寻找链表相交结点问题 - Grey Zeng
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/greyzeng/p/16926303.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

寻找链表相交结点问题
作者:Grey
原文地址:
题目描述#
给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的 第一个节点。如果不相交,返回 null。
要求:如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。
类似问题#
本题主要的难点是要分析所有可能的情况,因为题目中提到「可能有环也可能无环」。
主要思路#
先看大的情况,有如下三种情况
第一种情况:两个链表均无环;
第二种情况:两个链表均有环;
第三种情况:一个有环,一个无环。
首先,第三种情况下,两个链表一定不相交。针对第一种情况,就是寻找链表的入环节点和相交节点问题中提到LeetCode 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists,现在只分析第二种情况。
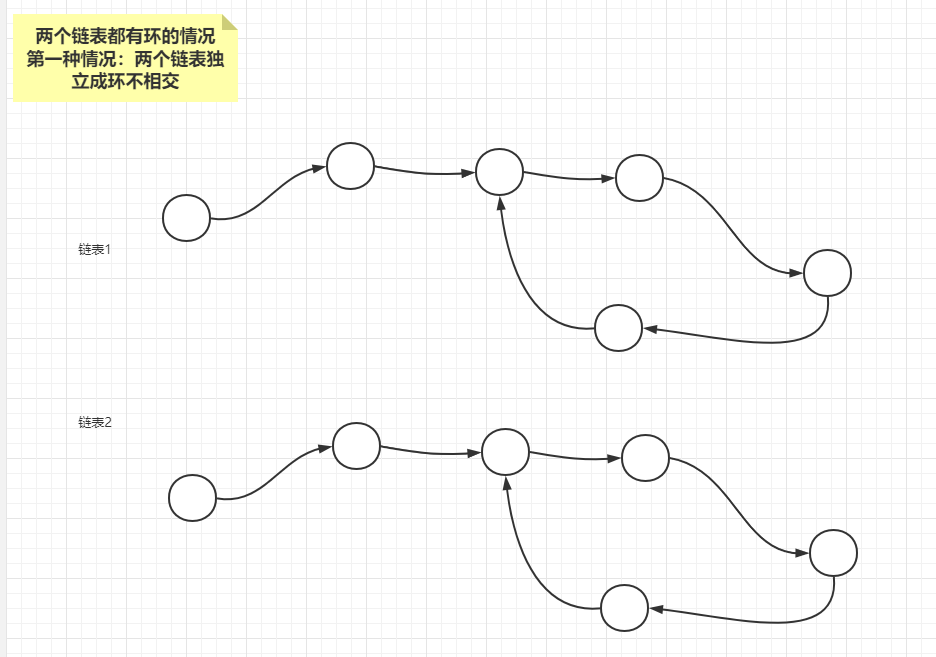
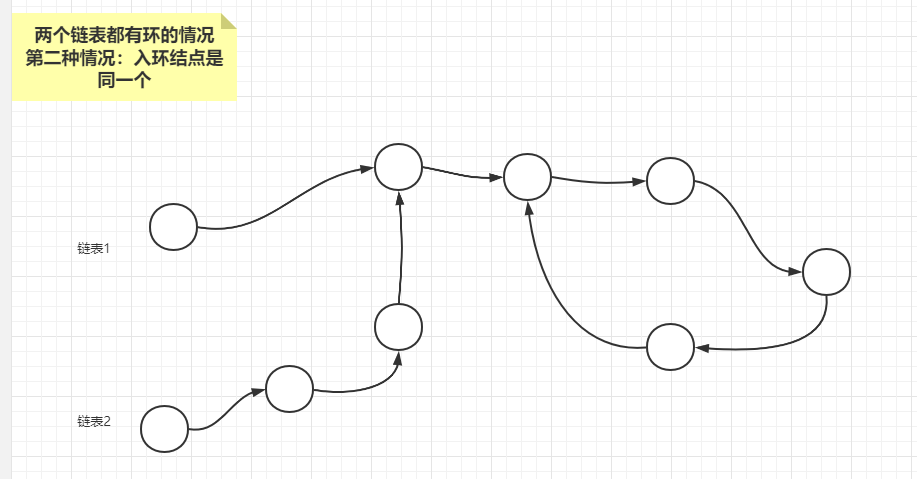
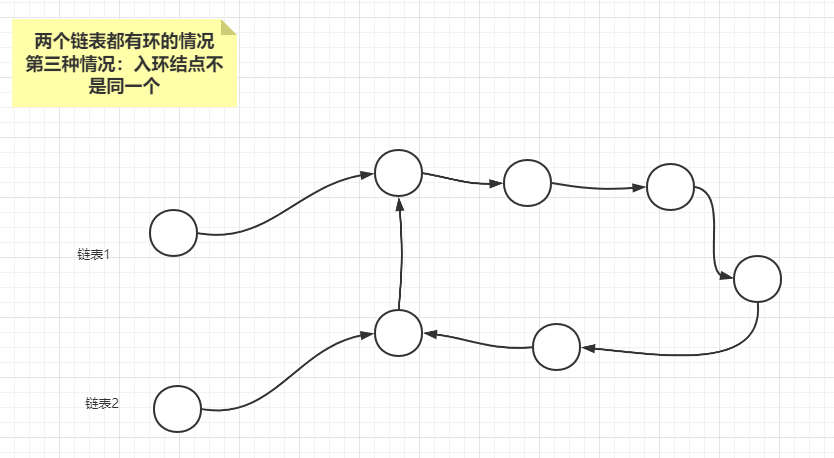
由于两个链表都有环,两个链表如果相交,一定只有如下三种情况
情况1:两个链表独立不相交
情况2:两个链表的入环结点是同一个
情况3:两个链表的入环结点不是同一个,此时任意一个链表的入环结点都是相交结点。
先从最简单的情况1和情况3进行分析,情况一发生的条件是:两个链表的入环结点(loop1,loop2)不是同一个,判断条件很简单,就是从任意一个链表的入环结点开始遍历一圈,如果都没有遇到另外一个链表的入环结点, 两个链表不相交,属于情况1;
如果从任意一个链表的入环结点开始遍历一圈,遇到了另外一个链表的入环结点,则说明两个链表相交,属于情况3,且任意一个链表的入环结点都是相交结点。
最后分析情况2,两个链表的入环结点如果是同一个,可以记录两个链表的差值,然后让短链表先走差值步以后,长短链表同时开始走,相遇的结点就是第一个相交结点。
完整代码见:
public class Code_FindFirstIntersectNode {
public static class List {
public int val;
public List next;
public List(int v) {
val = v;
}
}
public static List getIntersectNode(List head1, List head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
// 两个均无环
List loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);
List loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);
if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {
return noLoop(head1, head2);
}
// 两个均有环
if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);
}
// 一个有环一个无环 ,不可能相交
return null;
}
// 找到链表第一个入环节点,如果无环,返回null
public static List getLoopNode(List head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
// 慢指针 在第一个节点位置
List slow = head.next;
// 快指针,在第二个节点的位置
List fast = head.next.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
// 快指针每次走两步
fast = fast.next.next;
// 慢指针每次走一步
slow = slow.next;
}
// 两个指针遇上了,说明有环
// 让快指针回到头部, 慢指针停在原地
fast = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 快指针每次走一步,慢指针每次走一步,遇上后,就是入环节点处
return slow;
}
// 如果两个链表都无环,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交,返回null
public static List noLoop(List head1, List head2) {
if (head1 == null || head1 == null) {
return null;
}
// 判断两个链表的长度
int n = 0;
List t1 = head1;
List t2 = head2;
while (t1.next != null) {
n++;
t1 = t1.next;
}
while (t2.next != null) {
n--;
t2 = t2.next;
}
// 两个链表的末节点不相等
if (t2 != t1) {
return null;
}
// 记录长的链表头节点
List longer = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
// 记录短的链表头节点
List shorter = longer == head1 ? head2 : head1;
// 先让长链表走一段距离(这段的长度就是长链表和短链表的长度差)
int gap = Math.abs(n);
while (gap != 0) {
gap--;
longer = longer.next;
}
// 然后长链表和短链表同时开始走,直到相等的节点即为交点
while (longer != shorter) {
longer = longer.next;
shorter = shorter.next;
}
return shorter;
}
// 两个有环链表,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交返回null
public static List bothLoop(List head1, List loop1, List head2, List loop2) {
// 只有两种情况
if (loop1 == loop2) {
// 1. 未入环就相交
// 这种情况下,两个链表的入环节点是一样
int n = 0;
List t1 = head1;
List t2 = head2;
while (t1 != loop1) {
n++;
t1 = t1.next;
}
while (t2 != loop2) {
n--;
t2 = t2.next;
}
List longer = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
List shorter = longer == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0) {
n--;
longer = longer.next;
}
while (longer != shorter) {
longer = longer.next;
shorter = shorter.next;
}
return shorter;
} else {
// 2. 共用环,不在入环处相交,随便一个链表的入环点就是交点
// loop1 != loop2
// 从loop1开始,转一圈回到loop1
// 如果都没有遇到loop2,则不相交
// 如果遇到了loop1,则交点为loop1或者loop2都可以
List t1 = loop1.next;
while (t1 != loop1) {
if (t1 == loop2) {
return loop1;
}
t1 = t1.next;
}
return null;
}
}
}
更多#
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK