

redis之hash源码分析
source link: https://wakzz.cn/2019/07/06/redis/redis%E4%B9%8Bhash%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

hash的对象编码
hash数据类型的对象编码有两种,分别是OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST和OBJ_ENCODING_HT,即一种是以压缩数组;一种是哈希字典。两者的数据格式见下图:
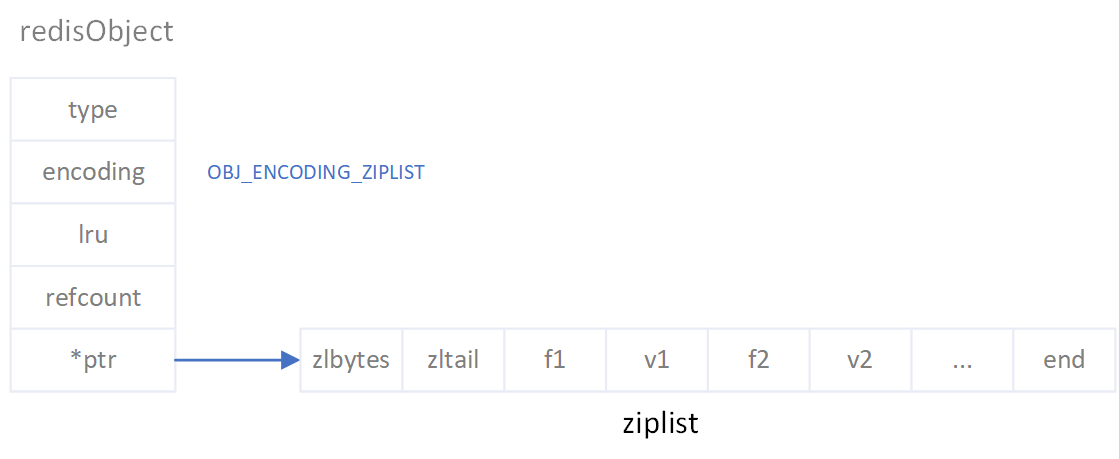
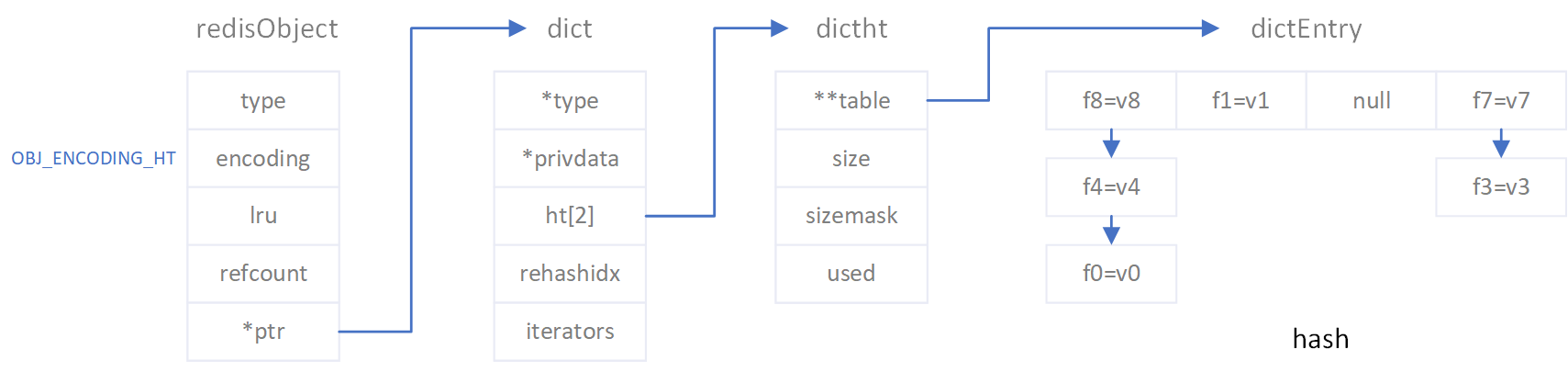
redis的hash数据之所以使用OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST和OBJ_ENCODING_HT两种编码格式,是为了当一个hash对象的键值对数据量比较小时,使用紧凑的数组格式来节省内存空间。
因此,当一个hash对象的键值对数据量增加到临界值时,就会触发编码转换,将该hash对象的键值对从OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST编码转换为OBJ_ENCODING_HT编码。其中的临界值的关键参数为hash-max-ziplist-entries和hash-max-ziplist-value,可在配置文件中修改该两个参数的默认值。
# Hashes are encoded using a memory efficient data structure when they have a
# small number of entries, and the biggest entry does not exceed a given
# threshold. These thresholds can be configured using the following directives.
hash-max-ziplist-entries 512
hash-max-ziplist-value 64
hash-max-ziplist-entries
hash-max-ziplist-entries的默认值为512,表示当hash对象的键值对数量大于该值时使用OBJ_ENCODING_HT编码,否则使用OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST编码。
如下测试,向hash对象中添加512个键值对,通过debug命令输出该hash对象的编码格式为encoding:ziplist,再添加一个键值对导致hash对象中的键值对数量大于hash-max-ziplist-entries时,该hash对象的编码格式转换为了encoding:hashtable。
127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "for i=1, 512 do redis.call('HSET', KEYS[1], i, i) end" 1 "members"
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> hlen members
(integer) 512
127.0.0.1:6379> debug object members
Value at:0x7fe27c2b34a0 refcount:1 encoding:ziplist serializedlength:2838 lru:2137578 lru_seconds_idle:7
127.0.0.1:6379> hset members 513 513
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> debug object members
Value at:0x7fe27c2b34a0 refcount:1 encoding:hashtable serializedlength:2826 lru:2137611 lru_seconds_idle:2
关键源码如下:
void hashTypeTryConversion(robj *o, robj **argv, int start, int end) {
int i;
if (o->encoding != OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) return;
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (sdsEncodedObject(argv[i]) &&
// 当key或者value的长度大于hash-max-ziplist-value时转换编码
sdslen(argv[i]->ptr) > server.hash_max_ziplist_value)
{
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
break;
}
}
}
hash-max-ziplist-value
hash-max-ziplist-value的默认值为64,表示hash对象中的键值对存在键的长度或值的长度大于该值时使用OBJ_ENCODING_HT编码,否则使用OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST编码。
如下测试,向hash对象中添加值的长度为64的键值对时,该hash对象的编码格式为encoding:ziplist。再重新添加一个值的长度为65的键值对时,hash对象的编码格式变成了encoding:hashtable。
127.0.0.1:6379> hset members f1 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> debug object members
Value at:0x7fe27c2b3490 refcount:1 encoding:ziplist serializedlength:38 lru:2137862 lru_seconds_idle:3
127.0.0.1:6379> hset members f1 12345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> debug object members
Value at:0x7fe27c2b3490 refcount:1 encoding:hashtable serializedlength:26 lru:2137871 lru_seconds_idle:6
关键源码如下:
int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, int flags) {
int update = 0;
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
...
// 当存放的键值对数量大于hash-max-ziplist-entries时转换编码
/* Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */
if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries)
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
}
...
}
当键值对数量超过hash槽长度的5倍时hash表扩容,扩容后为hash槽长度为大于键值对数量2倍大小的最小2的指数,即4、8、16、32、64…
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size; // 哈希表table的大小
unsigned long sizemask; // 用于位运算计算key对应的table位置,sizemask=size-1
unsigned long used; // 哈希表中键值对的数量
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; // 表示rehash时hash槽下次迁移数据的槽的位置,-1表示非rehash状态
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE 4
static unsigned int dict_force_resize_ratio = 5;
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
// 正在rehash,直接返回
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
// 刚初始化的hash表,hash槽长度为0,初始化为槽长度为4的hash表
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
// 当键值对数量超过hash槽长度的5倍时,扩容
// 扩容后为hash槽长度为键值对数量2倍大小的hash表
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size)
{
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
dictht n;
// 真正扩容大小永远是2的指数且不大于LONG_MAX
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
if (realsize == d->ht[0].size) return DICT_ERR;
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
// 未初始化的hash表直接创建
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
// 已经初始化的hash表,通过rehash实现扩容
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
rehash
redis的rehash最大的特点是该操作是渐进式的。redis是个单线程模型,对于数据量大的hash数据做耗时的rehash操作时会导致redis的长时间阻塞。因此redis对hash数据的rehash操作设计成了渐进式,即一个hash对象有两个hash表,当需要rehash操作时一点一点将旧hash表中的数据迁移到新hash表中。虽然慢了一点,但是不会造成长时间的阻塞。
当一个rehash状态的hash数据收到一个增删改查请求时,都会先进行一次渐进式rehash,再处理该增删改查操作。每次渐进式rehash会迁移10个hash槽中的数据。
当hash表处于扩容状态时,每次查询都会先读取旧hash表,旧hash表查询不到时再读取新hash表,即新旧hash表遍历查询。每次增删改则尝试操作旧hash表,旧hash表查询不到该数据时时则再操作新hash表。
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
// 渐进式rehash每次迁移10个hash槽的数据
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10;
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
// rehash完成,ht[1]指向ht[0],ht[1]初始化为空hash表
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
uint64_t h, idx, table;
// 如果新旧hash表都为空,直接返回null
if (d->ht[0].used + d->ht[1].used == 0) return NULL;
// 如果正在rehash,做一次渐进式rehash迁移10个hash槽的数据
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
// 如果正在rehash,则尝试从两个hash表获取数据
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{
long index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
// 如果正在rehash,做一次渐进式rehash迁移10个hash槽的数据
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)
return NULL;
// 如果正在rehash,则把新数据添加到新hash表
// 否则添加到ht[0]
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK