

Mybatis源码解析之执行SQL语句 - 京东云开发者
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/Jcloud/p/16977916.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Mybatis源码解析之执行SQL语句
作者:郑志杰
mybatis 操作数据库的过程
// 第一步:读取mybatis-config.xml配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 第二步:构建SqlSessionFactory(框架初始化)
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().bulid();
// 第三步:打开sqlSession
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 第四步:获取Mapper接口对象(底层是动态代理)
AccountMapper accountMapper = session.getMapper(AccountMapper.class);
// 第五步:调用Mapper接口对象的方法操作数据库;
Account account = accountMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
通过调用 session.getMapper (AccountMapper.class) 所得到的 AccountMapper 是一个动态代理对象,所以执行
accountMapper.selectByPrimaryKey (1) 方法前,都会被 invoke () 拦截,先执行 invoke () 中的逻辑。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 要执行的方法所在的类如果是Object,直接调用,不做拦截处理
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
//如果是默认方法,也就是java8中的default方法
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
// 直接执行default方法
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 从缓存中获取MapperMethod
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
从 methodCache 获取对应 DAO 方法的 MapperMethod
MapperMethod 的主要功能是执行 SQL 语句的相关操作,在初始化的时候会实例化两个对象:SqlCommand(Sql 命令)和 MethodSignature(方法签名)。
/**
* 根据Mapper接口类型、接口方法、核心配置对象 构造MapperMethod对象
* @param mapperInterface
* @param method
* @param config
*/
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
// 将Mapper接口中的数据库操作方法(如Account selectById(Integer id);)封装成方法签名MethodSignature
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
new SqlCommand()调用 SqlCommand 类构造方法:
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// 获取Mapper接口中要执行的某个方法的方法名
// 如accountMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1)
final String methodName = method.getName();
// 获取方法所在的类
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
// 解析得到Mapper语句对象(对配置文件中的<mapper></mapper>中的sql语句进行封装)
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
if (ms == null) {
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
// 如com.bjpowernode.mapper.AccountMapper.selectByPrimaryKey
name = ms.getId();
// SQL类型:增 删 改 查
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = (MapperMethod)this.methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration());
this.methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
调用 mapperMethod.execute (sqlSession, args)
在 mapperMethod.execute () 方法中,我们可以看到:mybatis 定义了 5 种 SQL 操作类型:
insert/update/delete/select/flush。其中,select 操作类型又可以分为五类,这五类的返回结果都不同,分别对应:
・返回参数为空:executeWithResultHandler ();
・查询多条记录:executeForMany (),返回对象为 JavaBean
・返参对象为 map:executeForMap (), 通过该方法查询数据库,最终的返回结果不是 JavaBean,而是 Map
・游标查询:executeForCursor ();关于什么是游标查询,自行百度哈;
・查询单条记录: sqlSession.selectOne (),通过该查询方法,最终只会返回一条结果;
通过源码追踪我们可以不难发现:当调用 mapperMethod.execute () 执行 SQL 语句的时候,无论是
insert/update/delete/flush,还是 select(包括 5 种不同的 select), 本质上时通过 sqlSession 调用的。在 SELECT 操作中,虽然调用了 MapperMethod 中的方法,但本质上仍是通过 Sqlsession 下的 select (), selectList (), selectCursor (), selectMap () 等方法实现的。
而 SqlSession 的内部实现,最终是调用执行器 Executor(后面会细说)。这里,我们可以先大概看一下 mybatis 在执行 SQL 语句的时候的调用过程:
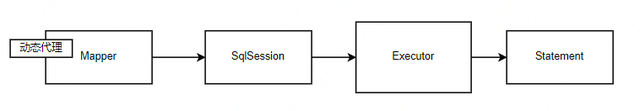
以accountMapper.selectByPrimaryKey (1) 为例:
・调用 SqlSession.getMapper ():得到 xxxMapper (如 UserMapper) 的动态代理对象;
・调用
accountMapper.selectByPrimaryKey (1):在 xxxMapper 动态代理内部,会根据要执行的 SQL 语句类型 (insert/update/delete/select/flush) 来调用 SqlSession 对应的不同方法,如 sqlSession.insert ();
・在 sqlSession.insert () 方法的实现逻辑中,又会转交给 executor.query () 进行查询;
・executor.query () 又最终会转交给 statement 类进行操作,到这里就是 jdbc 操作了。
有人会好奇,为什么要通过不断的转交,SqlSession->Executor->Statement,而不是直接调用 Statement 执行 SQL 语句呢?因为在调用 Statement 之前,会处理一些共性的逻辑,如在 Executor 的实现类 BaseExecutor 会有一级缓存相关的逻辑,在 CachingExecutor 中会有二级缓存的相关逻辑。如果直接调用 Statement 执行 SQL 语句,那么在每个 Statement 的实现类中,都要写一套一级缓存和二级缓存的逻辑,就显得冗余了。这一块后面会细讲。
// SQL命令(在解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件的时候生成的)
private final SqlCommand command;
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
// 从command对象中获取要执行操作的SQL语句的类型,如INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/SELECT
switch (command.getType()) {
// 插入
case INSERT: {
// 把接口方法里的参数转换成sql能识别的参数
// 如:accountMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1)
// 把其中的参数"1"转化为sql能够识别的参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// sqlSession.insert(): 调用SqlSession执行插入操作
// rowCountResult(): 获取SQL语句的执行结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
// 更新
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// sqlSession.insert(): 调用SqlSession执行更新操作
// rowCountResult(): 获取SQL语句的执行结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
// 删除
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// sqlSession.insert(): 调用SqlSession执行更新操作
// rowCountResult(): 获取SQL语句的执行结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
// 查询
case SELECT:
// method.returnsVoid(): 返参是否为void
// method.hasResultHandler(): 是否有对应的结果处理器
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) { // 查询多条记录
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) { // 查询结果返参为Map
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) { // 以游标的方式进行查询
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 参数转换 转成sqlCommand参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行查询 查询单条数据
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH: // 执行清除操作
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
在上面,有多处出现这样一行代码:
method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam (args),该方法的作用就是将方法参数转换为 SqlCommandParam;具体交由
paramNameResolver.getNamedParams () 实现。在看 paramNameResolver.getNamedParams () 之前,我们先来看下 paramNameResolver 是什么东西?
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);
}
在前面,我们在实例化 MethodSignature 对象 (new MethodSignature) 的时候,在其构造方法中,会实例化 ParamNameResolver 对象,该对象主要用来处理接口形式的参数,最后会把参数处放在一个 map(即属性 names)中。map 的 key 为参数的位置,value 为参数的名字。
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
...
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}
对 names 字段的解释:
假设在 xxxMapper 中有这么一个接口方法 selectByIdAndName ()
・selectByIdAndName (@Param ("id") String id, @Param ("name") String name) 转化为 map 为 {{0, "id"}, {1, "name"}}
・selectByIdAndName (String id, String name) 转化为 map 为 {{0, "0"}, {1, "1"}}
・selectByIdAndName (int a, RowBounds rb, int b) 转化为 map 为 {{0, "0"}, {2, "1"}}
构造方法的会经历如下的步骤
1. 通过反射得到方法的参数类型和方法的参数注解注解,
method.getParameterAnnotations () 方法返回的是注解的二维数组,每一个方法的参数包含一个注解数组。
2. 遍历所有的参数
- 首先判断这个参数的类型是否是特殊类型,RowBounds 和 ResultHandler,是的话跳过,咱不处理
- 判断这个参数是否是用来 Param 注解,如果使用的话 name 就是 Param 注解的值,并把 name 放到 map 中,键为参数在方法中的位置,value 为 Param 的值
- 如果没有使用 Param 注解,判断是否开启了 UseActualParamName,如果开启了,则使用 java8 的反射得到方法的名字,此处容易造成异常,
具体原因参考上一篇博文.
- 如果以上条件都不满足的话,则这个参数的名字为参数的下标
// 通用key前缀,因为key有param1,param2,param3等;
public static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
// 存放参数的位置和对应的参数名
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
// 是否使用@Param注解
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
// 通过注解得到方法的参数类型数组
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 通过反射得到方法的参数注解数组
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
// 用于存储所有参数名的SortedMap对象
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
// 参数注解数组长度,即方法入参中有几个地方使用了@Param
// 如selectByIdAndName(@Param("id") String id, @Param("name") String name)中,paramCount=2
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// 遍历所有的参数
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
// 判断这个参数的类型是否是特殊类型,RowBounds和ResultHandler,是的话跳过
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
continue;
}
String name = null;
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
// 判断这个参数是否使用了@Param注解
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
// 标记当前方法使用了Param注解
hasParamAnnotation = true;
// 如果使用的话name就是Param注解的值
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
// 如果经过上面处理,参数名还是null,则说明当前参数没有指定@Param注解
if (name == null) {
// 判断是否开启了UseActualParamName
if (config.isUseActualParamName()) {
// 如果开启了,则使用java8的反射得到该参数对应的属性名
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
// 如果name还是为null
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// 使用参数在map中的下标作为参数的name,如 ("0", "1", ...)
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
// 把参数放入到map中,key为参数在方法中的位置,value为参数的name(@Param的value值/参数对应的属性名/参数在map中的位置下标)
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
// 最后使用Collections工具类的静态方法将结果map变为一个不可修改类型
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
getNamedParams(): 该方法会将参数名和参数值对应起来,并且还会额外保存一份以 param 开头加参数顺序数字的值
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
// 这里的names就是ParamNameResolver中的names,在构造ParamNameResolver对象的时候,创建了该Map
// 获取方法参数个数
final int paramCount = names.size();
// 没有参数
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
// 只有一个参数,并且没有使用@Param注解。
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
// 直接返回,不做任务处理
return args[names.firstKey()];
} else {
// 包装成ParamMap对象。这个对象继承了HashMap,重写了get方法。
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
// 遍历names中的所有键值对
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
// 将参数名作为key, 对应的参数值作为value,放入结果param对象中
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// 用于添加通用的参数名称,按顺序命名(param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);
// 确保不覆盖以@Param 命名的参数
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
}
getNamedParams () 总结:
1. 当只有一个参数的时候,直接返回,不做任务处理;
2. 否则,存入 Map 中,键值对形式为:paramName=paramValue
・selectByIdAndName (@Param ("id") String id, @Param ("name") String name): 传入的参数是 ["1", "张三"],最后解析出来的 map 为:{“id”:”1”,”“name”:” 张三”}
・selectByIdAndName (String id, @Param ("name") String name): 传入的参数是 ["1", "张三"],最后解析出来的 map 为:{“param1”:”1”,”“name”:” 张三”}
假设执行的 SQL 语句是 select 类型,继续往下看代码
在 mapperMethod.execute (), 当
convertArgsToSqlCommandParam () 方法处理完方法参数后,假设我们此时调用的是查询单条记录,那么接下来会执行 sqlSession.selectOne () 方法。
sqlSession.selectOne () 源码分析:
sqlSession.selectOne () 也是调的 sqlSession.selectList () 方法,只不过只返回 list 中的第一条数据。当 list 中有多条数据时,抛异常。
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// 调用当前类的selectList方法
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
sqlSession.selectList () 方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 从Configuration里的mappedStatements里根据key(id的全路径)获取MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 调用Executor的实现类BaseExecutor的query()方法
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
在 sqlSession.selectList () 方法中,我们可以看到调用了 executor.query (),假设我们开启了二级缓存,那么 executor.query () 调用的是 executor 的实现类 CachingExecutor 中的 query (),二级缓存的逻辑就是在 CachingExecutor 这个类中实现的。
关于 mybatis 二级缓存:
二级缓存默认是不开启的,需要手动开启二级缓存,实现二级缓存的时候,MyBatis 要求返回的 POJO 必须是可序列化的。缓存中存储的是序列化之后的,所以不同的会话操作对象不会改变缓存。
怎么开启二级缓存:
<settings>
<setting name = "cacheEnabled" value = "true" />
</settings>
怎么使用二级缓存?
1. 首先肯定是要开启二级缓存啦~
2. 除此之外,要使用二级缓存还要满足以下条件:
・当会话提交之后才会填充二级缓存(为什么?后面会解释)
・SQL 语句相同,参数相同
・相同的 statementID
・RowBounds 相同
为什么要会话提交后才会填充二级缓存?
首先,我们知道,与一级缓存(会话级缓存)不同的是,二级缓存是跨线程使用的,也就是多个会话可以一起使用同一个二级缓存。假设现在不用提交便可以填充二级缓存,我们看看会存在什么问题?
假设会话二现在对数据库进行了修改操作,修改完进行了查询操纵,如果不用提交就会填充二级缓存的话,这时候查询操作会把刚才修改的数据填充到二级缓存中,如果此时刚好会话一执行了查询操作,便会查询到二级缓存中的数据。如果会话二最终回滚了刚才的修改操作,那么会话一就相当于发生了脏读。
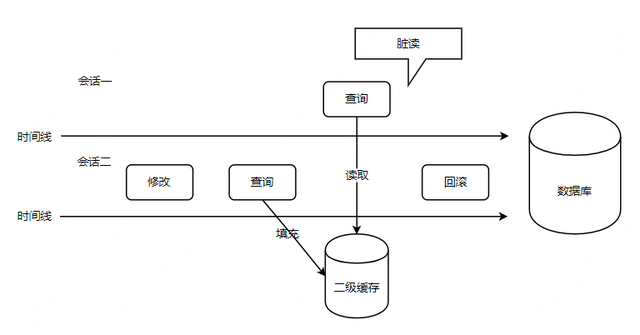
实际上,查询的时候会填充缓存,只不过此时是填充在暂存区,而不是填充在真正的二级缓存区中。而上面所说的要会话提交后才会填充二级缓存,指的是将暂存区中的缓存刷到真正的二级缓存中。啊???那不对呀,填充在暂存区,那此时会话一来查询,岂不是还会从暂存区中取到缓存,从而导致脏读?别急,接着往下看。
对于查询操作,每次取缓存都是从真正的二级缓存中取缓存,而不是从暂存区中取缓存。
好了,我们接着看源码~
CachingExecutor.query () 源码:
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取要执行的sql语句 sql语句在解析xml的时候就已经解析好了
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 生成二级缓存key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 调用重载方法
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
调用重载方法:query ()
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 获取mybatis的二级缓存配置<cache>
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 如果配置了二级缓存
if (cache != null) {
// 是否要刷新缓存,是否手动设置了需要清空缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 从二级缓存中获取值
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
// 从二级缓存中取不到值
if (list == null) {
// 交由delegate查询 这里的delegate指向的是BaseExecutor
// BaseExecutor中实现了一级缓存的相关逻辑
// 也就是说,当在二级缓存中获取不到值的时候,会从一级缓存中获取,一级缓存要是还是获取不到
// 才会去查询数据库
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 将查询结果存放在暂存区中,只有会话提交后才会将数据刷到二级缓存,避免脏读问题
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
接着,我们看下 BaseExecutor.query () 是怎么实现一级缓存逻辑的:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 尝试从缓存中获取结果 一级缓存
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {// 从缓存中获取不到结果时
// 从数据库中查询数据
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) { // 回到主查询
// 遍历延迟加载中的数据
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
// 把延迟加载的数据加载到结果集中
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
当从一级缓存中获取不到数据时,会查数据库:
调用
BaseExecutor.queryFromDatabase()
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 占位符 (解决循环依赖问题)
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 执行查询操作
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 将占位符从缓存中移除
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 将查询结果放入到一级缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
调用 BaseExecutor.doQuery ():在 BaseExecutor 中,doQuery () 只是个抽象方法,具体交由子类实现:
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
从前面的流程中可知,在每次执行 CURD 的时候,都需要获取 SqlSession 这个对象,接口如下:
可以看出来这个接口主要定义类关于 CRUD、数据库事务、数据库刷新等相关操作。下面看它的默认实现类:
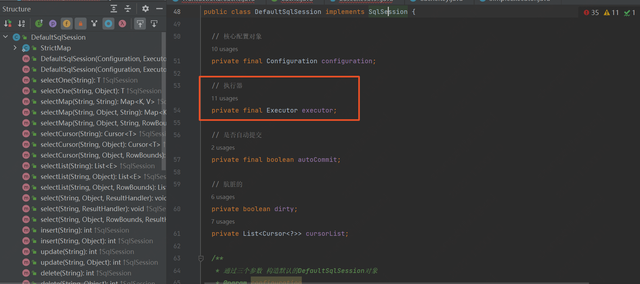
可以看到 DefaultSqlSession 实现了 SqlSession 中的方法,(其实我们自己也可根据需要去实现)。而在 DefaultSqlSession 类中有一个很重要的属性,就是 Mybatis 的执行器(Executor)。
Executor 介绍:
Executor 执行器,是 mybatis 中执行查询的主要代码,Executor 分为三种:
・简单执行器 SimpleExecutor
・可重用执行器 ReuseExecutor
・批量执行器 BatchExecutor
默认使用的执行器是 SimpleExecutor,可以在 mybatis 的配置文件中设置使用哪种执行器
public class Configuration {
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
}
Executor 类图:
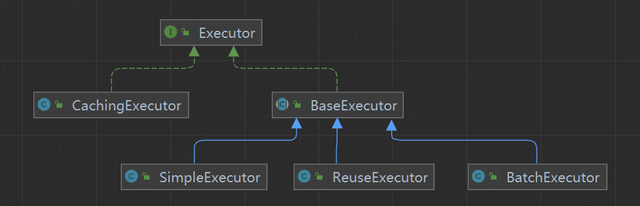
假设我们使用的就是默认的执行器,SimpleExecutor。我们来看下 SimpleExecutor.doQuery ()
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 这里就进入jdbc了
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 获取核心配置对象
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//预编译SQL语句
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取连接 这里的连接是代理连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 预编译
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 给预编译sql语句设置参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
在上面的源码中,我们可以看到 StatementHandler,它是用来干嘛的?
在 mybatis 中,通过 StatementHandler 来处理与 JDBC 的交互,我们看下 StatementHandler 的类图:
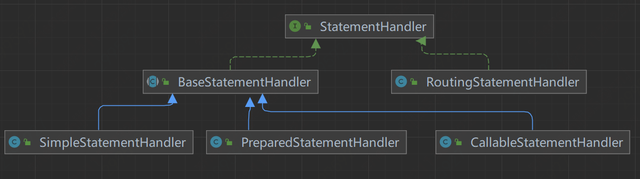
可以看出,跟 Executor 的继承实现很像,都有一个 Base,Base 下面又有几个具体实现子类,很明显,采用了模板模式。不同于 CacheExecutor 用于二级缓存之类的实际作用,这里的 RoutingStatementHandler 仅用于维护三个 Base 子类的创建与调用。
•BaseStatementHandler
・SimpleStatementHandler:JDBC 中的 Statement 接口,处理简单 SQL 的
・CallableStatementHandler:JDBC 中的 PreparedStatement,预编译 SQL 的接口
・PreparedStatementHandler:JDBC 中的 CallableStatement,用于执行存储过程相关的接口
・RoutingStatementHandler:路由三个 Base 子类,负责其创建及调用
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
// 策略模式:根据不同语句类型 选用不同的策略实现类
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
嗯,很眼熟的策略模式,按照 statementType 的值来决定返回哪种 StatementHandler。
那这里的 statementType 是在哪里赋值的呢?我们看下 MappedStatement 的构造方法:
public Builder(Configuration configuration, String id, SqlSource sqlSource, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType) {
...
// 构造方法中默认取值为PREPARED
mappedStatement.statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
...
}
如果不想使用的 StatementType.PREPARED,怎么自定义呢?
(1) 在 xxxMapper.xml 中:可以通过 <select /> 的 statementType 属性指定
<select id="getAll" resultType="Student2" statementType="CALLABLE">
SELECT * FROM Student
</select>
(2) 如果采用的是注解开发:通过 @SelectKey 的 statementType 属性指定
@SelectKey(keyProperty = "account",
before = false,
statementType = StatementType.STATEMENT,
statement = "select * from account where id = #{id}",
resultType = Account.class)
Account selectByPrimaryKey(@Param("id") Integer id);
到此,select 类型的 SQL 语句就基本执行完毕了,我们来总结一下 mybatis
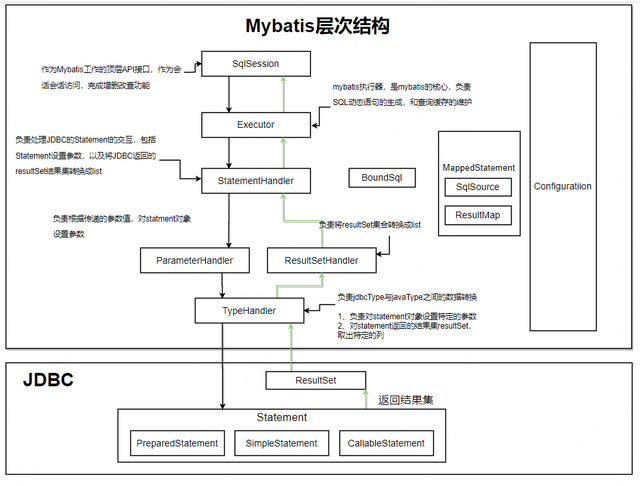
MyBatis 的主要的核心部件有以下几个:
SqlSession:作为 MyBatis 工作的主要顶层 API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能;
Executor:MyBatis 执行器,是 MyBatis 调度的核心,负责 SQL 语句的生成和查询缓存的维护;
StatementHandler:封装了 JDBC Statement 操作,负责对 JDBC statement 的操作,如设置参数、将 Statement 结果集转换成 List 集合。
ParameterHandler:负责对用户传递的参数转换成 JDBC Statement 所需要的参数;
ResultSetHandler:负责将 JDBC 返回的 ResultSet 结果集对象转换成 List 类型的集合;
TypeHandler:负责 java 数据类型和 jdbc 数据类型之间的映射和转换;
MappedStatement:MappedStatement 维护了一条 <select|update|delete|insert> 节点的封装;
SqlSource:负责根据用户传递的 parameterObject,动态地生成 SQL 语句,将信息封装到 BoundSql 对象中,并返回;
BoundSql:表示动态生成的 SQL 语句以及相应的参数信息;
Configuration:MyBatis 所有的配置信息都维持在 Configuration 对象之中;

Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK