

[Paper] - An Evolutionary Study of Linux Memory Management for Fun and Profit
source link: https://oopsmonk.github.io/posts/2017-06-13-linux-memory-management/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

[Paper] - An Evolutionary Study of Linux Memory Management for Fun and Profit
Memory management主要的功能是page mapping, memory protection, and sharing, 但隨著時間不斷的演進已經算是kernel裡不小的subsystem.
這份研究分析2009~2015年之間4587筆有關memory management(mm)的patches, Linux版本由v2.6.32.1 ~ v4.0-rc4.
Source: An Evolutionary Study of Linux Memory Management for Fun and Profit
Memory Bugs#
5種bugs存在mm: memory error, checking, concurrency, logic and programming.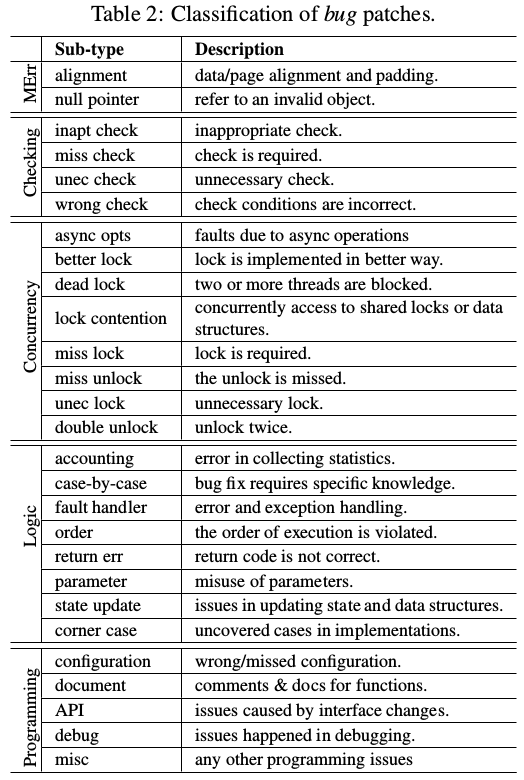
透過heat map可清楚看到主要bug發生地方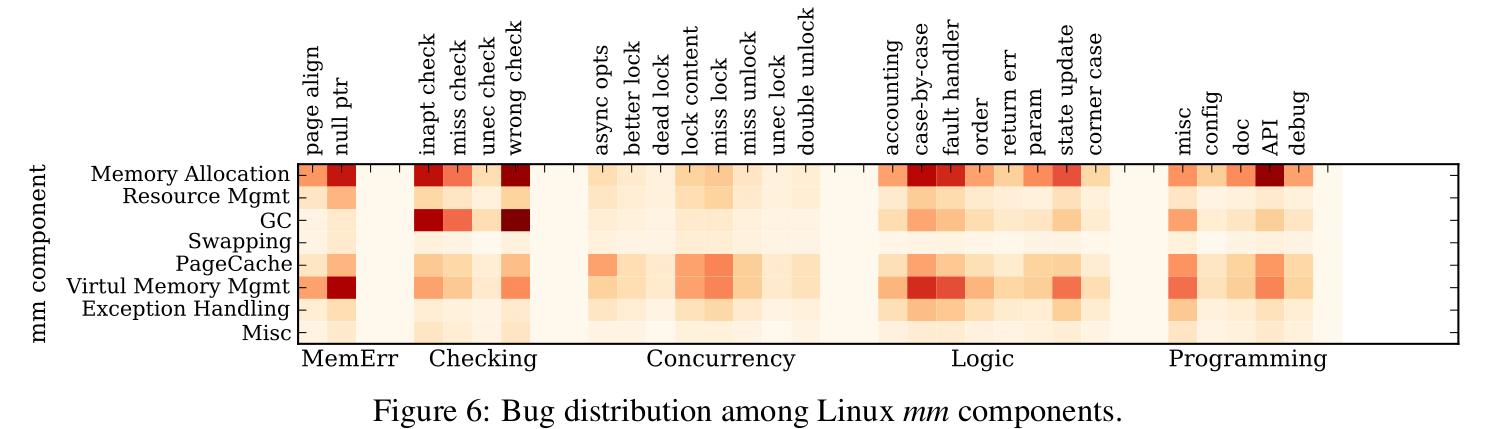
主要的bug fix在: Memory Allocation, Garbage Collection (GC), Virtual Memory Management.
大部份memory leak並不是因為忘了free, 而是錯誤的page fault handling和 free page的計算.
MM較大的問題是很難去track正確的狀態.
Memory optimization#
定義3種optimization patches
- data structure: 避免nested data structure. Scalability的實現, scalability問題是因為locking for atomic access to shared data structures.
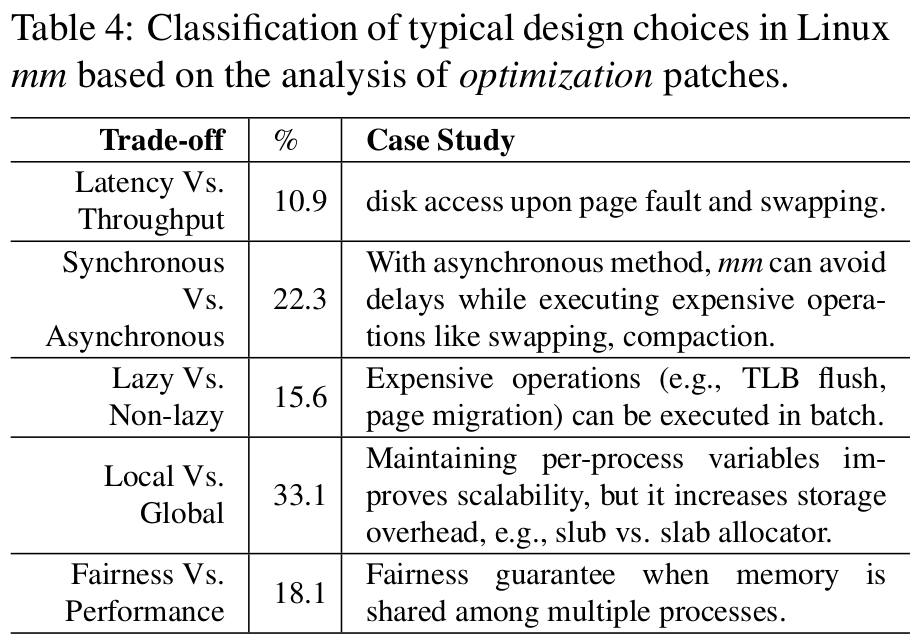
- memory policy: 使用合理的policy design (latency/throughput, sync/async, lazy/non-lazy, local/global, fairness/performance).
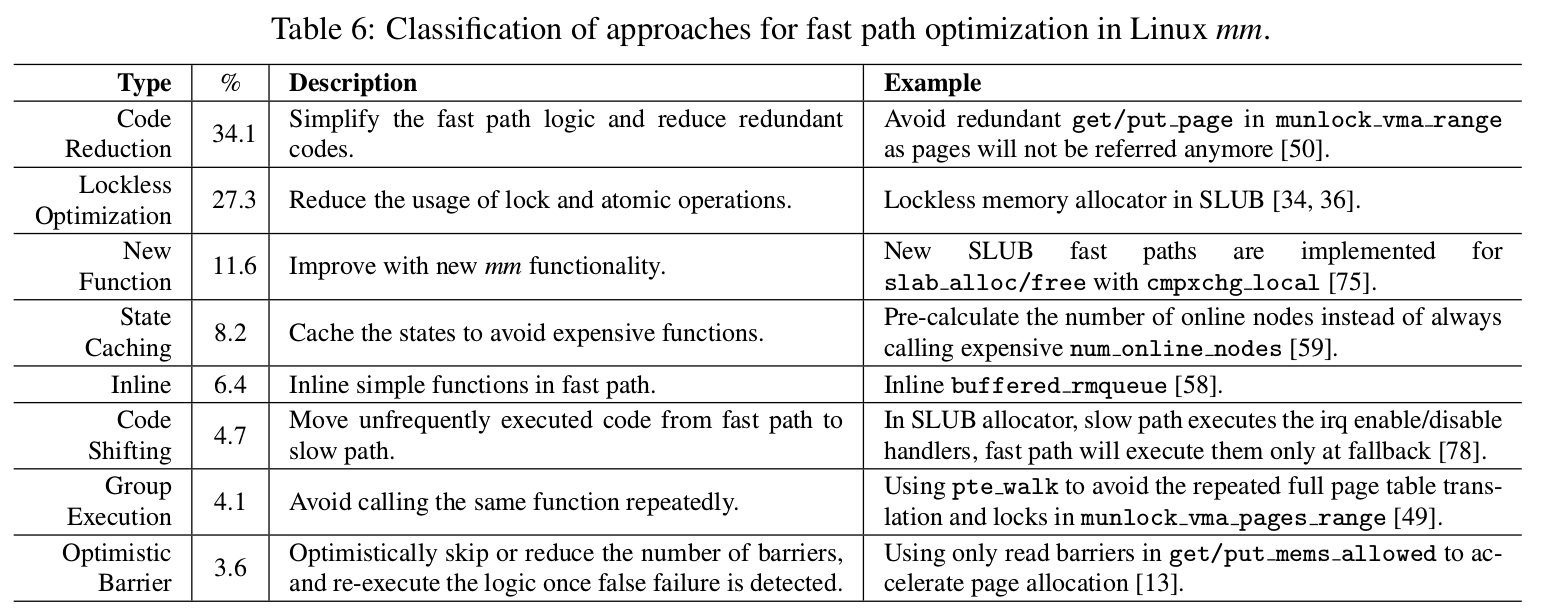
- fast path: 加速頻繁使用的source code, reduction跟lockless optimization是廣泛被使用. Optimistic barrier是為了減少呼叫barrier/fence system call時的synchronous overheads. (Code reduction, lockless optimization, new function, state caching, inline, code shifting, group excution, optimistic barrier)
MM常見的Data structure#
- Radix tree: In adress_space, 主要特色是有效率的存放(sparse)資料.
- Red-black tree: In vm_area_struct, 可快速的search, insert, delete. 相較於AVL 雖然在search上較快但需要額外的空間, insert/delete比較慢, rotation比較困難.
- Bitmap: 通常用在RAM的page indexing.
- List: 廣泛使用的DS, 例如LRU(Last Recently Used) list, 用來追蹤active/inactive pages.
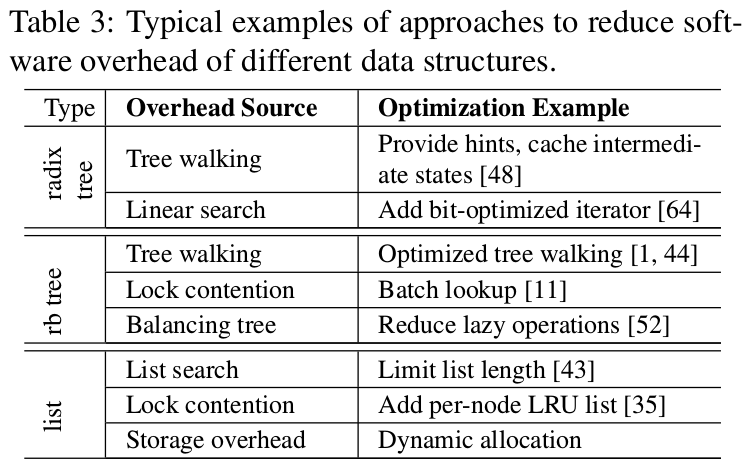
Data structure optimization#
- Reducing software overhead(76.2%): 避免nested data structure.
- Improving scalability for data structure(23.8%): Most of the scalability issues are caused by locking for atomic access to shared data structures.
Policy design tackling trade-offs#
Fast Path#
Memory Semantics#
Memory allocation: buddy system(page_alloc, slab, slub, slob)已成熟的發展, 但在maintain page status上有許多bug, 主要是checking/lock issues.
Memory Resource Controller: 主要的patches都在memcontrol. Concurrency是最大的問題,其次Fault handler(OOM/page fault)在於錯的page status資訊.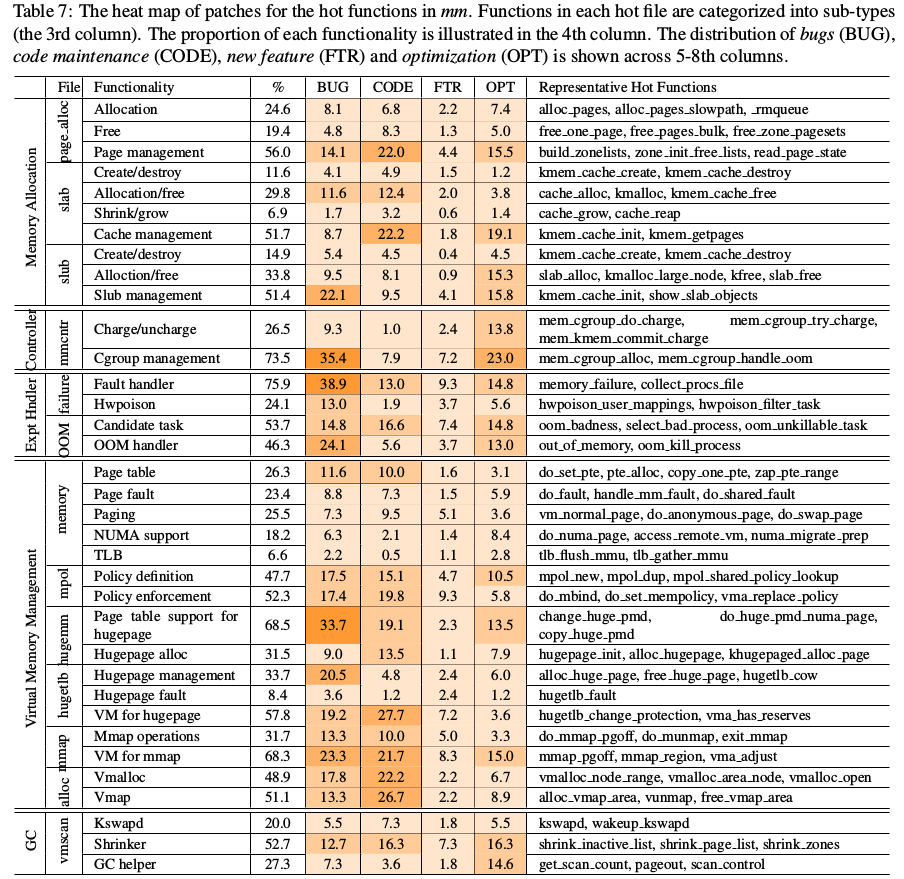
Virtual Memory Management: 是MM裡最大的一個component, 仍存在一堆bug, 因為新的硬體, 新的使用方法(huge page)
Garbage Collection: vmscan的kswapd, shrinker, 和 other GC helper, 大多的patch為shrinker的policy design, 為了減少scan時的overhead和決定哪些space該free. shrinker是造成memory performance難以預測的原因. A scalable and coordinated GC is desirable.
OSDI Next Page »
RaspberryPi3: GLMark2 using weston with DRM backend
Recommend
-
 45
45
除非特别声明,此文章内容采用知识共享署名 3.0许可,代码示例采用Apache 2.0许可。更多细节请查看我们的服务条款。
-
 40
40
:four_leaf_clover: Evolutionary optimization library
-
 49
49
Download ZIP |
-
 73
73
README.md Description A security oriented, feedback-driven, evolutionary, easy-to-use fuzzer with interesting analysis options. See the
-
 43
43
How evolutionary algorithms can speed up optimization of deep neural networks
-
 53
53
Reward Hacking in Evolutionary Algorithms How AI agents cheat the system by doing exactly what they’re told, and what we can learn from them ...
-
 13
13
Practicing Evolutionary Management at Trainline: Evolutionary Purpose and the Magic of Measuring Team Morale
-
 7
7
Many forces are at play behind modern asset liability management (ALM) strategies and liquidit...
-
 9
9
[Paper] A Fault-Tolerant Honeycomb Memory
-
 5
5
Jacking Off Has Evolutionary Benefits Going Back 40 Million Years, Study SaysMasturbation is an "ancient trait" in the world of primates, including humans, according to a study that looked at how self-pleasure helpe...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK