

一篇文章一次性搞定JavaScript 从 ES6 到 ES12的基础框架知识
source link: https://www.51cto.com/article/721691.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

一篇文章一次性搞定JavaScript 从 ES6 到 ES12的基础框架知识
Javascript 是前端三剑客技术最重要的技能之一。每个学习前端的人,这个JavaScript技术是必须要学的。随着技术不断更新迭代,所以现在有一些新的知识来支持我们去学习 ES6 ~ ES12。
一、ECMAScript简介
ECMA 规范由各方组成,包括浏览器供应商,他们会开会推动 JavaScript 提案。
二、ES6 (ES2015)
1.Class
JavaScript 是一种使用原型链的语言。
早期,类似OO的概念是通过原型链做出来的,相当复杂。Class 终于在 ES6 中推出。
class Animal {
constructor(name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
// This is a property on the prototype chain
toString() {
console.log('name:' + this.name + ', color:' + this.color);
}
}
var animal = new Animal('myDog', 'yellow'); // instantiate
animal.toString(); // name: myDog, color: yellow
console.log(animal.hasOwnProperty('name')); //true
console.log(animal.hasOwnProperty('toString')); // false
console.log(animal.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('toString')); // true
class Cat extends Animal {
constructor(action) {
// The subclass must call the super function in the constructor, otherwise an error will be reported when new comes out
// If the constructor was not written originally, the default constructor with super will be automatically generated
super('cat','white');
this.action = action;
}
toString() {
console.log(super.toString());
}
}
var cat = new Cat('catch')
cat.toString();
console.log(cat instanceof Cat); // true
console.log(cat instanceof Animal); // true每个模块都有自己的命名空间以避免冲突,使用导入和导出来导入和导出。
基本上将 .js 文件视为模块。
3.箭头函数
() => {…},是函数的缩写。最重要的是,他可以确保这始终指向自己
不再写 var self = this、var that = this 等等!
const add = (a, b) => { return a + b};
const res = add(1, 2); // 3
// If the syntax is simple, `{}` and `return` can be omitted. It will look neater
const minus = (a, b) => a - b;
const res1 = minus(3, 1); // 24.函数参数默认值
如果函数不传递参数,则使用默认值,更简洁的写法。
function example(height = 50, width = 40) {
const newH = height * 10;
const newW = width * 10;
return newH + newW;
}
example(); // 900 (50*10 + 40*10)5. 模板字面量
过去,长字符串的组合是通过 + 号来连接的。
它的可读性很差,使用模板字符串,它更容易阅读。
const firstName = 'Ken';
const lastName = 'Huang';
// not use template literal
const name = 'Hello, My name is' + firstName + ', ' + lastName;
// use template literal
const nameWithLiteralString = `Hello, My name is ${firstName}, ${lastName}`;6.解构赋值
允许 JavaScript 轻松地从数组和对象中获取内容。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const [one, two, three] = arr;
console.log(one); // 1
console.log(two); // 2
console.log(three); // 3
// To skip certain values
const [first,,,,last] = arr;
console.log(first); // 1
console.log(last); // 5
// Objects can also be destructurized and assigned
const student = {
name: 'Ken Huang',
age: 38,
city: 'Taipei'
};
const {name, age, city} = student;
console.log(name); // "Ken Huang"
console.log(age); // "38"
console.log(city); // "Taipei"7.扩展运算符
它是用三点(...)表示,Array是可以扩展的,如果是Object,会按照key-value进行扩展。
const stuendts = ['Angel', 'Ryan'];
const people = ['Sara', ...stuendts, 'Kelly', 'Eason'];
conslog.log(people); // ["Sara", "Angel", "Ryan", "Kelly", "Eason"]8. 对象属性简写
如果构成对象的字段名称与前面段落中的变量相同,则可以省略该值,看起来更流线型。
const name = 'Angel', age = 18, city = 'ChangHwa';
// Before ES6, we must write like this
const customer = {
name: name,
age: age,
city: city
} // // {name: 'Angel', age: 18, city: 'ChangHwa'}
// After ES6, we can do it
const newCustomer = {
name,
age,
city
} // {name: '小明Angel, age: 18, city: 'ChangHwa'}9. Promise
Promise 是一种异步(非同步)写法的解决方案,比原来的回调写法更加优雅。
早期是开源社区的套件,后来被纳入语言标准。
早期回调 hell……
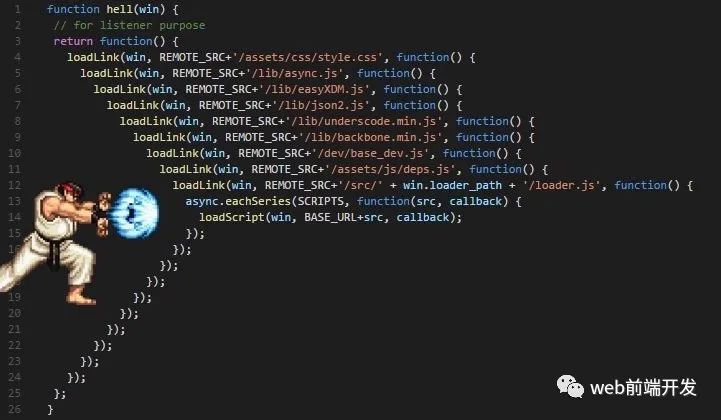
使用 Promise 后,回调 hell 扁平化
const waitSecond = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 1000);
});
waitSecond.then( () => {
console.log('hello World after 1 second.');
// output this line after 1 second
return waitSecond;
}).then( () => {
console.log('Hell World after 2 sceond.');
// output this line after 2second
})并且ES8(ES2017)发布了更完美的async,await,直接让异步写得像同步一样。
缺点是当思路落到复杂的业务逻辑上时,有时会错过await,在运行时发现错误。
10. let, const 替换 var
let:通用变量,可以被覆盖
const:一旦声明,其内容不可修改。因为数组和对象都是指标,所以它们的内容可以增加或减少, 但不改变其指标.
早期,JavaScript的var作用域是全局的。
也就是说,变量是在使用后声明的,执行的时候会自动提到顶层,后面会赋值。
更容易受到污染。
console.log(a); // undefined
var a = 10;使用 let 或 const
console.log(a); // ReferenceError: Cannot access 'a' before initialization
let a = 10;三、ES7 (ES2016)
1.Array.prototype.includes()
用于判断数组是否包含指定值,如果是,则返回true;否则,返回假。
和之前indexOf的用法一样,可以认为是返回一个布尔值,语义上更加清晰。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// Check if there is the number 3 in the array
arr.include(3); // true
if (arr.include(3)) { ... }
// ... Equivalent to the previous writing of indexOf
arr.indexOf(3); // 2 (return its array position)
// If you want to write it in the if, you must add `> -1`, which is not as clear as the include in ES7 in terms of semantics
if (arr.indexOf(3) > -1) { ... }2. 幂运算符
console.log(2**10); // 1024
// equal to
console.log(Math.pow(2, 10)); // 1024四、ES8 (ES2017)
1.async, await
异步函数是使用 async 关键字声明的函数,并且允许在其中使用 await 关键字。async 和 await 关键字使异步的、基于 Promise 的行为能够以更简洁的方式编写,避免了显式配置 Promise 链的需要。
async test() {
try {
const result = await otherAsyncFunction();
console.log(result); // output result
} catch(e) {
console.log(e); // Can catch errors if otherAsyncFunction() throws an error
}
}2. Object.values()
返回对象自身属性的所有值,不包括继承的值。
const exampleObj = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d:4};
console.log(Object.value(exampleObj)); // [1, 2, 3, 4];
// To do the same thing before, use the following notation. much verbose
const values = Object.keys(exampleObj).map(key => exampleObj[key]);3. Object.entries()
返回可枚举键,即传入对象本身的值。
const exampleObj = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d:4};
console.log(Object.entries(exampleObj)); // [["a", 1], ["b", 2], ["c", 3], ["d", 4]];
// Usually used with for
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(exampleObj)) {
console.log(`key: ${key}, value: ${value}`);
}
// key: a, value: 1
// key: b, value: 2
// key: c, value: 3
// key: d, value: 44. 字符串 padStart() & padEnd()
你可以在字符串的开头或结尾添加其他内容,并将其填充到指定的长度。
过去,这些功能通常是通过通用的辅助工具包(如 lodash)引入的,并将它们放在一起。
本机语法现在直接提供:
String.padStart(fillingLength, FillingContent);
// 如果要填充的内容过多,超过了“填充长度”,会从最左边填充到长度上限,超出的部分会被截断最常用的情况应该是金额,填写指定长度,不足加0。
// padStart
'100'.padStart(5, 0); // 00100
// If the content to be padded exceeds the "padding length". Then fill in from the left to the upper limit of the length
'100'.padStart(5, '987'); // 98100
// padEnd
'100'.padEnd(5, 9); // 10099
// If the content to be padded exceeds the "padding length". Then fill in from the right to the upper limit of the length
'100'.padStart(5, '987'); // 100985.尾随逗号
允许在函数参数列表末尾使用逗号
[
"foo",
+ "baz",
"bar",
- "baz",
]6. Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()
获取你自己的描述符,一般的开发业务需求通常不会用到。
const exampleObj = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d:4};
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(exampleObj);
// {a: {…}, b: {…}, c: {…}, d: {…}}
// a: {value: 1, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
// b: {value: 2, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
// c: {value: 3, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
// d: {value: 4, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
// __proto__: Object7. 共享数组缓冲区
SharedArrayBuffer 是一个固定长度的原始二进制数据缓冲区,类似于 ArrayBuffer。
可用于在共享内存上创建数据。与 ArrayBuffer 不同,SharedArrayBuffer 不能分离。
/**
* @param length size,unit byte
* @returns {SharedArrayBuffer} the default value is 0。
*/
const sab = new SharedArrayBuffer(length);8. Atomics object
Atomics 对象,它提供了一组静态方法来对 SharedArrayBuffer 执行原子操作。
原子的所有属性和函数都是静态的,就像数学一样,出不来新的。
如果一个多线程同时在同一个位置读写数据,原子操作保证了正在操作的数据如预期的那样:即在上一个子操作结束后执行下一个,操作不中断。
可以说是针对Node.Js中多线程Server的开发而加强的功能,在前端开发中使用的机会相当低。
chrome 已经提供了支持
五、ES9 (ES2018)
1.循环等待
在异步函数中,有时需要在同步 for 循环中使用异步(非同步)函数。
async function process(array) {
for (const i of array) {
await doSomething(i);
}
}
async function process(array) {
array.forEach(async i => {
await doSomething(i);
});
}上面的代码不会像预期的那样输出期望的结果。
for循环本身还是同步的,会在循环中的异步函数完成之前执行整个for循环,然后将里面的异步函数逐一执行。
ES9 增加了异步迭代器,允许 await 与 for 循环一起使用,逐步执行异步操作。
async function process(array) {
for await (const i of array) {
doSomething(i);
}
}2.promise.finally()
无论是成功(.then())还是失败(.catch()),Promise 后面都会执行的部分。
function process() {
process1()
.then(process2)
.then(process3)
.catch(err => {
console.log(err);
})
.finally(() => {
console.log(`it must execut no matter success or fail`);
});
}3. Rest, Spread
在 ES2015 中,Rest 不定长度参数…,可以转换成数组传入。
function restParams(p1, p2, ...p3) {
console.log(p1); // 1
console.log(p2); // 2
console.log(p3); // [3, 4, 5]
}
restParams(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);而传播则与其他相反,将数组转换为单独的参数。
例如,Math.max() 返回传入数字中的最大值。
const values = [19, 90, -2, 6, 25];
console.log( Math.max(...values) ); // 90它还提供了对Objects进行解构赋值的功能。
const myObject = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3
};
const { a, ...r } = myObject;
// a = 1
// r = { b: 2, c: 3 }
// Can also be used in function input parameters
function restObjectInParam({ a, ...r }) {
console.log(a); // 1
console.log(r); // {b: 2, c: 3}
}
restObjectInParam({
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3
});4. 正则表达式组
RegExp 可以返回匹配的数据包
const regExpDate = /([0-9]{4})-([0-9]{2})-([0-9]{2})/;
const match = regExpDate.exec('2020-06-25');
const year = match[1]; // 2020
const month = match[2]; // 06
const day = match[3]; // 25.正则表达式前瞻否定
TBD6.正则表达式 dotAll
. 表示匹配除输入以外的任何符号,添加这些标志后,允许匹配输入。
/hello.world/.test('hello\nworld'); // false
/hello.world/s.test('hello\nworld'); // true六、ES10 (ES2019)
1.更友好的 JSON.stringify
如果输入是 Unicode 但超出范围,则 JSON.stringify 最初会返回格式错误的 Unicode 字符串。
现在是第 3 阶段的提案,使其成为有效的 Unicode 并以 UTF-8 呈现
2. Array.prototype.flat() & Array.prototype.flatMap()
const arr1 = [1, 2, [3, 4]];
arr1.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
const arr2 = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]];
arr2.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]]
// Pass in a number in flat, representing the flattening depth
arr2.flat(2); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]flatMap(),相当于reduce with concat,可以展平一个维度
let arr = ["早安", "", "今天天氣不錯"]
arr.map(s => s.split(""))
// [["早", "安"], [""], ["今", "天", "天", "氣", "不", "錯"]]
arr.flatMap(s => s.split(''));
// ["早", "安", "", "今", "天", "天", "氣", "不", "錯"]3. String.prototype.trimStart() & String.prototype.trimEnd()
trimStart() 方法从字符串的开头删除空格,trimLeft() 是此方法的别名。
const greeting = ‘ Hello world! ‘;
console.log(greeting);
// expected output: “ Hello world! “;
console.log(greeting.trimStart());
// expected output: “Hello world! “;trimEnd() 方法从字符串末尾删除空格,trimRight() 是此方法的别名。
const greeting = ' Hello world! ';
console.log(greeting);
// expected output: " Hello world! ";
console.log(greeting.trimEnd());
// expected output: " Hello world!";4. Object.fromEntries()
Object.fromEntries() 方法将键值对列表转换为对象。
const entries = new Map([ ['foo', 'bar'], ['baz', 42]]);const obj = Object.fromEntries(entries);console.log(obj);// expected output: Object { foo: "bar", baz: 42 }5. String.prototype.matchAll
matchAll() 方法返回将字符串与正则表达式匹配的所有结果的迭代器,包括捕获组。
const regexp = /t(e)(st(\d?))/g;
const str = 'test1test2';
const array = [...str.matchAll(regexp)];
console.log(array[0]);
// expected output: Array ["test1", "e", "st1", "1"]
console.log(array[1]);
// expected output: Array ["test2", "e", "st2", "2"]6.fixed catch 绑定
在使用catch之前,不管有用与否,一定要传入一个eparameter来表示接收到的错误。
如果现在不用,可以省略。
try {...} catch(e) {...}
// If e is not used, it can be omitted
try {...} catch {...}7. BigInt(新数字类型)
BigInt 值,有时也称为 BigInt,是一个 bigint 原语,通过将 n 附加到整数文字的末尾,或通过调用 BigInt() 函数(没有 new 运算符)并给它一个整数值或字符串来创建 价值。
ES5:String, Number, Boolean, Null, Undefined
ES6 新增:Symbol,到ES6就一共有6 种类型
ES10 新增:BigInt,就达到 7 种类型
const theBiggestInt = 9007199254740991n;
const alsoHuge = BigInt(9007199254740991);
// ↪ 9007199254740991n
const hugeString = BigInt("9007199254740991");
// ↪ 9007199254740991n
const hugeHex = BigInt("0x1fffffffffffff");
// ↪ 9007199254740991n
const hugeBin = BigInt("0b11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111");
// ↪ 9007199254740991n七、ES11 (ES2020)
1.Promise.allSettled()
Promise.allSettled() 方法返回一个在所有给定的 Promise 都已实现或拒绝后实现的 Promise,并带有一组对象,每个对象都描述了每个 Promise 的结果。
它通常用于当你有多个不依赖于彼此成功完成的异步任务,或者你总是想知道每个 Promise 的结果时。
相比之下,Promise.all() 返回的 Promise 可能更合适,如果任务相互依赖/如果你想立即拒绝其中任何一个拒绝。
const promise1 = Promise.resolve(3);
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(reject, 100, 'foo'));
const promises = [promise1, promise2];
Promise.allSettled(promises).
then((results) => results.forEach((result) => console.log(result.status)));
// expected output:
// "fulfilled"
// "rejected"2. 可选链接?
在开发中,很容易遇到先判断数据是否存在,判断是否写入。
const isUserExist = user && user.info;
if (isUserExist) {
username = user.info.name;
}如果返回的数据为null或者用户对象下没有.intounder,则会抛出Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property...。
导致程序无法继续执行
使用 ?,语法更简单
const username = user?.info?.name;如果存在,获取name的值,如果不存在,赋值undefined
与 || 一起使用,只需一行!
const username = user?.name || 'guest';3. Nullish 合并运算符 ??
在JavaScript中,遇到0、null、undefuded时会自动转为false。
但有时0其实是一个正常的值,只能容错undefined和null
/**
* user = {
* level: 0
* }
*/
const level = user.level || 'no level'; // output as no level instead of expected 0
// to fix it, it must use if simple processing
const level = user.level !== undefined && user.level !== null ? user.level : 'no level';但是使用??,你可以保持简洁
const username = user.level ?? 'no level';
// output 0. if level is not available, it becomes 'no level'.4.Dynamic-import
从字面上看,应该很容易理解,就是在需要的时候加载相关的逻辑。
el.onclick = () => {
import(`/js/current-logic.js`)
.then((module) => {
module.doSomthing();
})
.catch((err) => {
handleError(err);
})
}5. GlobalThis
全局 globalThis 属性包含全局 this 值,类似于全局对象。
过去的做法是:
// https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/globalThis
const getGlobal = function () {
if (typeof self !== 'undefined') { return self; }
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') { return window; }
if (typeof global !== 'undefined') { return global; }
throw new Error('unable to locate global object');
};
var globals = getGlobal();现在,我们可以这样做:
function canMakeHTTPRequest() {
return typeof globalThis.XMLHttpRequest === 'function';
}
console.log(canMakeHTTPRequest());
// expected output (in a browser): true八、ES12 (ES2021)
1.Promise.any()
Promise.any() 接受一个可迭代的 Promise 对象。它返回一个单一的 Promise,只要 iterable 中的任何一个 Promise 完成,就会返回一个 Promise,并带有已完成的 Promise 的值。
如果可迭代的实现中没有任何承诺(如果所有给定的承诺都被拒绝),则返回的承诺会被 AggregateError 拒绝,AggregateError 是 Error 的一个新子类,它将单个错误组合在一起。
const p1 = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('p1 resolved value')
}, 1000)
})
const p2 = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('p2 resolved value')
}, 500)
})
const p3 = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('p3 resolved value')
}, 1800)
})
Promise.any([p1, p2, p3]).then(value=>{
console.log(value)
}) // p2 resolved value2. 逻辑赋值运算符
在开发过程中,我们可以使用 ES2020 中提出的逻辑运算符 ||、&& 和 ??(Nullish coalescing operator)来解决一些问题。
而 ES2021 会提出 ||= , &&= , ??= ,概念类似于 += :
let b = 2
b += 1
// equal to b = b + 1
let a = null
a ||= 'some random text' // a become to'some random text'
// equal a = a || 'some random text'
let c = 'some random texts'
c &&= null // c become to null
// equal to c = c && null
let d = null
d ??= false // d become to false
// equal to d = d ?? false3. WeakRef
WeakRef 对象包含对对象的弱引用,该对象称为其目标或引用对象。对对象的弱引用是不会阻止对象被垃圾收集器回收的引用。
相反,普通(或强)引用将对象保存在内存中,当一个对象不再有任何强引用时,JavaScript 引擎的垃圾收集器可能会销毁该对象并回收其内存。
如果发生这种情况,你将无法再从弱引用中获取对象。
此示例启动一个显示在 DOM 元素中的计数器,当该元素不再存在时停止:
class Counter {
constructor(element) {
// Remember a weak reference to the DOM element
this.ref = new WeakRef(element);
this.start();
}
start() {
if (this.timer) {
return;
}
this.count = 0;
const tick = () => {
// Get the element from the weak reference, if it still exists
const element = this.ref.deref();
if (element) {
element.textContent = ++this.count;
} else {
// The element doesn't exist anymore
console.log("The element is gone.");
this.stop();
this.ref = null;
}
};
tick();
this.timer = setInterval(tick, 1000);
}
stop() {
if (this.timer) {
clearInterval(this.timer);
this.timer = 0;
}
}
}
const counter = new Counter(document.getElementById("counter"));
setTimeout(() => {
document.getElementById("counter").remove();
}, 5000);到这里,今天要跟你分享的内容就全部结束了,这些都是我的一些练习和学习笔记总结,希望对你有用。
今天分享的内容,如果觉得有用的话,请记得点赞我,关注我,并将这篇文章与你的开发者朋友一起来分享它。
最后,感谢你的阅读。
如果你身边还有想学习前端开发的朋友,也请将我们的公众号分享给他,也许对他的学习有帮助。
Recommend
-
 42
42
JavaScript ES6 带来了新的语法和新的强大功能,使您的代码更现代,更易读。它允许您编写更少的代码并执行更多操作。 ES6 向我们介绍了许多强大的功能,如箭头函数,模板字符串,对象结构,模块等,让我们来看看。 const and le...
-
 40
40
-
 0
0
一篇文章让你了解 AWS 安全基础-51CTO.COM 一篇文章让你了解 AWS 安全基础 作者:肖力 翻译 2022-08-09 08:00:55 AWS密钥管理器可确保数据库凭证或 API 密钥等机密的安全。存储和控...
-
 4
4
WordPress批量删除文章在wordpress中如何批量删除所有文章?有几种方法可以删除掉所有文章,一种是重新安装wordpress,删除的彻底,所有插件都需要重新下载,重新设置,比较麻烦。还有一种就是在wordpress安装设置完毕后,安装一个UpdraftPlus的备份插件,...
-
 6
6
一篇文章带你掌握主流基础框架——Spring 这篇文章中我们将会介绍Spring的框架以及本体内容,包括核心容器,注解开发,AOP以及事务等内容 那么简单说明一下Spring的必要性: Spring技术是JavaEE...
-
 10
10
夯实Java基础,一篇文章全解析线程问题 作者:一灯架构 2022-11-04 10:45:11 进程是资源分配的最小单位,而线程是CPU调度的最小单位。每一个进程中至少有一个线程,同一进程的所有线程共享该进程的所有资源,多个...
-
 2
2
Shell 搜索与匹配 1、在文件中查找字符串 grep 命令可以搜索文件,查找指定的字符串。 $ grep myvar *.c 在这个例子中,我们搜索的文件全都位于当前目录下...
-
 2
2
一次性搞定 SHOW SLAVE STATUS 的解读 解析日志文件的位置 诚然, GTID(全局事务标识符)已经在 MySQL 5.6中得到支持, 此外,还可以通过 Tungsten replicator 软件来实现(2009年以后一直有谷歌在维护,不...
-
 4
4
现在前端的入门门槛越来越高了,不再是单纯 html+css+js,各种前端框架 层出不穷,各种ui组件库层出不穷。 模块化,打包化,各种工具库层出不穷,前端变成大前端 ,甚至前端可以搞定整个项目,通过node...
-
 4
4
一次性搞懂什么是AIGC!(一篇文章22个基本概念)
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK