

TFrecord写入与读取 - 多事鬼间人
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/yc0806/p/16518994.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

TFrecord写入与读取
Protocol buffers are Google's language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data.
Protocol buffers是由Google设计的无关程序语言、平台的、具有可扩展性机制的序列化数据结构。
The
tf.train.Examplemessage (or protosun) is a flexible message type that represents a{"string": value}mapping. It is designed for use with TensorFlow and is used throughout the higher-level APIs such as TFX.
tf.traom.Example是一种表示{“string”:value}映射关系的灵活的消息类型。它被设计用于TensorFlow以及更加高级的API。
tf.train.Example
一个tf.train.Example的实例是构建的是数个{”string“: tf.train.Feature}映射。
其中,tf.train.Feature可以是以下三种,其他类型的数据格式可以通过一个或多个Feature组合描述:
- tf.train.BytesList
- tf.train.FloatList
- tf.train.Int64List
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.io.TFRecordWriter("train.tfrecords","GZIP") as writer:
for i in range(200): # Assume there are 200 records
example_proto = tf.train.Example(
features=tf.train.Features(
feature= {
'feature0':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.int64List(value=feature0)),
'feature1':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=feature1)),
'feature2':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.BtyesList(value=feature2)),
'label':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.int64List(value=[label])),
}
)
)
writer.write(example_proto.SerializeToString())
tf.io.parse_single_example 和 tf.io.parse_example
One might see performance advantages by batching
Exampleprotos withparse_exampleinstead of using this function directly.
对Example protos分批并使用parse_example会比直接使用parse_single_example有性能优势。
# with map_func using tf.io.parse_single_example
def map_func(example):
# Create a dictionary describing the features.
feature_description = {
'feature0': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature0], tf.int64),
'feature1': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature1], tf.float32),
'feature2': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature2], tf.int64),
'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64),
}
parsed_example = tf.io.parse_single_example(example, features=feature_description)
feature0 = parsed_example["feature0"]
feature1 = parsed_example["feature1"]
feature2 = parsed_example["feature2"]
label = parsed_example["label"]
return image, label
raw_dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("train.tfrecords","GZIP")
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.map(map_func=map_func)
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
以下代码和前者的区别在于map_func中使用tf.io.parse_example替换tf.io.parse_single_example,并在调用map方法前先调用batch方法。
# with map_func using tf.io.parse_example
def map_func(example):
# Create a dictionary describing the features.
feature_description = {
'feature0': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature0], tf.int64),
'feature1': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature1], tf.float32),
'feature2': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature2], tf.int64),
'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64),
}
parsed_example = tf.io.parse_example(example, features=feature_description)
# features can be modified here
feature0 = parsed_example["feature0"]
feature1 = parsed_example["feature1"]
feature2 = parsed_example["feature2"]
label = parsed_example["label"]
return image, label
raw_dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(["./1.tfrecords", "./2.tfrecords"])
raw_dataset = raw_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.map(map_func=map_func)
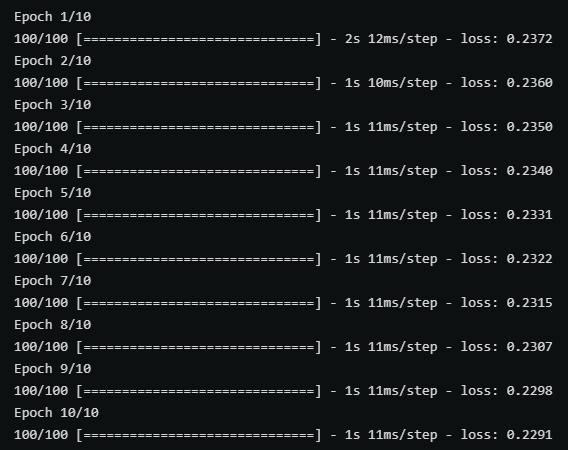
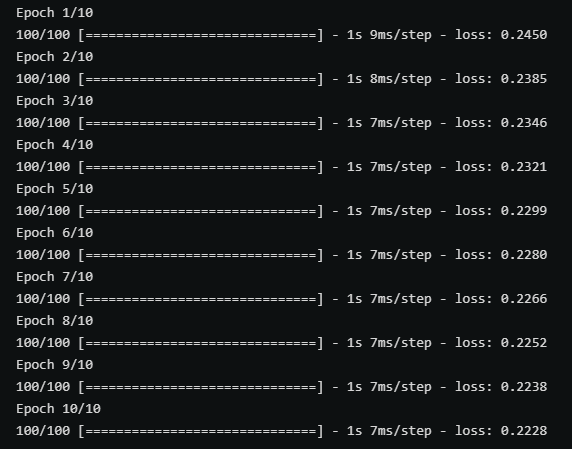
以上两张图分别时使用带有parse_single_example和parse_example的map_func在训练中的性能对比,后者(parse_example)明显性能更优秀。
不定长数据的读写 RaggedFeature
对于不定长且未padding的数据,写入过程中和定长数据没有区别,但在读取过程中需要使用tf.io.RaggedFeature替代tf.io.FixedLenFeature。
def map_func(example):
# Create a dictionary describing the features.
feature_description = {
'feature': tf.io.RaggedFeature(tf.float32),
'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64),
}
parsed_example = tf.io.parse_example(example, features=feature_description)
# feature = parsed_example["feature"]
feature = parsed_example["feature"].to_tensor(shape=[1,100])
label = parsed_example["label"]
return feature, label
raw_dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("train_unpadding.tfrecords").batch(1000)
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.map(map_func=map_func)
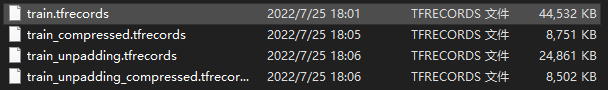
下图对比了是否对不定长数据进行padding分别在压缩和未压缩的情况下的文件大小。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK