

Seata源码分析——SessionManager - 飞僧明天起飞
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/leung-Gabriel/p/16322417.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

我们知道Seata服务端TC在全局事务中需要协调TM,RM分工干活,一个全局事务的也是由多个分支事务组成的,那么TC端必须要对这些全局事务和分支事务进行管理,比如事务的创建、更新、删除...我们今天就来聊一聊Seata中的事务管理者SessionManager。
*这里为什么叫SessionManager:有博客说Seata的中的事务也叫会话,会话管理器也叫事务管理器。我们就这样叫吧
事务管理器
SessionManager
SessionManager是一个接口,我们来看它的继承关系:
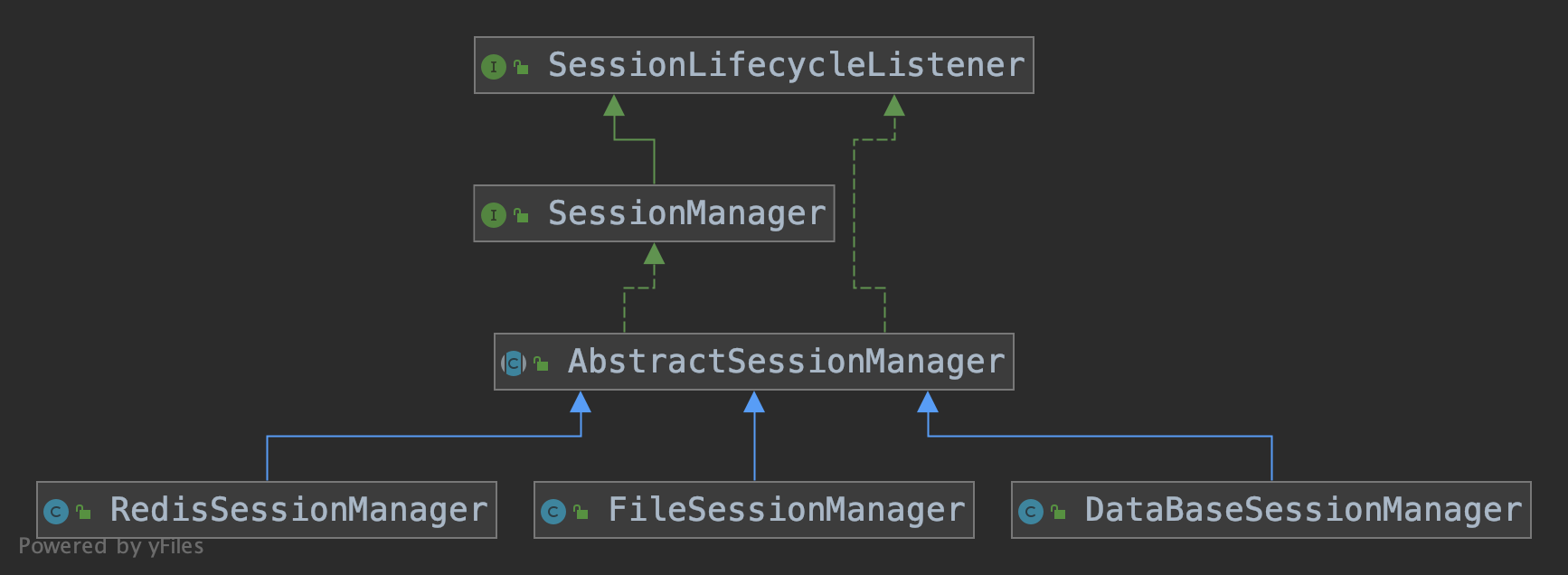
*这种结构还挺常见的,Seata的Netty模块也是这样,一个顶级接口,一个抽象类,然后下面就是具体模式的实现类。
SessionLifecycleListener
- 首先它继承了接口SessionLifecycleListener,这是一个会话生命周期的监听器,(使用了观察者模式),此接口定义了一系列要监听的事件:
public interface SessionLifecycleListener {
/**
* 监听全局事务的开启,当处理全局事务开启请求时,会调用该方法
*/
void onBegin(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听全局事务对象GlobalSession的状态变化,只要是GlobalSession的状态发生变化,就会调用该方法
*/
void onStatusChange(GlobalSession globalSession, GlobalStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听分支事务状态的变化,在处理分支状态报告请求时,会调用该方法
*/
void onBranchStatusChange(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession, BranchStatus status)
throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听新的分支事务注册
*/
void onAddBranch(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听分支事务从全局事务对象中移除,
* 当处理全局事务回滚请求全局事务提交请求时,都会有移除分支事务的动作,因此都会触发该方法
*/
void onRemoveBranch(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听全局事务关闭,也就是监听GlobalSession的close方法。
* 在处理全局事务提交请求和全局事务回滚请求时,都会调用GlobalSession的close方法。
*/
void onClose(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 监听全局事务终止,也就是监听GlobalSession的end方法。
* 当要求全局事务提交或者回滚时,无论最后成功与否,seata都会调用GlobalSession的end方法,因此都会触发onEnd
*/
void onEnd(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException;
}
SessionManager则定义了GlobalSession状态发生变化时应该执行的动作方法
public interface SessionManager extends SessionLifecycleListener, Disposable {
/**
* 将全局事务对象添加到会话管理器中,当全局事务异步提交或者异步回滚时,都会调用该方法
*/
void addGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 根据XID查找GlobalSession
*/
GlobalSession findGlobalSession(String xid) ;
/**
* 不同的存储模式下,本方法和上面的方法实现不同,如果存储模式是file,则两个方法完全一致,
* 如果存储模式是db,则上面的方法相当于调用findGlobalSession(xid, true)
* 如果第二个参数为true,表示返回的GlobalSession对象中带有分支事务集合
*/
GlobalSession findGlobalSession(String xid, boolean withBranchSessions);
/**
* 更新事务对象的状态
*/
void updateGlobalSessionStatus(GlobalSession session, GlobalStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 从管理器中移除GlobalSession
* 当异步提交重试超时时,会调用该方法
*/
void removeGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 向GlobalSession中添加分支事务对象,当分支事务注册时,会调用该方法
*/
void addBranchSession(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 更新分支事务状态
*/
void updateBranchSessionStatus(BranchSession session, BranchStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 从全局事务中移除分支事务,当全局事务提交或者回滚时,会调用该方法
*/
void removeBranchSession(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession session) throws TransactionException;
/**
* 返回所有的全局会话对象
*/
Collection<GlobalSession> allSessions();
/**
* 根据条件查找符合要求的GlobalSession
*/
List<GlobalSession> findGlobalSessions(SessionCondition condition);
/**
* 对全局事务对象加锁,当修改全局事务对象的状态时,都会加锁
*/
<T> T lockAndExecute(GlobalSession globalSession, GlobalSession.LockCallable<T> lockCallable)
throws TransactionException;
}
AbstractSessionManager
AbstractSessionManager是下一层的封装,它有三个实现类,分别对应三种存储模式:文件,数据库和Redis
它实现了SessionManager中定义的方法,还增加了一个重要的方法:writeSession,对Session管理的方法大多都直接或间接地调用了writeSession;我们简单来看一个:
@Override
public void removeGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("MANAGER[{}] SESSION[{}] {}", name, session, LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE);
}
writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE, session);
}
AbstractSessionManager中还持有一个变量:事务存储管理器,也有三种实现,分别是文件,数据库和Redis。下面就继续分析它。
/**
* The Transaction store manager.
*/
protected TransactionStoreManager transactionStoreManager;
事务存储管理器
上面我们基本了解了Seata的事务管理器,它们的作用是对Seata的事务进行管理,管理好了就要存储起来 。AbstractSessionManager这个类中还持有了TransactionStoreManager,它是真正用来实现存储事务状态的。
下面我们以RedisTransactionStoreManager为例进行分析:
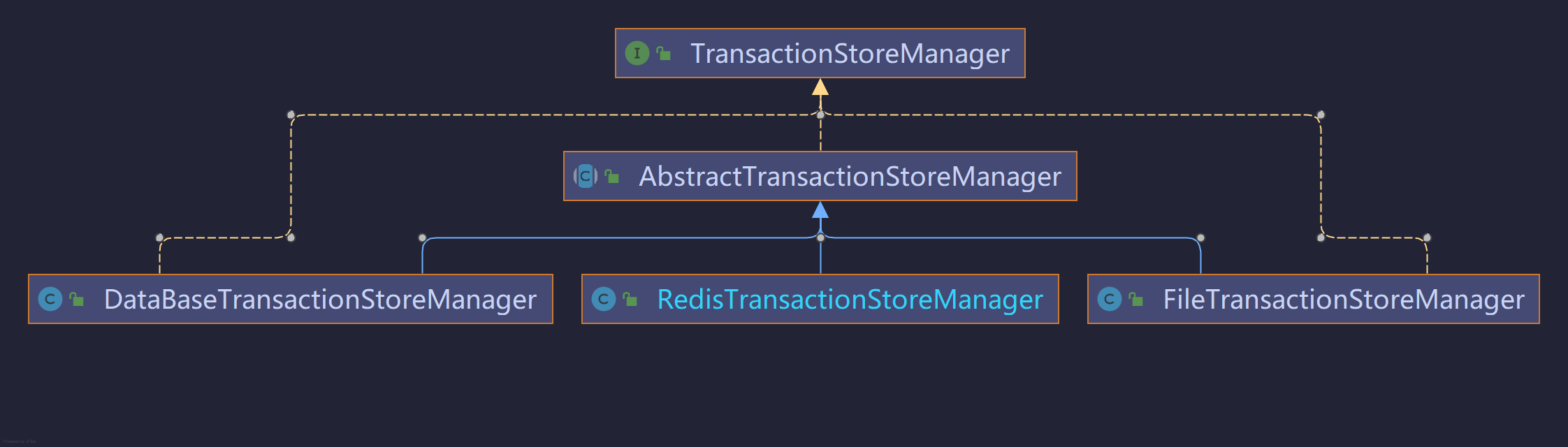
RedisTransactionStoreManager
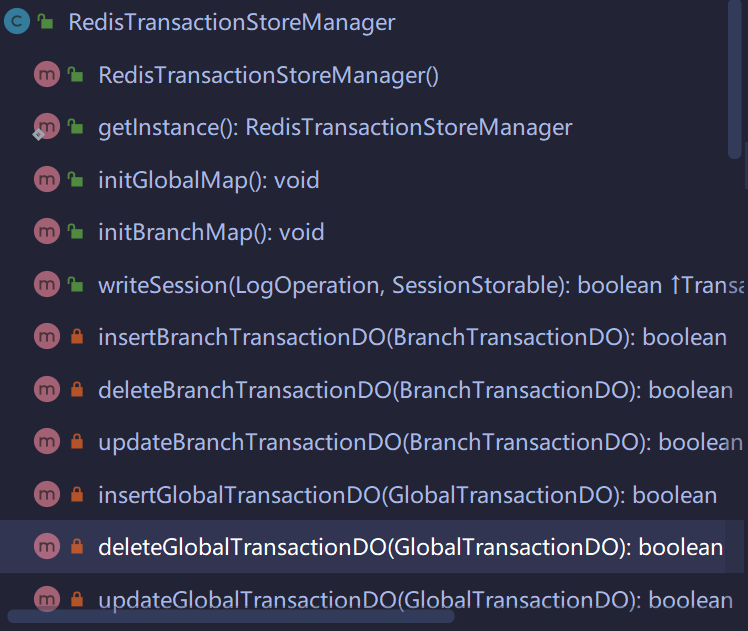
可以看到有不少insert,delete的操作,说明这里就真正将事务信息存到Redis的逻辑了,我们挑一个来看一下:
/**
* Insert the global transaction.
* @param globalTransactionDO
* @return
*/
// GlobalTransactionDO:要插入数据库的类,和global_table的字段是一一对应的
private boolean insertGlobalTransactionDO(GlobalTransactionDO globalTransactionDO) {
// 获取全局事务的键
String globalKey = buildGlobalKeyByTransactionId(globalTransactionDO.getTransactionId());
//使用了Jedis和Pipeline
try (Jedis jedis = JedisPooledFactory.getJedisInstance(); Pipeline pipelined = jedis.pipelined()) {
Date now = new Date();
//构建要插入的DO
globalTransactionDO.setGmtCreate(now);
globalTransactionDO.setGmtModified(now);
//通过pipeline执行
pipelined.hmset(globalKey, BeanUtils.objectToMap(globalTransactionDO));
pipelined.rpush(buildGlobalStatus(globalTransactionDO.getStatus()), globalTransactionDO.getXid());
pipelined.sync();
return true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RedisException(ex);
}
}
TO BE CONTINUE...
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK