Calico引入eBPF
source link: https://luckymrwang.github.io/2022/05/10/Calico%E5%BC%95%E5%85%A5eBPF/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Calico引入eBPF | iBlog
Calico团队在3.13版本引入了eBPF,这个新的dataplane与传统的linux dataplane有哪些区别呢?
- 它可以扩展到更高的吞吐量。
- 每个GBit使用更少的CPU。
- 它具有对Kubernetes服务的本机支持(无需kube-proxy),该支持:
- 减少服务数据包的第一个数据包延迟。
- 一直保留到外部主机的外部客户端源IP地址。
- 支持DSR(直接服务器返回),以实现更高效的服务路由。
- 与kube-proxy相比,使用更少的CPU来保持数据平面同步。
此外,社区对新dataplane进行了性能测试,在短连接延时、服务访问时间、cpu使用率等方面,性能都有明显提升,详见:https://www.tigera.io/blog/introducing-the-calico-ebpf-dataplane/
本文主要目的是通过分析calico源码,弄明白eBPF是如何被引入到calico中的。
Calico引入了多个eBPF hook点,本文重点分析connect_time_loadbalancer,即上面讲到的第一条支持:“减少服务数据包的第一个数据包延迟”
相关的工作是在Calico的felix项目中实现的
入口处:felix/dataplane/linux/int_dataplane.go 的 NewIntDataplaneDriver() 函数,进行dataplane的初始化
首先会判断是否开启了BPF,如果是开启状态,则进行以下操作:
1)注册 map manager,该manager的作用是负责管理ebpf的map(map用于userspace和kernel之间进行数据的共享)
2)注册endpoint manager,该manager的作用是负责各种ep的管理,包括host、workload等
3)创建各种map,比如nat的frontendMap、backendMap、routeMap、conntrackMap等
4)开启kube-proxy,注意此kube-proxy并非kubernetes的kube-proxy,而是proxy的一个封装,负责和kubernetes通信,维护各种map中的信息
5)若BPFConnTimeEnabled开启,则安装connect_time_loadbalancer,即加载相关的eBPF程序
6)启动dataplane(这部分暂不涉及connect_time_loadbalancer,本文暂不分析)
下面我们重点看第5)步代码是如何实现的
代码分析(加载eBPF程序)
入口 bpf/nat/connecttime.go的 InstallConnectTimeLoadBalancer() 函数
func InstallConnectTimeLoadBalancer(frontendMap, backendMap, rtMap bpf.Map, cgroupv2 string, logLevel string) error {
bpfMount, err := bpf.MaybeMountBPFfs() //挂载bpf路径,默认的挂载路径是:/sys/fs/bpf
if err != nil {
log.WithError(err).Error("Failed to mount bpffs, unable to do connect-time load balancing")
return err
}
cgroupPath, err := ensureCgroupPath(cgroupv2) //配置cgoupv2,位于/run/calico/cgroupv2/
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "failed to set-up cgroupv2")
}
repin := false //检查相关map
if pm, ok := frontendMap.(*bpf.PinnedMap); ok {
repin = pm.RepinningEnabled()
}
sendrecvMap := SendRecvMsgMap(&bpf.MapContext{
RepinningEnabled: repin,
})
err = sendrecvMap.EnsureExists()
if err != nil {
return errors.WithMessage(err, "failed to create sendrecv BPF Map")
}
maps := []bpf.Map{frontendMap, backendMap, rtMap, sendrecvMap}
err = installProgram("connect", "4", bpfMount, cgroupPath,logLevel, maps...) // 安装calico_connect_v4 bpf程序
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = installProgram("sendmsg", "4", bpfMount, cgroupPath, logLevel, maps...) //安装calico_sendmsg_v4 bpf程序
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = installProgram("recvmsg", "4", bpfMount, cgroupPath, logLevel, maps...) //安装calico_recvmsg_v4 bpf程序
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = installProgram("sendmsg", "6", bpfMount, cgroupPath, logLevel) //安装calico_sendmsg_v6 bpf程序
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = installProgram("recvmsg", "6", bpfMount, cgroupPath, logLevel, sendrecvMap) // 安装calico_recvmsg_v4 bpf程序
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
进入 installProgram() 函数,看如何加载程序
func installProgram(name, ipver, bpfMount, cgroupPath, logLevel string, maps ...bpf.Map) error {
progPinDir := path.Join(bpfMount, "calico_connect4")
_ = os.RemoveAll(progPinDir)
var filename string
//获取bpf程序所在的位置
if ipver == "6" {
filename = path.Join(bpf.ObjectDir, ProgFileName(logLevel, 6))
} else {
filename = path.Join(bpf.ObjectDir, ProgFileName(logLevel, 4))
}
args := []string{"prog", "loadall", filename, progPinDir, "type", "cgroup/" + name + ipver}
for _, m := range maps {
args = append(args, "map", "name", m.GetName(), "pinned", m.Path())
}
cmd := exec.Command("bpftool", args...) //使用bpftool加载ebpf程序
log.WithField("args", cmd.Args).Info("About to run bpftool")
progName := "calico_" + name + "_v" + ipver
out, err := cmd.CombinedOutput()
if err != nil {
err = errors.Wrapf(err, "failed to load program %s", progName)
goto out
}
//使用bpftool将ebpf程序attach到相应的挂载点。此处的挂载点是socket hook,由于关cgroup关联,因此对于calico这个cgroup下的所有程序,执行socket api时都会经过这个bpf程序
cmd = exec.Command("bpftool", "cgroup", "attach", cgroupPath,
name+ipver, "pinned", path.Join(progPinDir, progName))
log.WithField("args", cmd.Args).Info("About to run bpftool")
out, err = cmd.CombinedOutput()
if err != nil {
err = errors.Wrapf(err, "failed to attach program %s", progName)
goto out
}
out:
if err != nil {
log.WithError(err).WithField("output", string(out)).Error("Failed install cgroup program.")
}
return nil
}
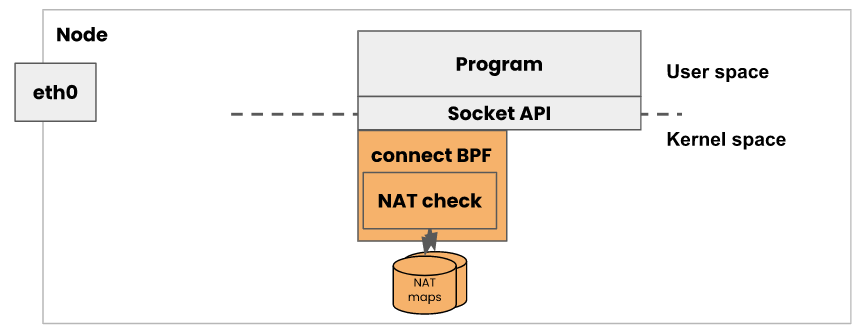
下图是加载attach bpf程序后,用户进程调用socket api时的路径。在建立connect、recvmsg、sendmsg时都会经过这个程序进行处理。而这个ebpf程序所做的工作就是:判断是否要访问的是k8s service,如果是的话,直接将请求转发到后端的pod上,这样就不在需要做nat了,节省了所有的nat开销。即实现了:“减少服务数据包的第一个数据包延迟”
image
接下来看看bpf程序是如何实现的,共实现三个section bpf-gpl/connect_balancer.c
__attribute__((section("calico_connect_v4"))) //section 1:在建立connection时,做nat转发,将请求转发至后端的pod
int cali_ctlb_v4(struct bpf_sock_addr *ctx)
{
CALI_DEBUG("calico_connect_v4\n");
/* do not process anything non-TCP or non-UDP, but do not block it, will be
* dealt with somewhere else.
*/
if (ctx->type != SOCK_STREAM && ctx->type != SOCK_DGRAM) {
CALI_INFO("unexpected sock type %d\n", ctx->type);
goto out;
}
uint8_t ip_proto;
switch (ctx->type) {
case SOCK_STREAM:
CALI_DEBUG("SOCK_STREAM -> assuming TCP\n");
ip_proto = IPPROTO_TCP;
break;
case SOCK_DGRAM:
CALI_DEBUG("SOCK_DGRAM -> assuming UDP\n");
ip_proto = IPPROTO_UDP;
break;
default:
CALI_DEBUG("Unknown socket type: %d\n", (int)ctx->type);
goto out;
}
do_nat_common(ctx, ip_proto);
out:
return 1;
}
__attribute__((section("calico_sendmsg_v4"))) //section2 : sendmsg只处理udp相关的发包操作,tcp忽略,因为tcp为面向连接的传输
int cali_ctlb_sendmsg_v4(struct bpf_sock_addr *ctx)
{
CALI_DEBUG("sendmsg_v4 %x:%d\n",
be32_to_host(ctx->user_ip4), be32_to_host(ctx->user_port)>>16);
if (ctx->type != SOCK_DGRAM) {
CALI_INFO("unexpected sock type %d\n", ctx->type);
goto out;
}
do_nat_common(ctx, IPPROTO_UDP);
out:
return 1;
}
__attribute__((section("calico_recvmsg_v4"))) // section3: recvmsg也只处理udp相关的收包操作,tcp忽略。因为tcp为面向连接的传输
int cali_ctlb_recvmsg_v4(struct bpf_sock_addr *ctx)
{
CALI_DEBUG("recvmsg_v4 %x:%d\n", be32_to_host(ctx->user_ip4), ctx_port_to_host(ctx->user_port));
if (ctx->type != SOCK_DGRAM) {
CALI_INFO("unexpected sock type %d\n", ctx->type);
goto out;
}
uint64_t cookie = bpf_get_socket_cookie(ctx);
CALI_DEBUG("Lookup: ip=%x port=%d(BE) cookie=%x",ctx->user_ip4, ctx->user_port, cookie);
struct sendrecv4_key key = {
.ip = ctx->user_ip4,
.port = ctx->user_port,
.cookie = cookie,
};
struct sendrecv4_val *revnat = cali_v4_srmsg_lookup_elem(&key);
if (revnat == NULL) {
CALI_DEBUG("revnat miss for %x:%d\n",
be32_to_host(ctx->user_ip4), ctx_port_to_host(ctx->user_port));
/* we are past policy and the packet was allowed. Either the
* mapping does not exist anymore and if the app cares, it
* should check the addresses. It is more likely a packet sent
* to server from outside and no mapping is expected.
*/
goto out;
}
ctx->user_ip4 = revnat->ip;
ctx->user_port = revnat->port;
CALI_DEBUG("recvmsg_v4 rev nat to %x:%d\n",
be32_to_host(ctx->user_ip4), ctx_port_to_host(ctx->user_port));
out:
return 1;
}
实际的nat操作是do_nat_common()来做的
static CALI_BPF_INLINE void do_nat_common(struct bpf_sock_addr *ctx, uint8_t proto)
{
/* We do not know what the source address is yet, we only know that it
* is the localhost, so we might just use 0.0.0.0. That would not
* conflict with traffic from elsewhere.
*
* XXX it means that all workloads that use the cgroup hook have the
* XXX same affinity, which (a) is sub-optimal and (b) leaks info between
* XXX workloads.
*/
nat_lookup_result res = NAT_LOOKUP_ALLOW;
uint16_t dport_he = (uint16_t)(be32_to_host(ctx->user_port)>>16);
struct calico_nat_dest *nat_dest;
nat_dest = calico_v4_nat_lookup(0, ctx->user_ip4, proto, dport_he, &res); //从map中查找k8s service相关的信息
if (!nat_dest) {
CALI_INFO("NAT miss.\n");
goto out;
}
uint32_t dport_be = host_to_ctx_port(nat_dest->port);
ctx->user_ip4 = nat_dest->addr; //修改socket地址的目的地址为后端pod
ctx->user_port = dport_be;
out:
return;
}
- 有关 eBPF 数据平面的更多信息和性能指标,请参阅公告博客文章。
- 如果您想在 Kubernetes 集群中尝试 eBPF 模式,请遵循启用 eBPF 数据平面指南。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK