

机器学习——人脸性别识别 - 安的石头
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/ChenWtai/p/16995988.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

机器学习——人脸性别识别
一、选题背景
人脸识别技术是模式识别和计算机视觉领域最富挑战性的研究课题之一,也是近年来的研究热点,人脸性别识别作为人脸识别技术的重要组成部分也受到了广泛地关注。人脸性别识别就是向计算机输入人脸图像,经过某种方法或运算,得出其性别。这种识别对人眼来说很简单,但对计算机却并不是一件容易的事情。
二、机器学习案例设计方案
从网站中下载相关的数据集,对数据集进行整理,在python的环境中,给数据集中的文件进行划分,对数据进行预处理,利用keras,构建神经网络,训练模型,导入图片测试模型。
数据来源:kaggle,网址:https://www.kaggle.com/maciejgronczynski/biggest-genderface-recognition-dataset
数据集包含27167个jpg文件,其中17678个是男性面部照片,9489个是女性照片。
三、机器学习的实验步骤
1.下载数据集
2.导入需要用到的库
1 import os 2 import random 3 from shutil import copy 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 from keras import optimizers 6 from keras import models 7 from keras import layers 8 from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator 9 from keras.models import load_model 10 from PIL import Image
3.数据集划分,由总的数据集生成分别生成训练集,测试集和验证集
1 # 女性图片训练集想保存到的根路径
2 woman_train_dir = r'sex\faces\train\woman'
3 # 女性图片验证集想保存到的根路径
4 woman_validation_dir = r'sex\faces\validation\woman'
5 # 女性图片测试集想保存到的根路径
6 woman_test_dir = r'sex\faces\test\woman'
7
8 # 男性图片训练集想保存到的根路径
9 man_train_dir = r'sex\faces\train\man'
10 # 男性图片验证集想保存到的根路径
11 man_validation_dir = r'sex\faces\validation\man'
12 # 男性图片测试集想保存到的根路径
13 man_test_dir = r'sex\faces\test\man'
14
15 # 创建列表,保存上方6个路径
16 dir_list = [woman_train_dir, woman_validation_dir, woman_test_dir,
17 man_train_dir, man_validation_dir, man_test_dir]
18 # 如果目录不存在,则创建
19 for dir_child in dir_list:
20 if not os.path.isdir(dir_child):
21 os.makedirs(dir_child)
22
23 # 女性图片根路径
24 woman_path = r'sex\faces\woman'
25 # 获取 woman_path 下的文件夹列表
26 woman_path_list = os.listdir(woman_path)
27 # 遍历列表,取6000张图片加入训练集,3000张图片加入验证集,其余加入测试集
28 for i in range(len(woman_path_list)):
29 child_path = os.path.join(woman_path, woman_path_list[i])
30 if i < 6000:
31 to_path = woman_train_dir
32 elif i < 9000:
33 to_path = woman_validation_dir
34 else:
35 to_path = woman_test_dir
36 copy(child_path, to_path)
37
38 # 男性图片根路径
39 man_path = r'sex\faces\man'
40 # 获取 man_path 下的文件夹列表
41 man_path_list = os.listdir(man_path)
42 # 遍历列表,取6000张图片加入训练集,3000张图片加入验证集,其余加入测试集
43 for i in range(len(man_path_list)):
44 child_path = os.path.join(man_path, man_path_list[i])
45 if i < 6000:
46 to_path = man_train_dir
47 elif i < 9000:
48 to_path = man_validation_dir
49 else:
50 to_path = man_test_dir
51 copy(child_path, to_path)
52
53 # 输出各目录中的文件数目
54 train_path = "sex/faces/train/"
55 print('total training woman images:', len(os.listdir(train_path+"woman")))
56 print('total training man images:', len(os.listdir(train_path+"man")))
57
58 valid_path = "sex/faces/validation/"
59 print('total validation woman images:', len(os.listdir(valid_path+"woman")))
60 print('total validation man images:', len(os.listdir(valid_path+"man")))
61
62 test_path = "sex/faces/test/"
63 print('total test woman images:', len(os.listdir(test_path+"woman")))
64 print('total test man images:', len(os.listdir(test_path+"man")))
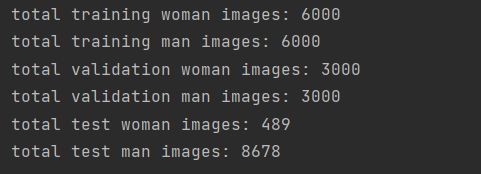
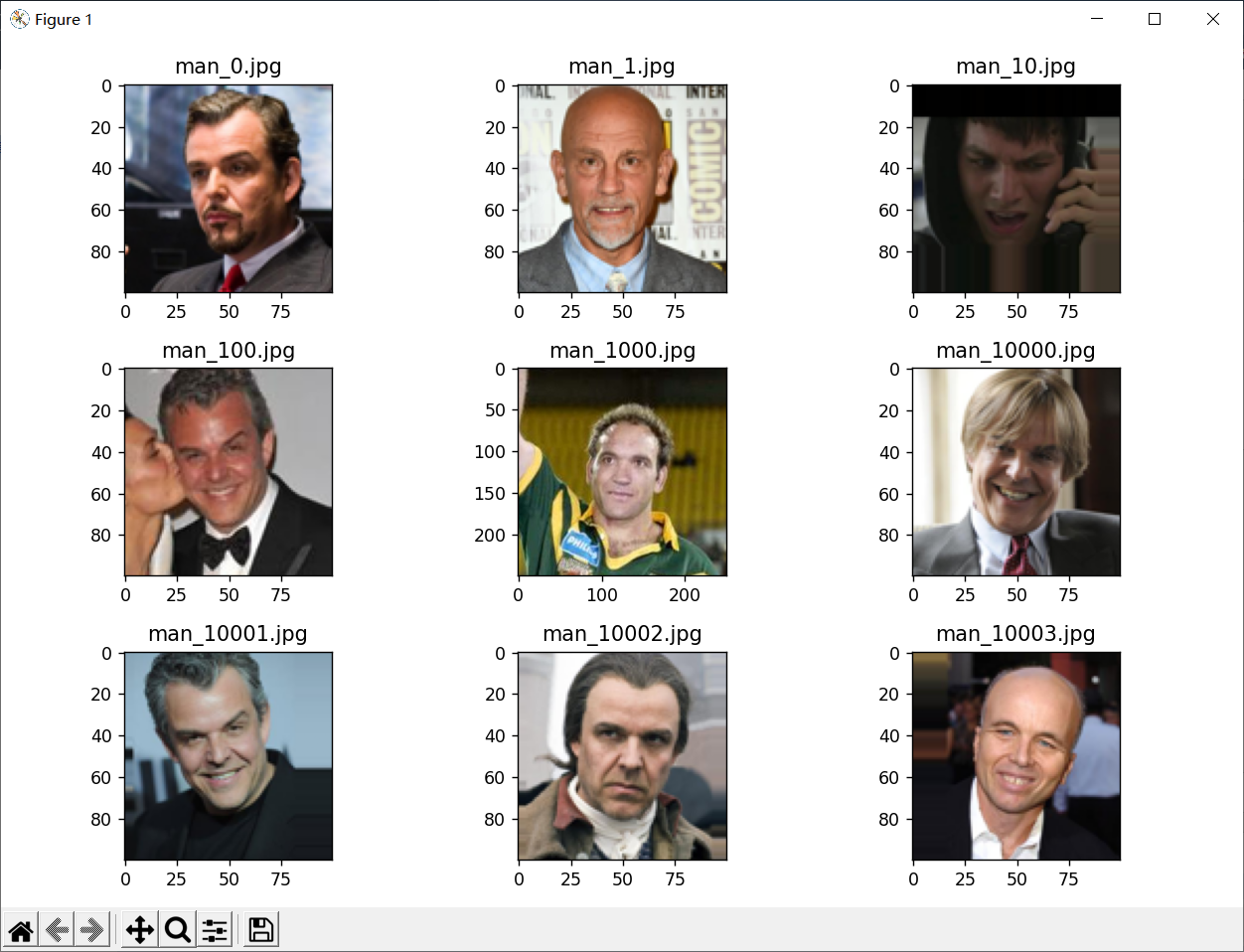
4.查看图像以及对应标签
1 # 查看图像以及对应的标签 2 fit, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 7)) 3 # 查看图像的根路径 4 test_view_path = r'sex\faces\test\man' 5 # 获取 test_view_path 下的文件夹列表 6 test_view_list = os.listdir(test_view_path) 7 for i, a in enumerate(ax.flat): 8 view_path = os.path.join(test_view_path, test_view_list[i]) 9 # 读取源图 10 a.imshow(plt.imread(view_path)) 11 # 添加图像名称 12 a.set_title(man_path_list[i]) 13 plt.tight_layout() # 自动调整子图参数,使之填充整个图像区域 14 plt.show()
5.图片预处理
1 # 图片预处理 2 # 批量大小 3 BATCH_SIZE = 20 4 # 输入图片的大小 5 IMG_SIZE = (150, 150) 6 7 # 归一化处理 8 train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255) 9 validation_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255) 10 test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255) 11 12 train_dir = 'sex/faces/train' # 指向训练集图片目录路径 13 14 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory( 15 train_dir, 16 target_size=IMG_SIZE, # 输入训练图像尺寸 17 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, 18 color_mode='rgb', 19 class_mode='binary') 20 21 validation_dir = 'sex/faces/validation' # 指向验证集图片目录路径 22 23 validation_generator = validation_datagen.flow_from_directory( 24 validation_dir, 25 target_size=IMG_SIZE, 26 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, 27 color_mode='rgb', 28 class_mode='binary') 29 30 test_dir = 'sex/faces/test' # 指向测试集图片目录路径 31 32 test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory( 33 test_dir, 34 target_size=IMG_SIZE, 35 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, 36 color_mode='rgb', 37 class_mode='binary')

6.查看经过处理的图片以及它的binary标签
1 # 查看经过处理的图片以及它的binary标签 2 fit, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 7)) 3 4 for i, a in enumerate(ax.flat): 5 img, label = test_generator.next() 6 a.imshow(img[0],) 7 a.set_title(label[0]) 8 9 plt.tight_layout() 10 plt.show()
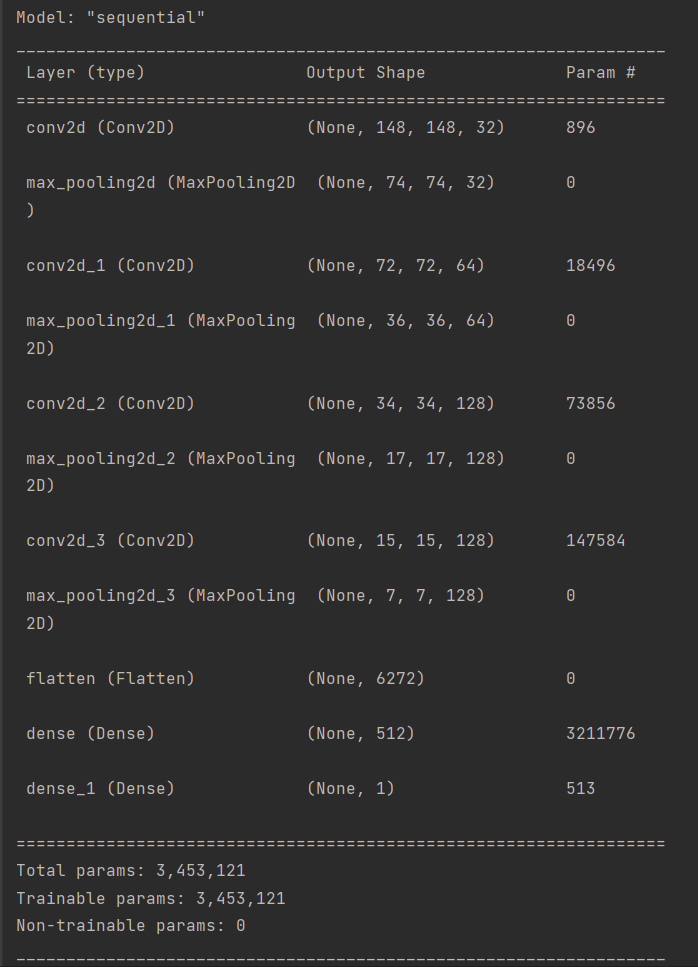
7.构建神经网络并对模型进行训练
1 # 构建神经网络 2 model = models.Sequential() 3 4 # 1.Conv2D层,32个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:150-3+1=148*148,参数数量:32*3*3*3+32=896 5 model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), 6 activation='relu', 7 input_shape=(150, 150, 3))) # 卷积层1 8 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层1。输出图片尺寸:148/2=74*74 9 10 # 2.Conv2D层,64个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:74-3+1=72*72,参数数量:64*3*3*32+64=18496 11 model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), 12 activation='relu')) # 卷积层2 13 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层2。输出图片尺寸:72/2=36*36 14 15 # 3.Conv2D层,128个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:36-3+1=34*34,参数数量:128*3*3*64+128=73856 16 model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), 17 activation='relu')) # 卷积层3 18 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层3。输出图片尺寸:34/2=17*17 19 20 # 4.Conv2D层,128个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:17-3+1=15*15,参数数量:128*3*3*128+128=147584 21 model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), 22 activation='relu')) # 卷积层4 23 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层4。输出图片尺寸:15/2=7*7 24 25 # 将输入层的数据压缩成1维数据,全连接层只能处理一维数据 26 model.add(layers.Flatten()) 27 28 # 全连接层 29 model.add(layers.Dense(512, 30 activation='relu')) # 全连接层1 31 model.add(layers.Dense(1, 32 activation='sigmoid')) # 全连接层2,作为输出层。sigmoid分类,输出是两类别 33 34 # 编译模型 35 # RMSprop 优化器。因为网络最后一层是单一sigmoid单元, 36 # 所以使用二元交叉熵作为损失函数 37 model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', 38 optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4), 39 metrics=['acc']) 40 41 # 看一下特征图的维度如何随着每层变化 42 model.summary()
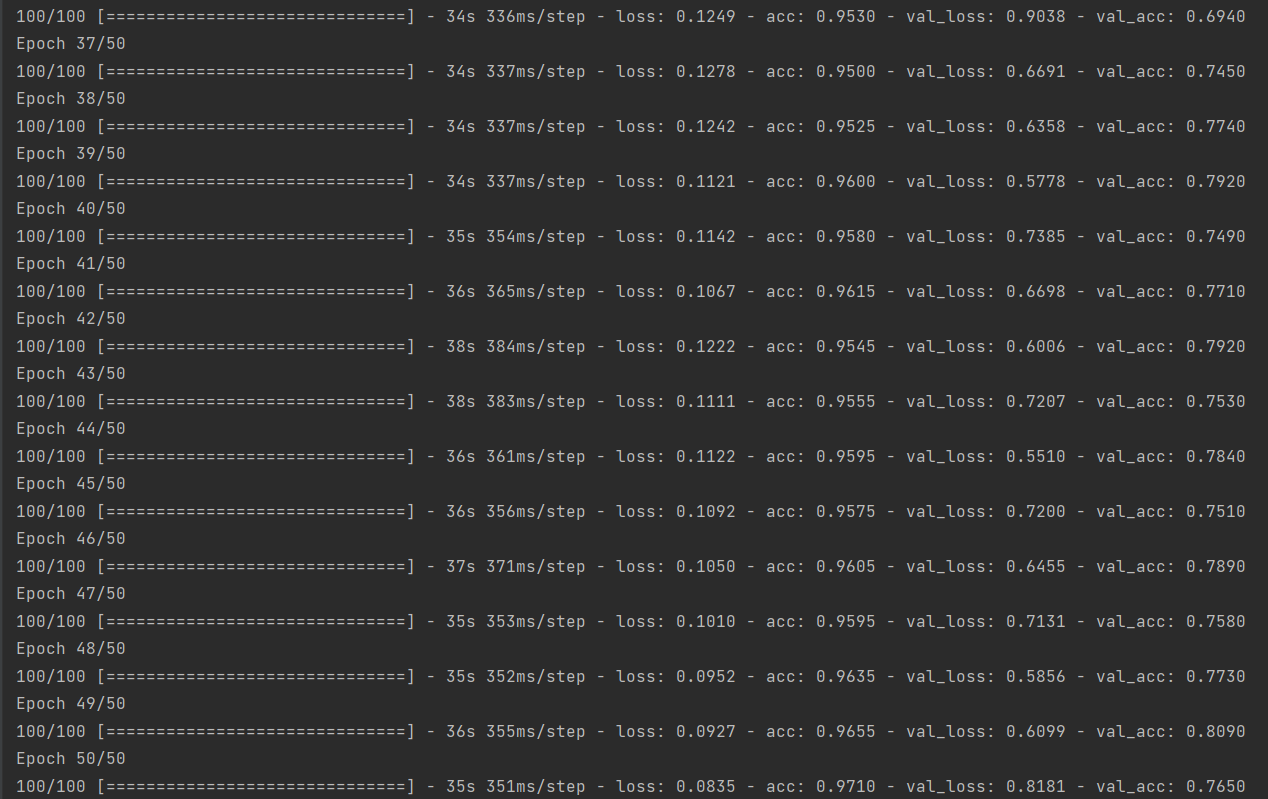
1 # 训练模型50轮次
2 history_save = model.fit(
3 train_generator,
4 steps_per_epoch=100,
5 epochs=50,
6 validation_data=validation_generator,
7 validation_steps=50)
8 # 将训练过程产生的数据保存为h5文件
9 model.save('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
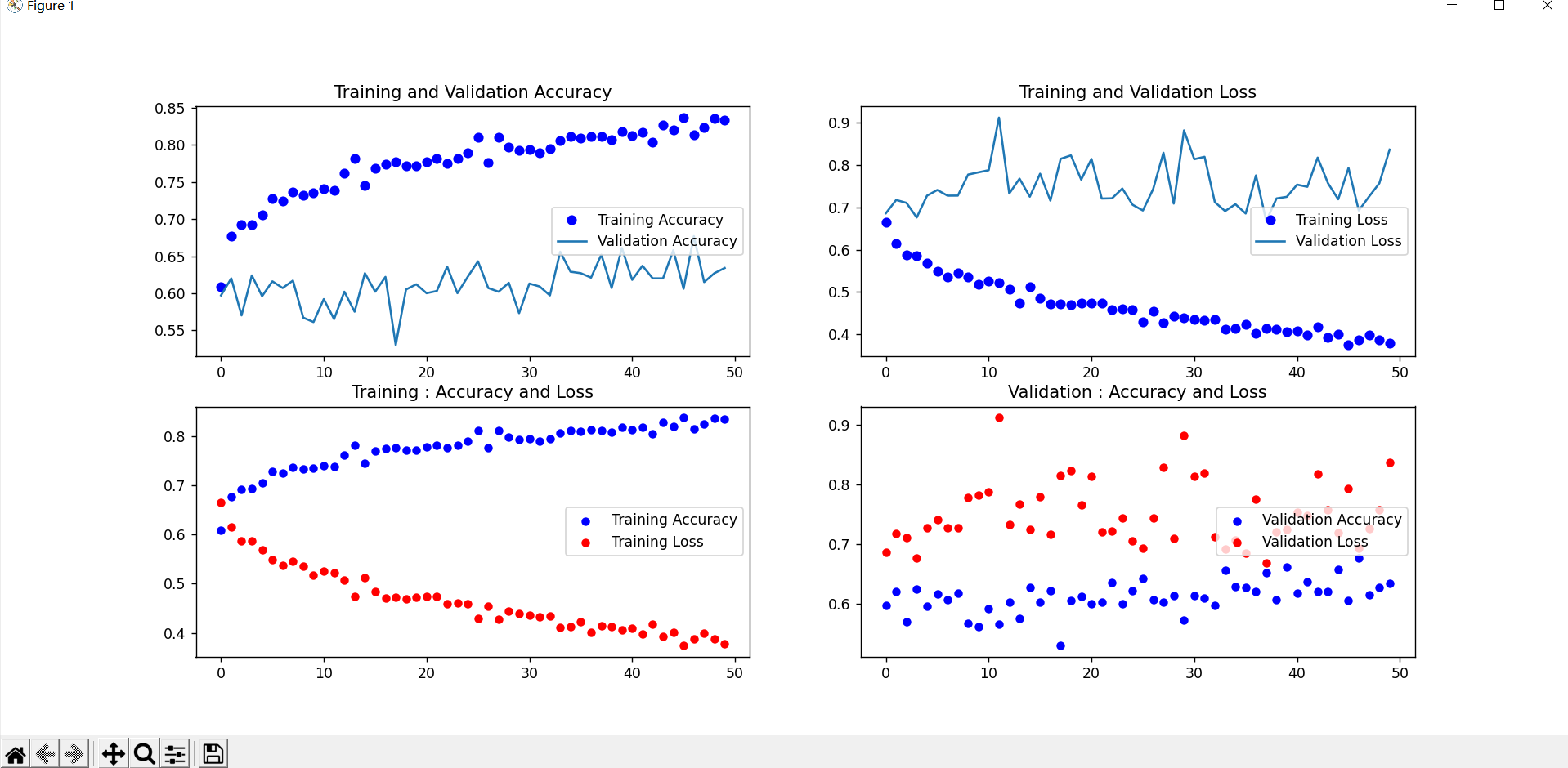
8.绘制损失曲线和精度曲线图
1 # 绘制损失曲线和精度曲线图
2 accuracy = history_save.history['acc'] # 训练集精度
3 loss = history_save.history['loss'] # 训练集损失
4 val_loss = history_save.history['val_loss'] # 验证集精度
5 val_accuracy = history_save.history['val_acc'] # 验证集损失
6 plt.figure(figsize=(17, 7))
7
8 # 训练集精度和验证集精度曲线图图
9 plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
10 plt.plot(range(50), accuracy, 'bo', label='Training Accuracy')
11 plt.plot(range(50), val_accuracy, label='Validation Accuracy')
12 plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
13 plt.legend(loc='center right')
14
15 # 训练集损失和验证集损失图
16 plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
17 plt.plot(range(50), loss, 'bo', label='Training Loss')
18 plt.plot(range(50), val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
19 plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
20 plt.legend(loc='center right')
21
22 # 训练集精度和损失散点图
23 plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
24 plt.scatter(range(50), accuracy, label="Training Accuracy", color='b', s=25, marker="o")
25 plt.scatter(range(50), loss, label="Training Loss", color='r', s=25, marker="o")
26 plt.title('Training : Accuracy and Loss')
27 plt.legend(loc='center right')
28
29 # 验证集精度和损失散点图
30 plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
31 plt.scatter(range(50), val_accuracy, label="Validation Accuracy", color='b', s=25, marker="o")
32 plt.scatter(range(50), val_loss, label="Validation Loss", color='r', s=25, marker="o")
33 plt.title('Validation : Accuracy and Loss')
34 plt.legend(loc='center right')
35
36 plt.show()

9.用ImageDataGenerator数据增强
1 train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255, 2 rotation_range=40, # 将图像随机旋转40度 3 width_shift_range=0.2, # 在水平方向上平移比例为0.2 4 height_shift_range=0.2, # 在垂直方向上平移比例为0.2 5 shear_range=0.2, # 随机错切变换的角度为0.2 6 zoom_range=0.2, # 图片随机缩放的范围为0.2 7 horizontal_flip=True, # 随机将一半图像水平翻转 8 fill_mode='nearest') # 填充创建像素 9 validation_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255) 10 11 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory( 12 train_dir, 13 target_size=IMG_SIZE, # 输入训练图像尺寸 14 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, 15 class_mode='binary') 16 17 validation_generator = validation_datagen.flow_from_directory( 18 validation_dir, 19 target_size=IMG_SIZE, 20 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, 21 class_mode='binary')
再次训练模型,并绘制绘制损失曲线和精度曲线图,得到结果图
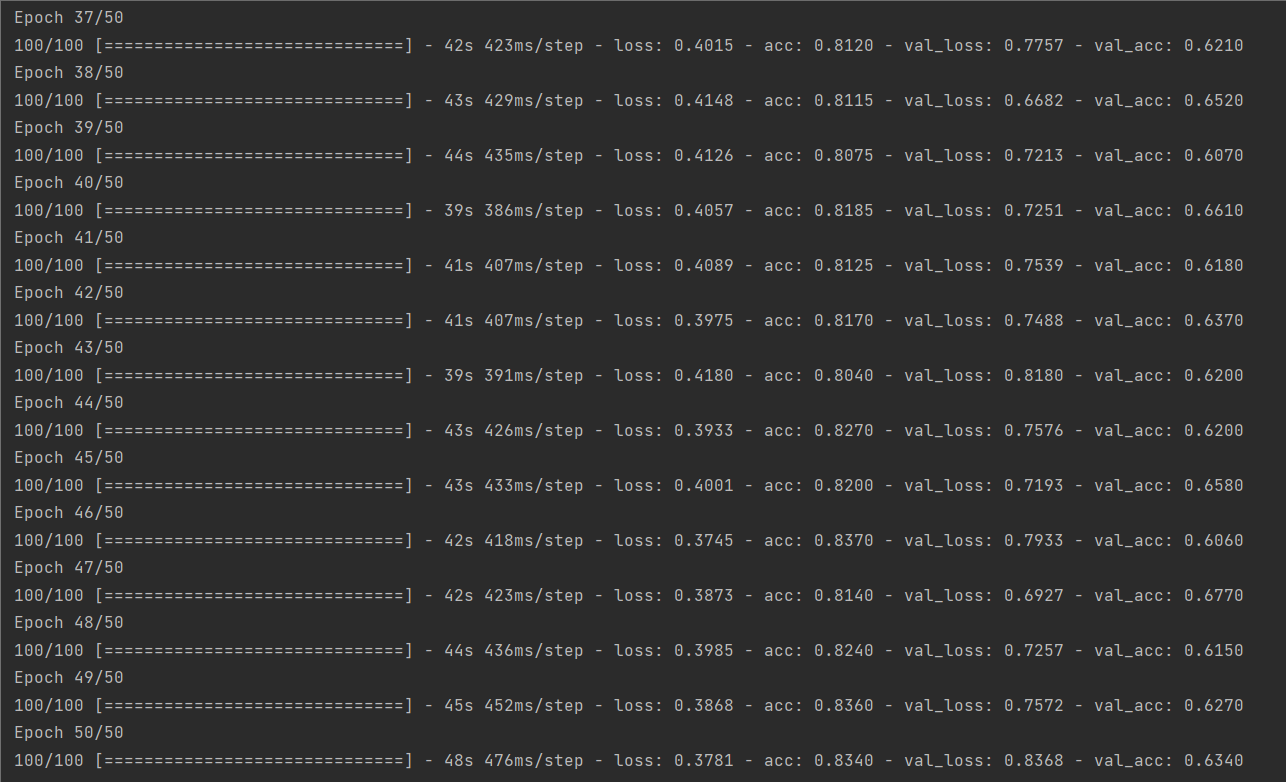
10.随机选取测试集的图片进行预测
1 # 将图片缩小到(150,150)的大小
2 def convertjpg(jpgfile, outdir, width=150, height=150):
3 img = Image.open(jpgfile)
4 try:
5 new_img = img.resize((width, height), Image.BILINEAR)
6 new_img.save(os.path.join(outdir, os.path.basename(jpgfile)))
7 except Exception as e:
8 print(e)
9
10 # 从测试集随机获取一张男性图片
11 man_test = r'sex\faces\test\man'
12 man_test_list = os.listdir(man_test)
13 key = random.randint(0, len(man_test_list))
14 img_key = man_test_list[key]
15 jpg_file = os.path.join(man_test, img_key)
16 convertjpg(jpg_file, "sex/faces/test") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
17 img_scale = plt.imread('sex/faces/test/' + img_key)
18 plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
19
20 # 调用训练模型结果进行预测
21 model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
22 img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
23 img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
24 result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
25 if result > 0.5:
26 print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
27 else:
28 print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
29 plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像

1 # 从测试集随机获取一张女性图片
2 woman_test = r'sex\faces\test\woman'
3 woman_test_list = os.listdir(woman_test)
4 key = random.randint(0, len(woman_test_list))
5 img_key = woman_test_list[key]
6 jpg_file = os.path.join(woman_test, img_key)
7 convertjpg(jpg_file, "sex/faces/test") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
8 img_scale = plt.imread('sex/faces/test/' + img_key)
9 plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
10
11 # 调用训练模型结果进行预测
12 model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
13 img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
14 img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
15 result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
16 if result > 0.5:
17 print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
18 else:
19 print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
20 plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像
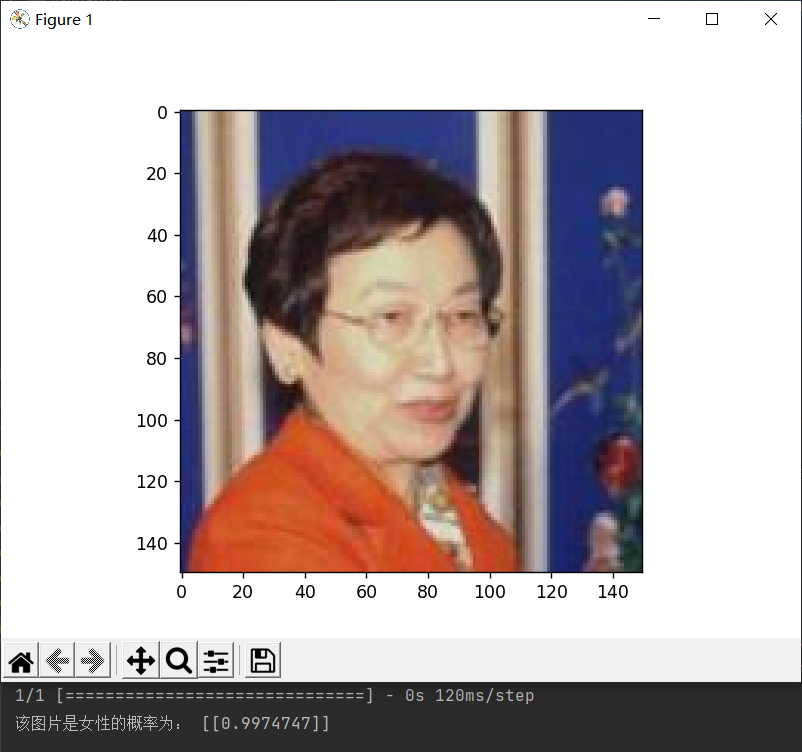
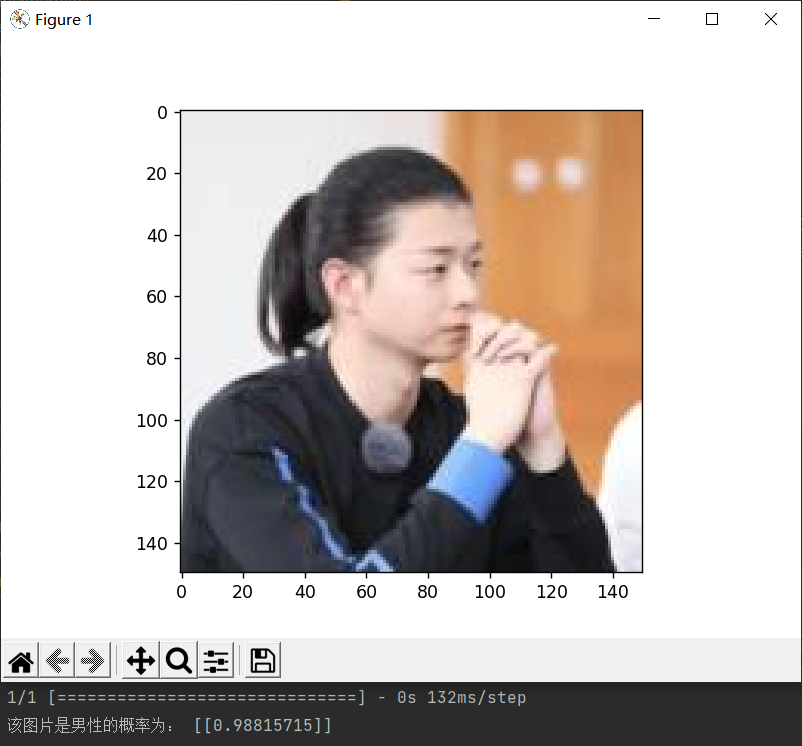
11.自定义一张图片进行预测
# 自定义一张男性图片进行预测
diy_img = 'sex/faces/man.jpg'
convertjpg(diy_img, "sex") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
img_scale = plt.imread('sex/man.jpg')
plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
# 调用数据增强后的训练模型结果进行预测
model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model_idg.h5')
img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
if result > 0.5:
print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
else:
print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像
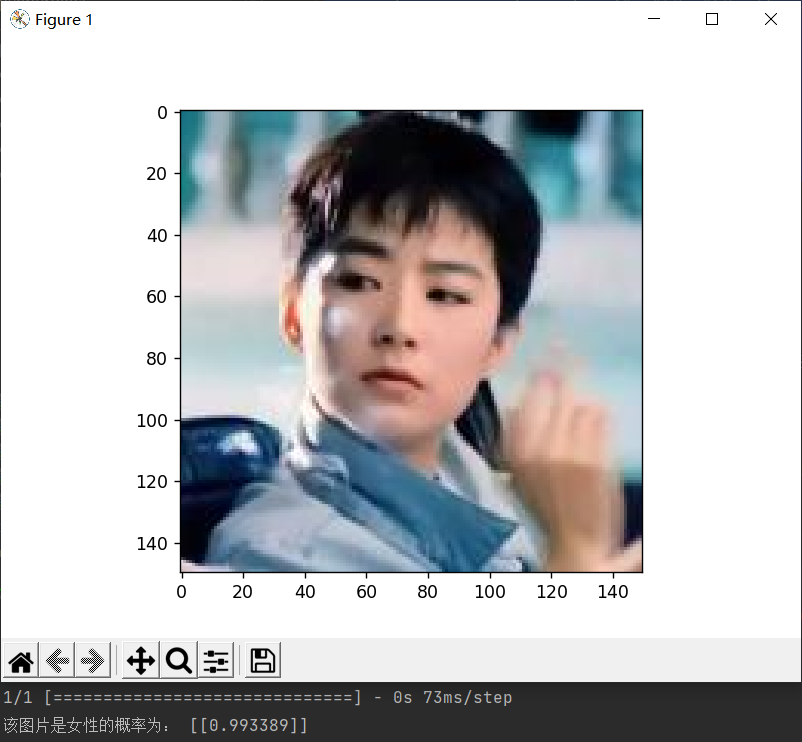
1 # 自定义一张女性图片进行预测
2 diy_img = 'sex/faces/woman_2.jpg'
3 convertjpg(diy_img, "sex") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
4 img_scale = plt.imread('sex/woman_2.jpg')
5 plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
6
7 # 调用数据增强后的训练模型结果进行预测
8 model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
9 img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
10 img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
11 result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
12 if result > 0.5:
13 print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
14 else:
15 print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
16 plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像
全部代码:
1 import os
2 import random
3 from shutil import copy
4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
5 from keras import optimizers
6 from keras import models
7 from keras import layers
8 from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
9 from keras.models import load_model
10 from PIL import Image
11
12 # 女性图片训练集想保存到的根路径
13 woman_train_dir = r'sex\faces\train\woman'
14 # 女性图片验证集想保存到的根路径
15 woman_validation_dir = r'sex\faces\validation\woman'
16 # 女性图片测试集想保存到的根路径
17 woman_test_dir = r'sex\faces\test\woman'
18
19 # 男性图片训练集想保存到的根路径
20 man_train_dir = r'sex\faces\train\man'
21 # 男性图片验证集想保存到的根路径
22 man_validation_dir = r'sex\faces\validation\man'
23 # 男性图片测试集想保存到的根路径
24 man_test_dir = r'sex\faces\test\man'
25
26 # 创建列表,保存上方6个路径
27 dir_list = [woman_train_dir, woman_validation_dir, woman_test_dir,
28 man_train_dir, man_validation_dir, man_test_dir]
29 # 如果目录不存在,则创建
30 for dir_child in dir_list:
31 if not os.path.isdir(dir_child):
32 os.makedirs(dir_child)
33
34 # 女性图片根路径
35 woman_path = r'sex\faces\woman'
36 # 获取 woman_path 下的文件夹列表
37 woman_path_list = os.listdir(woman_path)
38 # 遍历列表,取6000张图片加入训练集,3000张图片加入验证集,其余加入测试集
39 for i in range(len(woman_path_list)):
40 child_path = os.path.join(woman_path, woman_path_list[i])
41 if i < 6000:
42 to_path = woman_train_dir
43 elif i < 9000:
44 to_path = woman_validation_dir
45 else:
46 to_path = woman_test_dir
47 copy(child_path, to_path)
48
49 # 男性图片根路径
50 man_path = r'sex\faces\man'
51 # 获取 man_path 下的文件夹列表
52 man_path_list = os.listdir(man_path)
53 # 遍历列表,取6000张图片加入训练集,3000张图片加入验证集,其余加入测试集
54 for i in range(len(man_path_list)):
55 child_path = os.path.join(man_path, man_path_list[i])
56 if i < 6000:
57 to_path = man_train_dir
58 elif i < 9000:
59 to_path = man_validation_dir
60 else:
61 to_path = man_test_dir
62 copy(child_path, to_path)
63
64 # 输出各目录中的文件数目
65 train_path = "sex/faces/train/"
66 print('total training woman images:', len(os.listdir(train_path+"woman")))
67 print('total training man images:', len(os.listdir(train_path+"man")))
68
69 valid_path = "sex/faces/validation/"
70 print('total validation woman images:', len(os.listdir(valid_path+"woman")))
71 print('total validation man images:', len(os.listdir(valid_path+"man")))
72
73 test_path = "sex/faces/test/"
74 print('total test woman images:', len(os.listdir(test_path+"woman")))
75 print('total test man images:', len(os.listdir(test_path+"man")))
76
77 # 查看图像以及对应的标签
78 fit, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 7))
79 # 查看图像的根路径
80 test_view_path = r'sex\faces\test\man'
81 # 获取 test_view_path 下的文件夹列表
82 test_view_list = os.listdir(test_view_path)
83 for i, a in enumerate(ax.flat):
84 view_path = os.path.join(test_view_path, test_view_list[i])
85 # 读取源图
86 a.imshow(plt.imread(view_path))
87 # 添加图像名称
88 a.set_title(man_path_list[i])
89 plt.tight_layout() # 自动调整子图参数,使之填充整个图像区域
90 plt.show()
91
92 # 图片预处理
93 # 批量大小
94 BATCH_SIZE = 20
95 # 输入图片的大小
96 IMG_SIZE = (150, 150)
97
98 # 归一化处理
99 train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
100 validation_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
101 test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
102
103 train_dir = 'sex/faces/train' # 指向训练集图片目录路径
104
105 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
106 train_dir,
107 target_size=IMG_SIZE, # 输入训练图像尺寸
108 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
109 color_mode='rgb',
110 class_mode='binary')
111
112 validation_dir = 'sex/faces/validation' # 指向验证集图片目录路径
113
114 validation_generator = validation_datagen.flow_from_directory(
115 validation_dir,
116 target_size=IMG_SIZE,
117 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
118 color_mode='rgb',
119 class_mode='binary')
120
121 test_dir = 'sex/faces/test' # 指向测试集图片目录路径
122
123 test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
124 test_dir,
125 target_size=IMG_SIZE,
126 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
127 color_mode='rgb',
128 class_mode='binary')
129
130 # 查看经过处理的图片以及它的binary标签
131 fit, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 7))
132
133 for i, a in enumerate(ax.flat):
134 img, label = test_generator.next()
135 a.imshow(img[0],)
136 a.set_title(label[0])
137
138 plt.tight_layout()
139 plt.show()
140
141 # 构建神经网络
142 model = models.Sequential()
143
144 # 1.Conv2D层,32个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:150-3+1=148*148,参数数量:32*3*3*3+32=896
145 model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3),
146 activation='relu',
147 input_shape=(150, 150, 3))) # 卷积层1
148 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层1。输出图片尺寸:148/2=74*74
149
150 # 2.Conv2D层,64个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:74-3+1=72*72,参数数量:64*3*3*32+64=18496
151 model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3),
152 activation='relu')) # 卷积层2
153 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层2。输出图片尺寸:72/2=36*36
154
155 # 3.Conv2D层,128个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:36-3+1=34*34,参数数量:128*3*3*64+128=73856
156 model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3),
157 activation='relu')) # 卷积层3
158 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层3。输出图片尺寸:34/2=17*17
159
160 # 4.Conv2D层,128个过滤器。输出图片尺寸:17-3+1=15*15,参数数量:128*3*3*128+128=147584
161 model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3),
162 activation='relu')) # 卷积层4
163 model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) # 最大值池化层4。输出图片尺寸:15/2=7*7
164
165 # 将输入层的数据压缩成1维数据,全连接层只能处理一维数据
166 model.add(layers.Flatten())
167
168 # 全连接层
169 model.add(layers.Dense(512,
170 activation='relu')) # 全连接层1
171 model.add(layers.Dense(1,
172 activation='sigmoid')) # 全连接层2,作为输出层。sigmoid分类,输出是两类别
173
174 # 编译模型
175 # RMSprop 优化器。因为网络最后一层是单一sigmoid单元,
176 # 所以使用二元交叉熵作为损失函数
177 model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
178 optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4),
179 metrics=['acc'])
180
181 # 看一下特征图的维度如何随着每层变化
182 model.summary()
183 #
184
185 train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255,
186 rotation_range=40, # 将图像随机旋转40度
187 width_shift_range=0.2, # 在水平方向上平移比例为0.2
188 height_shift_range=0.2, # 在垂直方向上平移比例为0.2
189 shear_range=0.2, # 随机错切变换的角度为0.2
190 zoom_range=0.2, # 图片随机缩放的范围为0.2
191 horizontal_flip=True, # 随机将一半图像水平翻转
192 fill_mode='nearest') # 填充创建像素
193 validation_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
194
195 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
196 train_dir,
197 target_size=IMG_SIZE, # 输入训练图像尺寸
198 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
199 class_mode='binary')
200
201 validation_generator = validation_datagen.flow_from_directory(
202 validation_dir,
203 target_size=IMG_SIZE,
204 batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
205 class_mode='binary')
206 #
207 # 训练模型50轮次
208 history_save = model.fit(
209 train_generator,
210 steps_per_epoch=100,
211 epochs=50,
212 validation_data=validation_generator,
213 validation_steps=50)
214
215 # 将训练过程产生的数据保存为h5文件
216 model.save('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
217 # 保存数据增强后的训练模型
218 model.save('sex/faces/sex_model_idg.h5')
219
220 # 绘制损失曲线和精度曲线图
221 accuracy = history_save.history['acc'] # 训练集精度
222 loss = history_save.history['loss'] # 训练集损失
223 val_loss = history_save.history['val_loss'] # 验证集精度
224 val_accuracy = history_save.history['val_acc'] # 验证集损失
225 plt.figure(figsize=(17, 7))
226
227 # 训练集精度和验证集精度曲线图图
228 plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
229 plt.plot(range(50), accuracy, 'bo', label='Training Accuracy')
230 plt.plot(range(50), val_accuracy, label='Validation Accuracy')
231 plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
232 plt.legend(loc='center right')
233
234 # 训练集损失和验证集损失图
235 plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
236 plt.plot(range(50), loss, 'bo', label='Training Loss')
237 plt.plot(range(50), val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
238 plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
239 plt.legend(loc='center right')
240
241 # 训练集精度和损失散点图
242 plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
243 plt.scatter(range(50), accuracy, label="Training Accuracy", color='b', s=25, marker="o")
244 plt.scatter(range(50), loss, label="Training Loss", color='r', s=25, marker="o")
245 plt.title('Training : Accuracy and Loss')
246 plt.legend(loc='center right')
247
248 # 验证集精度和损失散点图
249 plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
250 plt.scatter(range(50), val_accuracy, label="Validation Accuracy", color='b', s=25, marker="o")
251 plt.scatter(range(50), val_loss, label="Validation Loss", color='r', s=25, marker="o")
252 plt.title('Validation : Accuracy and Loss')
253 plt.legend(loc='center right')
254
255 plt.show()
256
257 # 将图片缩小到(150,150)的大小
258 def convertjpg(jpgfile, outdir, width=150, height=150):
259 img = Image.open(jpgfile)
260 try:
261 new_img = img.resize((width, height), Image.BILINEAR)
262 new_img.save(os.path.join(outdir, os.path.basename(jpgfile)))
263 except Exception as e:
264 print(e)
265
266 # 从测试集随机获取一张男性图片
267 man_test = r'sex\faces\test\man'
268 man_test_list = os.listdir(man_test)
269 key = random.randint(0, len(man_test_list))
270 img_key = man_test_list[key]
271 jpg_file = os.path.join(man_test, img_key)
272 convertjpg(jpg_file, "sex/faces/test") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
273 img_scale = plt.imread('sex/faces/test/' + img_key)
274 plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
275
276 # 调用训练模型结果进行预测
277 model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
278 img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
279 img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
280 result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
281 if result > 0.5:
282 print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
283 else:
284 print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
285 plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像
286
287 # 从测试集随机获取一张女性图片
288 woman_test = r'sex\faces\test\woman'
289 woman_test_list = os.listdir(woman_test)
290 key = random.randint(0, len(woman_test_list))
291 img_key = woman_test_list[key]
292 jpg_file = os.path.join(woman_test, img_key)
293 convertjpg(jpg_file, "sex/faces/test") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
294 img_scale = plt.imread('sex/faces/test/' + img_key)
295 plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
296
297 # 调用训练模型结果进行预测
298 model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
299 img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
300 img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
301 result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
302 if result > 0.5:
303 print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
304 else:
305 print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
306 plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像
307
308 # 自定义一张男性图片进行预测
309 diy_img = 'sex/faces/man.jpg'
310 convertjpg(diy_img, "sex") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
311 img_scale = plt.imread('sex/man.jpg')
312 plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
313
314 # 调用数据增强后的训练模型结果进行预测
315 model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model_idg.h5')
316 img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
317 img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
318 result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
319 if result > 0.5:
320 print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
321 else:
322 print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
323 plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像
324
325 # 自定义一张女性图片进行预测
326 diy_img = 'sex/faces/woman_2.jpg'
327 convertjpg(diy_img, "sex") # 图像大小改变到(150,150)
328 img_scale = plt.imread('sex/woman_2.jpg')
329 plt.imshow(img_scale) # 显示改变图像大小后的图片确实变到了(150,150)大小
330
331 # 调用数据增强后的训练模型结果进行预测
332 model = load_model('sex/faces/sex_model.h5')
333 img_scale = img_scale.reshape(1, 150, 150, 3).astype('float32')
334 img_scale = img_scale/255 # 归一化到0-1之间
335 result = model.predict(img_scale) # 取图片信息
336 if result > 0.5:
337 print('该图片是女性的概率为:', result)
338 else:
339 print('该图片是男性的概率为:', 1-result)
340 plt.show() # 打印尺寸改变后的图像
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK