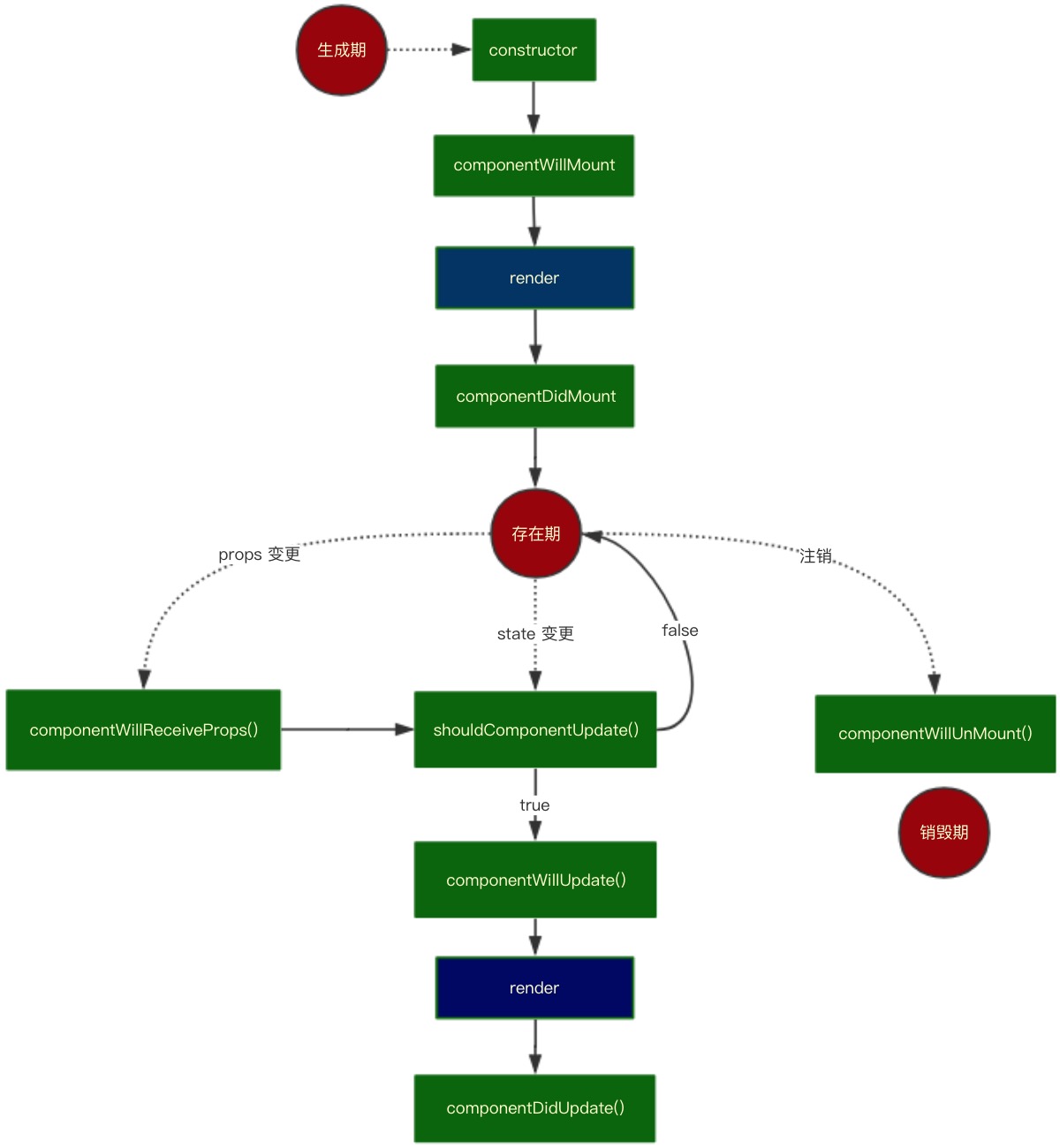
3.生命周期
先来回顾 React 的生命周期, 用流程图表示如下:
该流程图比较清晰地呈现了 react 的生命周期。其分为 3 个阶段 —— 生成期, 存在期, 销毁期。
因为生命周期钩子函数存在于自定义组件中, 将之前 _render 函数作些调整如下:
// 原来的 _render 函数, 为了将职责拆分得更细, 将 virtual dom 转为 real dom 的函数单独抽离出来
function vdomToDom(vdom) {
if (_.isFunction(vdom.nodeName)) { // 为了更加方便地书写生命周期逻辑, 将解析自定义组件逻辑和一般 html 标签的逻辑分离开
const component = createComponent(vdom) // 构造组件
setProps(component) // 更改组件 props
renderComponent(component) // 渲染组件, 将 dom 节点赋值到 component
return component.base // 返回真实 dom
我们可以在 setProps 函数内(渲染前)加入 componentWillMount, componentWillReceiveProps 方法, setProps 函数如下:
function setProps(component) {
if (component && component.componentWillMount) {
component.componentWillMount()
} else if (component.base && component.componentWillReceiveProps) {
component.componentWillReceiveProps(component.props) // 后面待实现
而后我们在 renderComponent 函数内加入 componentDidMount、shouldComponentUpdate、componentWillUpdate、componentDidUpdate 方法
function renderComponent(component) {
if (component.base && component.shouldComponentUpdate) {
const bool = component.shouldComponentUpdate(component.props, component.state)
if (!bool && bool !== undefined) {
return false // shouldComponentUpdate() 返回 false, 则生命周期终止
if (component.base && component.componentWillUpdate) {
component.componentWillUpdate()
const rendered = component.render()
const base = vdomToDom(rendered)
if (component.base && component.componentDidUpdate) {
component.componentDidUpdate()
} else if (component && component.componentDidMount) {
component.componentDidMount()
if (component.base && component.base.parentNode) { // setState 进入此逻辑
component.base.parentNode.replaceChild(base, component.base)
component.base = base // 标志符
测试生命周期
测试如下用例:
class A extends Component {
componentWillReceiveProps(props) {
console.log('componentWillReceiveProps')
render() {
return (
<div>{this.props.count}</div>
class B extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
count: 1
componentWillMount() {
console.log('componentWillMount')
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount')
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate', nextProps, nextState)
return true
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('componentWillUpdate')
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('componentDidUpdate')
click() {
this.setState({
count: ++this.state.count
render() {
console.log('render')
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.click.bind(this)}>Click Me!</button>
<A count={this.state.count} />
</div>
ReactDOM.render(
<B />,
document.getElementById('root')
页面加载时输出结果如下:
componentWillMount
render
componentDidMount
点击按钮时输出结果如下:
shouldComponentUpdate
componentWillUpdate
render
componentDidUpdate
React 16.3 生命周期调研
在这个版本中, 新加入了两个生命周期:
getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState): 更加语义化, 可以代替 componentWillMount、componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps);
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState): 可以将结果传入 componentDidUpdate 里, 从而达到 dom 数据统一, 可以替代 componentWillUpdate()(缺点就是前面讲的 react 开启异步渲染, componentWillUpdate() 与 componentDidUpdate() 间获取的 dom 会不统一)。
后文考虑实现上述 api。
React 16.3 生命周期相关文献