

Java 异步编程 (5 种异步实现方式详解) - mikechen的互联网架构
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/mikechenshare/p/16706624.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.


同步操作如果遇到一个耗时的方法,需要阻塞等待,那么我们有没有办法解决呢?让它异步执行,下面我会详解异步及实现@mikechen
什么是异步?
首先我们先来看看一个同步的用户注册例子,流程如下:
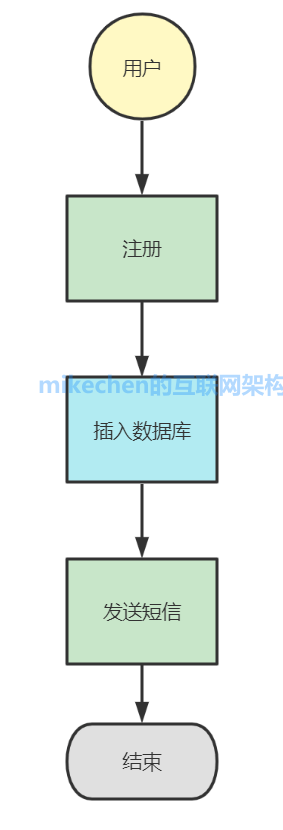
在同步操作中,我们执行到插入数据库的时候,我们必须等待这个方法彻底执行完才能执行“发送短信”这个操作,如果插入数据库这个动作执行时间较长,发送短信需要等待,这就是典型的同步场景。
于是聪明的人们开始思考,如果两者关联性不强,能不能将一些非核心业务从主流程中剥离出来,于是有了异步编程雏形,改进后的流程如下:
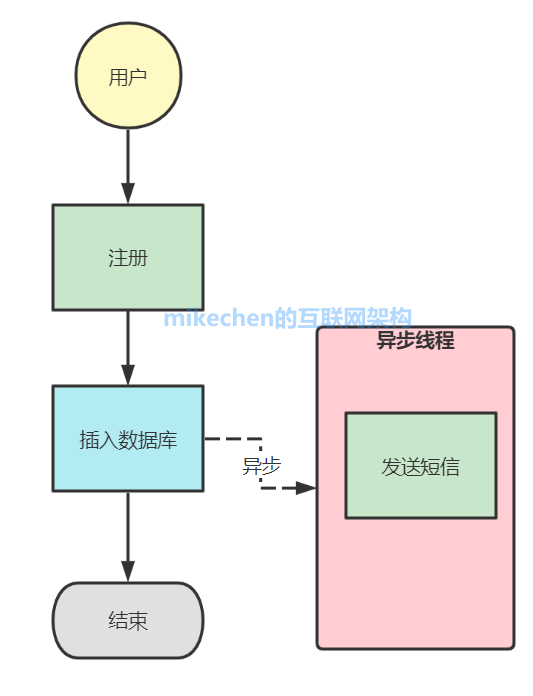
这就是异步编程,它是程序并发运行的一种手段,它允许多个事件同时发生,当程序调用需要长时间运行的方法时,它不会阻塞当前的执行流程,程序可以继续运行。
在聊完异步编程后,那么我们一起来看看Java里面实现异步编程究竟有哪些方式呢?
一、线程异步
在 Java 语言中最简单使用异步编程的方式就是创建一个 线程来实现,如果你使用的 JDK 版本是 8 以上的话,可以使用 Lambda 表达式 会更加简洁。
public class AsyncThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + this.getName() + ", 执行线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-hello");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 模拟业务流程
// .......
// 创建异步线程
AsyncThread asyncThread = new AsyncThread();
// 启动异步线程
asyncThread.start();
}
当然如果每次都创建一个 Thread线程,频繁的创建、销毁,浪费系统资源,我们可以采用线程池:
private ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool() ;
public void fun() throws Exception {
executor.submit(new Runnable(){
@override
public void run() {
try {
//要执行的业务代码,我们这里没有写方法,可以让线程休息几秒进行测试
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.print("睡够啦~");
}catch(Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("报错啦!!");
}
}
});
}
将业务逻辑封装到 Runnable 或 Callable 中,交由 线程池 来执行。
二、Future异步
上述方式虽然达到了多线程并行处理,但有些业务不仅仅要执行过程,还要获取执行结果,后续提供在JUC包增加了Future。
从字面意思理解就是未来的意思,但使用起来却着实有点鸡肋,并不能实现真正意义上的异步,获取结果时需要阻塞线程,或者不断轮询。
@Test
public void futureTest() throws Exception {
System.out.println("main函数开始执行");
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
Future<Integer> future = executor.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("===task start===");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("===task finish===");
return 3;
}
});
//这里需要返回值时会阻塞主线程,如果不需要返回值使用是OK的。倒也还能接收
//Integer result=future.get();
System.out.println("main函数执行结束");
System.in.read();
}
三、CompletableFuture异步
Future 类通过 get() 方法阻塞等待获取异步执行的运行结果,性能比较差。
JDK1.8 中,Java 提供了 CompletableFuture 类,它是基于异步函数式编程。相对阻塞式等待返回结果,CompletableFuture 可以通过回调的方式来处理计算结果,实现了异步非阻塞,性能更优。
CompletableFuture 实现了 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口, 并提供了多种实现异步编程的方法,如supplyAsync, runAsync以及thenApplyAsync。
下面我们使用CompletableFuture来实现上面的例子:
CompletableFuture<Long> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> factorial(number));
while (!completableFuture.isDone()) {
System.out.println("CompletableFuture is not finished yet...");
}
long result = completableFuture.get();
我们不需要显式使用 ExecutorService,CompletableFuture 内部使用了 ForkJoinPool 来处理异步任务,这使得我们的代码变的更简洁。
四、SpringBoot @Async异步
在@Async注解之前,使用多线程需要使用JDK的原生方法,非常麻烦,当有了@Async之后就比较简单了。
首先,使用 @EnableAsync 启用异步注解:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class StartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StartApplication.class, args);
}
}
自定义线程池:
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolConfiguration {
@Bean(name = "defaultThreadPoolExecutor", destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public ThreadPoolExecutor systemCheckPoolExecutorService() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 10, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10000),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("default-executor-%d").build(),
(r, executor) -> log.error("system pool is full! "));
}
}
在异步处理的方法上添加注解 @Async ,当对 execute 方法 调用时,通过自定义的线程池 defaultThreadPoolExecutor 异步化执行 execute 方法
@Service
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Async("defaultThreadPoolExecutor")
public Boolean execute(Integer num) {
System.out.println("线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " , 任务:" + num);
return true;
}
}
用 @Async 注解标记的方法,称为异步方法。在spring boot应用中使用 @Async 很简单:
-
调用异步方法类上或者启动类加上注解 @EnableAsync
-
在需要被异步调用的方法外加上 @Async
-
所使用的 @Async 注解方法的类对象应该是Spring容器管理的bean对象;
五、Guava异步
Guava 提供了 ListenableFuture 类来执行异步操作
1.首先我们需要添加 guava 的maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>28.2-jre</version>
</dependency>
2.现在我们使用ListenableFuture来实现我们之前的例子:
ExecutorService threadpool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); ListeningExecutorService service = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(threadpool); ListenableFuture<Long> guavaFuture = (ListenableFuture<Long>) service.submit(()-> factorial(number)); long result = guavaFuture.get();
这里使用MoreExecutors获取ListeningExecutorService类的实例,然后ListeningExecutorService.submit执行异步任务,并返回 ListenableFuture实例。
Java异步编程小结
异步编程受到了越来越多的关注,尤其是在 IO 密集型的业务场景中,相比传统的同步开发模式,异步编程的优势越来越明显,希望以上介绍的5种Java异步编程方式对你有所帮助!
陈睿|mikechen,10年+大厂架构经验,《BAT架构技术500期》系列文章作者,分享十余年BAT架构经验以及面试心得!
阅读mikechen的互联网架构更多技术文章合集
Recommend
-
 2
2
JVM内存模型和Java内存模型都是面试的热点问题,名字看感觉都差不多,实际上他们之间差别还...
-
 4
4
幂等性在我们的工作中无处不在,无论是支付场景还是下订单等核心场景都会涉及,也是分布式...
-
 6
6
MyBatis 是 Java 生态中非常著名的一款 ORM 框架,目前在一线互联网大厂中...
-
 1
1
很多技术框架都使用NIO技术,学习和掌握Java NIO技术对于高性能、高并发网络的应用是非常关...
-
 5
5
如果说 IOC 是 Spring 的...
-
 5
5
分布式架构会...
-
 5
5
Java...
-
 2
2
雪花算法简...
-
 2
2
...
-
 1
1
Promise, async, await实现异步编程,代码详解
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK