

CompletableFuture 使用总结 - 香吧香
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/zjdxr-up/p/17009219.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
转载请注明出处:
1.Future使用对比
Future表示一个异步计算的结果。它提供了isDone()来检测计算是否已经完成,并且在计算结束后,可以通过get()方法来获取计算结果。在异步计算中,Future确实是个非常优秀的接口。但是,它的本身也确实存在着许多限制:
-
并发执行多任务:Future只提供了get()方法来获取结果,并且是阻塞的。所以,除了等待别无他法;
-
无法对多个任务进行链式调用:如果你希望在计算任务完成后执行特定动作,比如发邮件,但Future却没有提供这样的能力;
-
无法组合多个任务:如果你运行了10个任务,并期望在它们全部执行结束后执行特定动作,那么在Future中这是无能为力的;
-
没有异常处理:Future接口中没有关于异常处理的方法;
Future 注意事项
-
当 for 循环批量获取 Future 的结果时容易 block,get 方法调用时应使用 timeout 限制
-
Future 的生命周期不能后退。一旦完成了任务,它就永久停在了“已完成”的状态,不能从头再来
针对 Future 使用中的同时对多个异步任务进行编排的不足,java 使用 CompletableFuture是Future接口的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富地扩展,完美地弥补了Future上述的种种问题。更为重要的是,CompletableFuture实现了对任务的编排能力。借助这项能力,我们可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。从某种程度上说,这项能力是它的核心能力。而在以往,虽然通过CountDownLatch等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理,不仅耗费精力且难以维护。
2.CompletableFuture 常用方法
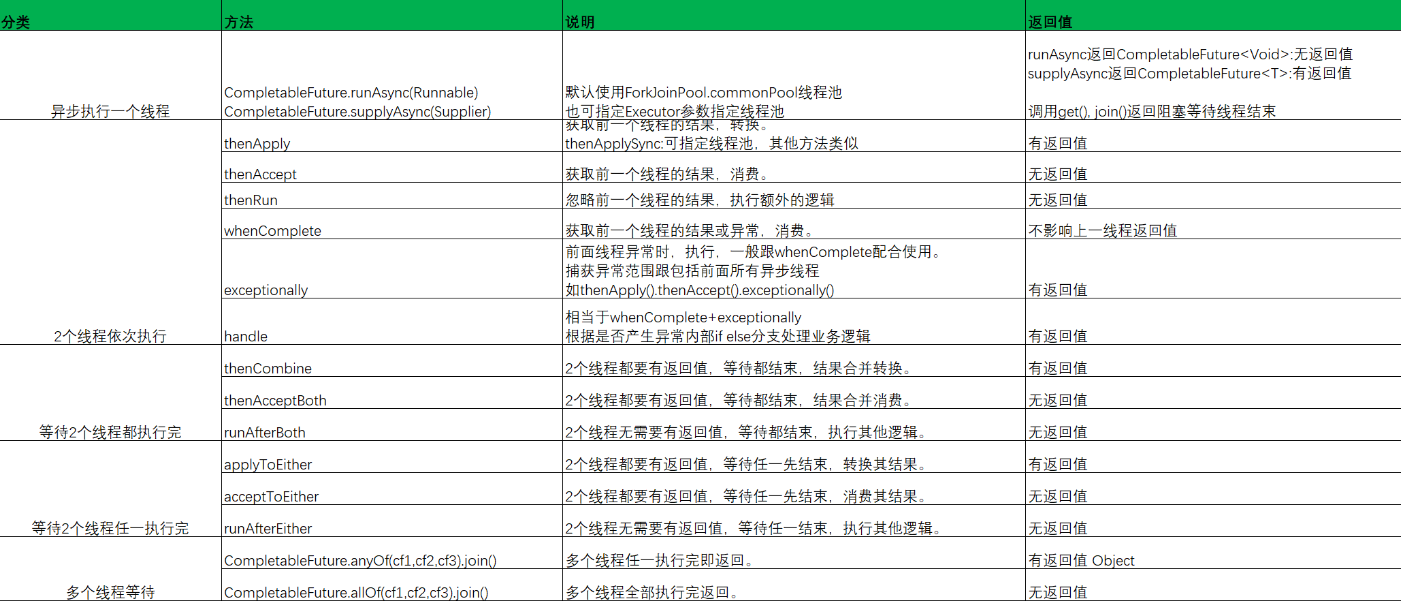
应用场景
描述依赖关系:
-
thenApply() 把前面异步任务的结果,交给后面的Function
-
thenCompose()用来连接两个有依赖关系的任务,结果由第二个任务返回
-
描述and聚合关系:
-
thenCombine:任务合并,有返回值
-
thenAccepetBoth:两个任务执行完成后,将结果交给thenAccepetBoth消耗,无返回值。
-
runAfterBoth:两个任务都执行完成后,执行下一步操作(Runnable)。
-
描述or聚合关系:
-
applyToEither:两个任务谁执行的快,就使用那一个结果,有返回值。
-
acceptEither: 两个任务谁执行的快,就消耗那一个结果,无返回值。
-
runAfterEither: 任意一个任务执行完成,进行下一步操作(Runnable)。
-
并行执行:
CompletableFuture类自己也提供了anyOf()和allOf()用于支持多个CompletableFuture并行执行
3.1创建异步操作
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作:
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
这四个方法区别在于:
-
runAsync 方法以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数,没有返回结果,supplyAsync 方法Supplier函数式接口类型为参数,返回结果类型为U;Supplier 接口的 get() 方法是有返回值的(会阻塞)
-
没有指定Executor的方法会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行。
-
默认情况下 CompletableFuture 会使用公共的 ForkJoinPool 线程池,这个线程池默认创建的线程数是 CPU 的核数(也可以通过 JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism 来设置 ForkJoinPool 线程池的线程数)。如果所有 CompletableFuture 共享一个线程池,那么一旦有任务执行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,就会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,进而影响整个系统的性能。所以,强烈建议你要根据不同的业务类型创建不同的线程池,以避免互相干扰
-
示例:
Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("执行无返回结果的异步任务");
CompletableFuture.runAsync(runnable);
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("执行有返回值的异步任务");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Hello World";
});
String result = future.get();
在使用过程中,可以使用 spring 提供的 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 作为 线程池的执行器
3.2 获取结果
join&get
join()和get()方法都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值。join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)
3.3 结果处理
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,我们可以执行特定的 Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
-
Action的类型是BiConsumer,它可以处理正常的计算结果,或者异常情况。
-
方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
-
这几个方法都会返回CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if (new Random().nextInt(10) % 2 == 0) {
int i = 12 / 0;
}
System.out.println("执行结束!");
return "test";
});
future.whenComplete(new BiConsumer<String, Throwable>() {
@Override
public void accept(String t, Throwable action) {
System.out.println(t+" 执行完成!");
}
});
future.exceptionally(new Function<Throwable, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Throwable t) {
System.out.println("执行失败:" + t.getMessage());
return "异常xxxx";
}
3.4 结果转换
所谓结果转换,就是将上一段任务的执行结果作为下一阶段任务的入参参与重新计算,产生新的结果。
thenApply
thenApply 接收一个函数作为参数,使用该函数处理上一个CompletableFuture 调用的结果,并返回一个具有处理结果的Future对象。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 100;
System.out.println("一阶段:" + result);
return result;
}).thenApply(number -> {
int result = number * 3;
System.out.println("二阶段:" + result);
return result;
});
thenCompose
thenCompose 的参数为一个返回 CompletableFuture 实例的函数,该函数的参数是先前计算步骤的结果。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn); public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) ;
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(30);
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
})
.thenCompose(new Function<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>>() {
@Override
public CompletionStage<Integer> apply(Integer param) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = param * 2;
System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
}
});
thenApply 和 thenCompose的区别
-
thenApply 转换的是泛型中的类型,返回的是同一个CompletableFuture;
-
thenCompose 将内部的 CompletableFuture 调用展开来并使用上一个CompletableFutre 调用的结果在下一步的 CompletableFuture 调用中进行运算,是生成一个新的CompletableFuture。
3.5 同时返回allOf
allOf方法用来实现多 CompletableFuture 的同时返回。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
@Resource
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor completableExecutor;
public void test() {
List<Student> allList = Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList();
List<Student> oneClassList = Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList();
List<Student> twoClassList = Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList();
CompletableFuture.allOf(
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
List<Student> firstList = service.doFirstList();
oneClassList.addAll(firstList);
}, completableExecutor),
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
List<Student> secondList = service.doSecondList();
twoClassList.addAll(secondList);
}, completableExecutor)
).join();
allList.addAll(oneClassList);
allList.addAll(twoClassList);
}
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK