

Spring实例化bean之源码分析
source link: https://nicky-chin.cn/2020/04/15/spring-bean-instantiation/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

1 实例化bean的主流程
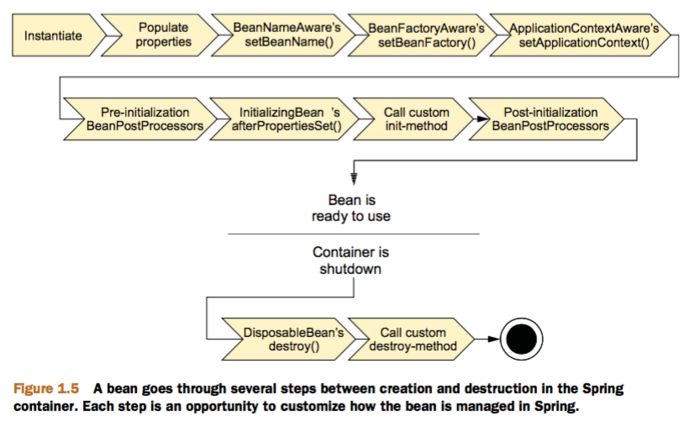
这张图是整体的bean的实例化的流程,我之前关于Spring的生命周期的加载bean和实例化bean的整体过程已有博文,可以 查看文章:Spring之Bean加载-解析-生命周期
本文中的Spring源码基于3.2.x版本,为最精简的Spring源码,选取Spring自带的测试用例进行debug调试, 本文只关注单例对象的实例化bean中各组件的源码分析, 入口如下:
@Test
public void testConfigLocationPattern() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(CONTEXT_WILDCARD);
assertTrue(ctx.containsBean("service"));
assertTrue(ctx.containsBean("logicOne"));
assertTrue(ctx.containsBean("logicTwo"));
Service service = (Service) ctx.getBean("service");
ctx.close();
assertTrue(service.isProperlyDestroyed());
}
2 各组件流程
实例化bean的流程主要关注AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的doCreateBean方法,源码如下:
2.1 整体流程解析
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// BeanWrapper是对Bean的包装,其接口中所定义的功能很简单包括设置获取被包装的对象,获取被包装bean的属性描述器
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 单例模型,则从未完成的 FactoryBean 缓存中删除
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
// 使用合适的实例化策略来创建新的实例:工厂方法、构造函数自动注入、简单初始化
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 包装的实例对象
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
// 包装的实例对象的类型
Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// 检测是否有后置处理
// 如果有后置处理,则允许后置处理修改 BeanDefinition
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
// 后置处理修改 BeanDefinition
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// 解决单例模式的循环依赖
// 单例模式 & 允许循环依赖&当前单例 bean 是否正在被创建
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 提前将创建的 bean 实例加入到ObjectFactory 中
// 这里是为了后期避免循环依赖 加入三级缓存删除二级缓存
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// 开始初始化 bean 实例对象
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 对 bean 进行填充,将各个属性值注入,其中,可能存在依赖于其他 bean 的属性
// 则会递归初始依赖 bean
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
// 调用初始化方法
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// 循环依赖处理
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
// 只有在存在循环依赖的情况下,earlySingletonReference 才不会为空
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
// 如果 exposedObject 没有在初始化方法中被改变,也就是没有被增强
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
// 处理依赖
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
// 注册 bean
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
2.2 populateBean-递归填充bean的属性
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
// bean 的属性值
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
// 没有实例化对象
if (bw == null) {
// 有属性抛出异常
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 在设置属性之前给 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 最后一次改变 bean 的机会
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
// bean 不是"合成"的,即未由应用程序本身定义
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 将会阻止在此 Bean 实例上调用任何后续的 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 实例。
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
// 如果后续处理器发出停止填充命令,则终止后续操作
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
// 将 PropertyValues 封装成 MutablePropertyValues 对象
// MutablePropertyValues 允许对属性进行简单的操作,
// 并提供构造函数以支持Map的深度复制和构造。
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
// 根据名称自动注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
// 根据类型自动注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
// 是否已经注册了 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
// 是否需要进行依赖检查
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
// 从 bw 对象中提取 PropertyDescriptor 结果集
// PropertyDescriptor:可以通过一对存取方法提取一个属性
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 这里会进行赋值处理,如通过 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor处理器处理注解 @autowired
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
// 依赖检查,对应 depends-on 属性
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
// 将属性应用到 bean 中
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
主要是获取需要注入的依赖bean,通过反射的方式将属性进行递归赋值
2.3 initializeBean方法之invokeAwareMethods
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
// 处理实现了aware接口相关类,调用方法
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
这部分也很简单根据Aware接口去对BeanNameAware , BeanFactoryAware 进行赋值
2.4 initializeBean方法之applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization-前置处理器
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
这部分源码主要是bean的前置处理,会调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,我们关注下ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
这个类,它的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法会调用invokeAwareInterfaces方法,去执行其他基于Aware
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(
new EmbeddedValueResolver(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory()));
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
ApplicationContextAware的setApplicationContext方法就在这里
2.5 invokeInitMethods-初始化方法
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
// 处理初始化方法 init-method
if (mbd != null) {
// 判断是否指定了 init-method(),
// 如果指定了 init-method(),则再调用制定的init-method
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
获取实现了InitializingBean的接口的bean,调用afterPropertiesSet方法处理,这里如果指定了init-method()方法,则还会执行相应的方法
2.6 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization-后置处理器
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
整体逻辑都很清晰,调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法去做后置处理
3 BeanPostProcessor注册
3.1 BeanPostProcessor的加载
前面分析了实例化调用各组件方法的流程,现在分析BeanPostProcessor的加载,具体在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法,
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 加载配置中的bean --> loadBeanDefinition方法
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 在实例化bean之前通过 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 最后一次机会对注册到该容器的 BeanDefinition 做出修改
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化所有遗留的非懒加载的单例对象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}
整体流程就是加载xml的配置,会调动loadBeanDefinition方法,然后注册BeanPostProcessor,
发送事件,实例化非懒加载的bean。
registerBeanPostProcessors注册处理器的方法如下:
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 获取所有的 BeanPostProcessor 的 beanName
// 这些 beanName 都已经全部加载到容器中去,但是没有实例化
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
// 注册 BeanPostProcessorChecker,它主要是用于在 BeanPostProcessor 实例化期间记录日志
// 当 Spring 中高配置的后置处理器还没有注册就已经开始了 bean 的实例化过程,这个时候便会打印 BeanPostProcessorChecker 中的内容
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 按优先级别分组
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
OrderComparator.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
OrderComparator.sort(orderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
OrderComparator.sort(internalPostProcessors);
// 注册
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// 加入ApplicationListenerDetector(探测器)
// 重新注册 BeanPostProcessor 以检测内部 bean,因为 ApplicationListeners 将其移动到处理器链的末尾
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector());
}
这部分源码,主要是去bean容器中获取BeanPostProcessor的beanName,然后根据该处理是否实现了PriorityOrdered,Ordered的接口, 进行分类,最后按优先级别排序,注册到beanFactory中。
3.2 自定义BeanPostProcessor导致Spring事务失效问题
如果自定义BeanPostProcessor并实现了PriorityOrdered接口,会导致事务失效
public class WrappingPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@autowired
private Service service;
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory(bean);
return pf.getProxy();
}
}
如果Service 这个类包含事务注解的方法,那么事务就会失效,原因是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个实现了 BeanPostProcessor的类的优先级别是Order级别,导致Service提前初始化
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK