用时用“类名::成员变量名”或“类名::成员变量函数”进行调用(当然也可用“对象名.静态函数名”),表示明确的隶属关系,不创建对象也可进行访问编辑
在Pstream类调用工具箱中函数时,我们常见到这样的调用方式,而且不创建Pstream对象也可进行调用
// 在head节点收集信息Pstream::gatherList(nInternalFaces);Pstream::gatherList(nBoundaries);
因为类的静态成员脱离了与对象的关系,普通成员变量的内存分配是在对象初始化时完成的,对于静态成员必须在程序的全局区进行清晰的初始化
全局区的初始化过程可由某个.cpp源文件的开头的静态成员函数完成,如下所示:
void Time::func(int testValue){ mystatic = testValue ;}
或者在全局区这样写:
int Time::mystatic=10;
这样能保证这个静态成员变量能够被正常使用。
此外静态成员函数只能调用静态成员变量,也没有this指针可以使用
这里上一张图可能更方便理解
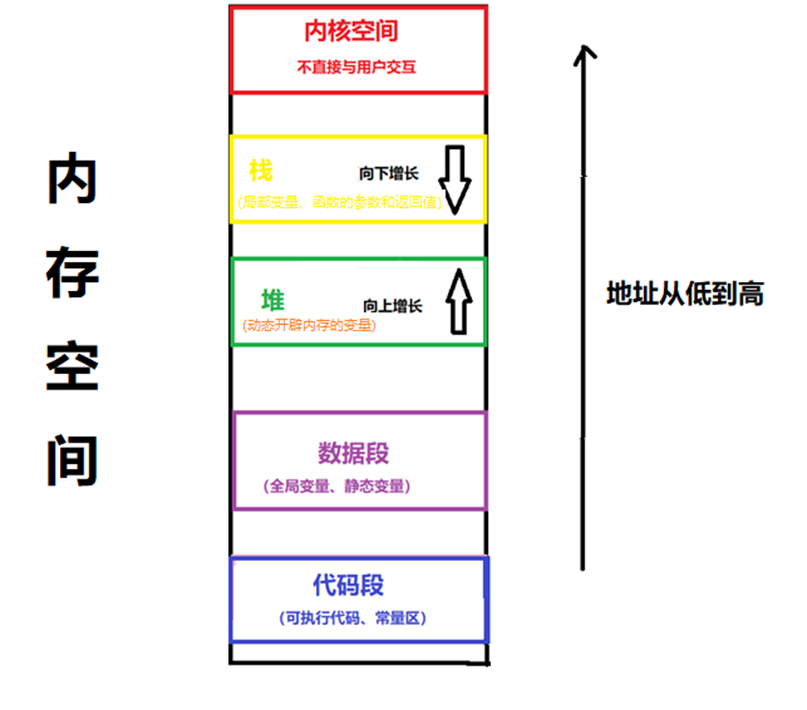
C++程序运行时,静态变量和全局变量存储在数据段,所以需要在全局区通过直接分配内存或者静态函数进行分配内存
因而静态成员的生命周期与程序运行周期相同,在程序中只有一份,无论创建对象与否,或者创建多少对象
说到这里可能大家对Openfoam的并行通信多了一些理解,只要开始了并行计算那么就可以通过Pstream类内的成员函数进行通信调用,在同样的数据段副本上进行信息流沟通
接下来依次说下类中各个工具的使用
收发数据
Pstream::gather()与Pstream::scatter()分别有两个重载,分别是收集以及散布数据,不如后面Pstream::gatherList()与Pstream::scatterList()常用,这里不细说了
Pstream::combineGather()、Pstream::combineScatter()重载情况与上同,用于就地集中收集或散布的数据,不太常用
Pstream::listCombineGather()、Pstream::listCombineScatter()重载情况与上同,用于一次整合list容器中的变量
Pstream::mapCombineGather()、Pstream::mapCombineScatter()重载情况与上同,用于一次整合整个map容器中的变量
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的第二个重载比较常用,
template<class T> static void gatherList ( List<T>& Values, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm );template<class T> static void scatterList ( List<T>& Values, const int tag = Pstream::msgType(), const label comm = UPstream::worldComm );
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的输入第一个参数是Values
这个Values需要自己整合下,Values是UPstream::nProcs()数量大小的List,比如说我要收集内部面可以这样创建需要收集的List,
List<label> nIternalFaces(Pstream::nProcs());nIternalFaces[Pstream::myProcNo()] = mesh.Cf().size();//比如说看看每个节点分到了多少网格Pstream::gatherList(nIternalFaces);//在头结点收集数据
Pstream::scatterList()与之类似
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的输入第二个参数是Pstream::msgType(),默认为1,可以不输入
int Foam::UPstream::msgType_(1);
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的输入第三个参数是Pstream::msgType(),默认为0,可以不输入
Foam::label Foam::UPstream::worldComm(0);
交换数据
Pstream::exchange()有两个重载,用于交换连续的数据,一般情况下等待其他所有传输完成再传输,可通过默认参数block()修改优先权
Pstream::exchangeSizes()用于交换数据的大小
下面是Pstream类函数相互关系
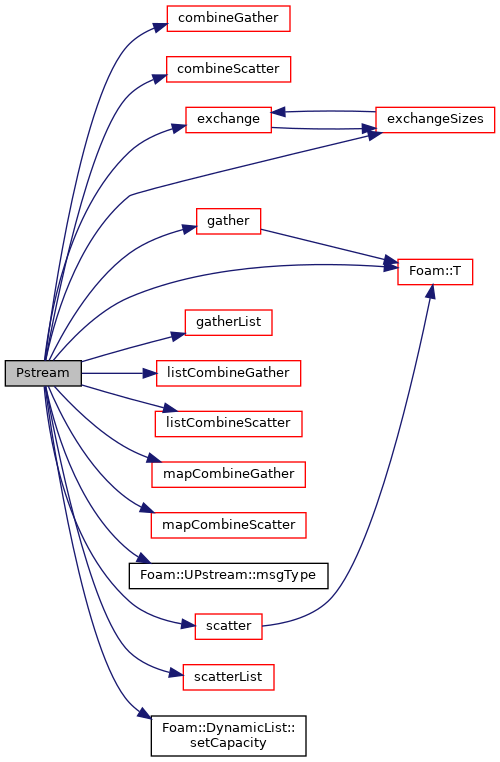
并行开发远不止收发数据这么简单,还有很多类可说的,后续会一一进行介绍,并对openfoam并行计算进行优化
一起探索openfoam也是相当有趣的一件事,非常欢迎私信讨论
指正的价值要比打赏更重要,下面是个人联系方式,能结交到志同道合的朋友是我的荣幸
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK