

10 张图告诉你 RocketMQ 是怎样保存消息的
source link: https://www.51cto.com/article/719620.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

大家好,我是君哥,今天分享 RocketMQ 是怎样保存消息的。
1、简介
首先,在 RocketMQ 集群中创建一个 Topic,叫做 MyTestTopic,配置如下图:
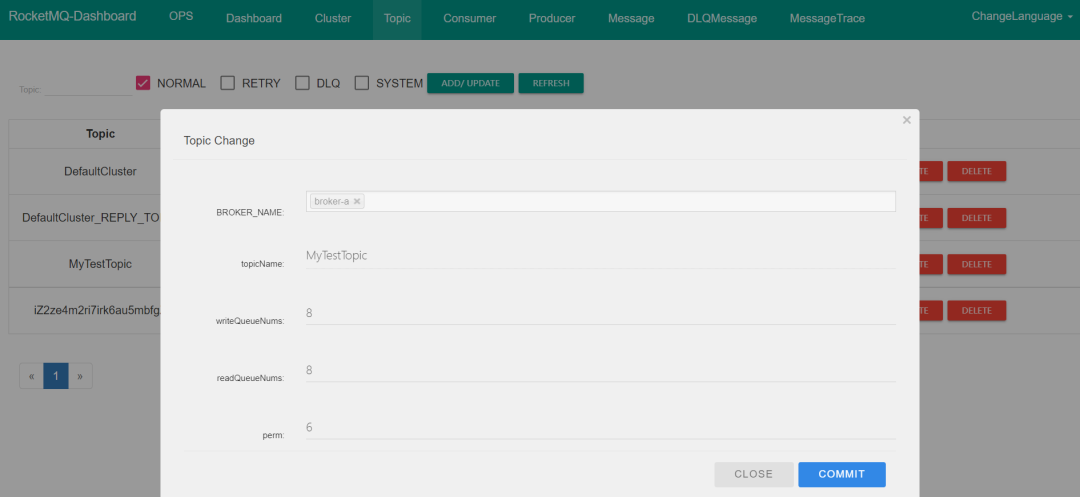
这里解释一下图中的几个参数:
writeQueueNums:客户端在发送消息时,可以向多少个队列进行发送;readQueueNums:客户端在消费消息时,可以从多少个队列进行拉取;perm:当前 Topic 读写权限,2 只允许读、4 只允许写、6 允许读写,默认是 6。
RocketMQ 主要有 3 个消息相关的文件:commitlog、consumequeue 和 index。下面是这几个文件默认的路径:
[root@xxx store]
/root/store
[root@xxx store]
abort checkpoint commitlog config consumequeue index lock上面的 writeQueueNums 参数控制 consumequeue 的文件的数量。作为测试,我往 MyTestTopic 这个 Topic 发送了 100 条消息,这些消息保存在了 commitlog 文件。而 consumequeue 文件如下:
[root@xxx MyTestTopic]
/root/store/consumequeue/MyTestTopic
[root@xxx MyTestTopic]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7可以看到,consumequeue 的保存是在 consumequeue 目录下为每个 Topic 建一个目录,用保存这个 Topic 的 consumequeue 文件。consumequeue 文件为每个 Topic 基于偏移量创建了一个索引。
index 文件保存的是消息基于 key 的 HASH 索引。
2、commitlog 文件
commitlog 是 RocketMQ 保存消息的文件。commitlog 并没有按照 Topic 来分割,所有 Topic 的消息都写入同一个 commitlog。
为了追求高效写入,RocketMQ 使用了磁盘顺序写。commitlog 文件大小默认是 1G,可以通过参数 mappedFileSizeCommitLog 来修改。
下面是服务器磁盘上保存的 commitlog 文件(文件大小 1G):
[root@xxx commitlog]
/root/store/commitlog
[root@xxx commitlog]
00000000000000000000 00000000001073741824如果配置 mappedFileSizeCommitLog 参数为 1048576,也就是 1M,则服务器磁盘上保存的 commitlog 文件如下:
[root@xxx commitlog]
/root/store/commitlog
[root@xxx commitlog]
00000000000000000000 00000000000001048576 00000000000002097152 00000000000003145728 00000000000004194304 00000000000005242880可以看到:commitlog 文件的命名以保存在文件中的消息最小的偏移量来命名的,后一个文件的名字是前一个文件名加文件大小。比如上面的前两个文件,第一个文件中消息最小偏移量是 0,第二个文件中消息最小偏移量是 1048576。这样通过偏移量查找消息时可以先用二分查找找到消息所在的文件,然后通过偏移量减去文件名就可以方便地找到消息在文件中的物理地址。
下面创建文件的代码可以看到 commitlog 文件的命名:
protected MappedFile tryCreateMappedFile(long createOffset) {
String nextFilePath = this.storePath + File.separator + UtilAll.offset2FileName(createOffset);
String nextNextFilePath = this.storePath + File.separator + UtilAll.offset2FileName(createOffset
+ this.mappedFileSize);
return doCreateMappedFile(nextFilePath, nextNextFilePath);
}
public static String offset2FileName(final long offset) {
final NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
nf.setMinimumIntegerDigits(20);
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(0);
nf.setGroupingUsed(false);
return nf.format(offset);
}为了让 commitlog 操作效率更高,RocketMQ 使用了 mmap 将磁盘上日志文件映射到用户态的内存地址中,减少日志文件从磁盘到用户态内存之间的数据拷贝。代码如下:
if (messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
try {
mappedFile = ServiceLoader.load(MappedFile.class).iterator().next();
mappedFile.init(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize(), messageStore.getTransientStorePool());
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
log.warn("Use default implementation.");
mappedFile = new MappedFile(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize(), messageStore.getTransientStorePool());
}
} else {
mappedFile = new MappedFile(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize());
}写入消息时,如果 isTransientStorePoolEnable 方法返回 true,则消息数据先写入堆外内存,然后异步线程把堆外内存数据刷到 PageCache,如果返回 false 则直接写入 PageCache。后面根据刷盘策略把 PageCache 中数据持久化到磁盘。如下图:
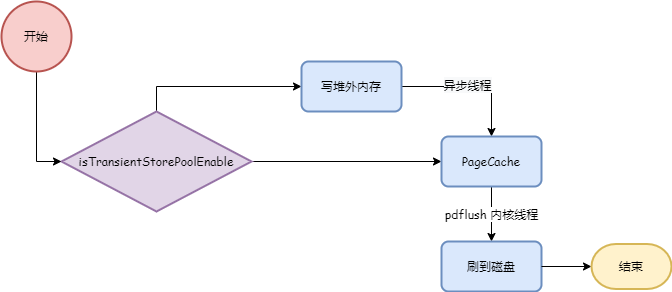
对应代码如下:
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> asyncPutMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
putMessageLock.lock();
try {
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile();
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback, putMessageContext);
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case PUT_OK:
break;
case END_OF_FILE:
unlockMappedFile = mappedFile;
mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(0);
if (null == mappedFile) {
log.error("create mapped file2 error, topic: " + msg.getTopic() + " clientAddr: " + msg.getBornHostString());
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.CREATE_MAPEDFILE_FAILED, result));
}
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback, putMessageContext);
break;
}
} finally {
putMessageLock.unlock();
}
CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> flushResultFuture = submitFlushRequest(result, msg);
}无论先写对堆外内存还是直接写 PageCache,文件数据都会映射到 MappedByteBuffer。如下图:
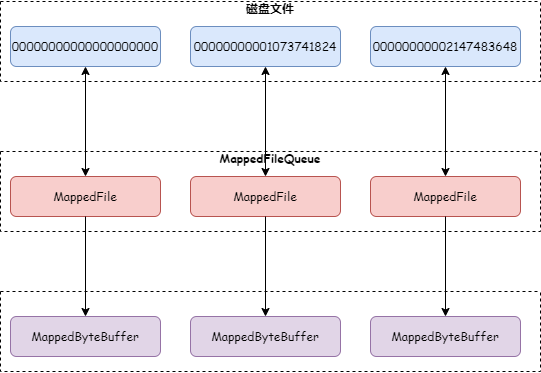
不同的是,如果消息先写入堆外内存,则 MappedByteBuffer 主要用来读消息,堆外内存用来写消息。这一定程度上实现了读写分离,减少 PageCache 写入压力。
再看一下文件映射的代码,如下:
private void init(final String fileName, final int fileSize) throws IOException {
this.fileName = fileName;
this.fileSize = fileSize;
this.file = new File(fileName);
this.fileFromOffset = Long.parseLong(this.file.getName());
try {
this.fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(this.file, "rw").getChannel();
this.mappedByteBuffer = this.fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileSize);
}
}这里使用了 Java 中 FileChannel 的 map 方法来实现 mmap。
有一个细节需要注意:创建 MappedFile 后会进行文件预热,目的是为了预先将 PageCache 加载到内存,防止读写数据发生缺页中断时再加载,影响性能。代码如下:
if (mappedFile.getFileSize() >= this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig()
.getMappedFileSizeCommitLog()
&&
this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isWarmMapedFileEnable()) {
mappedFile.warmMappedFile(this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType(),
this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushLeastPagesWhenWarmMapedFile());
}最后,附上一张写 commitlog 的 UML 类图:
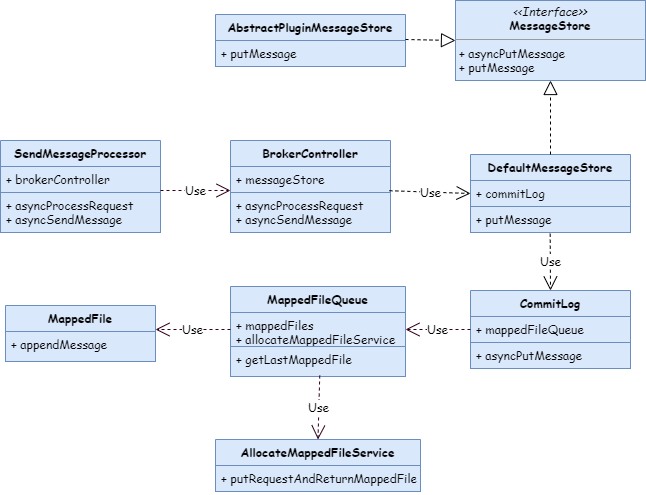
3、consumequeue 文件
前面讲到过,所有 Topic 的消息都写到同一个 commitlog 文件,如果直接在 commitlog 文件中查找消息,只能从文件头开始查找,肯定会很慢。因此 RocketMQ 引入了 consumequeue,基于 Topic 来保存偏移量。从 consumequeue 文件的保存目录也能看出来:
[root@xxx MyTestTopic]
/root/store/consumequeue/MyTestTopic
[root@xxx MyTestTopic]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7consumequeue 目录下会为每个 Topic 创建一个目录,每个 Topic 目录下为每一个 consumequeue 创建一个目录,比如上面的 MyTestTopic 这个 Topic 下面有 8 个 consumequeue。
每个 consumequeue 目录下保存了这个队列的文件内容。以上面第 7 个目录为例:
[root@xxx 7]
/root/store/consumequeue/MyTestTopic/7
[root@xxx 7]
00000000000000000000consumequeue 的文件结构如下图:

其中前 8 个字节保存消息在 commitlog 中的偏移量,中间 4 个字节保存消息消息大小,最后 8 个字节保存消息中 tag 的 hashcode。
这里为什么要保存一个 tag 的 hashcode 呢?
如果一个 Consumer 订阅了 TopicA 这个 Topic 中的 Tag1 和 Tag2 这两个 tag,那这个 Consumer 的订阅关系如下图:

可以看到,订阅关系这个对象封装了 Topic、tag 以及所订阅 tag 的 hashcode 集合。
Consumer 发送拉取消息请求时,会把订阅关系传给 Broker(Broker 解析成 SubscriptionData 对象),Broker 使用 consumequeue 获取消息时,首先判断判断最后 8 个字节的 tag hashcode 是否在 SubscriptionData 的 codeSet 中,如果不在就跳过,如果存在就根据偏移量从 commitlog 中获取消息返回给 Consumer。如下图:
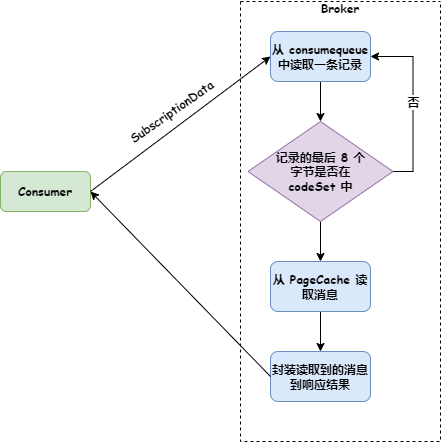
参考下面代码:
public boolean isMatchedByConsumeQueue(Long tagsCode, ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit cqExtUnit) {
return subscriptionData.getSubString().equals(SubscriptionData.SUB_ALL)
|| subscriptionData.getCodeSet().contains(tagsCode.intValue());
}跟 commitlog 一样,consumequeue 也会使用 mmap 映射为 MappedFile 存储对象。
4、index 文件
为了支持按照消息的某一个属性来查询,RocketMQ 引入了 index 索引文件。index 文件结构如下图:
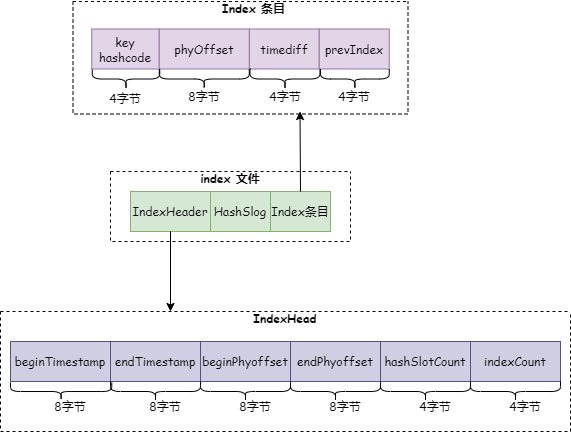
主要由三部分组成:IndexHeader、HashSlog 和 Index 条目。跟 commitlog 一样,Index 文件也会使用 mmap 映射为 MappedFile 存储对象。
(1)IndexHeader
IndexHead 由如下 6 个属性组成,这些熟悉定义在类 IndexHeader:
1.beginTimestamp:index 文件中最小的消息存储时间。
2.endTimestamp:index 文件中最大的消息存储时间。
3.beginPhyoffset:index 文件中包含的消息中最小的 commitlog 偏移量。
4.endPhyoffset:index 文件中包含的消息中最大的 commitlog 偏移量。
5.hashSlotcount:index 文件中包含的 hash 槽的数量。
6.indexCount:index 文件中包含的 index 条目个数。
(2)HashSlog
HashSlot 就是 Java HashMap 中的 hash 槽,默认有 500 万个。每个 HashSlot 使用 4 个字节 int 类型保存最后一个 Index 条目的位置。
注意:上面为什么说最后一个 Index 条目?因为 Index 条目保存的是 key 的 hashcode,存在 hash 冲突的情况下,HashSlot 使用链表法解决,在 Index 条目中会保存相同 Hash 值的前一个条目位置。如下图:
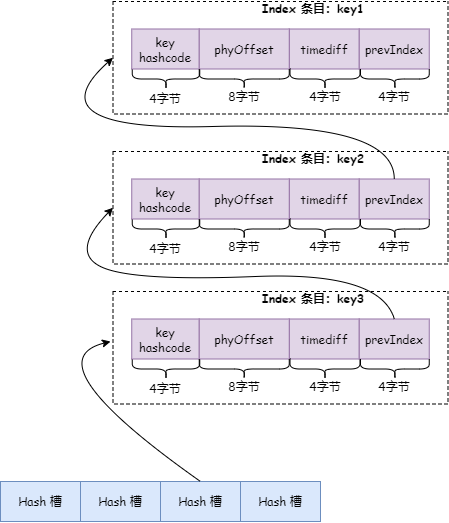
key 为 key1、key2、key3 的三条消息依次写入,并且这 3 个 key 有相同的 hashcode。写入 key1 时,hash 槽保存了 key1 消息的 index 条目位置,写入 key2 时 hash 槽保存了 key2 消息的 index 条目位置,同时 key2 消息 index 条目中的 prevIndex 保存了 key1 消息的 index 条目位置,写入 key3 时 hash 槽保存了 key3 消息的 index 条目位置,同时 key3 消息 index 条目的 prevIndex 保存了 key2 消息的 index 条目位置。
(3)index 条目
index 条目录由 4 个属性组成:
1.key hashcode:要查找消息的 key 的 hashcode。
2.phyOffset:消息在 commitlog 文件中的物理偏移量。
3.timediff:该消息存储时间与 beginTimestamp 的差值。通过 key 查找消息时,在 key 相同的情况下,还要看 timediff 是否在区间范围内 ,不在时间范围内的就不返回,参考下面代码:
long timeRead = this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() + timeDiff;
boolean timeMatched = (timeRead >= begin) && (timeRead <= end);
if (keyHash == keyHashRead && timeMatched) {
phyOffsets.add(phyOffsetRead);
}4.prevIndex:key 发生 hash 冲突后保存相同 hash code 的前一个 index 条目位置。
index 条目默认有 2000 万个。
(4)查找过程
整个查找过程如下图:
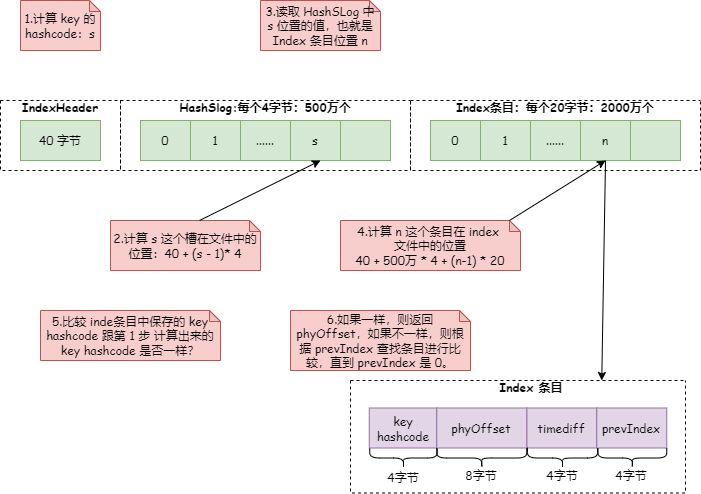
详细代码见 IndexFile 类 selectPhyOffset 这个方法。
5、文件构建
看到这里可能大家会有一个疑问,consumequeue 和 index 文件的内容是什么时候写入呢?
在 MessageStore 初始化的时候会启动一个线程 ReputMessageService,这个线程的逻辑是死循环里面每个 1ms 执行一次,从 commitlog 中获取消息然后写入 consumequeue 和 index 文件。参考下面代码:
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest =
DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.checkMessageAndReturnSize(result.getByteBuffer(), false, false);
int size = dispatchRequest.getBufferSize() == -1 ? dispatchRequest.getMsgSize() : dispatchRequest.getBufferSize();
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
if (size > 0) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.doDispatch(dispatchRequest);
}
}public void doDispatch(DispatchRequest req) {
for (CommitLogDispatcher dispatcher : this.dispatcherList) {
dispatcher.dispatch(req);
}
}下面是 dispatcherList 的定义:
this.dispatcherList = new LinkedList<>();
this.dispatcherList.addLast(new CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue());
this.dispatcherList.addLast(new CommitLogDispatcherBuildIndex());可以看到,即使 Broker 挂了,只要 commitlog 在,就可以重新构建出 consumequeue 和 index 文件。
本文主要介绍了 RocketMQ 的消息存储原理,RocketMQ 的存储很有艺术性,同时理解起来也比较困难。希望本文能带你入门 RocketMQ 的存储。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK