

一个简单的rust字符串时钟 - 啊哈彭
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/pingwen/p/17004872.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

用rust写的一个简单的练手的demo,一个字符串时钟,在终端用字符串方式显示当前时间。本质是对图片取灰度,然后每个像素按灰度门限用星号代替灰度值,就把图片变为由星号组成的字符型图案。把时间字符串的每个字符按照字母和数字图片的样式转换为字符,然后拼接字符图案就实现了字符时钟的效果。
主要用到的知识有:rust操作时间、字符串、vector,字符串和vector的转换、string,以及让人恼火的生命周期。对比python,rust的列表入门难度可以说是地狱级的,一会borrow、一会move,晕头转向。
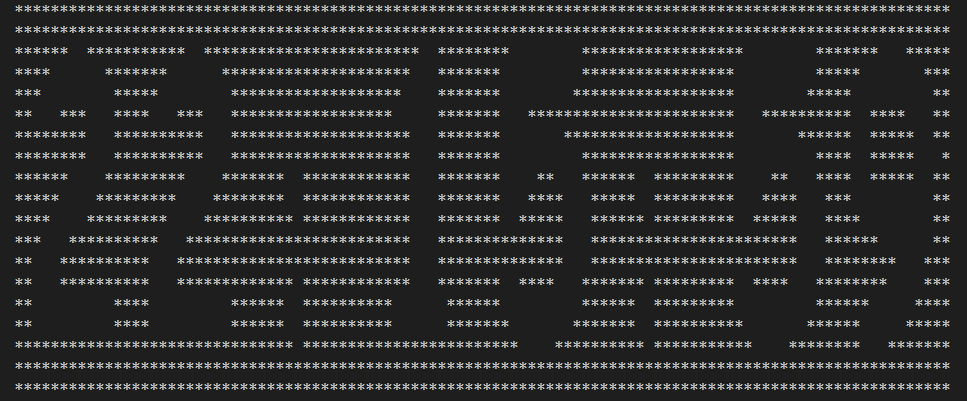
2、用到的知识点
2.1 取utc时间
时间库使用chrono = "0.4",获取秒数等时间。
let five_seconds = Duration::new(5, 0);
let five_seconds_and_five_nanos = five_seconds + Duration::new(0, 10);
assert_eq!(five_seconds_and_five_nanos.as_secs(), 5);
assert_eq!(five_seconds_and_five_nanos.subsec_nanos(), 10);
let five_seconds = Duration::from_secs(5);
assert_eq!(five_seconds, Duration::from_millis(5_000));
assert_eq!(five_seconds, Duration::from_micros(5_000_000));
assert_eq!(five_seconds, Duration::from_nanos(5_000_000_000));
let ten_seconds = Duration::from_secs(10);
let seven_nanos = Duration::from_nanos(7);
let total = ten_seconds + seven_nanos;
assert_eq!(total, Duration::new(10, 7));
获取实时utc时间。
let local:DateTime<Local>= Local::now();
println!("{:?}", local.format("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S").to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.format("%a %b %e %T %Y").to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.format("%c").to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.to_rfc2822());
println!("{:?}", local.to_rfc3339());
let dt = Local.with_ymd_and_hms(2020 as i32, 12, 05, 12, 0, 9).unwrap();
println!("{:?}", dt.format("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S").to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.format("%a %b %e %T %Y").to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.format("%c").to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.to_rfc2822());
println!("{:?}", dt.to_rfc3339());
"2022-12-25 23:20:03"
"Sun Dec 25 23:20:03 2022"
"Sun Dec 25 23:20:03 2022"
"2022-12-25 23:20:03.499293300 +08:00"
"Sun, 25 Dec 2022 23:20:03 +0800"
"2022-12-25T23:20:03.499293300+08:00"
"2020-12-05 12:00:09"
"Sat Dec 5 12:00:09 2020"
"Sat Dec 5 12:00:09 2020"
"2020-12-05 12:00:09 +08:00"
"Sat, 05 Dec 2020 12:00:09 +0800"
"2020-12-05T12:00:09+08:00"
获取当前时间,如下格式化为20:15:23类似的格式。
let curdate = Local::now();
let datecollect = curdate.format("%H:%M:%S").to_string();
2.2 图片变换为像素图案
1、读取图片
先准备每个数字的图片,然后读取图片,转换为灰度表示。
let cur_dir = std::env::current_dir().unwrap().
into_os_string().into_string().unwrap();
let _path = if number == ':' {
format!("{}/number_pic/{}.png", &cur_dir, "maohao")
}
else{
format!("{}/number_pic/{}.png", &cur_dir, number)
};
// println!("imagepath = {}", _path);
let gray_pic = image::open(_path).unwrap()
.resize(nwidth, nheight, image::imageops::FilterType::Nearest)
.into_luma8();
初始化pix_clock结构体,解析需要用到的10个数字和冒号时间分隔字符。
pub struct pix_clock {
words : HashMap<char, Vec<String>>,
}
impl pix_clock {
pub fn new() -> pix_clock {
let mut dict_result = HashMap::new();
let numbers = vec!['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', ':'];
for value in numbers {
let result = get_num_pic(value);
dict_result.insert(value, result);
// println!("num={} {:#?}", value, dict_result[&value]);
}
return pix_clock {
words: dict_result,
};
}
}
2、图片按像素灰度转换为字符图案
每行作为1个string字符串,按行处理,读取完一行后把当前行的字符串push到列表,然后清空行变量,准备解析下一行的像素。每行都解析完成后,pix_data就形成了一个由nheight行,每行nwidth个字符构成的列表。
let mut pix_data: Vec<String> = vec![];
let mut line = String::from("");
for (index, tmp) in gray_pic.to_vec().iter().enumerate() {
if index % nwidth as usize == 0 {
if line.len()>0 {
let line2 = line.clone();
pix_data.push(line2);
}
line.clear();
}
if tmp > &gap_value {
line.push_str("*");
}
else {
line.push_str(" ");
}
}
以数字3为例:println!("result data {} {:#?}", number, &pix_data);// 输出数据为:
result data 3 [
"*************",
"*************",
"****** ******",
"*** ***",
"*** ***",
"*** *** **",
"******** **",
"******* ***",
"**** ***",
"**** ***",
"******* **",
"******** **",
"********* **",
"** *** **",
"** ***",
"*** ***",
"***** *****",
"*************",
"*************",
]
2.3 字符方式显示当前时间
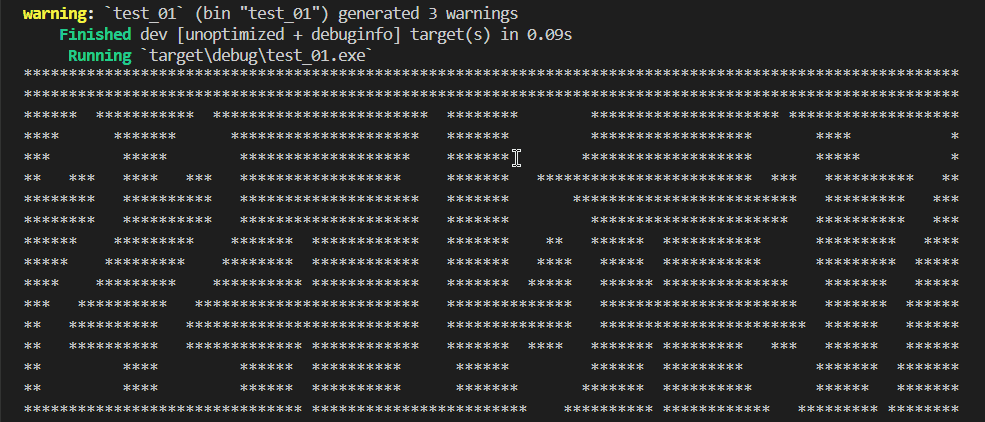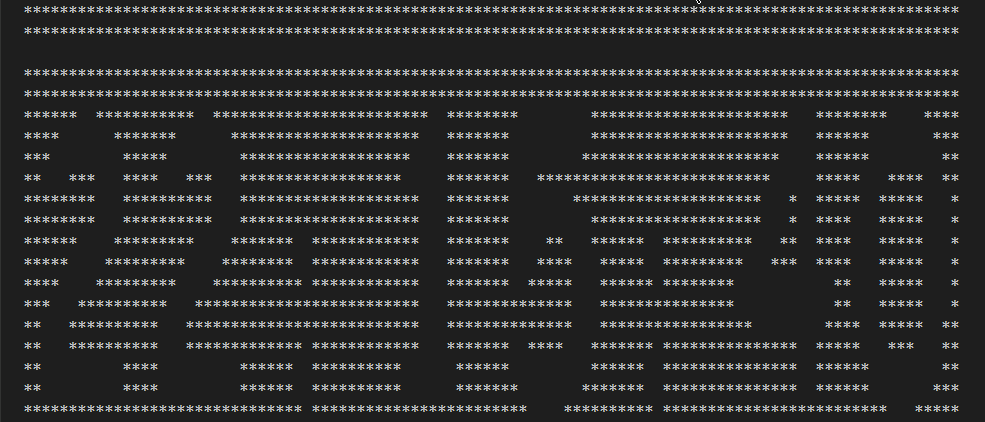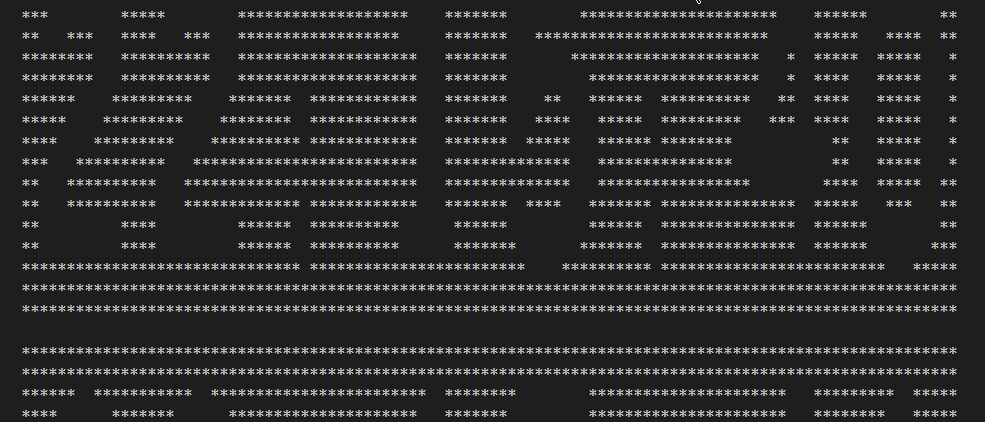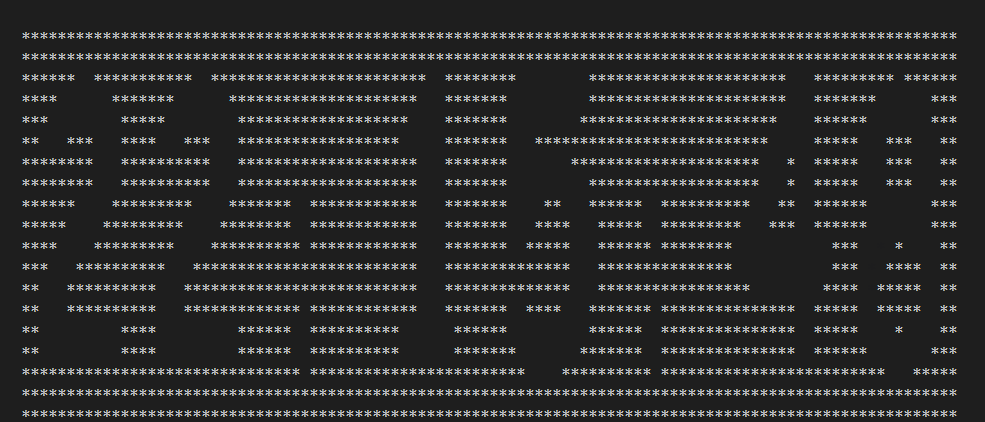
上一步已经完成了单个数字转换为字符图案,由于时间字符串由多位数字构成,所以需要拼接图案。例如20:15:23,就由6个数字和2个冒号组成,所以字符串“20:15:23”就需要按行合并。
1)合并每个数组的团案,而高度不变。
let time_str = datestr.chars(); // 把字符串解析为char型字符
let mut final_vector: Vec<String> = vec![];
for _index in 0..self.words.get(&'0').unwrap().len() { // 合并后的图案高度不变,即行数不变
final_vector.push("".to_string()); // 每行的字符串变长了,先预留空String来接收每行字符
}
2)按行合并每个字符,拼接字符串的图案
for value in time_str { //遍历时间字符串的每个字符
let value_pix = self.words.get(&value).unwrap(); //获取单个字符的图案
let mut index = 0;
for x in value_pix.iter() {
final_vector[index].push_str(&x); # 每个字符相同行的字符串合并为一个大字符串
index += 1;
}
}
for temp in final_vector { // 合并后的字符串,高度不变(即行数不变)
println!("{}", format!("{}", temp)); // 打印合并后的字符串,按行显示
}
println!("");
2.4 时间刷新
按秒刷新,每秒计算一次图案字符串,然后清屏后显示,实现时间跑秒的感觉。
fn main() {
let pix_clock = pix_clock::new();
let delay = time::Duration::from_secs(1);
loop {
let curdate = Local::now();
let datecollect = curdate.format("%H:%M:%S").to_string();
pix_clock.beautifyshow(&datecollect);
thread::sleep(delay);
Clear(ClearType::All);
}
}
参考文献:
1、特别感谢 https://github.com/yuanzhoulvpi2017/countdown
2、https://docs.rs/chrono/latest/chrono/
尊重原创技术文章,转载请注明:https://www.cnblogs.com/pingwen/p/17004872.html
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK