

基于matplotlib的动态甘特图
source link: https://dothinking.github.io/2021-08-15-%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8Ematplotlib%E7%9A%84%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E7%94%98%E7%89%B9%E5%9B%BE/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

基于matplotlib的动态甘特图¶
发布于:2021-08-15 | 分类:python/vba/cpp
本文在作业车间调度问题背景下,基于matplotlib库实现甘特图并监听数据进行动态更新。文中描述的基本流程也适用于其他类型图表的动态更新。最终效果如下。
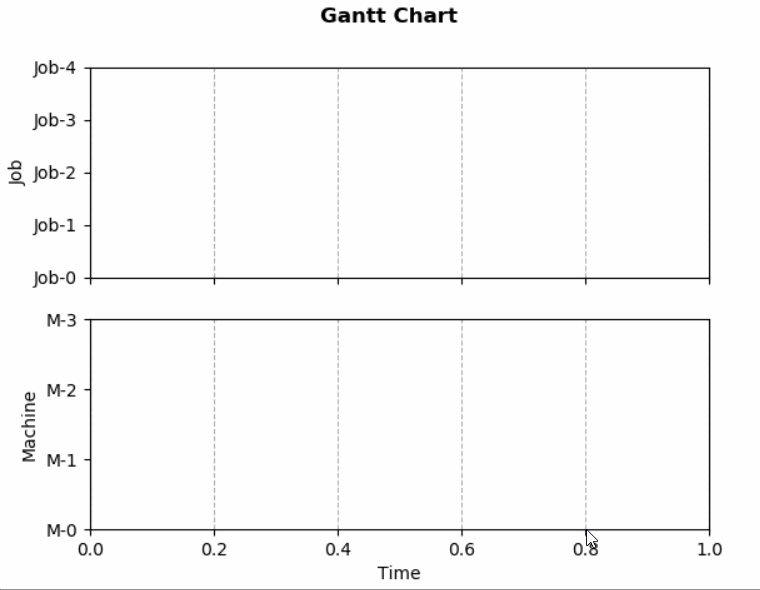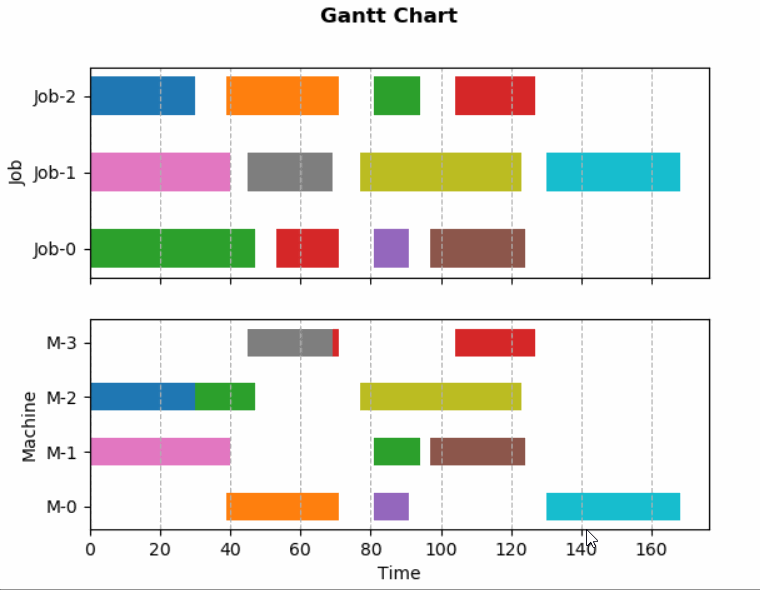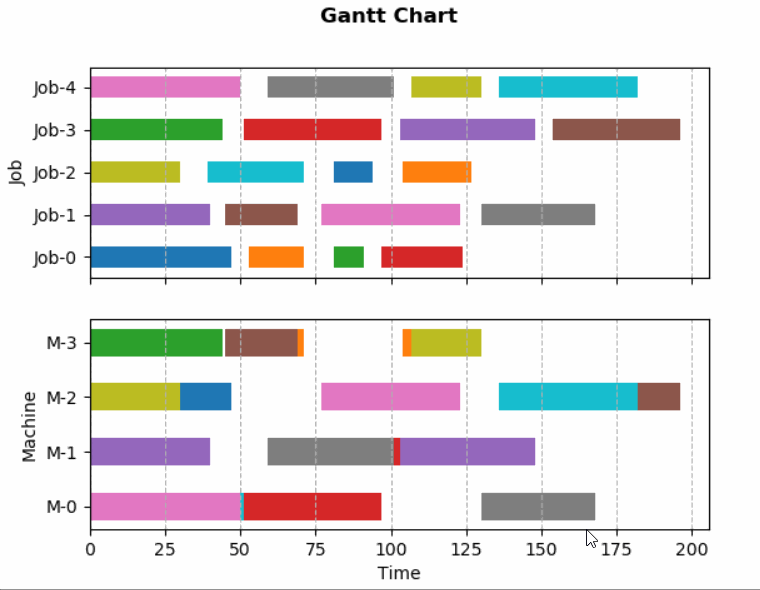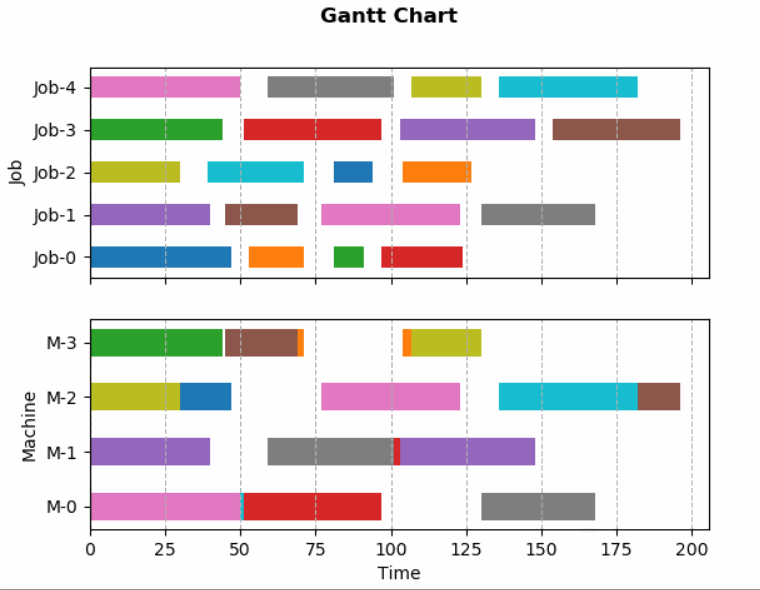
从静态甘特图开始¶
甘特图可以用matplotlib的条形图(水平柱状图)来模拟,横轴为时间,纵轴为工序/任务类型;每一个横条(bar)对应一个工序/任务。
matplotlib.pyplot.barh(y, width, height=0.8, left=None, *, align='center', **kwargs)-
y即为y轴坐标,对应 工序类别,例如从作业的视角即为作业ID,从机器的视角即为机器ID -
width为横条宽度,对应 工序加工时间 -
height为横条高度,没有直接意义 -
left为横条左边界的x坐标,对应 工序开始时间
通常,我们可以画出两类甘特图:
-
项目/作业视角,项目任务或者作业工序的时间安排
-
资源/设备视角,分配到同类资源/设备上的任务/工序的时间安排
本文将其绘制为同一幅图的两张子图,效果及代码如下。其中,工序属性用一个四元组表示:(作业号,机器号,开始时间,加工时长)。
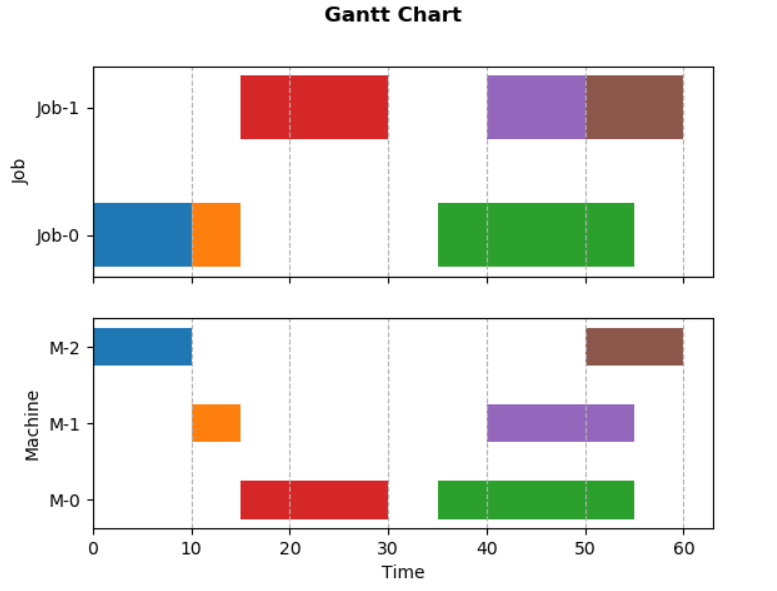
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# dummy data:
# - job number
# - machine number
# - task properties: (job id, machine id, start time, duration)
num_job, num_machine = 2, 3
tasks = [(0,2,0,10), (0,1,10,5), (0,0,35,20), (1,0,15,15),(1,1,40,15), (1,2,50,10)]
# create two subplots: job view and machine view
fig, (gnt_job, gnt_machine) = plt.subplots(2,1, sharex=True)
# title
fig.suptitle('Gantt Chart', fontweight='bold')
# axis style for job subplot
job_ids = range(num_job)
gnt_job.set(ylabel='Job', \
yticks=job_ids, \
yticklabels=[f'Job-{i}' for i in job_ids])
gnt_job.grid(which='major', axis='x', linestyle='--')
# axis style for machine subplot
machine_ids = range(num_machine)
gnt_machine.set(xlabel='Time', ylabel='Machine',\
yticks=machine_ids, \
yticklabels=[f'M-{i}' for i in machine_ids])
gnt_machine.grid(which='major', axis='x', linestyle='--')
# plot each task
for (jid,mid,start,duration) in tasks:
gnt_job.barh(jid, duration, left=start, height=0.5)
gnt_machine.barh(mid, duration, left=start, height=0.5)
plt.show()动态更新思路¶
动态更新即修改绘图对象/数据,通常有以下两种做法:
-
交互绘图模式:
plt.ion和plt.ioff -
动画模式:按照一定的频率执行自定义的方法来更新数据,每一次更新数据对应 一帧 的结果
本文采用动画模式:
matplotlib.animation.FuncAnimation(fig, func, frames=None, \
init_func=None, fargs=None, save_count=None, *, cache_frame_data=True, **kwargs)其中几个关键参数:
-
fig为当前画布 -
func为更新图形数据的自定义函数,参数构成如下:def func(frame, *fargs) -> iterable_of_artistsframe为每一帧的参数,由下面的frames参数传入fargs为额外的参数,由下面的fargs传入
-
frames一般为可迭代对象,控制整个动画过程,每一帧传一个元素给func- 如果是可迭代对象:每一帧传一个元素
- 如果是
int,等效为range(frames) - 如果是生成器,每一帧传一个生成的对象
- 如果是
None,每一帧传入当前运行次数
-
init_func是图形初始化函数,在绘制第一帧前调用def init_func() -> iterable_of_artists -
fargs为每一帧调用时传给func的额外的参数 -
interval为频率参数,表示两帧之间的间隔,默认200ms -
repeat表示frames定义的帧数结束后是否重复,默认False -
blit表示是否启用blitting技术优化绘图,默认False
更详细介绍参考:
https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.animation.FuncAnimation.html
关于func的进一步理解
-
一般在
func中更新已经创建好的对象的数据,例如plt.plot()返回的曲线;也可以清除之前的所有对象,再用新的数据重新绘图,特别是对不适用直接更新数据的场合,例如本文涉及的条形图。 -
func的返回值(该帧所有绘图对象组成的可迭代对象)主要用于blit=True时优化绘图显示,所以如果设置blit=False,完全可以不用返回值。
回到作业车间调度背景¶
matplotlib的animation以固定的频率刷新数据,然而,回到作业车间调度问题背景下,我们无法预知在哪一刻会产生一个新解。为了避免无意义的刷新,可以设置一个开关变量,一旦得到了新解则刷新甘特图,否则啥也不做。
针对作业车间调度问题,我们抽象出两个主要的类:
-
Problem:指定问题的规模,然后求解solve(),生成并动态更新甘特图__dynamic_gantt()class Problem: def __init__(self, num_job:int, num_machine:int, solution) -> None: '''Initialize problem with the count of job and machine.''' self.num_job = num_job self.num_machine = num_machine # a solution is a collection of tasks with determined start time self.__solution = solution # type: Solution # implement dynamic gantt chart by animation self.__animation = None def solve(self): '''Solve problem and update Gantt chart dynamically.''' pass def __dynamic_gantt(self, interval:int=1000): '''Create plot and define animation to update data dynamically.''' pass -
Solution:问题的解即一系列属性已知(主要是开始时间)的工序,主要负责更新解update()和绘制甘特图的图形区域plot()。class Solution: Task = namedtuple('Task',['jid','mid', 'start', 'duration']) def __init__(self) -> None: self.__tasks = [] # list[Task] self.__update_plot = False def update(self, num_job:int, num_machine:int): '''Simulate a real solving process to update solution iteratively.''' pass def plot(self, axes:tuple): '''Plot Gantt chart data area.''' pass
求解框架¶
problem.solve()方法模拟求解过程,主线程的甘特图持续监听新解:在获得新解之前,绘图状态为关,保持不动;一旦子线程的求解获得了更好的解,绘图选项被打开,从而更新甘特图。基本框架和相应代码如下:
-
在子线程中求解,即调用
Solution的update()方法 -
在主线程中展示和更新甘特图
problem.__dynamic_gantt(),即通过上一节介绍的animation.FuncAnimation对象以一定的频率执行Solution的plot()方法
class Problem:
def solve(self):
'''Solve problem and update Gantt chart dynamically.'''
# solve problem in child thread
thread = Thread(target=self.__solution.update, \
args=(self.num_job, self.num_machine))
thread.start()
# show gantt chart and listen to the solution update in main thread
self.__dynamic_gantt(interval=1000)
plt.show()定义甘特图动画¶
绘制甘特图的代码和第一节的静态甘特图类似,这里仅给出定义动画的部分:
-
因为无法预知动画的周期,所以
frames参数为空,即传入调用次数i -
虽然以固定频率刷新动画(调用
solution.plot()),但实际图形在获得新解之前并不会被无意义地重复绘制(具体参考前面的介绍和下面的实现)
class Problem:
def __dynamic_gantt(self, interval:int=1000):
'''Create plot and define animation to update data dynamically.'''
...
# animation
self.__animation = FuncAnimation(fig, \
func=lambda i: self.__solution.plot(axes=(gnt_job, gnt_machine)), \
interval=interval, \
repeat=False)更新甘特图¶
更新甘特图的代码如下:
-
self.__update_plot控制了是否真正重绘 -
对于甘特图中的每一个横条,这里采用了先清除再重绘的方式
class Solution:
def plot(self, axes:tuple):
'''Plot Gantt chart data area.'''
# update plot only if the solution is updated
if not self.__update_plot:
return
else:
self.__update_plot = False
# clear plotted bars
for axis in axes:
bars = [bar for bar in axis.containers if isinstance(bar, BarContainer)]
for bar in bars: bar.remove()
# plot new bars
gnt_job, gnt_machine = axes
for task in self.__tasks:
gnt_job.barh(task.jid, task.duration, left=task.start, height=0.5)
gnt_machine.barh(task.mid, task.duration, left=task.start, height=0.5)
# reset x-limit
for axis in axes:
axis.relim()
axis.autoscale()最后,完整代码参考:
https://github.com/dothinking/dothinking.github.io/tree/master/samples/gantt
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK