联邦学习:联邦异构知识图谱数据划分 - orion-orion
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/orion-orion/p/16829566.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

我们在博客《联邦学习:联邦场景下的多源知识图谱嵌入》中介绍了联邦场景下的知识图谱嵌入,现在让我们回顾一下其中关于数据部分的细节。在联邦场景下,CC个知识图谱{Gc}Cc=1={{Ec,Rc,Tc}}Cc=1{Gc}c=1C={{Ec,Rc,Tc}}c=1C位于不同的客户端上。知识图谱拥的实体集合EcEc之间可能会存在重叠,而其关系集合RcRc和元组集合TcTc之间则不会重叠[1]。我们联系一下现实场景看这是合理的,比如在不同客户端对应不同银行的情况下,由于不同银行都有着自己的业务流程,所以关系集合不重叠。
接下来我们来看具体在实验环节怎么去划分联邦异构知识图谱数据。
2 联邦异构知识图谱划分
我们在博客《分布式机器学习:PageRank算法的并行化实现(PySpark)》中所说,分布式图数据的划分可分为点划分和边划分两种,边划分是对图中某些边进行分裂,这使得不同的worker的点不同,但可能存有相同的边拷贝。而点划分是对图中某些点进行分裂,使得不同的worker的边不同,可能存有相同的点拷贝。不过知识图谱的情况要简化得多,因为知识图谱的图数据本身就是按一条条的边(元组)(h,r,t)(h,r,t)来存储的,直接对元组进行划分其实就等价于了点划分的方式。
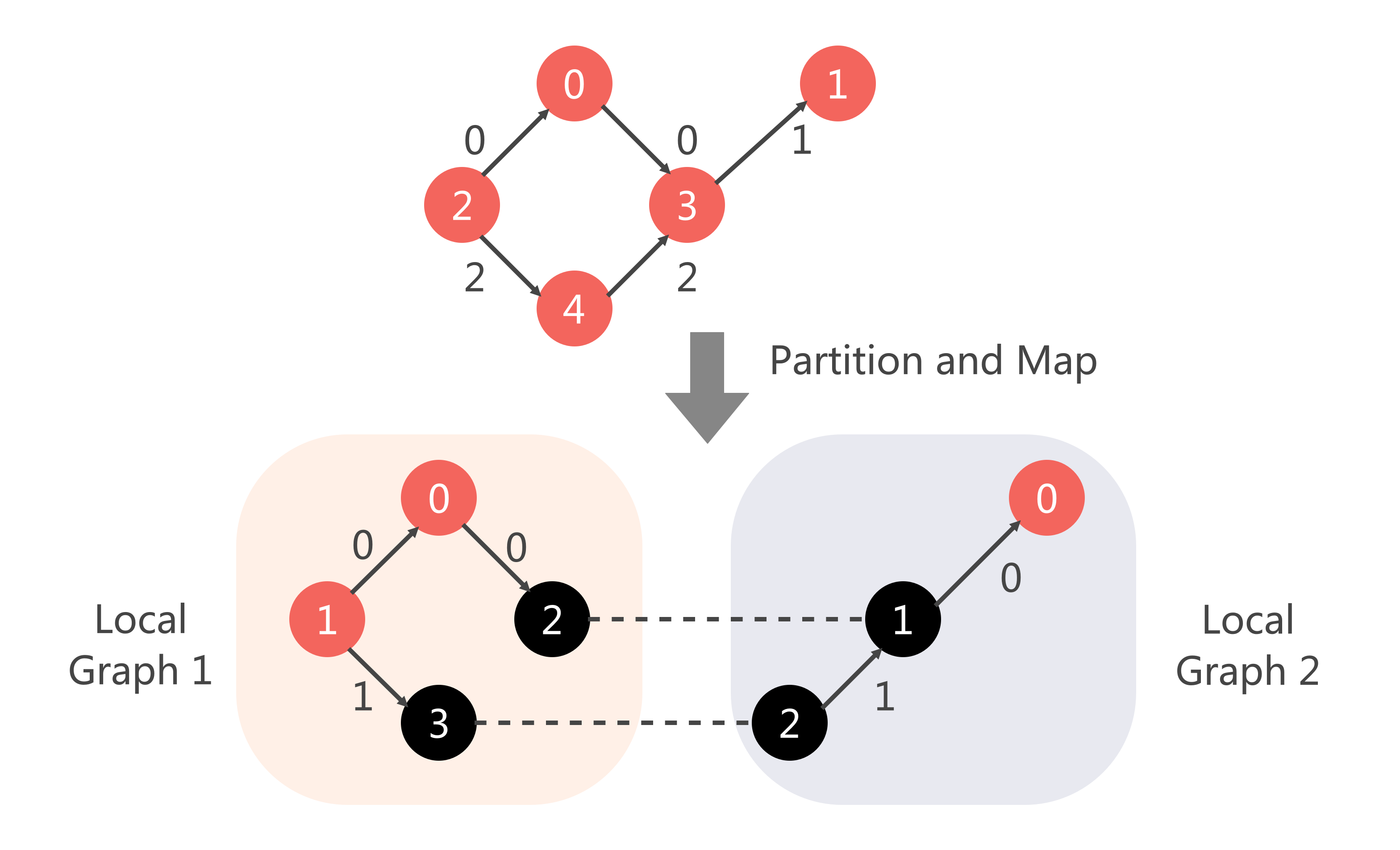
由于我们这里的本地知识图谱{Ec,Rc,Tc}{Ec,Rc,Tc}中每个知识图谱的关系RcRc(即边的种类)是不同的,我们在划分元组之前我们需要先对关系进行划分,然后针对关系划分的结果来划分元组。 待元组划分到本地后,还需要将原有的实体和关系的索引映射到本地索引。最后,再在本地进行训练/验证/测试集的拆分。整体数据划分流程图如下:
2.1 划分关系
我们选择随机地将关系RR不重叠地划分到不同的client上:
random.shuffle(triples)
# triples为元祖集合,大小为 (n_triples, 3)
# 每各元组按(h,t,r)顺序存储
triples = np.concatenate(triples)
# 先根据边的类型edge_type(即关系类型)将不同的edge_type映射到不同的client_id
edge_types = list(set(triples[:, 2]))
random.shuffle(edge_types)
edge_type_to_cid = {}
n_edge_types_per_client = len(edge_types)//n_clients
for id, edge_type in enumerate(edge_types):
c_id = id // n_edge_types_per_client
if c_id < n_clients - 1:
edge_type_to_cid[edge_type] = c_id
else:
edge_type_to_cid[edge_type] = n_clients - 1
2.2 确定元组划分
在关系的划分确定之后,我们可以根据每个元组(h,r,t)(h,r,t)中rr的划分情况来决定该元组的划分情况。代码如下:
# 然后根据edge_type到client_id的映射情况,来将元组triples划分到不同的client
c_id_triples = [[] for i in range(n_clients)]
for triple in triples:
edge_type = triple[2]
c_id = edge_type_to_cid[edge_type]
c_id_triples[c_id].append(triple.reshape(1, -1))
2.3 索引映射
划分好元组之后,子图就确定了,接下来我们还需要将子图的实体和关系的索引进行重新编号,如下图所示:
对于具体的局部索引如何安排,我们采用随机选择的方式。代码如下:
# mapping global indices to local indices
c_id_triples_ori = [[] for i in range(n_clients)]
for c_id in range(n_clients):
triples = np.concatenate(c_id_triples[c_id])
c_id_triples_ori[c_id] = triples
edge_index = triples[:, :2]
edge_type = triples[:, 2]
# map entity indices to local entity indices
index_mapping = {}
entities = list(set(edge_index.flatten()))
random.shuffle(entities)
for index, entity in enumerate(entities):
index_mapping[entity] = index
f = lambda x: index_mapping[x]
f = np.vectorize(f)
client_entity_local_index = f(edge_index)
# map edge indices to local entity indices
index_mapping = {}
edges = copy.deepcopy(list(set((edge_type))))
random.shuffle(edges)
for index, edge in enumerate(edges):
index_mapping[edge] = index
f = lambda x: index_mapping[x]
f = np.vectorize(f)
client_edge_local_index = f(edge_type)
c_id_triples[c_id] = np.concatenate([client_entity_local_index, \
client_edge_local_index.reshape(-1, 1)], axis=1)
2.4 训练/验证/测试集拆分
最后,还需要在本地划分训练集、验证集和测试集。如下面的代码展示了按照0.8/0.1/0.1对本地的元组进行拆分。数据集划分完毕之后,则训练/验证/测试集对应的实体(edge_index)和关系类型(edge_type)就都确立了:
# split train, valid, test dataset
for c_id in range(n_clients):
n_triples = c_id_triples[c_id].shape[0]
n_train = int(n_triples * 0.8)
n_val = int((n_triples - n_train) * 0.5)
n_test = n_triples - n_train - n_val
mod_to_slice = {"train": slice(0, n_train), \
"valid": slice(n_train, n_train+n_val), "test": slice(-n_test, n_triples)}
for mode in ["train", "valid", "test"]:
client_data[c_id][mode]["edge_index_ori"] = c_id_triples_ori[c_id][mod_to_slice[mode], : 2].T
client_data[c_id][mode]["edge_index"] = c_id_triples[c_id][mod_to_slice[mode], : 2].T
client_data[c_id][mode]["edge_type_ori"] = c_id_triples_ori[c_id][mod_to_slice[mode], 2]
client_data[c_id][mode]["edge_type"] = c_id_triples[c_id][mod_to_slice[mode], 2]
3 关于异构性的分析和解决
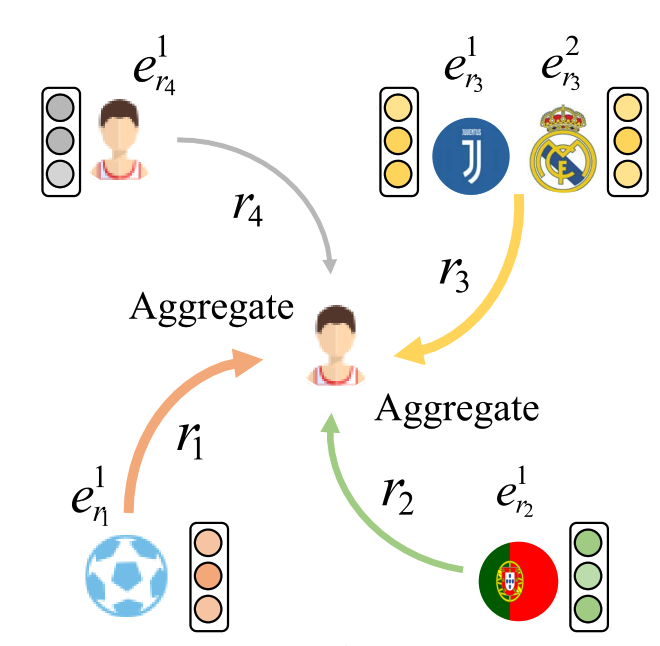
根据我们前面的定义,在联邦场景下不同客户端的知识图谱满足实体重叠,因此在进行联邦训练的过程中最简单的方式就是对重叠实体的embeddings进行平均。但是我们知道,知识图谱可能本身就具有一定的异构性,因为其中的某个实体可能会拥有着不同的关系路径[2],如下图所示:
在联邦场景下这种异构性则更加明显,因为如我们前面所说,同一个实体在不同的client的关系路径肯定不同,如果只采用本地嵌入的方法,那么不同的client会映射到不同的嵌入空间。此时,如果对来自不同嵌入空间embeddings直接进行聚合,就会丢失掉许多有用的语义信息。
如上图所示[3],知识图谱School中的元组表示Bob和Jack的学业信息,Amazon.com知识图谱中则表示他们的购物信息。对于Bob和Jack实体而言,在不同的知识图谱中他们拥有不同的关系,导致了他们的语义信息在不同知识图谱中的差异。
如何对联邦场景下知识图谱的异构性进行解决,成为一个必须要考虑的问题,目前文献[3]已采用对比学习对其进行了一定程度的解决,大家感兴趣的可以去阅读一下。
[1] Chen M, Zhang W, Yuan Z, et al. Fede: Embedding knowledge graphs in federated setting[C]//The 10th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Graphs. 2021: 80-88.
[2] Li Z, Liu H, Zhang Z, et al. Learning knowledge graph embedding with heterogeneous relation attention networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021.
[3] Chen M, Zhang W, Yuan Z, et al. Federated knowledge graph completion via embedding-contrastive learning[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 252: 109459.
__EOF__
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK