

Vuex极速入门 - 安木夕
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/anding/p/16906778.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.


01、什么是Vuex?
1.1、为什么需要状态管理?
在复杂的系统中,我们会把系统按照业务逻辑拆分为多个层次、多个模块,采用组件式的开发方式。而此时不同模块、父子模块之间的通信就成了一个问题。
为了解决这个问题,就有了状态管理,核心概念就是把大家共享的状态(数据)抽出来,放到一个全局共享的仓库里,按照一定约定统一管理,让状态的变化可预测。这就有两个关键点:
- 统一存储:共享的状态统一存储,全局共享。
- 可预测:共享的状态不可随意修改,需要按照约定的规则修改,才能监测状态变更、通知更新。
1.2、Vuex简介
Vuex 就是面向Vue的状态管理组件,采用集中式存储+管理应用的所有共享状态。Vuex只能在Vue中使用,深度使用了Vue的能力,如用Vue来实现state的响应式特性。
Vue2.*版本 ▶ 对应Vuex3.*版本,Vuex3.* 中文文档Vue3.*版本 ▶ 对应Vuex4.*版本,Vuex4.* 中文文档
简单来说,就是Vuex有一个全局公共的store(类似Vue里的data),作为公共数据仓库,保存了大家共享的状态(数据)。这个数据仓库store实现了数据响应、自动通知更新,这样就很容易实现了各个组件间的数据通信了。
其实,对于简单的应用不一定需要Vuex,不过Vuex文件并不大(gzip压缩后10K左右)。
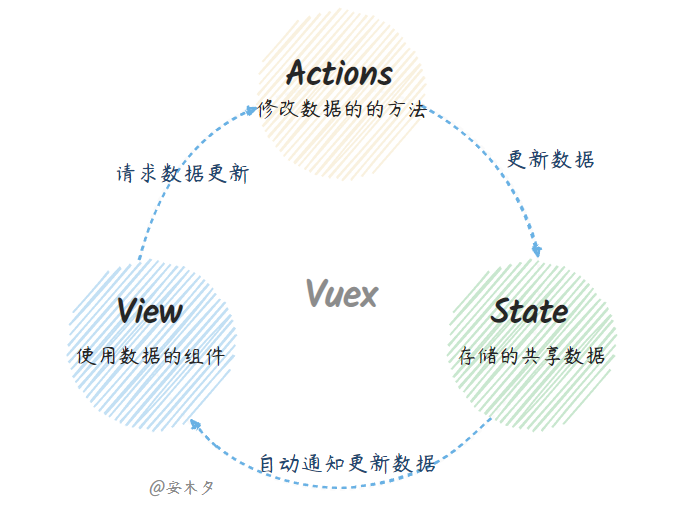
Vuex主要特点就是:单向数据流+单一数据源。
- state:存储数据仓库,类似Vue的
data,也是响应式的,变更后会自动通知View。 - views:组件视图,就是使用
state的Vue组件。 - actions:更新state状态,为了规范管理,state不能直接修改,必须通过
action进行提交。Vuex中分为同步Mutation、和异步Action。
02、安装使用
- 通过
<script>标签直接引用vuex.js:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3/dist/vuex.js"></script>// 注册插件Vue.use(Vuex);
- 通过
vue-cli脚手架搭建vue的开发框架,集成了vuex组件。 - 注册插件:
Vue.use(Vuex)
调试已经被集成在了Vue的调试工具Devtools中了。
03、Vuex3入门
3.1、Vuex选项&实例
| Store构造器选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| state | Vuex store 实例的根 state 对象 |
| mutations | 注册 mutation,就是修改数据的方法,参数为state。不支持异步,通过store.commit(name)调用 |
| actions | 注册 action,参数为context,同store实例,但不是她。支持异步,通过store.dispatch(name)调用 |
| getters | 注册 getter,{ [key: string]: Function },参数为state,定义、使用同计算属性 |
| modules | 子模块的对象,分割管理store,{ key(moduleName) : {state, namespaced?, mutations?, actions? ... }} |
| strict | 是否严格模式,默认false,true=严格模式下,任何 mutation 处理函数以外修改state 都会抛出错误。 |
| ✅store实例属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| state | 数据源state根对象 |
| getters | 所有注册的getter |
| ✅store 实例方法 | |
| commit(name, arg?, options?) | 提交 mutation 执行申请,name为mutation注册的方法名 |
| dispatch(name, arg?, options?) | 提交 action 执行申请,name为action注册的方法名 |
| replaceState(state: Object) | 替换 store 的根状态,用于合并状态,如加载持久化的state数据。 |
| watch(fn, callback) | 响应式地侦听 fn 的返回值,当值改变时调用回调函数 |
| subscribe(handler, option?) | 订阅 store 的 mutation,每一个mutation执行完调用 |
| subscribeAction(handler, option?) | 订阅 store 的 action |
| registerModule(path, module) | 注册一个动态模块 |
| unregisterModule(path) | 卸载一个动态模块 |
| hasModule(path) | 检查模块是否以注册 |
| hotUpdate(newOptions: Object) | 热替换新的 action 和 mutation |
const store = new Vuex.Store({ strict:false, state: { //定义数据结构-数据仓库 points: 1000, user: { id: '001', name: 'sam' } }, mutations: { //修改数据的方法 setUser(state, obj) { state.user.id = obj.uid; state.user.name = obj.uname; }, }, actions: { //修改数据的方法-异步 set(context, obj) { context.commit('setUser', obj) } }, getters: { //获取数据的计算属性 userExist(state) { return state.user.id != ''; } }})//提交数据修改store.commit('setUser',{uid:'007',uname:'zhangsan'});console.log(store.state.user); //id : "007" name : "zhangsan"console.log(store.getters.userExist); //true
3.2、Vuex核心流程
Vuex核心概念:
- 🔹Store 单一状态树:一个应用程序中只有一个Store实例(单例模式),Store包含了
state、actions、mutations、getter、modules。一般会在根Vue注册store实例,这样组件内所有地方都可以this.$store访问了。 - 🔸State 数据源:实现了响应式监听,可用
mapState辅助函数包装为计算属性访问。 - 🔹Getter 访问属性:返回对
state状态数据进行加工后的结果,类似Vue中的计算属性、过滤器,区别就是这是全局共享的。 - 🔸Mutation 修改数据:Vuex中用于修改状态数据的主要方式,是唯一修改
state数据的合理途径了。通过store.commit()调用mutation。(mutation /mjuːˈteɪʃ(ə)n/ 改变) - 🔹Action 异步操作:类似Vue的
methods,支持异步操作。通过store.dispatch()调用,实际修改数据也是要调用mutation的。Action 可用来发起异步ajax请求获取处理 state的数据,这是和mutation最大的不同了。 - 🔹Module 模块:当Store很复杂时,用Module拆分为多个模块管理,每个模块里有自己的
state、actions、mutations、getter、modules。
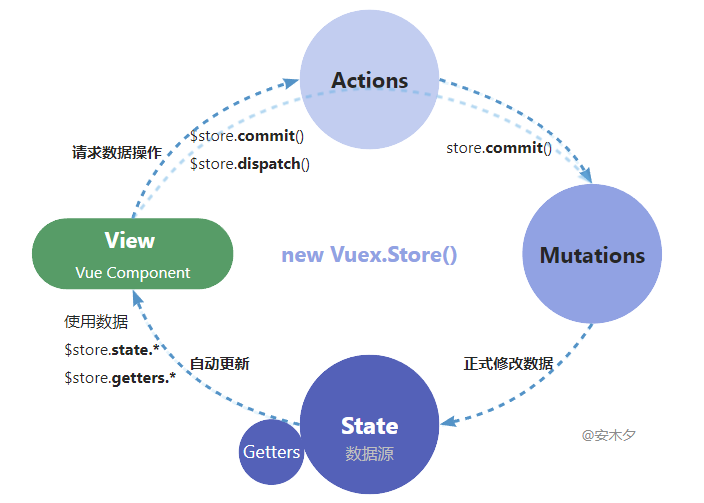
🔸基本流程:
❶ 定义数据 state,和data一样,预先定义好数据结构,以及数据更新的mutation方法。
❷ 使用数据 state
- 在根组件注入
store实例,组件内所有地方(包括后代组件)都可以this.$store访问了。 - 通过计算属性
computed包装所需的state数据。如果state数据需要双向绑定到表单元素,则需要用计算属性实现get、set来代理实现。 - 通过方法
methods包装数据的更新store.mutation。 - 在
View上绑定使用,可以绑定包装后的计算属性、方法,也可以直接绑定注入的$store。
❸ 触发更新,根据业务需要更新state数据。
- store.commit(name, arg?, options?)
- store.dispatch(name, arg?, options?)
❹ 正式修改state数据,并触发 View 自动更新。
<div id="app"> <button @click="login">登录</button> <p>用户:{{$store.state.user.name}}({{$store.state.user.id}})</p> <p v-text="`用户:${$store.state.user.name}(${$store.state.user.id})`"></p></div><script> // 注册插件 Vue.use(Vuex); //申明全局store const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { user: { id: '', name: '' } }, mutations: { setUser(state, obj) { state.user.id = obj.uid; state.user.name = obj.uname; }, }, getters: { userExist(state) { return state.user.id != ''; } } }) //根Vue let app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: {}, store: store, //在根组件注入store实例,组件内所有地方都可以 this.$store 通过访问了 methods: { login() { this.$store.commit('setUser',{ uid: '007', uname: 'zhangsan' }) } } })</script>

3.3、创建Vuex()-购物车案例
- 注册插件:
Vue.use(Vuex) - 创建全局共享的
Store实例,并配置数据、方法。 - 注入
store,在根Vue组件上注入store实例。 - 愉快的使用了。
<script> // 注册插件 Vue.use(Vuex); //申明全局store const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { cart: ['汽车01', '苹果', '梨子'] }, mutations: { add(state, item) { state.cart.push(item); }, delete(state, index) { state.cart.splice(index,1) } }, actions: { add(context, item) { context.commit('add', item) } }, getters: { cartTotal(state) { return state.cart.length; } } })</script> <div id="app1"> <p>购物车({{this.$store.getters.cartTotal}})(直接绑定)</p> <p>购物车({{cartTotal}}) <button @click="add">添加商品</button></p> <cart-box></cart-box></div><template id="cardBoxTemplate"> <!--购物列表模板--> <ul> <li v-for="(item,index) in cartList">{{item}} <button v-on:click="deleteItem(index)">删除</button></li> </ul></template><script> let app1 = new Vue({ el: "#app1", data: {}, store: store, //在根组件注入store实例,组件内所有地方都可以 this.$store 访问了 computed: { cartTotal: function () { return this.$store.getters.cartTotal; } }, methods: { add: function (item) { this.$store.dispatch('add', "西瓜") } }, components: { //购物车组件 'cart-box': { computed: { cartList() { return this.$store.state.cart; } }, template: '#cardBoxTemplate', methods: { deleteItem: function (index) { this.$store.commit("delete", index); } } } } })</script>

3.4、...mapState语法糖
mpaState是state的一种Vuex提供的 “语法糖”,主要作用是简化代码。比如当state有多个状态属性,在组件中都要用就得一个一个包装,代码冗余。这时,mapState就可以简化这个重复、无聊的代码了。
<script> let app1 = new Vue({ el: "#app1", data: {}, store: store, computed: { //做一个简单包装,使用时更方便 card() { return $store.state.card; }, user() { return $store.state.user; } }, computed: Vuex.mapState(['card', 'user']), //直接赋值,效果同上,简化了包装代理代码 computed: { cartTotal: function () { return this.$store.getters.cartTotal; }, //展开运算符展开 ...Vuex.mapState({ 'cart': 'cart', //计算属性名称:state状态名称 currentUserId: 'user', }), ...Vuex.mapState(['cart', 'user']) //更简洁的写法 },})</script>
- mpaState() 是Vuex提供一个辅助函数,帮助生成计算属性。返回的是一个对象(结构同计算属性
computed)。
mapState(namespace?: string, map: Array<string> | Object<string | function>): Object
- ...mapState,三个点
...是ES6的展开运算符,把对象展开混入当前环境。
其他还有 mapGetters、mapActions、mapMutations 都是类似作用和用法。
3.5、Module模块化
当共享的数据和操作太多时,就需要分模块管理了,如下模块示例。
const moduleA = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... }, getters: { ... }} const moduleB = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... }} const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { a: moduleA, b: moduleB }}) store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
每个模块 module 都包含完整的store结构。
module定义结构:
{ key(moduleName) : {state, namespaced?, mutations?, actions?, getters? modules? }}
- key:就是模块的名称,也是模块的命名空间。
- value,就是一个和
store结构相同的对象,存放模块的store信息。模块里方法的参数state、context都是命名空间内的局部对象。
模块化的项目结构:
├── index.html├── main.js├── api│ └── ... # 抽取出API请求├── components│ ├── App.vue│ └── ...└── store ├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方 ├── actions.js # 根级别的 action ├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation └── modules ├── cart.js # 购物车模块 └── products.js # 产品模块
04、Vuex4区别
几乎所有的 Vuex 4 API 都与 Vuex 3 保持不变,有少量差异。
- 创建方式不同,Vuex4 使用
createStore({})函数创建store对象,之前的方式依然支持。 - 安装方式,
app.use(store),已经注入了store实例,不用再注册store实例了。 - 打包产物已经与 Vue 3 配套。
- 新特性:
useStore组合式函数。//TODO
05、一些问题
❓Vuex的持久化?
如果用户刷新页面,导致页面的各种实例重新初始化,之前的全局状态就会丢失。解决方法就是把state数据仓库存起来,当刷新页面的时候读取出来,如果关闭页面就不用管了。
- 持久化
state:在页面刷新时的beforeunload事件中保存state到sessionStorage里。sessionStorage刷新页面不会丢失,关闭才清除。 - 加载
state:Vuecreate中加载持久化的state,并清除持久化的state数据。
created: function () { window.addEventListener('beforeunload', () => { sessionStorage.setItem('vstore', JSON.stringify(this.$store.state)); }); try { const vstore = sessionStorage.getItem('vstore') if (vstore) this.$store.replaceState(Object.assign({}, this.$store.state, JSON.parse(vstore))); } catch (ex) { console.log(ex) } sessionStorage.removeItem('vstore');}
©️版权申明:版权所有@安木夕,本文内容仅供学习,欢迎指正、交流,转载请注明出处!原文编辑地址-语雀
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK