

SPA路由实现的基本原理 - 暮冬有八
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/jaycethanks/p/17143638.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

1. SPA路由实现的基本原理
前端单页应用实现路由的策略有两种,分别是 基于hash 和 基于 History API
基于hash
通过将一个 URL path 用
#Hash 符号拆分。— 浏览器视作其为虚拟的片段。
最早前端路由的实现就是 基于 location.hash 来实现的, 有这样几个特性:
- URL 中hash值的改变不会被触发页面的重载
- 页面发送请求时, hash 部分不会被发送
- hash 值的改变,会记录在浏览器的历史记录,可使用浏览器的“后退” “前进”触发页面跳转
- 可以利用 hashchange 事件来监听 hash 的变化
触发hash 变化的方式有两种:
- 通过a 标签的 href 属性,用户点击后,URL 就会发生改变,进而触发 hashchange 事件
- 直接对 location.hash 赋值,从而改变 URL, 触发hashchange 事件。
基于 History API
普通的 URL path (无哈希的 URL path) — 服务器需要拦截路径请求返回 入口 index.html 文件
基于 hash 的实现,存在一些问题,例如
- URL 上很多
#影响美观。
因此 H5 中,提供了 History API 来实现 URL 的变化。 采用这种策略实现的前端路由, 主要是利用了 popstate 事件来监听历史记录的变化。
补在文章后面:
除此之外, 基于 Hash 的路由不需要对服务器做改动,但是基于 History API 的路由则需要对服务器做一些 hanle 处理。
2. 相关API 与方法
在开始手动实现之前,有必要先了解一下将会涉及的 API 与 方法。
基于 Location.hash 相关
location
实例属性 hash
返回 URL 中 # 部分的内容, 例如 http://www.example.com/index.html#hello 中的 #hello 部分。
window.hashchange 方法
该方法监听url 中, hash 部分改变时的回调。
注意⚠️: 用户点击 浏览器的前进后退 按钮,如果url 的hash 发生改变,同样也会触发该方法。
History API
History.length [只读属性]
返回 session 历史记录的长度,新打开的tab 页面该属性值为 1 。
History.scrollRestoration
控制页面刷新时是否记住用户页面的滚动位置。 该值是一个可设定值,有 auto 和 manual 两种:
auto: 保存页面滚动位置(默认)manual: 不保存页面滚动位置
新打开tab 页面时,滚动位置始终回到页面顶部。 这两个属性仅对 页面刷新有效。
History.state [只读属性]
浏览器页面历史记录是一个栈结构,该属性将返回栈顶页面的 状态, 在使用pushState() 或者 replaceState() 方法之前, 这个值为 null. state 是一个 js 对象,该对象将会被存储到用户的本地磁盘, 浏览器关闭重启之后,还能够访问历史值。 但是该对象有大小限制(具体大小根据浏览器的实现而定),一旦所设定内容超出该限制,浏览器将会抛出错误。
History.go()
该方法控制页面回到历史中的某个相对位置,仅一个可选参数表示前进的步进值,它可以为正值,也可以为负值。
- 如果不传入参数,或者传入
0, 则等同于页面刷新。 - 该方法无返回值。
History.back()
该方法,不接受任何参数。 它等同于 history.go(-1), 也就是页面的 回退 按钮。
History.forward()
该方法同样不接受参数,等同于 history.go(1), 也就是页面的 前进 按钮
History.pushState() 和 History.replaceState()
pushState(state, unused)pushState(state, unused, url)
state 是一个 js 对象,可以是任意被序列化的值。 第二个参数被废弃了,但是由于历史缘故,依然保留,在使用时,应该传入一个空字符串。
这两个方法用于手动操作History对象。
.├── foo.html└── index.html
<head> <title>History demo</title></head><body> <button onclick="handleClick()">test</button> <p> some text here... </p></body>
function handleClick() { window.history.pushState({ hello: 'world' }, '', 'foo.html');}
chrome 浏览器中,可以将鼠标按住后退按钮,查看到 History 数组:
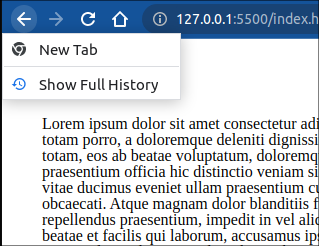
此时点击 test 按钮后:

浏览器新打开tab 就会入栈一个 “New Tab”, 点击test 触发 pushState() 之后, 会将当且页面“History demo”入栈, 然后当前页面变为 foo.html, 页面的状态变作:{hello: 'world'}, 可以通过history.state 访问到。
值得注意的是, 页面虽然改变了,但是还没有更新渲染。 此时如果刷新页面,就会更新渲染了。
但是注意pushState 的目标url,必须是一个子域地址,且如果pushState 的目标页面不存在,页面刷新之后会报404错误。
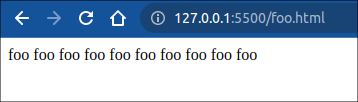
在 foo.html 中新增一个按钮,测试 replaceState 方法:
<!--foo.html--> <body> <button onclick="handleReplace()">replace</button> foo foo foo foo foo foo foo foo foo foo <script src="script.js"></script> </body>
// script.jsfunction handleReplace() { window.history.replaceState({ foo: 'bar' }, '', 'bar.html');}
当前页面foo.html 将会被替换为 bar.html, 状态改变为 {foo: 'bar'}, 页面同样在刷新后会更新。
注意, 该方法并不会新增一个记录到历史记录。
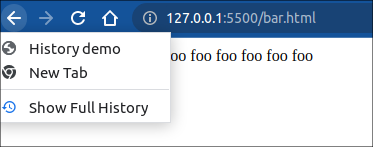
关于History.pushState() 和 History.replaceState() 这两个API 的补充:
- 这两个API的,第三个参数可以可选的,如果缺省,那么操作默认以当前页面为目标。 第二个参数可以认为始终传入
""一个空串。 - 页面不仅仅
window.popstate 方法
该方法当用户通过点击 前进后退 按钮,或者通过js, 调用 history.go(), history.back(), history.forward() 时,将会被触发
了解了所必须的 API,下面详细的试试如何手动实现路由。
3. 手写一个简单的路由
1.0 预准备
因为接下来的两种实现,我们都将用到同样的文件目录结构,所以在这里我们先创建好他们。
1.0.1 文件目录
.├── index.html├── js│ └── router.js└── templates ├── 404.html ├── about.html ├── contact.html └── index.html
1.0.2 创建服务器 serve 的主 html 文件
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <meta name="description" /> <title></title> </head> <body> <nav> <a href="/">Home</a> <a href="#about">About</a> <a href="#contact">Contact</a> </nav> <div id="content"></div> <script src="js/router.js"></script> </body></html>
1.0.3 创建脚本文件
注意一个步骤中的代码,在body闭合标签的上方,我们引入了js脚本。
1.1 基于 History API
1.1.1 添加路由导航
将以下代码添加到 <nav></nav> 标签内,作为我们的路由导航。
<a href="/">Home</a><a href="/about">About</a><a href="/contact">Contact</a>
1.1.2 创建路由数组
// route.jsconst routes = { 404: { template: "/templates/404.html", title: "404", description: "Page not found", }, "/": { template: "/templates/index.html", title: "Home", description: "This is the home page", }, "/about": { template: "/templates/about.html", title: "About Us", description: "This is the about page", }, "/contact": { template: "/templates/contact.html", title: "Contact Us", description: "This is the contact page", },};
1.1.3 给导航添加点击事件监听器
//script.jsconst route = (event) => { event = event || window.event; // get window.event if event argument not provided event.preventDefault(); // window.history.pushState(state, unused, target link); window.history.pushState({}, "", event.target.href); locationHandler();}; // create document click that watches the nav links onlydocument.addEventListener("click", (e) => { const { target } = e; if (!target.matches("nav a")) { return; } e.preventDefault(); route();});
1.1.4 创建处理 location URL 的函数
//script.jsconst locationHandler = async () => { const location = window.location.pathname; // get the url path // if the path length is 0, set it to primary page route if (location.length == 0) { location = "/"; } // get the route object from the urlRoutes object const route = routes[location] || routes["404"]; // get the html from the template // 注意这里是怎么获取到html模板的,很具有技巧性 const html = await fetch(route.template).then((response) => response.text()); // set the content of the content div to the html document.getElementById("content").innerHTML = html; // set the title of the document to the title of the route document.title = route.title; // 如何选中 meta 标签 // set the description of the document to the description of the route document .querySelector('meta[name="description"]') .setAttribute("content", route.description);};
1.1.5 完成脚本
最后,我们需要在页面首次加载的时候调用一下 locationHandler 方法,否则,首页无法呈现。
此外,我们还需要添加 URL 变化的 watcher
//script.js// add an event listener to the window that watches for url changeswindow.onpopstate = locationHandler;// call the urlLocationHandler function to handle the initial urlwindow.route = route;// call the urlLocationHandler function to handle the initial urllocationHandler();
注意,点击导航,以及用户控制页面前进后退,都会触发页面的渲染。 所以需要调用 locationHandler 方法。
1.2 基于hash 的实现
1.2.1 添加路由导航
将以下内容添加在 <nav></nav> 标签内:
<a href="/">Home</a><a href="#about">About</a><a href="#contact">Contact</a>
1.2.2 创建路由数组
//script.jsconst routes = { 404: { template: "/templates/404.html", title: "404", description: "Page not found", }, "/": { template: "/templates/index.html", title: "Home", description: "This is the home page", }, about: { template: "/templates/about.html", title: "About Us", description: "This is the about page", }, contact: { template: "/templates/contact.html", title: "Contact Us", description: "This is the contact page", },};
1.2.3 创建处理 location URL 的函数
//script.jsconst locationHandler = async () => { // get the url path, replace hash with empty string var location = window.location.hash.replace("#", ""); // if the path length is 0, set it to primary page route if (location.length == 0) { location = "/"; } // get the route object from the routes object const route = routes[location] || routes["404"]; // get the html from the template const html = await fetch(route.template).then((response) => response.text()); // set the content of the content div to the html document.getElementById("content").innerHTML = html; // set the title of the document to the title of the route document.title = route.title; // set the description of the document to the description of the route document .querySelector('meta[name="description"]') .setAttribute("content", route.description);};
1.2.4 完成脚本
同样的,页面首次加载,以及 hashchange 的时候都需要调用 locationHandler 函数
//script.js// create a function that watches the hash and calls the urlLocationHandlerwindow.addEventListener("hashchange", locationHandler);// call the urlLocationHandler to load the pagelocationHandler();
4.1 原理总结
总结的来说, 基于 History API 的实现,主要是利用了 h5 提供的 pushState, replaceState方法。去改变当前页面的 URL, 同时,利用点击事件 结合 window.popState 监听事件触发页面的更新渲染逻辑。
而 基于 location.hash 的实现,则更为简单,直接 利用 a 便签的 href 属性,触发 hashchange 事件,进而触发页面的更新逻辑。
对比起来, 基于 location.hash 的实现要更为简单。 但是基于 History API 实现的路由,URL 中不含有 # 而显得用户体验更加良好。
4.2 基于History API 的实现需要注意的事项
此外值得注意的一点是, 现在的框架中,大都提供了这两中实现方案。 在实际应用中。 如果应用了 基于 History API 的实现方式,服务器通常需要做一些配置。
因为由于单页应用路由的实现是前端实现的, 可以理解为是 “伪路由”, 路由的跳转逻辑都是前端代码完成的,这样就存在一个问题, 例如上面的实现中, http://127.0.0.1:5500/about 这个页面用户点击了页面刷新,就会找不到页面。 因为浏览器会向服务器 “http://127.0.0.1:5500/about” 这个地址发送 GET 请求, 希望请求到一个单独的 index.html 文件, 而实际上这个文件我们服务器上是不存在的。 我们需要将其处理为:
http://127.0.0.1:5500/ server 返回首页
http://127.0.0.1:5500/about server 返回首页, 然后前端路由跳转到 about 页
http://127.0.0.1:5500/contact server 返回首页, 然后前端路由跳转到 contact 页
为了做到这点,所以我们需要对服务器做一些转发处理,
// root 是我本地的页面地址// try_files 将匹配子级路由全部尝试返回 index.html 文件server { listen 7000; location / { root /home/jayce/Desktop/temp/demo/front-end-router-implement/HistoryApi; index index.html; try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html; }}
4.3 两种实现模式的优势和挑战对比
4.3.1 基于 History API 的实现
- URL 看起来和普通的url 一样, 更加美观简洁
- 在 SEO 方面, 普通 url 会有更多的优势
- 现代框架通常默认支持该模式
- 客户端刷新时,会把 SPA 的路由误当作 资源请求链接,所以需要配置 web 服务器以处理这些 “路由形式的URL” 以统一放回入口 index.html 文件。
- 通常为了让服务器区分这些 “路由形式的URL”, 所以通常需要用一些前缀以区分和普通 请求的区别,如
/api/* - 通过这种方式实现时,定义路由的时候需要特别注意, 因为不当的链接跳转可能会导致全页面重载。
4.3.2 基于 Location.hash 的实现
- 浏览器不会将 URL.path 中
#hash 后面的部分视作一个分页,因此默认的就不会触发页面的重载 - 在前端定义带有 hash 的链接总是安全的,因为它不会触发页面的重载
- 服务端不需要额外配置。
- 实现起来更加简单
- SEO 并不友好
- 用户体验不好
Recommend
-
 24
24
为充分利用机器性能,人们发明了多线程。但同时带来了线程安全问题,于是人们又发明了同步锁。 这个问题自然人人知道,但你真的了解同步锁吗?还是说你会用其中的上锁与解锁功能? 今天我们就一起来深入看同步锁的原理和实...
-
 21
21
路由功能是web框架中一个很重要的功能,它将不同的请求转发给不同的函数(handler)处理,很容易能想到,我们可以用一个字典保存它们之间的对应关系,字典的key存放path,value存放handler。当一个请求过来后,使用 routers.get(pa...
-
 15
15
何为前端路由?路由(Router)这个概念最先是后端出现的,是用来跟后端服务器进行交互的一种方式,通过不同的路径,来请求不同的资源,请求不同的页面是路由的其中一种功能。前端随着 ajax 的流行,数据请求可以在不刷新浏览...
-
 16
16
语音识别技术 – ASR丨Automatic Speech Recognition语音识别是什么?他有什么价值,以及他的技术原...
-
 8
8
[toc] 本文主要回顾一下Slice实现的使用和基本原理 Slice数据结构 源码包中 src/runtime/slice.go:slice 定义了Slice的数据结构: array指针指向底层数组,len表示切片长度,cap表示底层数组容量。 type slice stru...
-
 8
8
一开始我还担心 git 的原理会不会很难懂,但在阅读了官方文档后我发现其实并不难懂,似乎可以动手实现一个简单的 git,于是就有了下面这篇学习记录。 本文的叙述思路参照了官方文档Book的原理介绍部分,在一些节点上探讨代码实现,
-
 8
8
积分与排名 1. Re:C#多线程(9):多阶段并行线程 @眯着 在这里加上去 或者将 3 改成 2 private st...
-
 3
3
1.vector类的实现重要结构定义:template<class T> class myVector{ public: typedef T value_type;//元素类型 起别名 typedef value_type* pointer;// typedef value_type* iterator;//迭代器...
-
 4
4
聊聊TokenBucket限流器的基本原理及实现 yudotyang · 3天之前 · 160 次点击 · 预计阅读时间 6 分...
-
 8
8
动态网站实现SPA般的速度 发布者:1900 Aug 21, 2023 Posted in 分...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK